Hydrochemical Characteristics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Natural Water System: A Case Study in Kangding County, Southwestern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Sampling and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Water Samples
4.2. Hydrochemcial Process of Surface Water and Groundwater
4.2.1. Correlation of Major Ions
4.2.2. Mineral Saturations
4.2.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
4.3. Mixing Model of Groundwater and Thermal Water
4.4. Evaluation for δD and δ18O Isotopes
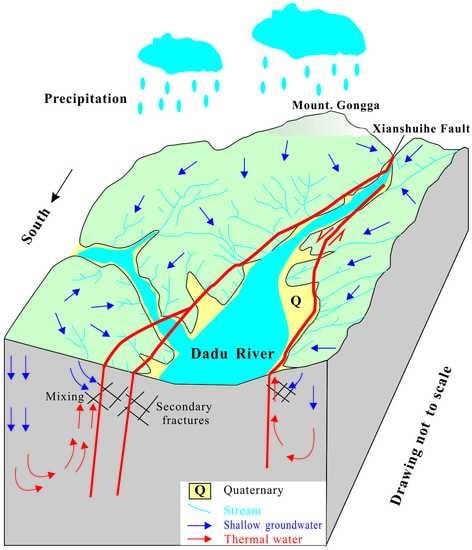
4.5. Hydrological Conceptual Model of Natural Water System
5. Conclusions
- Surface water and groundwater are dominated by Ca-HCO3 type, while thermal water belongs to Ca-HCO3 and Na-Cl-SO4 types.
- Correlations of major ions, multivariate statistical analysis, and saturation index indicated that the dissolution of carbonates and silicate minerals were the main hydrochemical processes affecting chemical components of natural water systems in limestone and granite aquifers. Detailed effects of anthropogenic activity on hydrochemistry have yet to be further investigated by more minor elements in the future.
- Thermal water is typical of immature water that is involved with a cold-water fraction of 0.56–0.79. The estimated reservoir temperatures have a range of 130 to 199 °C.
- δD and δ18O isotopes revealed a meteoric origin of hydrological system. Thermal water is recharged by precipitation from high elevation, while surface water and groundwater are recharged by precipitation from low elevation.
- The Xianshuihe fault is the rising channel for thermal water, while adjacent secondary fractures provide the chambers for groundwater-surface water interaction and groundwater recharging with thermal water.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rakotondrabe, F.; Ngoupayou, J.R.N.; Mfonka, Z.; Rasolomanana, E.H.; Abolo, A.J.N.; Ako, A.A. Water quality assessment in the Betare-Oya gold mining area (East-Cameroon): Multivariate Statistical Analysis approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakis, N.; Matta, C.; Pavlou, A.; Patrikaki, O.; Voudouris, K. Multivariate statistical analysis for the assessment of groundwater quality under different hydrogeological regimes. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, Z.; Aris, A.Z.; Ramli, M.F.; Juahir, H.; Narany, T.S. Groundwater quality assessment using integrated geochemical methods, multivariate statistical analysis, and geostatistical technique in shallow coastal aquifer of Terengganu, Malaysia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Gu, X.M.; Yin, S.Y.; Pan, X.Y.; Shao, J.L.; Cui, Y.L. Investigation of Geochemical Characteristics and Controlling Processes of Groundwater in a Typical Long-Term Reclaimed Water Use Area. Water 2017, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.M.; Zhang, Q.L.; Cui, Y.L.; Shao, J.L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.X. Hydrogeochemistry and Genesis Analysis of Thermal and Mineral Springs in Arxan, Northeastern China. Water 2017, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.; Wang, S.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.G.; Meng, X. Investigating Hydrochemical Groundwater Processes in an Inland Agricultural Area with Limited Data: A Clustering Approach. Water 2017, 9, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasvanoğlu, S.; Çelik, M. A conceptual model for groundwater flow and geochemical evolution of thermal fluids at the Kızılcahamam geothermal area, Galatian volcanic Province. Geothermics 2018, 71, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurteri, C.; Simsek, S. Hydrogeological and hydrochemical studies of the Kaman-Savcili-Büyükoba (Kirsehir) geothermal area, Turkey. Geothermics 2017, 65, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.H.; Cheng, Q.; Xie, S.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Chang, L.R.; Yu, Q.; Zhan, Z.J.; Chen, F. Hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of deep thermal water in the carbonate formation in the main urban area of Chongqing, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.H.; Song, C.; Long, M.; Chen, T.; Ren, Z.H.; Yang, M.L.; Li, X.L.; Guo, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and mixing behavior of thermal springs along the Bijiang River in the Lanping basin of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziritis, E.P.; Datta, P.S.; Barzegar, R. Characterization and Assessment of Groundwater Resources in a Complex Hydrological Basin of Central Greece (Kopaida basin) with the Joint Use of Hydrogeochemical Analysis, Multivariate Statistics and Stable Isotopes. Aquat. Geochem. 