Assessment of Air Quality Status in Wuhan, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
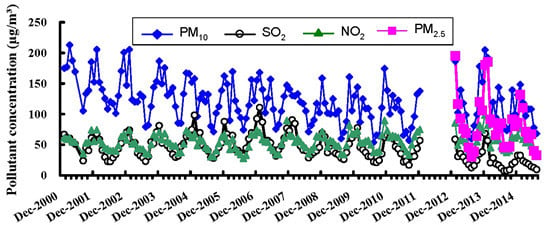
3.1. Overview of Air Pollution in Urban Wuhan
3.2. Monthly Variation of Air Pollution
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Burden of Disease from the Joint Effects of Household and Ambient Air Pollution for 2012; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, H.; Chen, B.; Hong, C. Health impact of outdoor air pollution in China: Current knowledge and future research needs. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (CMEP). Report on the State of Environment in China in 2013; CMEP: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Matus, K.; Nam, K.M.; Selin, N.E.; Lamsal, L.N.; Reilly, J.M.; Paltsev, S. Health damages from air pollution in China. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Teng, E.; Wu, G.; Hu, W.; Wilson, W.E.; Chapman, R.S.; Pau, J.C.; Zhang, J. Ambient concentrations and elemental compositions of PM10 and PM2.5 in four Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 4188–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Zhuang, X.G.; Alastuey, A.; Viana, M.; Lv, W.W.; Wang, Y.X.; Lopez, A.; Zhu, Z.C.; Wei, H.M.; Xu, S.Q. Speciation and sources of atmospheric aerosols in a highly industrialized emerging mega-city in Central China. J. Environ. Monit. 2006, 8, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.R.; Gong, W.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.M.; Lv, X.P.; Liu, J.; Fu, X.X.; Zhang, G. Ionic composition of submicron particles (PM1.0) during the long-lasting haze period in January 2013 in Wuhan, central China. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 810–817. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Wu, S.; Du, Y.; Li, X.D.; Ling, F.; Xue, H.P.; Cai, S.M. Variations of PM10 concentrations in Wuhan, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 176, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, W.J.; Arimoto, R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, C.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Sheng, L.F.; Fu, G. Spatial distribution and interannual variation of surface PM10 concentrations over eighty-six Chinese cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5641–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, T.; Määttä, A.; Anttila, P.; Ruoho-Airola, T.; Amnell, T. Detecting Trends of Annual Values of Atmospheric Pollutants by the Mann-Kendall Test and Sen’s Slope Estimates—The Excel Template Application MAKESENS; Report Code FMI-AQ-31; Finnish Meteorological Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pavón-Domínguez, P.; Jiménez-Hornero, F.J.; Gutiérrez de Ravé, E. Proposal for estimating ground-level ozone concentrations at urban areas based on multivariate statistical methods. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominick, D.; Juahir, H.; Latif, M.T.; Zain, S.M.; Aris, A.Z. Spatial assessment of air quality patterns in Malaysia using multivariate analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zema, D.A.; Nicotra, A.; Tamburino, V.; Zimbone, S.M. Performance assessment of collective irrigation in Water Users’ Associations of Calabria (Southern Italy). Irrig. Drain. 2015, 64, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; He, K.; Zhang, Q.; Chai, L. Sulfate-nitrate-ammonium aerosols over China: Response to 2000–2015 emission changes of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and ammonia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2635–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.T.; Zhang, P.; Tan, S.B.; Zhao, X.J.; Cheng, D.D.; Wei, W.; Su, J.; Pan, X.M. Assessment of urban air quality in China using Air Pollution Indices (APIs). J. Air Waste Manag. 2013, 63, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.K.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.X.; He, K.B.; Hao, J.M. Particulate matter distributions in China during a Winter Period with Frequent Pollution Episodes (January 2013). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Pollutant | Old Standard (µg/m3) | New Standard (µg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| SO2 | 60 | 60 |
| NO2 | 40 | 40 |
| PM10 | 100 | 70 |
| PM2.5 | -- | 35 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Guang, W.; Li, L.; Xiang, R. Assessment of Air Quality Status in Wuhan, China. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040056
Song J, Guang W, Li L, Xiang R. Assessment of Air Quality Status in Wuhan, China. Atmosphere. 2016; 7(4):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040056
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jiabei, Wu Guang, Linjun Li, and Rongbiao Xiang. 2016. "Assessment of Air Quality Status in Wuhan, China" Atmosphere 7, no. 4: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040056
APA StyleSong, J., Guang, W., Li, L., & Xiang, R. (2016). Assessment of Air Quality Status in Wuhan, China. Atmosphere, 7(4), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040056