An Optimized Cr(VI)-Removal System Using Sn-based Reducing Adsorbents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Chromium Uptake Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Adsorbent Properties
3.2. Adsorption Evaluation
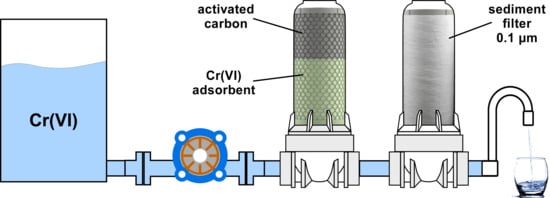
3.3. Filter Efficiency
3.4. Uptake Mechanism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, M. Potential hazards of hexavalent chromate in our drinking water. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 188, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Klein, C.B. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of chromium compounds in humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, J.J.; Sedman, R.M.; Reynolds, S.D.; Sherman, C.D.; Li, L.H.; Howd, R.A.; Sandy, M.S.; Zeise, L.; Alexeeff, G.V. Cancer mortality in a Chinese population exposed to hexavalent chromium in drinking water. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaprara, E.; Kazakis, N.; Simeonidis, K.; Coles, S.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Samaras, P.; Mitrakas, M. Occurrence of Cr(VI) in drinking water of Greece and relation to the geological background. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 281, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziritis, E.; Kelepertzis, E.; Korres, G.; Perivolaris, D.; Repani, S. Hexavalent chromium contamination in groundwaters of Thiva Basin, Central Greece. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chromium-6 Drinking Water MCL, California State Water Quality Control Board. Available online: https://www.waterboards.ca.gov/drinking_water/certlic/drinkingwater/Chromium6.html (accessed on 20 October 2019).
- Simeonidis, K.; Martinez-Boubeta, C.; Zamora-Pérez, P.; Rivera-Gil, P.; Kaprara, E.; Kokkinos, E.; Mitrakas, M. Implementing nanoparticles for competitive drinking water purification. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengaraj, S.; Yeon, K.H.; Moon, S.H. Removal of chromium from water and wastewater by ion exchange resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 87, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korus, I.; Loska, K. Removal of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions by means of polyelectrolyte-enhanced ultrafiltration. Desalination 2009, 273, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golder, A.K.; Chanda, A.K.; Samanta, A.N.; Ray, S. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution: Electrocoagulation vs chemical coagulation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 2177–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampanpanish, P.; Pongsapich, W.; Khaodhiar, S.; Khan, E. Chromium removal from soil by phytoremediation with weed plant species in Thailand. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2006, 6, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, P.; Palanivelu, K. Solvent extraction of hexavalent chromium with tetrabutyl ammonium bromide from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 40, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrakas, M.G.; Pantazatou, A.S.; Tzimou-Tsitouridou, R.; Sikalidis, C.A. Influence of pH and temperature on Cr(VI) removal from a natural water using Fe(II): A pilot and full scale case study. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 33, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, M.J.; Blute, N.K.; Seidel, C.; Qin, G.; Fong, L. Pilot-scale studies of hexavalent chromium removal from drinking water. J.-Am. Water Works Assoc. 2006, 98, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, S.; Simeonidis, K.; Mitrakas, M.; Zouboulis, A.; Ernst, M.; Katsoyiannis, I.A. Reductive precipitation and removal of Cr(VI) from groundwaters by pipe flocculation-microfiltration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 12256–12262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Candela, M.; Martín-Martínez, J.; Torregrosa-Maciá, R. Chromium(VI) removal with activated carbons. Water Res. 1995, 29, 2174–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U. Activated carbons and low cost adsorbents for remediation of tri- and hexavalent chromium from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 762–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, G.; Tang, J.; Xu, X. Highly active nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI)-Fe 3O 4 nanocomposites for the removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 369, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; Traina, S.J. Cr(VI) reduction and immobilization by magnetite under alkaline pH conditions: The role of passivation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4499–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaprara, E.; Simeonidis, K.; Zouboulis, A.; Mitrakas, M. Rapid small-scale column tests for Cr(VI) removal by granular magnetite. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2016, 16, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaprara, E.; Tziarou, N.; Kalaitzidou, K.; Simeonidis, K.; Balcells, L.; Pannunzio, E.V.; Zouboulis, A.; Mitrakas, M. The use of Sn(II) oxy-hydroxides for the effective removal of Cr(VI) from water: Optimization of synthesis parameters. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Centre for Diffraction Data, Joint Center for Powder Diffraction Studies. Powder Diffraction File (PDF); International Centre for Diffraction Data, Joint Center for Powder Diffraction Studies: Newton Square, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Amy, G.; Chen, H.W.; Drizo, A.; von Gunten, U.; Brandhuber, P.; Hund, R.; Chowdhury, Z.; Kommineni, S.; Sinha, S.; Jekel, M.; et al. Adsorbent Treatment Technologies for Arsenic Removal, 1st ed.; AWWA Research Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kazakis, N.; Kantiranis, N.; Voudouris, K.S.; Mitrakas, M.; Kaprara, E.; Pavlou, A. Geogenic Cr oxidation on the surface of mafic minerals and the hydrogeological conditions influencing hexavalent chromium concentrations in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparazzo, E. XPS analysis of oxides. Surf. Interface Anal. 1988, 12, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.A.; Kiser, J.R.; Kwon, H.; Kanel, S.R. Spectroscopic investigation of Cr(III)- and Cr(VI)-treated nanoscale zerovalent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinakidou, F.; Kaprara, E.; Katsikini, M.; Paloura, E.C.; Simeonidis, K.; Mitrakas, M. Sn(II) oxy-hydroxides as potential adsorbents for Cr(VI)-uptake from drinking water: An X-ray absorption study. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresintsi, S.; Simeonidis, K.; Mitrakas, M. Mn-feroxyhyte: The role of synthesis conditions on As(III) and As(V) removal capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 251, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadopoulos, G.; Asimakidou, T.; Karfaridis, D.; Kellartzis, I.; Vourlias, G.; Mitrakas, M.; Simeonidis, K. An Optimized Cr(VI)-Removal System Using Sn-based Reducing Adsorbents. Water 2019, 11, 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122477
Papadopoulos G, Asimakidou T, Karfaridis D, Kellartzis I, Vourlias G, Mitrakas M, Simeonidis K. An Optimized Cr(VI)-Removal System Using Sn-based Reducing Adsorbents. Water. 2019; 11(12):2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122477
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadopoulos, George, Theopoula Asimakidou, Dimitrios Karfaridis, Ioannis Kellartzis, George Vourlias, Manassis Mitrakas, and Konstantinos Simeonidis. 2019. "An Optimized Cr(VI)-Removal System Using Sn-based Reducing Adsorbents" Water 11, no. 12: 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122477
APA StylePapadopoulos, G., Asimakidou, T., Karfaridis, D., Kellartzis, I., Vourlias, G., Mitrakas, M., & Simeonidis, K. (2019). An Optimized Cr(VI)-Removal System Using Sn-based Reducing Adsorbents. Water, 11(12), 2477. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122477