Effect of Pollution Controls on Atmospheric PM2.5 Composition during Universiade in Shenzhen, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Total Elemental Analysis
2.3. Soluble Ions Analysis
2.4. Iron Oxidation State Analysis
2.5. Stable Pb Isotope Analysis
2.6. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Results and Discussion
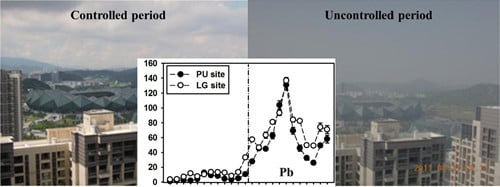
3.1. Trace Element Concentrations
3.2. Crustal Enrichment Factors
3.3. Soluble Fe Oxidation State Analysis
3.4. Stable Pb Isotope Ratios
3.5. Source Identification Using Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hagler, G.S.; Bergin, M.H.; Salmon, L.G.; Yu, J.Z.; Wan, E.C.H.; Zheng, M.; Zeng, L.M.; Kiang, C.S.; Zhang, Y.H.; Lau, A.K.H.; et al. Source areas and chemical composition of fine particulate matter in the Pearl River Delta region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3802–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Q.; Du, Z.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Duan, F.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Q. Characteristics of PM2.5 speciation in representative megacities and across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5207–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Che, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Jing, J.; Cao, J.; Hsu, S.C. PM2.5 pollution in a megacity of southwest China: Source apportionment and implication. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8679–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A.; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G., Jr.; Speizer, F.E. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englert, N. Fine particles and human health—A review of epidemiological studies. Toxicol Lett. 2004, 149, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, C.I.; Phalen, R.F.; Solomon, P.A. Airborne particulate matter and human health: A review. Aerosol. Sci. Tech. 2005, 39, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, J.M.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.A., Jr.; Hansen, J.E.; Hofmann, D.J. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.L.; Sequeira, R. Water-soluble aerosol and visibility degradation in Hong Kong during autumn and early winter, 1998. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 116, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.J.; Tie, X.X.; Wu, D.; Zhou, X.J.; Bi, X.Y.; Tan, H.B.; Li, F.; Hang, C.L. Long-term trend of visibility and its characterizations in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chameides, W.L.; Yu, H.; Liu, S.C.; Bergin, M.; Zhou, X.; Mearns, L.; Wang, G.; Kiang, C.S.; Saylor, R.D.; Luo, C.; et al. Case study of the effects of atmospheric aerosols and regional haze on agriculture: an opportunity to enhance crop yields in China through emission controls? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999, 96, 13626–13633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, F.C.; Apte, M.G.; Daisey, J.M. An exploratory analysis of the relationship between mortality and the chemical composition of airborne particulate matter. Inhal. Toxicol. 2000, 12, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Polidori, A.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Cassee, F.R.; Sioutas, C. Physicochemical and toxicological profiles of particulate matter in Los Angeles during the October 2007 Southern California wildfires. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valavanidis, A.; Fiotakis, K.; Bakeas, E.; Vlahogianni, T. Electron paramagnetic resonance study of the generation of reactive oxygen species catalysed by transition metals and quinoid redox cycling by inhalable ambient particulate matter. Redox Rep. 2005, 10, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.M.; Schins, R.P.F.; Knaapen, A.M.; Kuhlbusch, T.; Pitz, M.; Heinrich, J.; Borm, P.J.A. Hydroxyl radical generation by electron paramagnetic resonance as a new method to monitor ambient particulate matter composition. J. Environ. Monitor. 2003, 5, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahalad, A.K.; Soukup, J.M.; Inmon, J.; Willis, R.; Ghio, A.J.; Becker, S.; Gallagher, J.E. Ambient air particles: Effects on cellular oxidant radical generation in relation to particulate elemental chemistry. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1999, 158, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils; Blackie Academic & Professional: Glasgow, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.S.; Li, X.D.; Shi, W.Z.; Cheung, S.C.; Thornton, I. Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 356, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nriagu, J.O. A silent epidemic of environmental metal poisoning. Environ. Pollut. 1988, 50, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.M.; Markesbery, W.R.; Ehmann, W.D.; Mao, Y.X.; Vance, D.E. Regional Brain Trace-Element Studies in Alzheimers-Disease. Neurotoxicology 1988, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bocca, B.; Alimonti, A.; Petrucci, F.; Violante, N.; Sancesario, G.; Forte, G.; Senofonte, O. Quantification of trace elements by sector field inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in urine, serum, blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson's disease. Spectrochim Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2004, 59, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zou, S.C.; Fung, K.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in Pearl River Delta Region, China during 2001 winter period. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F.; Zou, S.C.; Fung, K.; Li, Y.; Watson, J.G.; Chow, J.C. Spatial and seasonal variations of atmospheric organic carbon and elemental carbon in Pearl River Delta Region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Gao, J.; Cao, G.; Ouyang, F. Chemical composition and source identification of PM2.5 in the suburb of Shenzhen, China. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Air quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/69477/1/WHO_SDE_PHE_OEH_06.02_eng.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2016).
