Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Submicron Particles in a City with Heavy Pollution in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Methodology
2.1. City Description
2.2. Sampling Program
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Positive Matrix Factorization Model
2.5. Back Trajectory and Clustering Analysis
2.6. Potential Source Contribution Function Analysis

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Characteristics of PM1 and PM2.5
3.1.1. Mass Concentration of PM
3.1.2. Characteristics of Chemical Species
3.2. Analysis of PM1 in Haze Episodes
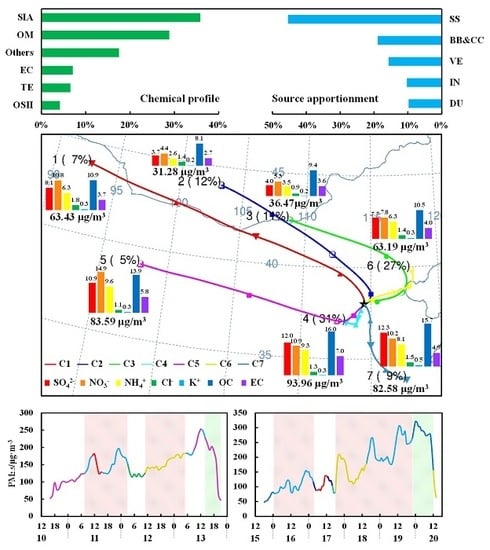
3.3. Sectoral Source Apportionment and Regional Source Identification
3.4. Chemical Distribution and Transport Pathways
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, R.; Wang, S.; Shen, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, K.; Ren, Z.; Feng, M. Spatial and temporal variation of haze in China from 1961 to 2012. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 46, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Ying, Q.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, H.L.; Hu, J.L.; Tang, Y.; Chen, X. Source apportionment of PM2.5 for 25 Chinese provincial capitals and municipalities using a source-oriented Community Multiscale Air Quality model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Bloss, W.J.; Pope, F.D. 60 years of UK visibility measurements: Impact of meteorology and atmospheric pollutants on visibility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2085–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Cui, L.L.; Liu, S.Q.; Yin, X.X.; Li, H.C. Ambient air pollution, smog episodes and mortality in Jinan, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, L. Causative impact of air pollution on evapotranspiration in the North China Plain. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, S.; Parworth, C.; Zheng, B.; Canonaco, F.; et al. Wintertime aerosol chemistry and haze evolution in an extremely polluted city of the North China Plain: Significant contribution from coal and biomass combustion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4751–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Shen, Z.X.; Zhu, C.S.; Yue, J.H.; Cao, J.J.; Liu, S.X.; Zhu, L.H.; Zhang, R.J. Seasonal variations and chemical characteristics of sub-micrometer particles (PM1) in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 118, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Huang, R.J.; Ni, H.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Li, G.H.; Tie, X.X.; Shen, Z.X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.X.; et al. Chemical composition, sources and secondary processes of aerosols in Baoji city of northwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 158, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.K.; Cheng, M.T.; Ji, D.S.; Liu, Z.R.; Hu, B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.S. Characterization of submicron particles during biomass burning and coal combustion periods in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filep, A.; Fodor, G.H.; Kun-Szabo, F.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Razga, Z.; Bozso, G.; Bozoki, Z.; Szabo, G.; Petak, F. Exposure to urban PM1 in rats: Development of bronchial inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness. Respir. Res. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widziewicz, K.; Rogula-Kozlowska, W.; Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Majewski, G.; Loska, K. PM1 and PM1-bound metals during dry and wet periods: Ambient concentration and health effects. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2017, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Drooge, B.L.; Marqueno, A.; Grimalt, J.O.; Fernandez, P.; Porte, C. Comparative toxicity and endocrine disruption potential of urban and rural atmospheric organic PM1 in JEG-3 human placental cells. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.K.; Gupta, T. Source apportionment and risk assessment of PM, bound trace metals collected during foggy and non-foggy episodes at a representative site in the Indo-Gangetic plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.T.; Tang, C.S.; Pan, Y.Z.; Chan, C.C. Association of heart rate variability of the elderly with personal exposure to PM1, PM1-2.5, and PM2.5-10. B. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2007, 79, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbi, A.; Kerchich, Y.; Kerbachi, R.; Boughedaoui, M. Assessment of annual air pollution levels with PM1, PM2.5, PM10 and associated heavy metals in Algiers, Algeria. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yausheva, E.P.; Kozlov, V.S.; Belan, B.D.; Arshinov, M.Y.; Chernov, D.G.; Shmargunov, V.P. In differences in seasonal average concentrations of aerosol and black carbon and particle size distributions from the data of monitoring in tomsk and under background conditions in 2014–2015. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics—Atmospheric Physics, Tomsk, Russia, 30 June–3 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Canonaco, F.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Fu, P.; Li, J.; Jayne, J.; Worsnop, D.R.; et al. Source apportionment of organic aerosol from 2-year highly time-resolved measurements by an aerosol chemical speciation monitor in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8469–8489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Wang, X.; Pang, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon aerosols in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wen, T.X.; Miao, H.Y.; Gao, W.K.; Wang, Y.S. Concentrations and size distributions of water-soluble inorganic ions in aerosol particles in Taiyuan, Shanxi. Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3249–3257. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Tian, S.; Tang, G.; Gao, W.; Ji, D.; Song, T.; et al. Redefining the importance of nitrate during haze pollution to help optimize an emission control strategy. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; et al. Aerosol characterization over the North China Plain: Haze life cycle and biomass burning impacts in summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2508–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.P.; Wang, H.; Chan, C.K. Diurnal and day-to-day characteristics of ambient particle mass size distributions from HR-ToF-AMS measurements at an urban site and a suburban site in Hong Kong. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13605–13624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Chen, C.; Han, T.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; et al. Simultaneous measurements of particle number size distributions at ground level and 260 m on a meteorological tower in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6797–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arndt, J.; Sciare, J.; Mallet, M.; Roberts, G.C.; Marchand, N.; Sartelet, K.; Sellegri, K.; Dulac, F.; Healy, R.M.; Wenger, J.C. Sources and mixing state of summertime background aerosol in the north-western Mediterranean basin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6975–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caggiano, R.; Macchiato, M.; Trippetta, S. Levels, chemical composition and sources of fine aerosol particles (PM1) in an area of the Mediterranean basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lang, J.; Cheng, S.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Chemical composition and sources of PM1 and PM2.5 in Beijing in autumn. Sci Total Environ. 2018, 630, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Official Website of China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Available online: http://www.cnemc.cn/ (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- The Official Website of Shijiazhuang Environmental Protection Bureau. Available online: http://www.sjzhb.gov.cn/ (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Wang, Y.; Bao, S.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, M.; Wu, M.; et al. Local and regional contributions to fine particulate matter in Beijing during heavy haze episodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, K.J.; Arora, M.; Dikshit, A.K. Burden of disease attributed to ambient PM2.5 and PM10 exposure in 190 cities in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11559–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Hu, M.; Hu, W.W.; Zheng, J.; Chen, C.; Wu, Y.S.; Guo, S. Seasonal variations in high time-resolved chemical compositions, sources, and evolution of atmospheric submicron aerosols in the megacity Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9979–10000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Xing, X.; Lang, J.; Chen, D.; Cheng, S.; Wei, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, C. A comprehensive biomass burning emission inventory with high spatial and temporal resolution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2839–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Official Website of Shijiazhuang Municipal People’s Government. Available online: http://www.sjz.gov.cn/ (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Shijiazhuang Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Shijiazhuang Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shijiazhuang Municipal People’s Government. Heat Supply Regulations in Shijiazhuang. Available online: http://www.sjz.gov.cn/col/1497948667745/2013/06/05/1497954766982.html (accessed on 4 September 2018).
