The Threshold Effect of Environmental Regulation, FDI Agglomeration, and Water Utilization Efficiency under “Double Control Actions”—An Empirical Test Based on Yangtze River Economic Belt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Efficiency Measurement Model
2.2. Threshold Regression Model
3. Results and Discussion
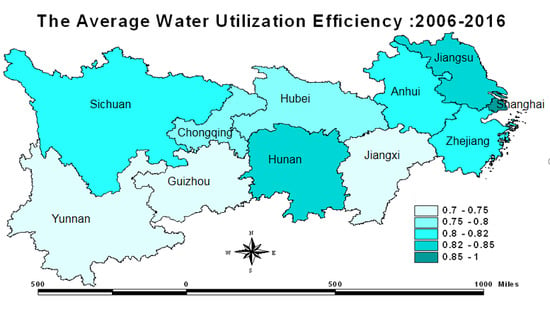
3.1. Water Resource Utilization Efficiency
3.1.1. Data Selection and Description
3.1.2. Empirical Estimation Results
3.2. The Threshold Effects Regression
3.2.1. Variable Selection and Description
3.2.2. Threshold Effect Estimation
3.2.3. Discuss of the Threshold Effects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, X.H.; Tang, N.; Yu, X.Y. Spatial Correlation of Water Resource Consumption Intensity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt under the Dual-Control Action. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. (HK, China) 2018, 208, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.G. Exploring China’s water governance. J. Chin. Soc. Sci. 2015-06-12(A04).
- Taylor, M. Unbundling the Pollution Haven Hypothesis. Adv. Econ. Anal. Policy 2004, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.J.; He, C.F. China’s Regional Difference of Water Resource Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2011, 21, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.J.; Liang, S.X.; Meng, Y. Evaluation of Water Resources Comprehensive Utilization Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 16, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Huang, J.W.; Li, B.; Fu, S.D.; Zhang, X. Data Mining Model in Regional Target Decomposition of Water Resources Utilization Efficiency. In Architecture and Building Materials (CEABM); Trans Tech Publications: Haikou, China, 2014; Volume 5, pp. 24–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Huang, X.F. Study on Efficiency of Rainfall and Flood Water Resources Utilization in Coastal Area. In In Architectural and Hydraulic Engineering (ICCAHE 2013); TRANS TECH PUBLICATIONS LTD: Zhuhai, China, 2013; Volume 7, pp. 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.H.; He, J.H.; Wang, L.Y. Inter-provincial Water Resources Utilization Efficiency and Its Driving Factors considering Undesirable Outputs. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.H.; Gao, S.H.; He, J.H. Spatial-temporal Differentiation and Driving Factors of Regional Innovation System Wfficiency—From the Perspective of Water Ecological Security. East China Econ. Manag. 2019, 33, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Bian, Y.Z.; Nie, W.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L. Water Resources Utilization Efficiency in Key Environmental Protection Cities in China. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2018, 36, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Xu, C.D. Dynamic Efficiency and Unconditional β Convergence of Water Resources Utilization on the Yangtze River Economic Belt: Based on Three-stage DEA-Malmquist Index Method. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2017, 26, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, I.; Ugelow, J.I. Environmental Policies in Developing Countries. Ambio 1997, 8, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Copeland, B.R.; Taylor, M.S. Trade, Growth and the Environment. J. Econ. Lit. 2004, 42, 7–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esty, D.C.; Dua, A. Sustaining the Asia Pacific Miracle: Environmental Protection and Economic Integration. Asia Pac. J. Environ. Law 1997, 3, 150–152. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D.C. FDI, Government Regulation and the Water-Pollution in China: An Empirical Test Based on the Decomposition of Industry Structure and the Technology Progress. China Econ. Q. 2014, 13, 491–514. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.; Linde, C. Toward a New Conception of the Environment Competitiveness Relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchumanan, R.; Kodama, F. Reconciling the Conflict between the Pollution-Haven Hypothesis and an Emerging Trajectory of International Technology Transfer’ Research. Res. Policy 2000, 29, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskeland, G.; Harrison, E. Moving to Greener Pastures? Multinationals and the Pollution Haven Hypothesis. J. Dev. Econ. 2003, 70, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Lv, Y. Impact of Foreign Direct Investment on China’s Environment: An Empirical Study Based on Industrial Panel Data. Soc. Sci. China 2012, 5, 54–75. [Google Scholar]