- HORIBA Technical Reports—The Trends in Environmental Regulations in China. Available online: http://www.horiba.com/uploads/media/R41E_05_010_01.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2016).
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.Q.; He, L.Y.; Huang, X.F. Characterization of carbonaceous aerosols during and post-Shenzhen UNIVERSIADE period. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 1622–1632. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Westerdahl, D.; Chen, L.C.; Wu, Y.; Hao, J.M.; Pan, X.C.; Guo, X.B.; Zhang, K.M. Evaluating the air quality impacts of the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games: On-road emission factors and black carbon profiles. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4535–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/China (accessed on 13 April 2016).
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J. Design and application of a novel atmospheric particle sampler. Environ. Monit. China 2014, 30, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2003-154/pdfs/5040.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2016).
- Rolph, G.D. Real-Time Environmental Applications and Display System (READY); NOAA Air Resources Laboratory: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jayarathne, T.; Stockwell, C.E.; Yokelson, R.J.; Nakao, S.; Stone, E.A. Emissions of fine particle fluoride from biomass burning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12636–12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stookey, L.L. Ferrozine—A new spectrophotometric reagent for iron. Anal. Chem 1970, 42, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majestic, B.J.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Turner, J.R.; Fine, P.M.; Singh, M.; Sioutas, C. Development of a wet-chemical method for the speciation of iron in atmospheric aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2346–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaug, J.; Rambaek, J.P.; Steinnes, E.; Henry, R.C. Multivariate-analysis of trace-element data from moss samples used to monitor atmospheric deposition. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.C.; Woodward, W.A. IBM SPSS by Example: A Practical Guide to Statistical Data Analysis; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- List of major power stations in Guangdong. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_major_power_stations_in_Guangdong (accessed on 1 March 2016).
- Arimoto, R.; Duce, R.A.; Savoie, D.L.; Prospero, J.M.; Talbot, R.; Cullen, J.D.; Tomza, U.; Lewis, N.F.; Ray, B.J. Relationships among aerosols constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during PEM-West A. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Fang, M.; Cadle, S.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P.; He, K.; Ye, B. The water-soluble ionic composition of PM2.5 in Shanghai and Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Caritat, P.D. Intrinsic flaws of element Enrichment Factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 5084–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buat-Menard, P.; Chesselet, R. Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 42, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; Mclennan, S.M. The geochemical evolution of the continental-crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.; Daher, N.; Kam, W.; Shafer, M.M.; Ning, Z.; Schauer, J.J.; Sioutas, C. Spatial and temporal variation of chemical composition and mass closure of ambient coarse particulate matter (PM10–2.5) in the Los Angeles area. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2651–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, N.; Eav, J.; Xie, M.J.; Hannigan, M.P.; Miller, S.L.; Navidi, W.; Peel, J.L.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Milford, J.B. Concentrations and source insights for trace elements in fine and coarse particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Y.N.; Yang, F.; Chan, K.L.; Ning, Z. Water solubility of metals in coarse PM and PM2.5 in typical urban environment in Hong Kong. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majestic, B.J.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M. Application of synchrotron radiation for measurement of iron red-ox speciation in atmospherically processed aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2475–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartledge, B.T.; Marcotte, A.R.; Herckes, P.; Anbar, A.D.; Majestic, B.J. The impact of particle size, relative humidity, and sulfur dioxide on iron solubility in simulated atmospheric marine aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7179–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakes, M.; Ingall, E.D.; Lai, B.; Shafer, M.M.; Hays, M.D.; Liu, Z.G.; Russell, A.G.; Weber, R.J. Iron solubility related to particle sulfur content in source emission and ambient fine particles. Environ. Sci Technol 2012, 46, 6637–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry: An Introduction Emphasizing Chemical Equilibria in Natural Waters, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Pehkonen, S.O.; Siefert, R.; Erel, Y.; Webb, S.; Hoffman, M.R. Photoreduction of iron oxyhydroxides in the presence of important atmospheric organic compounds. Environ. Sci Technol 1993, 27, 2056–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbas, J.T.; Sigman, M.E.; Buchanan, A.C.; Chevis, E.A. Photolysis of substituted naphthalenes on SiO2 and Al2O3. Photochem. Photobiol. 1993, 58, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, R.; Desboeufs, K.V. Effect of atmospheric organic complexation on iron-bearing dust solubility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickin, A.P. Radiogenic Isotope Geology, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, C.; McDonnell, J.J. Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology, 1st ed.; Elsevier B.V.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998; pp. 51–86. [Google Scholar]