- Zhao, X.J.; Zhao, P.S.; Xu, J.; Meng, W.; Pu, W.W.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Shi, Q.F. Analysis of a winter regional haze event and its formation mechanism in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5685–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Yu, H.; Ding, A.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Hua, Y.; Yang, X. Regional contribution to PM1 pollution during winter haze in Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paatero, P. Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis. Chem. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1997, 37, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R. A review of current knowledge concerning PM2.5 chemical composition, aerosol optical properties and their relationships across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9485–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, G.; Samara, C.; Diapouli, E.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Papaoikonomou, K.; Kungolos, A. Source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in major urban Greek agglomerations using a hybrid source-receptor modeling process. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laakso, L.; Hussein, T.; Aarnio, P.; Komppula, M.; Hiltunen, V.; Viisanen, Y.; Kulmala, M. Diurnal and annual characteristics of particle mass and number concentrations in urban, rural and Arctic environments in Finland. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2629–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourcier, L.; Sellegri, K.; Chausse, P.; Pichon, J.M.; Laj, P. Seasonal variation of water-soluble inorganic components in aerosol size-segregated at the puy de Dome station (1,465 m a.s.l.), France. J. Atmos. Chem. 2012, 69, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Tang, L.L.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.X.; Sun, Y.L.; Liu, D.; Qin, W.; Canonaco, F.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Zhang, H.L.; et al. Insights into characteristics, sources, and evolution of submicron aerosols during harvest seasons in the Yangtze River delta region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1331–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Cong, X.; Cheng, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, H. Characterization of the size-segregated inorganic compounds in Lin’an, a regional atmosphere background station in the Yangtze River Delta region. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Lee, B.P.; Su, L.; Fung, J.C.H.; Chan, C.K. Seasonal characteristics of fine particulate matter (PM) based on high-resolution time-of-flight aerosol mass spectrometric (HR-ToF-AMS) measurements at the HKUST Supersite in Hong Kong. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhu, Z.M.; Ma, Y.Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, W. Characteristics of PM1.0, PM2.5, and PM10, and Their Relation to Black Carbon in Wuhan, Central China. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yang, L.X.; Yan, W.D.; Zhang, J.M.; Lu, W.; Yang, Y.M.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, W.X. Chemical characteristics of PM1/PM2.5 and influence on visual range at the summit of Mount Tai, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennanen, A.S.; Sillanpaa, M.; Hillamo, R.; Quass, U.; John, A.C.; Branis, M.; Hunova, I.; Meliefste, K.; Janssen, N.A.H.; Koskentalo, T.; et al. Performance of a high-volume cascade impactor in six European urban environments: Mass measurement and chemical characterization of size-segregated particulate samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 374, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, F.; Moreno, T.; Pandolfi, M.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Delgado, A.; Pedrero, M.; Cots, N. Concentrations, sources and geochemistry of airborne particulate matter at a major European airport. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rashki, A.; Rautenbach, C.J.D.; Eriksson, P.G.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Gupta, P. Temporal changes of particulate concentration in the ambient air over the city of Zahedan, Iran. Air Qual. Atmos. Health. 2013, 6, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, J.F.; Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Crespo, J.; Soler, R. PM1 variability and transport conditions between an urban coastal area and a high mountain site during the cold season. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 118, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchi, C.; Bazzini, C.; Fontana, F.; Pinto, G.; Martino, A.; Cassoni, F. Characterization of urban aerosol: Seasonal variation of mutagenicity and genotoxicity of PM2.5, PM1 and semi-volatile organic compounds. Mutation Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2016, 809, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Naseri, S.; Yunesian, M.; Taghipour, H.; Rastkari, N.; Nazmara, S.; Faridi, S.; Mahvi, A.H. Exposure and health impacts of outdoor particulate matter in two urban and industrialized area of Tabriz, Iran. J. Environ. Sci. Health. Eng. 2014, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ripoll, A.; Pey, J.; Minguillon, M.C.; Perez, N.; Pandolfi, M.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Three years of aerosol mass, black carbon and particle number concentrations at Montsec (southern Pyrenees, 1570 m a.s.l.). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Rastogi, N.; Sharma, D.; Singh, D. Inter and Intra-Annual Variability in Aerosol Characteristics over Northwestern Indo-Gangetic Plain. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W. PM2.5 Characteristics in Qingdao and across Coastal Cities in China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Luo, S.; Zhou, Q.; Bi, C.; Ma, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; et al. Investigation of submicron aerosol characteristics in Changzhou, China: Composition, source, and comparison with co-collected PM2.5. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turpin, B.J.; Lim, H.J. Species contributions to PM2.5 mass concentrations: Revisiting common assumptions for estimating organic mass. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardoni, V.; Elser, M.; Valli, G.; Valentini, S.; Bigi, A.; Ferrno, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Vecchi, R. Size-segregated aerosol in a hot-spot pollution urban area: Chemical composition and three-way source apportionment. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakkanen, T.A.; Kerminen, V.M.; Loukkola, K.; Hillamo, R.E.; Aarnio, P.; Koskentalo, T.; Maenhaut, W. Size distributions of mass and chemical components in street-level and rooftop PM1 particles in Helsinki. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1673–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Aggarwal, S.G.; Okuzawa, K.; Kawamura, K. Size distributions of dicarboxylic acids, ketoacids, alpha-dicarbonyls, sugars, WSOC, OC, EC and inorganic ions in atmospheric particles over Northern Japan: implication for long-range transport of Siberian biomass burning and East Asian polluted aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5839–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budisulistiorini, S.H.; Baumann, K.; Edgerton, E.S.; Bairai, S.T.; Mueller, S.; Shaw, S.L.; Knipping, E.M.; Gold, A.; Surratt, J.D. Seasonal characterization of submicron aerosol chemical composition and organic aerosol sources in the southeastern United States: Atlanta, Georgia, and Look Rock, Tennessee. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5171–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.E.; Allan, J.D.; Williams, P.I.; Green, D.C.; Flynn, M.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Yin, J.; Gallagher, M.W.; Coe, H. Investigating the annual behaviour of submicron secondary inorganic and organic aerosols in London. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6351–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, J.; Ji, D.; Liu, Z.; Tang, G.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y. Characterization of submicron particles during autumn in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2018, 63, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Website of National Meteorological Information Center. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/site/index.html (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Ye, X.N.; Chen, J.M. Haze and particulate matter moisture absorption increased. Chin. J. Nat. 2013, 35, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Cai, M.; Fan, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, F.; Chan, P.W.; Deng, X.; Wu, D. An analysis of aerosol liquid water content and related impact factors in Pearl River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, H.L.; Lou, S.R.; Qiao, L.P.; Chen, Y.R.; Li, L.; Huang, C.H.; Chen, M.H. The variation characteristics of organic and element carbon during air pollution episodes in autumn in Shanghai, China. Acta Sci. Circ. 2013, 33, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, C.H.; Qiao, L.P.; Lou, S.R.; Wang, H.L.; Huang, H.Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M.H.; Chen, Y.R.; Li, L.; et al. The chemical characteristics of particulate matters in Shanghai during heavy air pollution episode in Central and Eastern China in January 2013. Acta Sci. Circ. 2013, 33, 3118–3126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Yu, Y.; Canonaco, F.