Evolution of Plant B Chromosome Enriched Sequences
Abstract
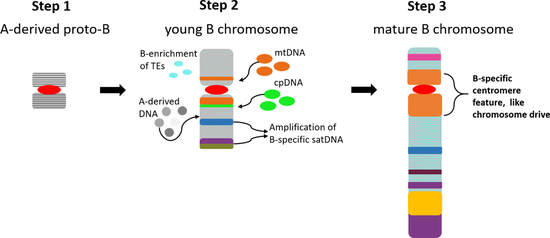
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Tools to Characterize the High-Copy DNA Composition of B Chromosomes—Past and Future
3. Accumulation of B-Specific Repeats
3.1. Rye
3.2. Maize
3.3. Brachycome dichromosomatica
3.4. Aegilops speltoides
3.5. Plantago lagopus
3.6. Cestrum
3.7. Crepis capillaris
4. B Chromosome-Specific Accumulation of Organelle DNA
5. B Chromosome-Specific Accumulation of Transposable Elements
5.1. Rye
5.2. Maize
6. Rapid Evolution of Repeats on Bs
7. Evolutionary Aspects of Repeat Accumulation
8. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martis, M.M.; Klemme, S.; Banaei-Moghaddam, A.M.; Blattner, F.R.; Macas, J.; Schmutzer, T.; Scholz, U.; Gundlach, H.; Wicker, T.; Simkova, H.; et al. Selfish supernumerary chromosome reveals its origin as a mosaic of host genome and organellar sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13343–13346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, D.M.; Pansonato-Alves, J.C.; Utsunomia, R.; Araya-Jaime, C.; Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Daniel, S.N.; Hashimoto, D.T.; Oliveira, C.; Camacho, J.P.; Porto-Foresti, F.; et al. Delimiting the origin of a B chromosome by FISH mapping, chromosome painting and DNA sequence analysis in Astyanax paranae (Teleostei, Characiformes). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, G.T.; Conte, M.A.; Fantinatti, B.E.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C.; Carvalho, R.F.; Vicari, M.R.; Kocher, T.D.; Martins, C. Origin and evolution of B chromosomes in the Cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata based on integrated genomic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croll, D.; McDonald, B.A. The accessory genome as a cradle for adaptive evolution in pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Domínguez, B.; Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Cabrero, J.; Corral, J.M.; López-León, M.D.; Sharbel, T.F.; Camacho, J.P.M. Protein-coding genes in B chromosomes of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Cabrero, J.; Lopez-Leon, M.D.; Camacho, J.P.M. Satellite DNA content illuminates the ancestry of a supernumerary (B) chromosome. Chromosoma 2017, 126, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.; Banaei-Moghaddam, A.M.; Klemme, S.; Blattner, F.R.; Niwa, K.; Guerra, M.; Houben, A. B chromosomes of rye are highly conserved and accompanied the development of early agriculture. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Pajares, A.; Martinez-Rodriguez, L.; Teruel, M.; Cabrero, J.; Camacho, J.P.M.; Perfectti, F. A single, recent origin of the accessory B chromosome of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Genetics 2011, 187, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, G.T.; Nakajima, R.T.; Fantinatti, B.E.; Marques, D.F.; Almeida, R.O.; Simoes, R.P.; Martins, C. B chromosomes: From cytogenetics to systems biology. Chromosoma 2017, 126, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruban, A.; Schmutzer, T.; Scholz, U.; Houben, A. How next-generation sequencing has aided our understanding of the sequence composition and origin of B chromosomes. Genes 2017, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makunin, A.I.; Dementyeva, P.V.; Graphodatsky, A.S.; Volobouev, V.T.; Kukekova, A.V.; Trifonov, V.A. Genes on B chromosomes of vertebrates. Mol. Cytogenet. 2014, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmis, J.N.; Ingle, J.; Sinclair, J.; Jones, R.N. Genomic quality of rye B chromosomes. J. Exp. Bot. 1975, 26, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilton, M.D.; Mccarthy, B.J. DNA from Maize with and without B-Chromosomes—Comparative Study. Genetics 1973, 74, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amos, A.; Dover, G. The distribution of repetitive DNAs between regular and supernumerary chromosomes in species of Glossina (Tsetse)—A 2-step process in the origin of supernumeraries. Chromosoma 1981, 81, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreissig, S.; Fuchs, J.; Himmelbach, A.; Mascher, M.; Houben, A. Sequencing of single pollen nuclei reveals meiotic recombination events at megabase resolution and circumvents segregation distortion caused by postmeiotic processes. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, P.; Avila Robledillo, L.; Koblizkova, A.; Vrbova, I.; Neumann, P.; Macas, J. TAREAN: A computational tool for identification and characterization of satellite DNA from unassembled short reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, P.; Neumann, P.; Pech, J.; Steinhaisl, J.; Macas, J. RepeatExplorer: A Galaxy-based web server for genome-wide characterization of eukaryotic repetitive elements from next-generation sequence reads. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumke, K.; Macas, J.; Fuchs, J.; Altschmied, L.; Kour, J.; Dhar, M.K.; Houben, A. Plantago lagopus B Chromosome Is Enriched in 5S rDNA-Derived Satellite DNA. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2016, 148, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ruano, F.J.; Lopez-Leon, M.D.; Cabrero, J.; Camacho, J.P. High-throughput analysis of the satellitome illuminates satellite DNA evolution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmutzer, T.; Ma, L.; Pousarebani, N.; Bull, F.; Stein, N.; Houben, A.; Scholz, U. Kmasker—A tool for in silico prediction of single-copy FISH probes for the large-genome species Hordeum vulgare. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 142, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, P.; Neumann, P.; Macas, J. Graph-based clustering and characterization of repetitive sequences in next-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maluszynska, J.; Schweizer, D. Ribosomal RNA genes in B chromosomes of Crepis capillaris detected by non-radioactive in situ hybridization. Heredity 1989, 62, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, T.M.; Houben, A.; Leach, C.R.; Timmis, J.N. Ribosomal RNA genes specific to the B chromosomes in Brachycome dichromosomatica are not transcribed in leaf tissue. Genome 1997, 40, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, T.M.; Leach, C.R.; Clough, A.; Timmis, J.N. Ribosomal RNA genes and the B chromosome of Brachycome dichromosomatica. Heredity 1995, 74, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friebe, B.; Jiang, J.; Gill, B. Detection of 5S-rDNA and other repeated DNA on supernumerary B-chromosomes of Triticum species (Poaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 1995, 196, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, A.B.; Ferreira, I.A.; Martins, C. The B chromosomes of the African cichlid fish Haplochromis obliquidens harbour 18S rRNA gene copies. BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Leon, M.D.; Neves, N.; Schwarzacher, T.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S.; Hewitt, G.M.; Camacho, J.P. Possible origin of a B chromosome deduced from its DNA composition using double FISH technique. Chromosome Res. 1994, 2, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishak, B.; Jaafar, H.; Maetz, J.L.; Rumpler, Y. Absence of transcriptional activity of the B chromosomes of Apodemus peninsulae during pachytene. Chromosoma 1991, 100, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, C.R.; Houben, A.; Field, B.; Pistrick, K.; Demidov, D.; Timmis, J.N. Molecular evidence for transcription of genes on a B chromosome in Crepis capillaris. Genetics 2005, 171, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Estevez, M.; Lopez-Leon, M.D.; Cabrero, J.; Camacho, J.P. B-chromosome ribosomal DNA is functional in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carchilan, M.; Kumke, K.; Mikolajewski, S.; Houben, A. Rye B chromosomes are weakly transcribed and might alter the transcriptional activity of A chromosome sequences. Chromosoma 2009, 118, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumke, K.; Jones, R.N.; Houben, A. B chromosomes of Puschkinia libanotica are characterized by a reduced level of euchromatic histone H3 methylation marks. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 121, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschner, S.; Kumke, K.; Houben, A. B chromosomes of B. dichromosomatica show a reduced level of euchromatic histone H3 methylation marks. Chromosome Res. 2007, 15, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.W.; Lamb, J.C.; Zhang, W.L.; Kolano, B.; Birchler, J.A.; Jiang, J.M. Histone modifications associated with both A and B chromosomes of maize. Chromosome Res. 2008, 16, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carchilan, M.; Delgado, M.; Ribeiro, T.; Costa-Nunes, P.; Caperta, A.; Morais-Cecilio, L.; Jones, R.N.; Viegas, W.; Houben, A. Transcriptionally active heterochromatin in rye B chromosomes. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dover, G. Concerted evolution, molecular drive and natural selection. Curr. Biol. 1994, 4, 1165–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.Y.; Kovarik, A.; Matyasek, R.; Bezdek, M.; Lichtenstein, C.P.; Leitch, A.R. Gene conversion of ribosomal DNA in Nicotiana tabacum is associated with undermethylated, decondensed and probably active gene units. Chromosoma 2000, 109, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dadejova, M.; Lim, K.Y.; Souckova-Skalicka, K.; Matyasek, R.; Grandbastien, M.A.; Leitch, A.; Kovarik, A. Transcription activity of rRNA genes correlates with a tendency towards intergenomic homogenization in Nicotiana allotetraploids. New Phytol. 2007, 174, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vugt, J.; de Nooijer, S.; Stouthamer, R.; de Jong, H. NOR activity and repeat sequences of the paternal sex ratio chromosome of the parasitoid wasp Trichogramma kaykai. Chromosoma 2005, 114, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, M.K.; Friebe, B.; Koul, A.K.; Gill, B.S. Origin of an apparent B chromosome by mutation, chromosome fragmentation and specific DNA sequence amplification. Chromosoma 2002, 111, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csonka, E.; Cserpan, I.; Fodor, K.; Hollo, G.; Katona, R.; Kereso, J.; Praznovszky, T.; Szakal, B.; Telenius, A.; de Jong, G.; et al. Novel generation of human satellite DNA-based artificial chromosomes in mammalian cells. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 3207–3216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borisjuk, N.; Borisjuk, L.; Komarnytsky, S.; Timeva, S.; Hemleben, V.; Gleba, Y.; Raskin, I. Tobacco ribosomal DNA spacer element stimulates amplification and expression of heterologous genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, I.; Wobus, U. In situ hybridisation confirms jumping nucleolus organizing regions in Allium. Chromosoma 1985, 92, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirached-Darmency, M.; Prado-Vivant, E.; Chelysheva, L.; Pouthier, T. Variation in rDNA locus number and position among legume species and detection of 2 linked rDNA loci in the model Medicago truncatula by FISH. Genome 2005, 48, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubcovsky, J.; Dvorak, J. Ribosomal RNA multigene loci: Nomads of the Triticeae genomes. Genetics 1995, 140, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Datson, P.M.; Murray, B.G. Ribosomal DNA locus evolution in Nemesia: Transposition rather than structural rearrangement as the key mechanism? Chromosome Res. 2006, 14, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandery, M.J.; Forster, J.W.; Blunden, R.; Jones, R.N. Identification of a family of repeated sequences on the rye B chromosome. Genome 1990, 33, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunden, R.; Wilkes, T.J.; Forster, J.W.; Jimenez, M.M.; Sandery, M.J.; Karp, A.; Jones, R.N. Identification of the E3900 family, a second family of rye B chromosome specific repeated sequences. Genome 1993, 36, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langdon, T.; Jenkins, G.; Seago, C.; Jones, R.N.; Ougham, H.; Thomas, H.; Forster, J.W. De novo evolution of satellite DNA on the rye B chromosome. Genetics 2000, 154, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.; Klemme, S.; Guerra, M.; Houben, A. Cytomolecular characterization of de novo formed rye B chromosome variants. Mol. Cytogenet. 2012, 5, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaei-Moghaddam, A.M.; Schubert, V.; Kumke, K.; Weibeta, O.; Klemme, S.; Nagaki, K.; Macas, J.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, M.; Heredia, V.; Gomez-Revilla, D.; et al. Nondisjunction in favor of a chromosome: The mechanism of rye B chromosome drive during pollen mitosis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4124–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemme, S.; Banaei-Moghaddam, A.M.; Macas, J.; Wicker, T.; Novak, P.; Houben, A. High-copy sequences reveal distinct evolution of the rye B chromosome. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamb, J.C.; Han, F.; Auger, D.L.; Birchler, J. A trans-acting factor required for non-disjunction of the B chromosome is located distal to the TB-4Lb breakpoint on the B chromosome. Maize Genet. Coop. Newsl. 2006, 80, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, E.J. Nondisjunction: Localization of the controlling site in the maize B chromosome. Genetics 1973, 73, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alfenito, M.R.; Birchler, J.A. Molecular characterization of a maize B chromosome centric sequence. Genetics 1993, 135, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lamb, J.C.; Riddle, N.C.; Cheng, Y.M.; Theuri, J.; Birchler, J.A. Localization and transcription of a retrotransposon-derived element on the maize B chromosome. Chromosome Res. 2007, 15, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, E.A.; Connerton, I.; Bennett, S.T.; Barnes, S.R.; Parker, J.S.; Forster, J.W. Molecular analysis of the structure of the maize B-chromosome. Chromosome Res. 1996, 4, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.M.; Lin, B.Y. Cloning and characterization of maize B chromosome sequences derived from microdissection. Genetics 2003, 164, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.M.; Lin, B.Y. Molecular organization of large fragments in the maize B chromosome: Indication of a novel repeat. Genetics 2004, 166, 1947–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Lamb, J.C.; Vega, J.M.; Dawe, R.K.; Birchler, J.A.; Jiang, J. Molecular and functional dissection of the maize B chromosome centromere. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, J.C.; Kato, A.; Birchler, J.A. Sequences associated with A chromosome centromeres are present throughout the maize B chromosome. Chromosoma 2005, 113, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, U.P.; Leach, C.R.; Timmis, J.N. A sequence specific to B chromosomes of Brachycome dichromosomatica. Genome 1991, 34, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, C.R.; Donald, T.M.; Franks, T.K.; Spiniello, S.S.; Hanrahan, C.F.; Timmis, J.N. Organisation and origin of a B chromosome centromeric sequence from Brachycome dichromosomatica. Chromosoma 1995, 103, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franks, T.K.; Houben, A.; Leach, C.R.; Timmis, J.N. The molecular organisation of a B chromosome tandem repeat sequence from Brachycome dichromosomatica. Chromosoma 1996, 105, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, A.; Leach, C.R.; Verlin, D.; Rofe, R.; Timmis, J.N. A repetitive DNA sequence common to the different B chromosomes of the genus Brachycome. Chromosoma 1997, 106, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, A.; Verlin, D.; Leach, C.R.; Timmis, J.N. The genomic complexity of micro B chromosomes of Brachycome dichromosomatica. Chromosoma 2001, 110, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, A.; Wanner, G.; Hanson, L.; Verlin, D.; Leach, C.R.; Timmis, J.N. Cloning and characterisation of polymorphic heterochromatic segments of Brachycome dichromosomatica. Chromosoma 2000, 109, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belyayev, A.; Raskina, O. Chromosome evolution in marginal populations of Aegilops speltoides: Causes and consequences. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskina, O.; Brodsky, L.; Belyayev, A. Tandem repeats on an eco-geographical scale: Outcomes from the genome of Aegilops speltoides. Chromosome Res. 2011, 19, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosid, E.; Brodsky, L.; Kalendar, R.; Raskina, O.; Belyayev, A. Diversity of long terminal repeat retrotransposon genome distribution in natural populations of the wild diploid wheat Aegilops speltoides. Genetics 2012, 190, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruban, A.; Fuchs, J.; Marques, A.; Schubert, V.; Soloviev, A.; Raskina, O.; Badaeva, E.; Houben, A. B Chromosomes of Aegilops speltoides are enriched in organelle genome-derived sequences. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paula, A.A.; Fernandes, T.; Vignoli-Silva, M.; Vanzela, A.L.L. Comparative cytogenetic analysis of Cestrum (Solanaceae) reveals different trends in heterochromatin and rDNA sites distribution. Plant Biosyst. 2015, 149, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregonezi, J.N.; Rocha, C.; Torezan, J.M.; Vanzela, A.L. The occurrence of different Bs in Cestrum intermedium and C. strigilatum (Solanaceae) evidenced by chromosome banding. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2004, 106, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobti, S.N.; Verma, V.; Rao, B.L.; Pushpangadan, P. In IOPB chromosome number reports LXV. Taxon 1979, 28, 627. [Google Scholar]