2017, 23, 271–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Kumar, A.; Shashtri, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Mallick, J. Multivariate statistical analysis and geochemical modeling for geochemical assessment of groundwater of Delhi, India. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 175, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hoth, N.; Drebenstedt, C.; Sun, Y.J.; Xi, Z.M. Hydro-geochemical paths of multi-layer groundwater system in coal mining regions-Using multivariate statistics and geochemical modeling approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Márquez, J.M.; Barberá, J.A.; Mudarra, B.A.M. Hydrological and geochemical processes constraining groundwater salinity in wetland areas related to evaporitic (karst) systems. A case study from Southern Spain. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 538–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Li, P.Y.; Qian, H.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, X.D. Using correlation and multivariate statistical analysis to identify hydrogeochemical processes affecting the major ion chemistry of waters: A case study in Laoheba phosphorite mine in Sichuan, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 7, 3973–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.; Dhakate, R.; Yadagiri, G.; Reddy, K.S. Principal component and multivariate statistical approach for evaluation of hydrochemical characterization of fluoride-rich groundwater of Shaslar Vagu watershed, Nalgonda District, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argamasilla, M.; Barbera, J.A.; Andreo, B. Factors controlling groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in coastal aquifers from southern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.F.; Xu, F.; Deng, G.S.; Tang, Y.Q. Using stable isotopes and major ions to identify hydrogeochemical characteristics of karst groundwater in Xide country, Sichuan Province. Carbonates Evaporites 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, D.C.; Cociuba, I.; Baciu, C.; Cozma, A. Origin and Geochemistry of Mine Water and its Impact on the Groundwater and Surface Running Water in Post-mining Environments: Zlatna Gold Mining Area (Romania). Aquat. Geochem. 2017, 23, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Liu, Z.; Shao, J.L. Hydrochemistry and H-O-C-S Isotopic Geochemistry Characteristics of Geothermal Water in Nyemo-Nagqu, Tibet. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Rai, S.K.; Bartarya, S.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Negi, M. Stable isotopes (δ13CDIC, δD, δ18O) and geochemical characteristics of geothermal springs of Ladakh and Himachal (India): Evidence for CO2 discharge in northwest Himalaya. Geothermics 2016, 64, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ma, R.; Wang, Y.X.; Hu, Y.L.; Sun, L.J. Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical control of groundwater salinity in an arid inland basin: Dunhuang Basin, northwestern China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1884–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.H.; Xu, M.; An, C.J.; Wu, M.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, G.P. Characterizations of geothermal springs along the Moxi deep fault in the western Sichuan plateau, China. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2017, 263, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Pang, Z.H.; Kong, Y.K.; Wang, Y.C. Geothermal potential evaluation and development prioritization based on geochemistry of geothermal waters from Kangding area, western Sichuan, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Pang, Z.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Tian, J. Fluid geochemistry and geothermometry applications of the Kangding high-temperature geothermal system in eastern Himalayas. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 81, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Replumaz, A.; Leloup, P.H.; Wang, G.C.; Bernet, M.; Beek, P.; Paquette, J.L.; Chevalier, M.L. Cooling history of the Gongga batholith: Implications for the Xianshuihe Fault and Miocene kinematics of SE Tibet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 465, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Lin, A.M. Holocene activity and paleoseismicity of the Selaha Fault, southeastern segment of the strike-slip Xianshuihe Fault Zone, Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics 2017, 694, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3: A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. In Groundwater in Book 6 Modeling Techniques; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2013. Available online: https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/tm6A43 (accessed on 20 October 2017).