- Manello, A. Productivity Growth, Environmental Regulation and Win-Win Opportunities: The Case of Chemical Industry in Italy and Germany. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 262, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; He, Q.; Black, A.; Ghobadian, A.; Gallear, D. Environmental Regulations, Innovation and Firm Performance: A Revist of the Porter Hypothesis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 155, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.S.; Wang, Y.Z. Fiscal decentralization, environmental regulation and regional eco-efficiency: Based on the dynamic spatial Durbin model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 27, 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, N. Environmental Efficiency, Industrial Heterogeneity and Intensity of Optimal Regulation—Nonlinear Test Based on Industrial Panel-data. China Ind. Econ. 2012, 3, 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.Q. Study on the Threshold Effect of Environmental Regulation on Industrial Green Productivity in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 2018, 35, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Mao, G.X.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, C.X. Threshold Effect of FDI and Environmental Regulation on Industrial Water Efficiency. Int. Bus. 2018, 2, 100–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.T.; Jiang, Y. Did FDI improve the performance of water supply enterprises in China? Henan Soc. Sci. 2012, 20, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, H.R.; Xu, X.Y.; Xie, Q. Relevant issues on utilization efficiency and evaluation methods for water resources. J. Econ. Water Resour. 2010, 28, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.L. Data Envelopment Analysis Model for Evaluating Relative Effectiveness—DEA and Network DEA; Renmin University Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.L.; Wang, R.; Zeng, X.Q. Water Resources Utilization Efficiency and Influence Factors under Environmental Restrictions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.M.; Liu, X.C. Environmental Regulation and Green Economic Efficiency. Stat. Res. 2015, 32, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.J.; Guo, S.L.; Shi, Y.D. Environmental regulation, industrial structure upgrading and employment effects: Linear or non-linear? Econ. Sci. 2012, 6, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.Q.; Miao, Z. Heterogeneity threshold effect of R&D investment on green innovation efficiency based on Chinese high-tech industries. Sci. Res. Manag. 2016, 37, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Peng, X.; Ouyang, M.H. Environmental Regulation, Green Total Factor Productivity and the Transformation of China’s Industrial Development Mode—Analysis Based on Data of China’s 36 Industries. China Ind. Econ. 2013, 4, 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, B. Sample Splitting and Threshold Estimation. Econometrica 2000, 63, 575–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold Effects in Non-dynamic Panels: Estimation, Testing and Inference. J. Econom. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.L.; Huang, D.C.; Zhang, J.G. Water Resource Utility Efficiency and Its Influencing Factors Considering Undesirable Goods. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.S.; Sun, C.Z.; Liu, F.C. Interprovincial Two-stage Water Resource Utilization Efficiency under Environmental Constraint and Spatial Spillover Effects in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, R.W. A Perpetual Inventory of National Wealth. Stud. Income Wealth 1951, 14, 5–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, G.Y.; Zhang, J.P. The Estimation of China’s provincial capital stock: 1952–2000. Econ. Res. J. 2004, 10, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.Z.; Xie, W. Measurement of the Driving Effects on Industrial Water Utilization Change and its Spatial Difference Analysis in China. Econ. Geogr. 2011, 31, 666–672. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ma, X.C. The Utilization Efficiency of Industrial Water under the Dual Constraints of Resource and Environmet—An Empirical Study Based on SBM-Undesirable and Meta-frontier Model. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 920–933. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.H.; He, J.H.; Yu, X.Y. Spatial Differentiation of Carbon Emission Efficiency of “Silk Road Economic Belt” based on Environmental Regulation. Iop Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. (HK, China) 2018, 208, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, D. Environmental Regulation and Revealed Comparative Advantages in Europe: Is China a Pollution Haven. Rev. Int. Econ. 2012, 20, 616–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Song, X.N.; Xue, H.F. Decoupling Relationship and Dynamic Response between Industrial Water Intensity, Environmental Regulation and Technological Progress. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 27, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, W.; Zakaria, M.; Shahzad, S.J.H. Effect of FDI on Pollution in China: New Insights Based on Wavelet Approach. Sustainablity 2018, 10, 3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Zhu, F.P. The Threshold Effect of Human Capital in China’s Economic Growth. Stat. Res. 2016, 33, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Qiu, J.Q. Research on Water Environment Regulation Based on Environmental Kuznets Curve. J. Jiangxi Univ. Financ. Econ. 2018, 4, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Deng, Y.X.; Lu, Z.N.; Chen, H. Is Environmental Regulation Effective in China? Evidence from City-level Panel Data. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.W. Eutrophic Status and Causing Factors for a Large, Shallow and Subtropical Lake Taihu, China. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T. Is There Environmental Regulation Competition under Land Fiance? China Econ. Stud. 2016, 5, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sinn, H.W. The Green Paradox; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, S.S.; Hong, D.L. River Leaders in China: Party-state Hierarchy and Transboundary Governance. Polit. Geogr. 2018, 62, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, V.; Mazzanti, M. Environmental Performance, Innovation and Spillovers: Evidence from a Regional NAMEA. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 89, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Qi, S.Z. Is the Hypothesis “FDI Decreasing Energy Intensity of the Host Country” Valid in China? Based on empirical analysis of Chinese provincial industrial panel data. World Econ. Stud. 2016, 3, 108–122. [Google Scholar]
- Javorcik, B.S.; Spatareanu, M. Does it Matter Where you Come from? Vertical Spillovers from Foreign Direct Investment and the Origin of Investors. J. Dev. Econ. 2011, 96, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.Y.; Hu, J.; Cao, X. Different Sources of FDI, Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity. J. Int. Trade 2018, 2018, 134–148. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A. Economic Growth and Environment. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Guo, L.; Yu, T.S. The Intensity of Environmental Regulation Technological Progress of Production. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 2, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.Q.; Kolstad, C.D. Do Lax Environmental Regulations Attract Froeign Direct Investment? Environ. Resour. Econ. 2002, 21, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.Q.; Xing, Z.C. Re-Examining Regional Total-Factor Water Efficiency and Its Determinants in China: A Parametric Distance Function Approach. Water 2018, 10, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Province | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | 0.9457 | 1.0055 | 0.9830 | 0.8429 | 0.8515 | 0.9180 | 0.9525 | 1.0111 | 1.0045 | 1.0054 | 1.0410 |
| Jiangsu | 0.8495 | 0.8413 | 0.8059 | 0.8031 | 0.8075 | 0.8090 | 0.8227 | 0.8450 | 0.8650 | 0.8801 | 0.9102 |
| Zhejiang | 0.7671 | 0.7795 | 0.7831 | 0.7834 | 0.7871 | 0.7872 | 0.7979 | 0.8131 | 0.8300 | 0.8396 | 0.8697 |
| Anhui | 0.9794 | 0.8926 | 0.8158 | 0.7863 | 0.7949 | 0.7664 | 0.7690 | 0.7692 | 0.7727 | 0.7771 | 0.8324 |
| Jiangxi | 0.7436 | 0.7413 | 0.7513 | 0.7485 | 0.7486 | 0.7333 | 0.7366 | 0.7417 | 0.7545 | 0.7537 | 0.7661 |
| Hubei | 0.7365 | 0.7389 | 0.7402 | 0.7420 | 0.7502 | 0.7486 | 0.7574 | 0.7632 | 0.7691 | 0.7725 | 0.8452 |
| Hunan | 1.0183 | 0.9682 | 0.8732 | 0.7769 | 0.7718 | 0.7724 | 0.7651 | 0.7698 | 0.7776 | 0.7886 | 0.8188 |
