Groundwater Quality Assessment: An Improved Approach to K-Means Clustering, Principal Component Analysis and Spatial Analysis: A Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Case: Santo Domingo Aquifer
2.2. Geology Setting
2.3. Hydrogeology Setting
2.4. Water Sampling
2.5. Analytical Techniques
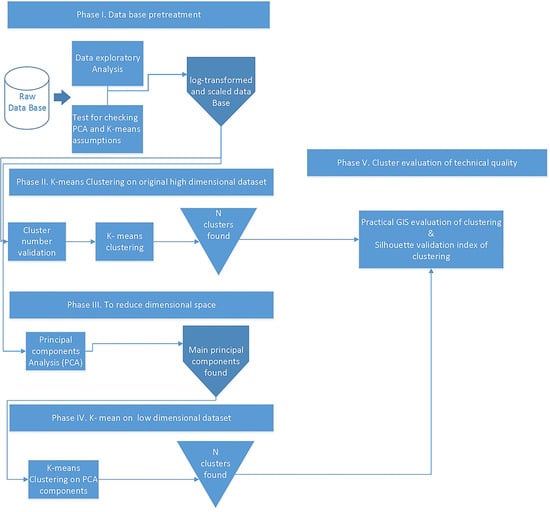
2.6. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. Research Approach
2.6.2. Phase I Database Pretreatment
2.6.3. Phase II K-Means on the Original High Dimensional Dataset
2.6.4. Phase III to Reduce Dimensional Space
2.6.5. Phase IV K-Means Clustering on the Low Dimensional Dataset
2.6.6. Phase V Cluster Evaluation of Technical Quality
2.7. Spatial Analysis and Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrochemical Analysis
3.2. Water Types
3.2.1. Mixed of Ca2+-Mg2+-Na+-Cl−-HCO3− (38%)
3.2.2. Mixed of Ca2+-Mg2+-Na+-Cl− (30.8%)
3.2.3. Mixed of Na+-Mg2+-Cl−-HCO3− (13.7%)
3.3. K-Means Clustering on High Dimensional Dataset
3.4. Principal Component Analyst (PCA)
3.4.1. PCA1
3.4.2. PCA2
3.4.3. PCA3
3.4.4. PCA4
3.5. K-Means Clustering on Low Dimensional Dataset
3.5.1. First Class: 160 Wells
3.5.2. Second Class: 166 Wells
3.5.3. Third Class: 256 Wells
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Mutairi, N.; Abahussain, A.; El-Battay, A. Spatial and temporal characterizations of water quality in Kuwait Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddameri, V.; Honnungar, V.; Hernandez, E.A. Assessment of groundwater water quality in central and southern Gulf Coast aquifer, TX using principal component analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 2653–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, U.N.; Toriman, M.E.; Juahir, H.; Abdullahi, M.G.; Rabiu, A.A.; Isiyaka, H. Assessment of groundwater quality using multivariate statistical techniques in Terengganu. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Belkhiri, L.; Narany, T.S. Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis, Geostatistical Techniques and Structural Equation Modeling to Identify Spatial Variability of Groundwater Quality. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 2073–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.M.; Kusin, F.M.; Asha’ari, Z.H.; Aris, A.Z. Characterization of Water Quality Conditions in the Klang River Basin, Malaysia Using Self Organizing Map and K-means Algorithm. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.-Y.; Soo, C.-L.; Liew, J.-J.; Nyanti, L.; Sim, S.-F.; Grinang, J. Application of multivariate statistical analysis in evaluation of surface river water quality of a tropical river. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 5737452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qian, H.; Chen, J.; Qiao, L. Assessment of Groundwater Chemistry and Status in a Heavily Used Semi-Arid Region with Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Water 2014, 6, 2212–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, R. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Natural Water System: A Case Study in Kangding County, Southwestern China. Water 2018, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh, D.; Singh, S.K.; Shukla, D.N. Assessment of river water quality and ecological diversity through multivariate statistical techniques, and earth observation dataset of rivers Ghaghara and Gandak, India. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2017, 15, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.A. Groundwater quality assessment of the shallow aquifers west of the Nile Delta (Egypt) using multivariate statistical and geostatistical techniques. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 95, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Advances in K-Means Clustering: A Data Mining Thinking; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Ding, C.; Liu, J.; Luo, B. PCA-guided search for K-means. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2015, 54, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, M.; Karypis, G.; Kumar, V. A Comparison of Document Clustering Techniques. In Proceedings of the Sixth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Boston, MA, USA, 20–23 August 2000; pp. 525–526. [Google Scholar]
- Mooi, E.; Sarstedt, M. Cluster Analysis. A Concise Guide to Market Research: The Process, Data, and Methods Using IBM SPSS Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 237–284. [Google Scholar]
- Charrad, M.; Ghazzali, N.; Boiteau, V.; Niknafs, A. NbClust: An R Package for Determining the Relevant Number of Clusters in a Data Set. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 61, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Chen, S.H.; Lin, J.M. K-means method for rough classification of R&D employees’ performance evaluation. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2006, 13, 365–377. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I. Mining Multivariate Associations within GIS Environments. In Innovations in Applied Artificial Intelligence, Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Industrial and Engineering Applications Intelligence and Expert Systems, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 17–20 May 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek, W.F.; Delmerico, A.M. Geographic information systems. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2009, 1, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CNA. Determinación de la Disponibilidad de Agua en el Acuífero Santo Domingo Estado de Baja California Sur, Subgerencia de Evaluación y Modelación Hidrogeológica, Mexico; Comisión Nacional del Agua: Mexico City, Mexico, 2002. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Jobst, W.; Miguel, I.; Aurora, S.; Enrique, T.; Alba, V.; Bernardo, M. El problema del agua en zonas áridas: Dos ejemplos de Baja California Sur. In Uso y Gestión del Agua en las Zonas Semiáridas y áridas: El Caso de La Región de Murcia (España) y Baja California Sur (Mexico); Editum Series; Universidad de Murcia: Murcia, Spain, 2010; pp. 91–110. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- CONAGUA. Estadísticas Agrícolas de los Distritos de Riego; Año agrícola 2013–2014; Comisión Nacional del Agua: Mexico City, Mexico, 2015; p. 408. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Mina, U. Bosquejo geológico del territorio sur de la Baja California. Boletín de la Asociación Mexicana de Geólogos Petroleros 1957, 9, 139–267. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- De Cserna, Z. An Outline of the Geology of Mexico. In The Geology of North America An Overview; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1989; pp. 233–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zenteno, D.J.M. The Geology of the Mexican Republic; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Boulder, CO, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, A.; Carrillo-Rivera, J.J.; Huizar-Álvarez, R.; Graniel-Castro, E. Salinization in coastal aquifers of arid zones: An example from Santo Domingo, Baja California Sur, Mexico. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurl, J.; Imaz-Lamadrid, M.A. Coupled surface water and groundwater model to design managed aquifer recharge for the valley of Santo Domingo, B.C.S., Mexico. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DESISA. Actualización del Estudio Geohidrológico del Valle de Santo Domingo, Baja California Sur; Comisión Nacional del Agua: Mexico City, Mexico, 1997. Unpublished. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- APHA; WPCF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.; Skougstad, M.; Fishmen, M. Method for Collection and Analyzing of Water Samples for Dissolved Minerals and Gases; US Govt Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1983; Volume 75.
- Simeonov, V.; Stratis, J.A.; Samara, C.; Zachariadis, G.; Voutsa, D.; Anthemidis, A.; Sofoniou, M.; Kouimtzis, T. Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4119–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, W.D.; del Pilar, D.A.M.A.; Valeria, A.M.A.; Fabiana, P.S.; Cecilia, H.A.; de los Ángeles, B.M.A. Pattern Recognition Techniques for the Evaluation of Spatial and Temporal Variations in Water Quality. A Case Study: Suquı́a River Basin (Córdoba–Argentina). Water Res. 2001, 35, 2881–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žalik, K.R. An efficient k′-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2008, 29, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, L.; Chartier, S. The k-means clustering technique: General considerations and implementation in Mathematica. Tutor. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2013, 9, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherill, G.; Burton, P.W. Delineation of shallow seismic source zones using K-means cluster analysis, with application to the Aegean region. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 176, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juahir, H.; Zain, S.; Yusoff, M.; Hanidza, T.I.T.; Armi, A.S.M.; Toriman, M.; Mokhtar, M. Spatial water quality assessment of Langat River Basin (Malaysia) using environmetric techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatvani, I.; Magya, N.; Tanos, P.; Korponai, J.; Székely, I.; Herzig, A.; Kovács, J. Determining Anthropogenic Effects Using Principal Component Analysis on a Fluvial (E Hungary) and Two Lake Ecosystems (W Hungary, E Austria). In Proceedings of the CMA4HC: Use of Multivariate Analysis and Chemometrics in Cultural Heritage and Environment, Rome, Italy, 27–30 May 2012; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, G.; Ma, C.; Wu, J. Data Clustering: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications; SIAM (Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics): Philadelphia, PA, USA; American Statistical Association: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfi, S.; Zouari, K.; Feki, S.; Mami, E. Study of variation in groundwater quality in a coastal aquifer in north-eastern Tunisia using multivariate factor analysis. Quat. Int. 2013, 302, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Bellomo, S.; Brusca, L.; D’Alessandro, W.; Federico, C. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting groundwater quality of an active volcano (Mt. Etna, Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 863–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Groves, C.; Yuan, D.; Kambesis, P. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in the Nandong karst underground river system in Yunan, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2009, 109, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xie, D.; Zhang, C. Assessing the impact of natural and anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality in coastal alluvial aquifers of the lower Liaohe River Plain, NE China. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mexican Official Norm. Environmental Health, Water Use and Human Consumption: Permissible Limits of Quality and Treatments to Be Bound Water for Drinking Water; Mexican Official Norm: D.F. Mexico, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 29, Rev. 1; U. N. Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1985; Available online: http://www.fao.org/DOCReP/003/T0234e/T0234e00.htm (accessed on 27, July, 2016).