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Titus, R.; Pietersen, K.; Tredoux, G.; Harris, C. Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. J. Hydrol. 2001, 241, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F.; Goguel, R.L. Collection and analysis of geothermal and volcanic water and gas discharges. In DSIR Report CD 2401, 4th ed.; Pentone: Carlstadt, NJ, USA, 1989; Volume 81, Available online: https://openei.org/wiki/Collection_and_Analysis_of_Geothermal_and_Volcanic_Water_and_Gas_Discharges (accessed on 1 November 2017).
- Fournier, R.O. Geochemical indicators of subsurface temperature-part 2, estimation of temperature and fraction of hot water mixed with cold. J. Res. US Geol. Surv. 1974, 2, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, R.O. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems. Geothermics 1977, 5, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.L.; Sun, X.Y.; Wang, G.X. A study on precipitation stable isotopes characteristics and vapor sources of the subalpine Gongga Mountain, China. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 1860–1869, (In Chinese and English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Blasch, K.W.; Bryson, J.R. Distinguishing sources of ground water recharge by using δ2H and δ18O. Groundwater 2007, 45, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artemieva, I.M.; Thybo, H.; Jakobsen, K.; Sørensen, N.K.; Nielsen, L.S. Heat production in granitic rocks: Global analysis based on a new data compilation GRANITE2017. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 172, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Correlation | pH | TDS | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||
| TDS | 0.340 | 1 | |||||||
| K+ | 0.168 | 0.359 | 1 | ||||||
| Na+ | 0.268 | 0.662 | 0.601 | 1 | |||||
| Ca2+ | 0.304 | 0.902 | 0.139 | 0.419 | 1 | ||||
| Mg2+ | 0.355 | 0.780 | 0.181 | 0.383 | 0.617 | 1 | |||
| Cl− | 0.084 | 0.281 | 0.015 | 0.204 | 0.256 | 0.277 | 1 | ||
| SO42− | 0.182 | 0.707 | 0.261 | 0.516 | 0.512 | 0.555 | 0.144 | 1 | |
| HCO3− | 0.288 | 0.924 | 0.357 | 0.644 | 0.874 | 0.751 | 0.252 | 0.435 | 1 |
| Scaled Coordinates | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.428 | 0.164 | 0.393 |
| TDS | 0.988 | 0.064 | −0.100 |
| K+ | 0.364 | −0.819 | 0.170 |
| Na+ | 0.766 | −0.367 | 0.226 |
| Ca2+ | 0.868 | 0.223 | −0.115 |
| Mg2+ | 0.830 | 0.162 | −0.066 |
| Cl− | 0.098 | 0.419 | 0.735 |
| SO42− | 0.585 | 0.214 | −0.488 |
| HCO3− | 0.921 | −0.052 | 0.068 |
| Eigenvalues | 4.521 | 1.136 | 1.044 |
| Variance (%) | 50.229 | 12.622 | 11.604 |
| Cumulative (%) | 50.229 | 62.852 | 74.456 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, R. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Natural Water System: A Case Study in Kangding County, Southwestern China. Water 2018, 10, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10010080
Zhang Y, Xu M, Li X, Qi J, Zhang Q, Guo J, Yu L, Zhao R. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Natural Water System: A Case Study in Kangding County, Southwestern China. Water. 2018; 10(1):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10010080
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yunhui, Mo Xu, Xiao Li, Jihong Qi, Qiang Zhang, Jian Guo, Leilei Yu, and Rui Zhao. 2018. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Natural Water System: A Case Study in Kangding County, Southwestern China" Water 10, no. 1: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10010080
APA StyleZhang, Y., Xu, M., Li, X., Qi, J., Zhang, Q., Guo, J., Yu, L., & Zhao, R. (2018). Hydrochemical Characteristics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Natural Water System: A Case Study in Kangding County, Southwestern China. Water, 10(1), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10010080