| Chongqing | 0.6983 | 0.7150 | 0.7103 | 0.7219 | 0.7636 | 0.7860 | 0.8110 | 0.8204 | 0.8405 | 0.8640 | 0.8023 |
| Sichuan | 0.8537 | 0.8138 | 0.7636 | 0.7737 | 0.7948 | 0.8014 | 0.8181 | 0.8162 | 0.8129 | 0.8199 | 0.8275 |
| Guizhou | 0.7092 | 0.7261 | 0.7335 | 0.7336 | 0.7435 | 0.7204 | 0.7044 | 0.7067 | 0.6776 | 0.6780 | 0.7536 |
| Yunnan | 0.7810 | 0.7802 | 0.7930 | 0.7982 | 0.7963 | 0.7141 | 0.7111 | 0.7150 | 0.7111 | 0.6998 | 0.7180 |
| Variable | Variable Definitions | Unit | Variable Type | Mean | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| effic | Water Utilization efficiency | Relative number | Dependent | 0.8001 | 0.6776 | 1.041 |
| regul | Environmental regulation | % | Independent | 0.0030 | 0.0006 | 0.0118 |
| fdi | Foreign direct investment | Hundred million | Independent | 548.3356 | 11.6684 | 2257.14 |
| pergdp | Per capita GDP | Thousand yuan | Independent | 3.7419 | 0.5787 | 11.6562 |
| indus | Proportion of second industry | % | Independent | 0.4630 | 0.2983 | 0.5635 |
| techn | Technological innovation | Pieces/10,000 | Independent | 8.1150 | 0.3540 | 42.4234 |
| city | Urbanization | % | Independent | 0.5151 | 0.2746 | 0.8960 |
| trade | Foreign trade dependence | % | Independent | 0.3319 | 0.0293 | 1.6742 |
| water | Per capita water resource | cubic meter | Independent | 1816.57 | 89.1160 | 5116.68 |
| Threshold Variable | Hypothetical Test | F Value | p Value | Threshold Estimated | lnpergdp | Per Capita gdp (yuan) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| regul | Single threshold | 16.2362 | 0.0010 | First threshold | 0.5642 | 1.7580 ten thousand |
| Double threshold | 12.2115 | 0.0050 | Second threshold | 2.0803 | 8.0068 ten thousand | |
| lnfdi | Single threshold | 19.7932 | 0.0000 | First threshold | 0.3721 | 1.4507 ten thousand |
| Double threshold | 16.3543 | 0.0000 | Second threshold | 2.1230 | 9.1431 ten thousand | |
| regul*lnfdi | Single threshold | 25.0760 | 0.0000 | First threshold | 0.3721 | 1.4507 ten thousand |
| Double threshold | 13.1933 | 0.0010 | Second threshold | 2.0803 | 8.0068 ten thousand |
| Variable | Estimated Parameter | Variable | Estimated Parameter | Variable | Estimated Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| regul | 8.1223(0.0664) Lnpergdp < 0.5642 | lnfdi | 0.0094(0.5563) Lnpergdp < 0.3721 | Regul*lnfdi | 2.8850(0.0257) Lnpergdp < 0.3721 |
| −5.3649(0.1070) [0.5642, 2.0803] | −0.0068(0.6186) [0.3721, 2.1230] | −0.6631 (0.2369) [0.3721, 2.0803] | |||
| 22.3831(0.0019) Lnpergdp > 2.0803 | 0.0062(0.6721) Lnpergdp > 2.1230 | 3.1695(0.0024) Lnpergdp > 2.0803 | |||
| lnpergdp | 0.0343 (0.4104) | lnpergdp | 0.0527 (0.2138) | lnpergdp | 0.0498 (0.1768) |
| indus | −0.4023 (0.0244) | indus | −0.2340 (0.1113) | indus | −0.3718 (0.0378) |
| techn | 0.0015 (0.0983) | techn | 0.0019 (0.0294) | techn | 0.0015 (0.0807) |
| city | −0.1411 (0.6305) | city | −0.2734 (0.3653) | city | −0.2414 (0.3976) |
| trade | 0.2261 (0.0001) | trade | 0.2196 (0.0001) | trade | 0.2282 (0.0000) |
| lnwater | 0.0113 (0.1224) | lnwater | 0.0081 (0.2535) | lnwater | 0.0070 (0.3031) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, X.; Tang, N.; He, J. The Threshold Effect of Environmental Regulation, FDI Agglomeration, and Water Utilization Efficiency under “Double Control Actions”—An Empirical Test Based on Yangtze River Economic Belt. Water 2019, 11, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030452
Ding X, Tang N, He J. The Threshold Effect of Environmental Regulation, FDI Agglomeration, and Water Utilization Efficiency under “Double Control Actions”—An Empirical Test Based on Yangtze River Economic Belt. Water. 2019; 11(3):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030452
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Xuhui, Ning Tang, and Juhua He. 2019. "The Threshold Effect of Environmental Regulation, FDI Agglomeration, and Water Utilization Efficiency under “Double Control Actions”—An Empirical Test Based on Yangtze River Economic Belt" Water 11, no. 3: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030452
APA StyleDing, X., Tang, N., & He, J. (2019). The Threshold Effect of Environmental Regulation, FDI Agglomeration, and Water Utilization Efficiency under “Double Control Actions”—An Empirical Test Based on Yangtze River Economic Belt. Water, 11(3), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030452