- Sykorova, E.; Lim, K.Y.; Fajkus, J.; Leitch, A.R. The signature of the Cestrum genome suggests an evolutionary response to the loss of (TTTAGGG)n telomeres. Chromosoma 2003, 112, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urdampilleta, J.D.; Chiarini, F.; Stiefkens, L.; Bernardello, G. Chromosomal differentiation of Tribe Cestreae (Solanaceae) by analyses of 18-5.8-26S and 5S rDNA distribution. Plant Syst. Evol. 2015, 301, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanzela, A.L.L.; de Paula, A.A.; Quintas, C.C.; Fernandes, T.; Baldissera, J.; de Souza, T.B. Cestrum strigilatum (Ruiz & Pavon, 1799) B chromosome shares repetitive DNA sequences with A chromosomes of different Cestrum (Linnaeus, 1753) species. Comp. Cytogenet. 2017, 11, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jamilena, M.; Ruiz Rejon, C.; Ruiz Rejon, M. A molecular analysis of the origin of the Crepis capillaris B chromosome. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jamilena, M.; Garrido-Ramos, M.; Ruiz Rejon, M.; Ruiz Rejon, C.; Parker, J.S. Characterisation of repeated sequences from microdissected B chromosomes of Crepis capillaris. Chromosoma 1995, 104, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobza, R.; Cegan, R.; Jesionek, W.; Kejnovsky, E.; Vyskot, B.; Kubat, Z. Impact of repetitive elements on the Y chromosome formation in plants. Genes 2017, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmis, J.N.; Ayliffe, M.A.; Huang, C.Y.; Martin, W. Endosymbiotic gene transfer: Organelle genomes forge eukaryotic chromosomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleine, T.; Maier, U.G.; Leister, D. DNA transfer from organelles to the nucleus: The idiosyncratic genetics of endosymbiosis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, A.H.; Timmis, J.N. The origin and characterization of new nuclear genes originating from a cytoplasmic organellar genome. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2011, 28, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lloyd, A.H.; Timmis, J.N. Environmental stress increases the entry of cytoplasmic organellar DNA into the nucleus in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2444–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, M.; Ito, Y.; Yamauchi, R.; Obokata, J. The rice nuclear genome continuously integrates, shuffles, and eliminates the chloroplast genome to cause chloroplast-nuclear DNA flux. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.E.; Keith, K.C.; Hall, S.E.; Copenhaver, G.P.; Preuss, D. The rapidly evolving field of plant centromeres. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.N.; Viegas, W.; Houben, A. A century of B chromosomes in plants: So what? Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Ayliffe, M.A.; Timmis, J.N. Direct measurement of the transfer rate of chloroplast DNA into the nucleus. Nature 2003, 422, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, A.E.; Ayliffe, M.A.; Blatch, L.; Day, A.; Delaney, S.K.; Khairul-Fahmy, N.; Li, Y.; Madesis, P.; Pryor, A.J.; Timmis, J.N. Transfer of plastid DNA to the nucleus is elevated during male gametogenesis in tobacco. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, A.E.; Timmis, J.N. Instability of plastid DNA in the nuclear genome. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graves, J.A. The origin and function of the mammalian Y chromosome and Y-borne genes—An evolving understanding. BioEssays 1995, 17, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, B.F. Isolation and characterization of a retroelement from B chromosome (PSR) in the parasitic wasp Nasonia vitripennis. Insect Mol. Boil. 1995, 4, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, B.F.; Werren, J.H. Hybrid origin of a B chromosome (PSR) in the parasitic wasp Nasonia vitripennis. Chromosoma 1997, 106, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, C.G.; Lamatsch, D.K.; Steinlein, C.; Engel, W.; Schartl, M.; Schmid, M. The giant B chromosome of the cyprinid fish Alburnus alburnus harbours a retrotransposon-derived repetitive DNA sequence. Chromosome Res. 2003, 11, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, J.P.; Sharbel, T.F.; Beukeboom, L.W. B-chromosome evolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2000, 355, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shirasu, K.; Schulman, A.H.; Lahaye, T.; Schulze-Lefert, P. A contiguous 66-kb barley DNA sequence provides evidence for reversible genome expansion. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, B.; Sniegowski, P.; Stephan, W. The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 1994, 371, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez, M.; Jimenez, M.M.; Santos, J.L. Synaptic patterns of rye B chromosomes. II. The effect of the standard B chromosomes on the pairing of the A set. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1993, 87, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, G.; Manzanero, S.; Puertas, M.J. Relationship between pachytene synapsis, metaphase I associations, and transmission of 2B and 4B chromosomes in rye. Genome 2000, 43, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, D. Plant sex chromosomes. Genome Dyn. 2008, 4, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, D. Plant Sex Chromosomes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 397–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, J.C.; Meyer, J.M.; Corcoran, B.; Kato, A.; Han, F.; Birchler, J.A. Distinct chromosomal distributions of highly repetitive sequences in maize. Chromosome Res. 2007, 15, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, M.M.; Romera, F.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, M.; Puertas, M.J. Genetic control of the rate of transmission of rye B chromosomes. III. Male meiosis and gametogenesis. Heredity 1997, 78, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, M.M.; Romera, F.; Gallego, A.; Puertas, M.J. Genetic control of the rate of transmission of rye B chromosomes. II. 0Bx2B crosses. Heredity 1995, 74, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kejnovsky, E.; Hobza, R.; Cermak, T.; Kubat, Z.; Vyskot, B. The role of repetitive DNA in structure and evolution of sex chromosomes in plants. Heredity 2009, 102, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Houben, A.; Thompson, N.; Ahne, R.; Leach, C.R.; Verlin, D.; Timmis, J.N. A monophyletic origin of the B chromosomes of Brachycome dichromosomatica (Asteraceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 1999, 219, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkali, M.; Camacho, J.P.M. The B chromosome polymorphism of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans in North Africa: III. Mutation rate of B chromosomes. Heredity 2004, 92, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lia, V.V.; Confalonieri, V.A.; Poggio, L. B chromosome polymorphism in maize landraces: Adaptive vs. demographic hypothesis of clinal variation. Genetics 2007, 177, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieber, V.K.; Murray, B.G. Structural and numerical chromosomal polymorphism in natural populations of Alopecurus (Poaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 1981, 139, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.S.; Lozano, R.; Taylor, S.; Rejon, M.R. Chromosomal structure of populations of Scilla autumnalis in the Iberian Peninsula. Heredity 1991, 67, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, A. B Chromosomes—A Matter of Chromosome Drive. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, A.; Klemme, S.; Houben, A. Evolution of Plant B Chromosome Enriched Sequences. Genes 2018, 9, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9100515
Marques A, Klemme S, Houben A. Evolution of Plant B Chromosome Enriched Sequences. Genes. 2018; 9(10):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9100515
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, André, Sonja Klemme, and Andreas Houben. 2018. "Evolution of Plant B Chromosome Enriched Sequences" Genes 9, no. 10: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9100515
APA StyleMarques, A., Klemme, S., & Houben, A. (2018). Evolution of Plant B Chromosome Enriched Sequences. Genes, 9(10), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9100515