- Al-Kalbani, M.S.; Price, M.F.; Ahmed, M.; Abahussain, A.; O’Higgins, T. Environmental quality assessment of groundwater resources in Al Jabal Al Akhdar, Sultanate of Oman. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3539–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh; Malik, A.; Mohan, D.; Singh, V.K.; Sinha, S. Evaluation of groundwater quality in northern Indo-Gangetic alluvium region. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 112, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, R.; Rajmohan, N.; Mahendran, U.; Senthamilkumar, S. Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Thanjavur city, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 171, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subba, R.N. Geochemistry of groundwater in parts of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Geol. 2002, 41, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAGUA. Programa de medidas preventivas y de mitigación de la sequía Consejo de Cuenca Baja California Sur; Comisión Nacional del Agua: Mexico City, Mexico, 2018. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]








| Parameter | Min | Max | Mean Value | S.D. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.40 | 8.78 | 8.10 | 0.31 |
| TDS | 326.40 | 5606.40 | 1285.10 | 765.79 |
| EC | 0.01 | 8.76 | 2.01 | 1.20 |
| HCO3− | 36.60 | 683.20 | 237.50 | 60.83 |
| Cl− | 42.54 | 2613.37 | 456.32 | 355.44 |
| SO42− | 2.73 | 325.73 | 29.23 | 34.53 |
| Ca2+ | 4.41 | 731.26 | 109.46 | 99.20 |
| Mg2+ | 11.79 | 238.50 | 64.68 | 42.46 |
| K+ | 1.17 | 24.24 | 6.90 | 3.49 |
| Na+ | 16.10 | 1051.10 | 194.00 | 126.50 |
| NO3− | 0.01 | 30.30 | 6.85 | 4.14 |
| PO43− | 0.001 | 4.27 | 0.03 | 0.23 |
| B | 0.18 | 5.00 | 0.50 | 0.43 |
| Fe3+ | 0.001 | 5.06 | 0.23 | 0.56 |
| Mn2+ | 0.001 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| F− | 0.03 | 0.95 | 0.34 | 0.14 |
| Br− | 0.02 | 5.67 | 0.98 | 0.66 |
| Li+ | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Sr2+ | 0.07 | 4.33 | 0.64 | 0.52 |
| Cu2+ | 0.001 | 8.83 | 0.07 | 0.38 |
| Zn2+ | 0.0004 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Al3+ | 0.001 | 7.47 | 0.19 | 0.43 |
| Cr3+ | 0.001 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Ni2+ | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.005 | 0.01 |
| Pb2+ | 0.0002 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Co2+ | 0.0002 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.0044 |
| Cd3+ | 0.00002 | 0.003 | 0.0001 | 0.0004 |
| S.W.L. | 16.91 | 81.00 | 55.89 | 14.00 |
| Variable | EC | TDS | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | Cl− | SO42− | Br | Li | Sr | Zn | Cr | Static Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 1 | |||||||||||||
| TDS | 0.99 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Ca2+ | 0.82 | 0.82 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Mg2+ | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Na+ | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.37 | 0.58 | 1 | |||||||||
| K+ | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 1 | ||||||||
| Cl− | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.72 | 0.49 | 1 | |||||||
| SO42− | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.61 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.28 | 0.72 | 1 | ||||||
| Br | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.75 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 0.75 | 0.53 | 1 | |||||
| Li | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.66 | 0.38 | 0.57 | 1 | ||||