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Li, G. Chemical characterization of submicron aerosol particles during wintertime in a northwest city of China using an Aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometry. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; He, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Chen, M. Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Fine Particulate Nitrate in Typical Urban Areas in China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China Energy Statistics Division. China Energy Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Larese, C.; Galisteo, F.C.; Granados, M.L.; Mariscal, R.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Furio, M.; Ruiz, R.F. Deactivation of real three way catalysts by CePO4 formation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 40, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, P.; Harrison, R.M. Estimation of the contribution of road traffic emissions to particulate matter concentrations from field measurements: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, C.L.; Park, S. Exhaust nanoparticle emissions from internal combustion engines: A review. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2012, 13, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, T.; Dong, M.; Kasoar, M.; Han, Y.; Xie, M.; Li, S.; Zhuang, B.; Li, M.; Huang, T. Characterization of major natural and anthropogenic source profiles for size-fractionated PM in Yangtze River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Yao, Z.; Dai, Y.; Wang, C.H. A comparison of PM exposure related to emission hotspots in a hot and humid urban environment: Concentrations, compositions, respiratory deposition, and potential health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; Luan, W.; Song, Z.; Ma, Y. A study of the spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in urban soil in Shijiazhuang City. Geol. Chin. 2016, 43, 683–690. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Y.; Liu, L.; Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; Qu, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, G. Deposited atmospheric dust as influenced by anthropogenic emissions in northern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.T.; Wei, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.F.; Su, J.; Meng, C.C.; Zhang, Q. The 2013 severe haze over southern Hebei, China: Model evaluation, source apportionment, and policy implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3151–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behrooz, R.D.; Esmaili-Sari, A.; Bahramifar, N.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Saeb, K.; Rajaei, F. Trace-element concentrations and water-soluble ions in size-segregated dust-borne and soil samples in Sistan, southeast Iran. Aeolian Res. 2017, 25, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, B.; Wen, T.; Tang, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F.; Ji, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Chemical characterization and source identification of PM2.5 at multiple sites in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 12941–12962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Official Website of Hebei Provincial Department of Environmental Protection. Available online: http://www.hebhb.gov.cn/ (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Liu, B.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Liang, D.N.; Dai, Q.L.; Wang, L.; Jin, W.; Zhang, L.Z.; Ren, Y.B.; Zhou, J.B.; et al. Effectiveness evaluation of temporary emission control action in 2016 winter in Shijiazhuang, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7019–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Cao, J.; Arimoto, R.; Han, Y.; Zhu, C.; Tian, J.; Liu, S. Chemical Characteristics of Fine Particles (PM1) from Xi’an, China. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.L. Study of Chemical Composition Features and Sources Apportionment of Atmospheric Particulate Matter during Haze in Shijiazhuang. Master Thesis, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China Industrial Statistics. China Industry Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- The Official Website of Tianjin Municipal People’s Government. Available online: http://www.tj.gov.cn/ (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- The Official Website of Tangshan Municipal People’s Government. Available online: http://www.tangshan.gov.cn/ (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Wang, L.; Wei, Z.; Wei, W.; Fu, J.S.; Meng, C.; Ma, S. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in top polluted cities in Hebei, China using the CMAQ model. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Official Website of Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.zhb.gov.cn/ (accessed on 6 August 2018).










