On the Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves, Partial-Area Effect and the Rational Method: Theory and the Engineering Practice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. The Rational Method
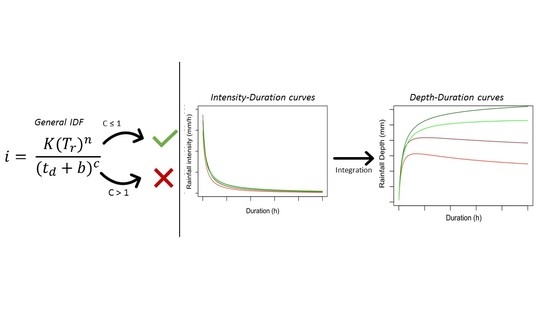
2.2. Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Relationship
2.3. The Partial-Area Effect
2.4. Critical Rainfall Duration for a Given ID Equation in Rational Method Conceptual Framework
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. On the Consistency of IDF Equation and the Partial-Area Effect
3.2. The Inexistence of Partial-Area Effect for Any IDF Relationship
3.3. IDF Equations with in Different Regions of the World
3.3.1. The IDF Equations with in Brazil
3.3.2. IDF Equations in Mexico
3.3.3. IDF Equations in India
3.3.4. IDF Equations in Indiana (USA)
3.4. The IDF and DDF Curves
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grimaldi, S.; Petroselli, A. Avons-nous encore besoin de la formule rationnelle? Une méthode empirique alternative pour l’estimation du débit de pointe dans les petits bassins et les bassins non jaugés. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 60, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, S.; Petroselli, A.; Tauro, F.; Porfiri, M. Temps de concentration: Un paradoxe dans l’hydrologie moderne. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.S. Hydrology and Hydraulic Systems; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce, V.M. Engineering Hydrology: Principles and Practices; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- McCuen, R.H. Hydrologic Analysis and Design, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nzewi, E.U. The McGraw-Hill Civil Engineering PE Exam Depth Guide: Water Resources; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, J.N.B. Liçoes em Modelo e Simulação Hidrológica; Expressão Gráfica: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.S.; Koo, J.H.; Chun, J.A.; Her, Y.G.; Park, S.W.; Yoo, K. Design of drainage culverts considering critical storm duration. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 104, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, K.N.; Ffolliott, P.F.; Magner, J.A. Hydrology and the Management of Watersheds; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Maidment, D.R. Handbook of Hydrology; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, T.S.W. Influence of Loss Model on Design Discharge of Homogeneous Plane. J. Irrig. Drain Eng. 2005, 131, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Kozonis, D.; Manetas, A. A mathematical framework for studying rainfall intensity-duration-frequency relationships. J. Hydrol. 1998, 206, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooge, J.C. The rational method for estimating flood peaks. Engineering 1957, 184, 311–313. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.P.; Woolhiser, D.A. Mathematical Modeling of Watershed Hydrology. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2002, 7, 270–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beven, K.J. Rainfall-Runoff Modelling: The Primer; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.K. History of Hydrology; North-Holland Publishing Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany, T. On the use of self-registering rain and flood gauges in making observations of the relations of rain fall and of flood discharges in a given catchment. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Irel. 1851, 4, 18–33. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, V.; Maidment, D.R.; Mays, L.W. Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Betson, R.P. What is watershed runoff? J. Geophys. Res. 1964, 69, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinks, R.W.; Mays, L.W. Hydrology for Water Excess Management. In Water Resources Handbook; Mays, L., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, B.H. Critical rainfall duration for overland flow from an infiltrating plane surface. J. Hydrol. 1997, 193, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debo, T.N.; Reese, A. Municipal Stormwater Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigon, R.; Odorico, P.; Bertoldi, G. The geomorphic structure of the runoff peak. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1853–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burke, C.C.; Burke, T.T. Stormwater Drainage Manual 2015; Indiana Local Technical Assistance Program (LTAP) Publications: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pruski, F.F.; Teixeira, A.F.; Silva, D.D.; Cecílio, R.A.; Silva, J.M.A. Plúvio 2.1: Chuvas intensas para o Brasil. In HIDROS Dimens. Sist. Hidroagrícolas; Pruski, F.F., Silva, D.D., Teixeira, A.F., Cecílio, R.A., Silva, J.M.A., Griebeler, N.P., Eds.; Editora UFV: Viçosa, Brazil, 2006; pp. 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Manzano-Agugliaro, F.; Zapata-Sierra, A.; Rubí-Maldonado, J.F.; Hernández-Escobedo, Q. Assessment of obtaining IDF curve methods for Mexico. Technol. Cienc. Del. Agua. 2014, 5, 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Formulas. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 1603–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Sierra, A.J.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F.; Ayuso Muñoz, J.L. Assessment of methods for obtaining rainfall intensity-duration-frequency ratios for various geographical areas. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 7, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, H.G., Jr. Rainfall for Urban Stormwater Design. Urban Stormwater Hydrol; American Geophysical Union (AGU): Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 35–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanya, K. Engineering Hydrology, 4th ed.; Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Limited: New Delhi, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- New Jersey Department of Transportation. Roadway Design Manual; New Jersey Department of Transportation: Trenton, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, T.S.W. Call for Awakenings in Storm Drainage Design. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2002, 7, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Class | Frequency | Cumulative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| t* < 2 h | 0 | 0 |
| 2 h < t* < 5 h | 10/544 | 10/544 |
| 5 h < t* < 24 h | 51/544 | 61/544 |
| t* > 24 h | 19/544 | 80/544 |
| Class | Frequency | Cumulative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| t* < 2 h | 8/63 | 8/63 |
| 2 h < t* < 5 h | 11/63 | 19/63 |
| 5 h < t* < 24 h | 7/63 | 26/63 |
| t* > 24 h | 1/63 | 27/63 |
| Class | Frequency | Cumulative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| t* < 2 h | 0/19 | 0/19 |
| 2 h < t* < 5 h | 3/19 | 3/19 |
| 5 h < t* < 24 h | 3/19 | 6/19 |
| t* > 24 h | 1/19 | 7/19 |
| Station | K | n | b | c | t* (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indianapolis | 2.1048 | 0.1733 | 0.47 | 1.1289 | 3.65 |
| South Bend | 1.7204 | 0.1753 | 0.485 | 1.6806 | 0.71 |
| Evansville | 1.9533 | 0.1743 | 0.522 | 1.6408 | 0.81 |
| Fort Wayne | 2.003 | 0.1655 | 0.516 | 1.4643 | 1.11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos, J.N.B.; Studart, T.M.d.C.; Souza Filho, F.d.A.d.; Porto, V.C. On the Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves, Partial-Area Effect and the Rational Method: Theory and the Engineering Practice. Water 2020, 12, 2730. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102730
Campos JNB, Studart TMdC, Souza Filho FdAd, Porto VC. On the Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves, Partial-Area Effect and the Rational Method: Theory and the Engineering Practice. Water. 2020; 12(10):2730. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102730
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos, José Nilson B., Ticiana Marinho de Carvalho Studart, Francisco de Assis de Souza Filho, and Victor Costa Porto. 2020. "On the Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves, Partial-Area Effect and the Rational Method: Theory and the Engineering Practice" Water 12, no. 10: 2730. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102730
APA StyleCampos, J. N. B., Studart, T. M. d. C., Souza Filho, F. d. A. d., & Porto, V. C. (2020). On the Rainfall Intensity–Duration–Frequency Curves, Partial-Area Effect and the Rational Method: Theory and the Engineering Practice. Water, 12(10), 2730. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102730