| Sr | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.85 | 0.57 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 1 | |||
| Zn | −0.04 | −0.04 | −0.04 | −0.03 | 0.01 | −0.02 | −0.02 | −0.06 | −0.02 | −0.02 | −0.03 | 1 | ||
| Cr | −0.03 | −0.03 | −0.03 | −0.02 | 0.00 | −0.05 | −0.02 | −0.05 | −0.01 | −0.02 | −0.03 | 0.92 | 1 | |
| Static water Level | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.01 | −0.06 | 0.50 | 0.07 | −0.13 | 0.03 | −0.03 | 0.18 | −0.04 | −0.03 | 1 |
| Variables | Component Matrix | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | Communality | |
| pH | 0.155 | 0.147 | 0.360 | 0.110 | 0.187 |
| TDS | −0.952 | 0.364 | −0.043 | −0.007 | 1.041 |
| EC | −0.950 | 0.303 | −0.033 | −0.007 | 1.036 |
| HCO3− | 0.543 | −0.030 | −0.843 | 0.250 | 0.929 |
| Cl− | −0.954 | −0.059 | −0.250 | 0.020 | 0.916 |
| SO42− | −0.800 | −0.121 | −0.210 | 0.163 | 0.725 |
| Ca2+ | −0.819 | 0.197 | 0.112 | −0.201 | 0.762 |
| Mg2+ | −0.843 | 0.285 | −0.042 | −0.057 | 0.797 |
| K+ | −0.203 | −0.100 | 0.764 | 0.153 | 0.659 |
| Na+ | −0.864 | −0.010 | −0.323 | 0.302 | 0.888 |
| NO3− | −0.081 | 0.047 | −0.399 | −0.293 | 0.254 |
| Fe3+ | −0.134 | −0.187 | 0.120 | 0.768 | 0.658 |
| Mn2+ | −0.238 | −0.053 | 0.142 | 0.896 | 0.883 |
| Cu2+ | 0.310 | 0.865 | −0.039 | 0.018 | 0.846 |
| Zn2+ | 0.201 | 0.794 | −0.033 | −0.164 | 0.698 |
| Cr3+ | 0.216 | 0.910 | −0.049 | −0.141 | 0.897 |
| Pb2+ | 0.059 | 0.792 | −0.029 | 0.010 | 0.631 |
| Static water level | 0.372 | −0.044 | 0.823 | −0.137 | 0.836 |
| Eigen values | 6.113 | 3.311 | 2.414 | 1.804 | |
| Variability (%) | 33.96 | 16.553 | 12.072 | 9.021 | |
| Cumulative (%) | 33.96 | 50.514 | 62.586 | 71.607 | |
| Parameter | Class 1 (n = 160) | Class 2 (n = 166) | Class 3 (n = 256) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Median | S.D. | Min | Max | Mean | Median | S.D. | Min | Max | Mean | Median | S.D. | |
| pH | 6.40 | 8.38 | 7.85 | 7.84 | 0.24 | 7.14 | 8.78 | 8.21 | 8.21 | 0.32 | 6.97 | 8.78 | 8.18 | 8.15 | 0.26 |
| TDS | 6.40 | 5606.40 | 2169.94 | 1926.40 | 883.22 | 326.40 | 998.40 | 671.77 | 665.60 | 130.56 | 576.00 | 2035.20 | 1126.48 | 1100.80 | 280.38 |
| EC | 0.01 | 8.76 | 3.39 | 3.01 | 1.38 | 0.51 | 1.56 | 1.05 | 1.04 | 0.20 | 0.90 | 3.18 | 1.76 | 1.72 | 0.44 |
| HCO3− | 85.40 | 683.20 | 235.29 | 228.14 | 71.91 | 131.76 | 475.80 | 247.56 | 244.00 | 54.45 | 36.60 | 500.20 | 232.45 | 231.80 | 56.44 |
| Cl− | 141.80 | 2613.37 | 872.41 | 754.02 | 409.32 | 42.54 | 384.99 | 169.31 | 170.16 | 53.60 | 192.49 | 811.45 | 380.81 | 357.69 | 117.91 |
| SO42− | 4.64 | 325.73 | 57.07 | 40.32 | 51.97 | 2.89 | 35.91 | 11.15 | 9.22 | 6.65 | 2.73 | 99.23 | 23.50 | 19.32 | 16.51 |
| Ca2+ | 46.89 | 731.26 | 217.96 | 183.57 | 123.91 | 4.41 | 129.06 | 43.51 | 40.48 | 21.20 | 16.83 | 257.71 | 83.81 | 76.25 | 40.77 |
| Mg2+ | 18.58 | 238.50 | 116.16 | 107.77 | 41.84 | 11.79 | 61.11 | 29.14 | 28.37 | 9.60 | 17.62 | 123.44 | 55.35 | 53.22 | 19.79 |
| K+ | 1.95 | 24.24 | 9.18 | 8.60 | 4.23 | 1.17 | 9.78 | 4.55 | 4.30 | 2.03 | 1.96 | 15.25 | 6.98 | 7.04 | 2.63 |
| Na+ | 80.50 | 1051.10 | 287.90 | 239.20 | 185.26 | 16.10 | 264.50 | 119.84 | 112.70 | 44.62 | 66.70 | 533.60 | 183.21 | 174.80 | 67.49 |
| NO3− | 0.01 | 29.60 | 8.38 | 7.41 | 4.93 | 0.43 | 30.30 | 6.83 | 5.90 | 4.10 | 0.37 | 23.70 | 5.90 | 5.17 | 3.26 |
| PO43− | 0.001 | 2.49 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.002 | 4.27 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.39 | 0.001 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| B | 0.18 | 3.47 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.55 | 0.18 | 5.00 | 0.005 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.19 | 2.45 | 0.005 | 0.37 | 0.30 |