| PM1 μg·m−3 | PM2.5 μg·m−3 | PM1/PM2.5 | Study Year | City | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62 | – | – | 2009 | Guangzhou | China | [7] |
| 25 | 38 | 0.66 | 2011 | Hangzhou | China | [45] |
| 16 a | – | – | 2011 | Hongkong | China | [46] |
| 41 | – | – | 2012 | Beijing | China | [31] |
| 46 | – | – | 2013 | Nanjing | China | [44] |
| 64 | 73 | 0.88 | 2014 | Wuhan | China | [47] |
| 43 | 59 | 0.72 | 2014 | Mount Tai | China | [48] |
| 71 | 92 | 0.75 | 2016 | Shijiazhuang | China | This study |
| 4 | 6 | 0.63 | 2000 | Hyytiälä | Finland | [42] |
| 12 | 19 | 0.66 | 2002 | Duisburg | Germany | [49] |
| 3 | – | – | 2006 | Puy-de-dôme | France | [43] |
| 17 | 21 | 0.81 | 2007 | Barcelona airport | Spain | [50] |
| 12 | 29 | 0.41 | 2008–2009 | Zahedan | Iran | [51] |
| 7 | – | – | 2010 | Mediterranean basin | Spain | [52] |
| 32 | 49 | 0.66 | 2011 | Bologna | Italy | [53] |
| 23 | 39 | 0.59 | 2012 | Tabriz | Iran | [54] |
| 5 | 8 | 0.62 | 2012 | Montsec | Spain | [55] |
| 65 | 91 | 0.71 | 2013 | Patiala | India | [56] |
| 12 | 19 | 0.66 | 2013 | Bologna | Italy | [53] |
| Species | PM1 | PM2.5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Standard Deviation | Average | Standard Deviation | |
| PM | 70.51 | 47.30 | 91.68 | 54.85 |
| Na | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.23 |
| Mg b | 28.43 | 31.26 | 85.53 | 65.00 |
| Al | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.28 |
| S | 3.51 | 3.46 | 3.92 | 3.60 |
| Ca | 0.27 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 1.08 |
| Ti b | 24.10 | 12.13 | 35.91 | 24.52 |
| Cr b | 12.99 | 7.48 | 19.10 | 17.12 |
| Mn b | 19.61 | 10.38 | 27.05 | 16.00 |
| Fe | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.53 | 0.39 |
| Ni b | 0.30 | 0.14 | 0.37 | 0.18 |
| Cu b | 13.65 | 9.10 | 17.11 | 10.69 |
| Zn | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.11 |
| Sr b | 2.35 | 1.56 | 3.52 | 2.35 |
| Pb b | 65.87 | 43.04 | 92.47 | 71.65 |
| Na+ | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 0.33 |
| NH4+ | 7.11 | 6.19 | 7.95 | 6.50 |
| K+ | 0.28 | 0.23 | 1.18 | 0.84 |
| Ca2+ | 0.43 | 0.42 | 1.71 | 2.16 |
| Mg2+ | 0.58 | 0.48 | 1.63 | 2.29 |
| F− | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.11 |
| Cl− | 1.33 | 0.95 | 3.69 | 3.49 |
| NO2− | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| NO3− | 9.08 | 6.65 | 10.55 | 6.90 |
| SO42− | 9.09 | 6.87 | 11.12 | 7.06 |
| OC | 12.71 | 5.23 | 15.43 | 5.57 |
| EC | 4.99 | 2.45 | 5.91 | 2.62 |
| Pollutants | Unit | Non-Polluted | Polluted | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM1 | μg/m3 | 33.90 | 98.67 | 70.51 |
| PM2.5 | μg/m3 | 48.06 | 125.23 | 91.68 |
| PM1/PM2.5 | - | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.75 |
| Meteorological conditions | ||||
| PBL | m | 356.1 | 332.4 | 342.7 |
| P | hPa | 1017.3 | 1010.8 | 1013.6 |
| T | °C | 10.6 | 14.9 | 13.0 |
| RH | % | 67.1 | 79.9 | 74.3 |
| WS | m/s | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
| Year | Season | SS | IN | TR | CC | BB | DU | Others | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Autumn | 42.4 | 10.2 | 12.2 | 18.8 c | 16.4 | This study | ||
| 2013–2014 | Annual | 17.6–19.4 | 10.5–11.6 | 20.0–21.9 | 15.8–17.3 | 6.2–6.8 | [84] | ||
| 2013–2014 | Annual | 15.6 | 26.8 | 21.6 | 11.0 | 13.4 | 12.1 | [87] | |
| 2014 | Autumn | 52.0 | 10.0 | 13.1 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 6.7 | 6.9 | [83] |
| 2014–2015 | Annual | 36.4 | 7.0 | 17.3 | 15.5 | 2.8 | 8.5 | [83] | |
| 2015–2017 | Annual | 32.7 | 5.3 | 13.4 | 31.7 | 19.5 | 3.3 | [85] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lang, J.; Li, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Submicron Particles in a City with Heavy Pollution in China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100388
Lang J, Li S, Cheng S, Zhou Y, Chen D, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Wang H. Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Submicron Particles in a City with Heavy Pollution in China. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(10):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100388
Chicago/Turabian StyleLang, Jianlei, Shengyue Li, Shuiyuan Cheng, Ying Zhou, Dongsheng Chen, Yanyun Zhang, Hanyu Zhang, and Haiyan Wang. 2018. "Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Submicron Particles in a City with Heavy Pollution in China" Atmosphere 9, no. 10: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100388
APA StyleLang, J., Li, S., Cheng, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, D., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., & Wang, H. (2018). Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Submicron Particles in a City with Heavy Pollution in China. Atmosphere, 9(10), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100388