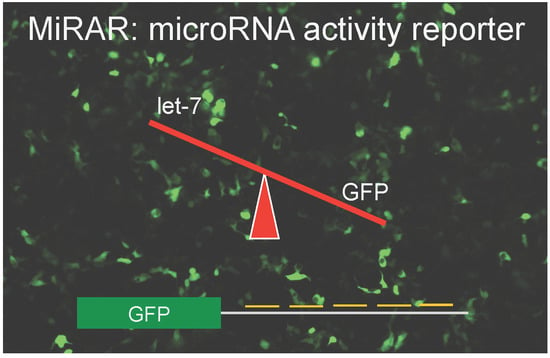
MiRAR—miRNA Activity Reporter for Living Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic DNA Extraction
2.2. Reporter Gene Construct for Let-7
2.3. Reporter Gene Construct for miR-122
2.4. Quantification of Green Fluorescent Protein Fluorescence in Live Cells
2.5. MicroRNA Quantification by Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
3. Results
3.1. Let-7 micro RNA Reduces Green Fluorescent Proteins Fluorescence in Live Cells
3.2. Visualizing Let-7 Accumulation due to Inhibition of Let-7 Degradative Enzymes
3.3. Mutation of Let-7 Binding Sites Abolishes the Sensitivity of the pMiRAR to Changes in Let-7 Levels
3.4. Adapting the Optogenetic Reporter for Quantifying miR-122
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, C.Z.; Seidl, L.E.; Mann, M.R.; Heinemann, I.U. Tipping the balance of RNA stability by 3′ editing of the transcriptome. Biochim Biophys Acta 2017, 1861, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.P.; Shih, I.H.; Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Prediction of mammalian miRNA targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganantharaj, R.; Randall, T.A. The limitations of existing approaches in improving miRNA target prediction accuracy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1617, 133–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cammarata, G.; Augugliaro, L.; Salemi, D.; Agueli, C.; La Rosa, M.; Dagnino, L.; Civiletto, G.; Messana, F.; Marfia, A.; Bica, M.G.; et al. Differential expression of specific miRNA and their targets in acute myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2010, 85, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Salomon, C.; Tapia, J.; Illanes, S.E.; Mitchell, M.D.; Rice, G.E. Ovarian cancer cell invasiveness is associated with discordant exosomal sequestration of let-7 mirna and mir-200. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulrane, L.; McGee, S.F.; Gallagher, W.M.; O’Connor, D.P. MiRNA dysregulation in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6554–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.M.; Wu, L.J.; Xu, J.; Yang, R.; Wu, F.S. Let-7c miRNA expression and clinical significance in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2011, 39, 2323–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provost, P. MicroRNAs as a molecular basis for mental retardation, Alzheimer’s and prion diseases. Brain Res. 2010, 1338, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, S.; McClelland, A.; Kantharidis, P. miRNA in diabetic nephropathy: Renin angiotensin, age/rage, and oxidative stress pathway. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 173783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Lin, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Ma, G.; Li, K. mir-137: A new player in schizophrenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 3262–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roush, S.; Slack, F.J. The let-7 family of microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; You, Y. Regulation of let-7 and its target oncogenes. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyerinas, B.; Park, S.M.; Hau, A.; Murmann, A.E.; Peter, M.E. The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, F19–F36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyerinas, B.; Park, S.M.; Shomron, N.; Hedegaard, M.M.; Vinther, J.; Andersen, J.S.; Feig, C.; Xu, J.; Burge, C.B.; Peter, M.E. Identification of let-7-regulated oncofetal genes. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2587–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.D.; Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Stefani, G.; Byrom, M.; Kelnar, K.; Ovcharenko, D.; Wilson, M.; Wang, X.; Shelton, J.; Shingara, J.; et al. The let-7 miRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7713–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.M.; Grosshans, H.; Shingara, J.; Byrom, M.; Jarvis, R.; Cheng, A.; Labourier, E.; Reinert, K.L.; Brown, D.; Slack, F.J. Ras is regulated by the let-7 miRNA family. Cell 2005, 120, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, W.P.; Kwok, T.T. Let-7a miRNA suppresses therapeutics-induced cancer cell death by targeting caspase-3. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—MicroRNA with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloosterman, W.P.; Plasterk, R.H. The diverse functions of miRNA in animal development and disease. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Naoe, T. Let-7 miRNA functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon cancer cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, V.B.; Rong, N.H.; Han, J.; Yang, Q.; Aris, V.; Soteropoulos, P.; Petrelli, N.J.; Dunn, S.P.; Krueger, L.J. miRNA let-7a down-regulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9762–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Wang, X.J.; Li, G.X.; Yang, E.; Yang, N.M. Detection of let-7a miRNA by real-time PCR in gastric carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2883–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamizawa, J.; Konishi, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Osada, H.; Endoh, H.; Harano, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Nagino, M.; Nimura, Y.; et al. Reduced expression of the let-7 miRNA in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3753–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, C.; Hemann, M.T.; Bartel, D.P. Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science 2007, 315, 1576–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barh, D.; Malhotra, R.; Ravi, B.; Sindhurani, P. MicroRNA let-7: An emerging next-generation cancer therapeutic. Curr. Oncol. 2010, 17, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussecker, D. Current issues of RNAi therapeutics delivery and development. J. Control Release 2014, 195, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightfoot, H.L.; Miska, E.A.; Balasubramanian, S. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of the lin28-mediated blockage of pre-let-7g processing. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 10208–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, J.; Zheng, G. Antiproliferative effect of urolithin A, the ellagic acid-derived colonic metabolite, on hepatocellular carcinoma Hepg2.2.15 cells by targeting Lin28a/let-7a axis. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of Zcchc11 TUTase activity. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redshaw, N.; Wilkes, T.; Whale, A.; Cowen, S.; Huggett, J.; Foy, C.A. A comparison of miRNA isolation and RT-qPCR technologies and their effects on quantification accuracy and repeatability. Biotechniques 2013, 54, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Sharma, P.C. Next generation sequencing-based emerging trends in molecular biology of gastric cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Blahna, M.T.; Kozlowski, E.; Matsuura, K.Y.; Ferrari, J.D.; Morris, S.A.; Powers, J.T.; Daley, G.Q.; Quinton, L.J.; Mizgerd, J.P. Zcchc11 uridylates mature miRNA to enhance neonatal IGF-1 expression, growth, and survival. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Remuzgo-Martinez, S.; Aranzamendi-Zaldunbide, M.; Pilares-Ortega, L.; Icardo, J.M.; Acosta, F.; Martinez-Martinez, L.; Ramos-Vivas, J. Interaction of macrophages with a cytotoxic Serratia liquefaciens human isolate. Microbes Infect. 2013, 15, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.S.; Lu, J.; Mercer, K.L.; Golub, T.R.; Jacks, T. Impaired miRNA processing enhances cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varkonyi-Gasic, E.; Wu, R.; Wood, M.; Walton, E.F.; Hellens, R.P. Protocol: A highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of miRNA. Plant Methods 2007, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hagan, J.P.; Piskounova, E.; Gregory, R.I. Lin28 recruits the TUTase Zcchc11 to inhibit let-7 maturation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thornton, J.E.; Chang, H.M.; Piskounova, E.; Gregory, R.I. Lin28-mediated control of let-7 miRNA expression by alternative TUTases Zcchc11 (TUT4) and Zcchc6 (TUT7). RNA 2012, 18, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, D.M.; D’Ambrogio, A.; Nottrott, S.; Richter, J.D. CPEB and two poly(A) polymerases control miR-122 stability and p53 mRNA translation. Nature 2011, 473, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brustikova, K.; Sedlak, D.; Kubikova, J.; Skuta, C.; Solcova, K.; Malik, R.; Bartunek, P.; Svoboda, P. Cell-based reporter system for high-throughput screening of miRNA pathway inhibitors and its limitations. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Morin, P.J.; Gorospe, M. Novel miRNA reporter uncovers repression of let-7 by GSK-3β. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66330. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, M.; Ohtaka, M.; Iijima, M.; Nakasu, A.; Kato, Y.; Nakanishi, M. Sensitive and long-term monitoring of intracellular miRNA using a non-integrating cytoplasmic RNA vector. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flor, T.B.; Blom, B. Pathogens use and abuse miRNA to deceive the immune system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, K.; Tian, Y.; Peng, M.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Gong, G. HBx down-regulated Gld2 plays a critical role in HBV-related dysregulation of miR-122. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Ree, M.H.; van der Meer, A.J.; van Nuenen, A.C.; de Bruijne, J.; Ottosen, S.; Janssen, H.L.; Kootstra, N.A.; Reesink, H.W. Miravirsen dosing in chronic hepatitis C patients results in decreased microRNA-122 levels without affecting other microRNAs in plasma. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Nasser, M.W.; Wang, B.; Hsu, S.H.; Datta, J.; Kutay, H.; Yadav, A.; Nuovo, G.; Kumar, P.; Ghoshal, K. miRNA-122 inhibits tumorigenic properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and sensitizes these cells to sorafenib. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32015–32027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Giovannini, C.; Veronese, A.; Ferracin, M.; Sabbioni, S.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Croce, C.M.; Tavolari, S.; et al. mir-122/cyclin G1 interaction modulates p53 activity and affects doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5761–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.H.; Wang, W.H.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, Y. miRNA-122 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration of renal cell carcinoma cells through the PI3k/Akt signaling pathway. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 5017–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfe, V.; Biskup, E.; Rosbjerg, A.; Kamstrup, M.; Skov, A.G.; Lerche, C.M.; Lauenborg, B.T.; Odum, N.; Gniadecki, R. mir-122 regulates p53/Akt signalling and the chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Yu, F.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Zou, H.; Long, X. miRNA-122-3p inhibits tumor cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting Forkhead box O in A549 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2695–2699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turk, M.A.; Chung, C.Z.; Manni, E.; Zukowski, S.A.; Engineer, A.; Badakhshi, Y.; Bi, Y.; Heinemann, I.U. MiRAR—miRNA Activity Reporter for Living Cells. Genes 2018, 9, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060305
Turk MA, Chung CZ, Manni E, Zukowski SA, Engineer A, Badakhshi Y, Bi Y, Heinemann IU. MiRAR—miRNA Activity Reporter for Living Cells. Genes. 2018; 9(6):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060305
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurk, Matthew A., Christina Z. Chung, Emad Manni, Stephanie A. Zukowski, Anish Engineer, Yasaman Badakhshi, Yumin Bi, and Ilka U. Heinemann. 2018. "MiRAR—miRNA Activity Reporter for Living Cells" Genes 9, no. 6: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060305
APA StyleTurk, M. A., Chung, C. Z., Manni, E., Zukowski, S. A., Engineer, A., Badakhshi, Y., Bi, Y., & Heinemann, I. U. (2018). MiRAR—miRNA Activity Reporter for Living Cells. Genes, 9(6), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060305