| Fe3+ | 0.002 | 4.13 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0.65 | 0.003 | 3.82 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.001 | 5.06 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.52 |
| Mn2+ | 0.001 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| F− | 0.091 | 0.66 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.95 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.76 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.13 |
| Br− | 0.04 | 5.67 | 0.02 | 1.61 | 0.73 | 0.02 | 2.86 | 0.005 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.24 | 2.30 | 0.01 | 0.88 | 0.39 |
| Li+ | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Sr2+ | 0.29 | 4.33 | 0.01 | 1.10 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 0.68 | 0.003 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 1.50 | 0.01 | 0.50 | 0.19 |
| Cu2+ | 0.001 | 0.66 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.001 | 8.83 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.70 | 0.001 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| Zn2+ | 0.0004 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 0.30 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Al3+ | 0.001 | 1.22 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.001 | 7.47 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 0.002 | 4.76 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.35 |
| Cr3+ | 0.001 | 0.45 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 0.30 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Ni2+ | 0.001 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.05 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Pb2+ | 0.0002 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Co2+ | 0.0002 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.005 |
| Cd3+ | 0.00002 | 0.0029 | 0.0001 | 0.00002 | 0.0005 | 0.00002 | 0.002 | 0.00005 | 0.00002 | 0.0002 | 0.00002 | 0.003 | 0.0001 | 0.00002 | 0.0004 |
| S.W.L. | 16.91 | 77.105 | 54.69 | 61.01 | 16.67 | 17.76 | 74.76 | 52.39 | 54.09 | 12.54 | 21.18 | 81.00 | 58.89 | 61.28 | 12.91 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marín Celestino, A.E.; Martínez Cruz, D.A.; Otazo Sánchez, E.M.; Gavi Reyes, F.; Vásquez Soto, D. Groundwater Quality Assessment: An Improved Approach to K-Means Clustering, Principal Component Analysis and Spatial Analysis: A Case Study. Water 2018, 10, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040437
Marín Celestino AE, Martínez Cruz DA, Otazo Sánchez EM, Gavi Reyes F, Vásquez Soto D. Groundwater Quality Assessment: An Improved Approach to K-Means Clustering, Principal Component Analysis and Spatial Analysis: A Case Study. Water. 2018; 10(4):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040437
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarín Celestino, Ana Elizabeth, Diego Armando Martínez Cruz, Elena María Otazo Sánchez, Francisco Gavi Reyes, and David Vásquez Soto. 2018. "Groundwater Quality Assessment: An Improved Approach to K-Means Clustering, Principal Component Analysis and Spatial Analysis: A Case Study" Water 10, no. 4: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040437
APA StyleMarín Celestino, A. E., Martínez Cruz, D. A., Otazo Sánchez, E. M., Gavi Reyes, F., & Vásquez Soto, D. (2018). Groundwater Quality Assessment: An Improved Approach to K-Means Clustering, Principal Component Analysis and Spatial Analysis: A Case Study. Water, 10(4), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040437