- Komerek, M.; Ettler, V.; Chrastny, V.; Mihailovic, M. Lead isotopes in environmental sciences: A review. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 562–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, N.; Majestic, B.J.; Ketterer, M.E.; Miller-Schulze, J.P.; Shafer, M.M.; Schauer, J.J.; Solomon, P.A.; Artamonova, M.; Chen, B.B.; Imashev, S.A.; et al. Stable isotopes of lead and strontium as tracers of sources of airborne particulate matter in Kyrgyzstan. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monna, F.; Lancelot, J.; Croudace, I.W.; Cundy, A.B.; Lewis, J.T. Pb isotopic composition of airborne particulate material from France and the southern United Kingdom: Implications for Pb pollution sources in urban areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, A.; Gariepy, C.; Carignan, J. Pb and Sr isotopic compositions of snowpack from Quebec, Canada: Inferences on the sources and deposition budgets of atmospheric heavy metals. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Tan, M.G.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Lu, W.W.; Tong, Y.P.; Zhang, G.L.; Li, Y. A lead isotope record of shanghai atmospheric lead emissions in total suspended particles during the period of phasing out of leaded gasoline. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.L.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Ding, A.J.; Wang, T. Heavy metals and Pb isotopic composition of aerosols in urban and suburban areas of Hong Kong and Guangzhou, South China—Evidence of the long-range transport of air contaminants. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollhofer, A.; Rosman, K.J.R. Isotopic source signatures for atmospheric lead: The Northern Hemisphere. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widory, D.; Liu, X.D.; Dong, S.P. Isotopes as tracers of sources of lead and strontium in aerosols (TSP & PM2.5) in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3679–3687. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.M.; Tang, J.W.; Lee, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.F. Lead concentrations and isotopes in aerosols from Xiamen, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, G.D.; Ito, K.; Lall, R. A source apportionment of U.S. fine particulate matter air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3924–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, J.L.; Koncz, I. Petroleum Geochemistry of the Zala Basin, Hungary. Aapg. Bull. 1994, 78, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, D.; Uibel, S.; Takemura, M.; Klingelhoefer, D.; Groneberg, D.A. Ships, ports and particulate air pollution—An analysis of recent studies. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2011, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, J.; Tao, J.; Hsu, S.C.; Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Lee, C.S.L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing: Seasonal perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7053–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, B.D.; Cadle, S.H.; Mulawa, P.A.; Groblicki, P.J. Brake wear particulate matter emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4463–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, M.; Weber, R.J.; Lai, B.; Russell, A.; Ingall, E.D. Characterization of iron speciation in urban and rural single particles using XANES spectroscopy and micro X-ray fluorescence measurements: investigating the relationship between speciation and fractional iron solubility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cartledge, B.T.; Majestic, B.J. Metal concentrations and soluble iron speciation in fine particulate matter from light rail activity in the Denver-Metropolitan area. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SZ News. Available online: http://sztqb.sznews.com/html/2011-08/08/content_1694922.htm (accessed on 8 February 2016). (In Chinese)
- GD.Xinhuanet. Available online: http://www.gd.xinhuanet.com/newscenter/2011-06/01/content_22914683.htm (accessed on 8 February 2016). (In Chinese)






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dewan, N.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.-Y.; Huang, X.-F.; Majestic, B.J. Effect of Pollution Controls on Atmospheric PM2.5 Composition during Universiade in Shenzhen, China. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040057
Dewan N, Wang Y-Q, Zhang Y-X, Zhang Y, He L-Y, Huang X-F, Majestic BJ. Effect of Pollution Controls on Atmospheric PM2.5 Composition during Universiade in Shenzhen, China. Atmosphere. 2016; 7(4):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleDewan, Nitika, Yu-Qin Wang, Yuan-Xun Zhang, Yang Zhang, Ling-Yan He, Xiao-Feng Huang, and Brian J. Majestic. 2016. "Effect of Pollution Controls on Atmospheric PM2.5 Composition during Universiade in Shenzhen, China" Atmosphere 7, no. 4: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040057
APA StyleDewan, N., Wang, Y. -Q., Zhang, Y. -X., Zhang, Y., He, L. -Y., Huang, X. -F., & Majestic, B. J. (2016). Effect of Pollution Controls on Atmospheric PM2.5 Composition during Universiade in Shenzhen, China. Atmosphere, 7(4), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040057