Machine Learning to Evaluate Impacts of Flood Protection in Bangladesh, 1983–2014
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Context and Related Works
2. Methods
2.1. Machine-Learning Approaches
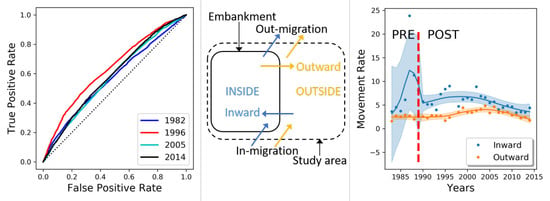
- Based on multidecadal socio-economic survey data, are there any significant differences in socio-economic status of households living inside vs. outside embankment over time, and which variables are most informative of the differences?
- Based on multidecadal events data, are there significant differences in mortality and migration patterns of households living inside vs. outside embankment over time?
2.1.1. Classification Approaches
2.1.2. Regression Approaches
2.2. Evaluation Metric
3. Data
3.1. Socio-Economic Survey Data
3.2. Events Data
4. Results
4.1. Socio-Economic Survey Data Analysis
4.2. Events Data Analysis
4.3. Hydro-Climatic Data Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FAP | Flood Action Plan |
| NWP | National Water Policy |
| NWMP | National Water Management Plan |
| MDIP | Meghna–Dhonagoda Irrigation Project |
| HYV | High Yielding Variety |
| HDSS | Health and Demographic Surveillance System |
| SES | Socio-Economic Survey |
| icddr,b | International Centre for Diarrheal Disease Research, Bangladesh |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| RF | Random Forest |
| SAE | Stacked Auto-Encoders |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| GP | Gaussian Processes |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristics |
| AUC | Area Under ROC Curve |
References
- Whitehead, P.G.; Jin, L.; Macadam, I.; Janes, T.; Sarkar, S.; Rodda, H.J.; Sinha, R.; Nicholls, R.J. Modelling impacts of climate change and socio-economic change on the Ganga, Brahmaputra, Meghna, Hooghly and Mahanadi river systems in India and Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hossain, M.A.; Ahmed, M.; Ojea, E.; Fernandes, J.A. Impacts and responses to environmental change in coastal livelihoods of south-west Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, G.M.M.; Alam, K.; Mushtaq, S.; Filho, W.L. How do climate change and associated hazards impact on the resilience of riparian rural communities in Bangladesh? Policy implications for livelihood development. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 84, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.T.; Mia, M.E.; Ford, J.D.; Robinson, B.E.; Hickey, G.M. Livelihood exposure to climatic stresses in the north-eastern floodplains of Bangladesh. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.M.Q. Global warming and changes in the probability of occurrence of floods in Bangladesh and implications. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2002, 12, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruane, A.C.; Major, D.C.; Yu, W.H.; Alam, M.; Hussain, S.G.; Khan, A.S.; Hassan, A.; Hossain, B.M.T.A.; Goldberg, R.; Horton, R.M.; et al. Multi-factor impact analysis of agricultural production in Bangladesh with climate change. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adger, W.N.; Arnell, N.W.; Tompkins, E.L. Successful adaptation to climate change across scales. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2005, 15, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.S.G.; Haque, A.; Hall, J.W. Have coastal embankments reduced flooding in Bangladesh? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, R.; Fazey, I.; Smith, M.S.; Park, S.; Eakin, H.; Garderen, E.A.V.; Campbell, B. Reconceptualising adaptation to climate change as part of pathways of change and response. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 28, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abel, G.J.; Brottrager, M.; Cuaresma, J.C.; Muttarak, R. Climate, conflict and forced migration. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2019, 54, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sills, E.O.; de Sassi, C.; Jagger, P.; Lawlor, K.; Miteva, D.A.; Pattanayak, S.K.; Sunderlin, W.D. Building the evidence base for REDD+: Study design and methods for evaluating the impacts of conservation interventions on local well-being. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 43, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WARPO. National Water Management Plan (NWMP) Development Strategy; Technical Report; Water Resources Planning Organization (WARPO), Ministry of Water Resources: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, R.; Salehin, M. Flood Risks and Reduction Approaches in Bangladesh. In Disaster Risk Reduction Approaches in Bangladesh; Shaw, R., Mallick, F., Islam, A., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; pp. 65–90. [Google Scholar]
- HTSL. FCD/I Agricultural Study, FAP-12, Main Report; Technical Report; Hunting Technological Services Ltd. FPCO: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, J.U.; Rahman, M.R.; Salehin, M. Flood Control in a Floodplain Country, Experiences of Bangladesh; Islamic Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (ISESCO): Rabat, Morocco, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Shawinigan-Lavalin-Inc. Water Transport Study, Northeast Regional Water Management FAP-6; Technical Report; FPCO: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Shawinigan-Lavalin-Inc. Fisheries Specialist Study, North East Regional Plan; Technical Report; FPCO: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- ODA. FAP-17 Fisheries Studies and Pilot Project—Final Report; Technical Report; Overseas Development Administration: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- MOWR. National Water Policy; The Ministry of Water Resources (MOWR), Government of the Peoples Republic of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1999.
- Rasul, G.; Chowdhury, A.K.M.J.U. Key highlights in sustainable agriculture and natural resource management. In Equity and Social Justice in Water Resource Management in Bangladesh; The Gatekeeper Series; IIED: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- GED. Bangladesh Delta Plan 2100 Bangladesh in the 21st Century; General Economics Division, Bangladesh Planning Commission: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, N.; Ali, T.; Razzaque, A.; Rahman, M.; Zahirul Haq, M.; Saha, S.K.; Ahmed, A.; Sarder, A.; Moinuddin Haider, M.; Yunus, M.; et al. Health and Demographic Surveillance System (HDSS) in Matlab, Bangladesh. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haq, M.Z.; Shajratul Alam, M.; Haider, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Mustafa, A.H.M.G.; Saha, S.K.; Barua, S.; Alam, S.S.; Ali, T.; Alam, N.; et al. Health and Demographic Surveillance System—Matlab; International Centre for Diarrhoeal Diseases Research, Bangladesh (ICDDR,B): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2018; Volume 51. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsul Huda, A.T.M.; Emdadul Huq, M.D.; Bhuiyan, A.I. The Bangladesh Meghna-Dhonagoda Irrigation Project. Pub. Adm. Dev. 1991, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrel, M.; Emch, M.; Streatfield, P.K.; Yunus, M. Spatio-temporal clustering of cholera: The impact of flood control in Matlab, Bangladesh, 1983–2003. Health Place 2009, 15, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhuiya, A.; Wojtyniak, B.; Karim, R. Malnutrition and child mortality: Are socioeconomic factors important? J. Biosoc. Sci. 1989, 21, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myaux, J.A.; Ali, M.; Chakraborty, J.; de Francisco, A. Flood control embankments contribute to the improvement of the health status of children in rural Bangladesh. Bull. World Health Organ. 1997, 75, 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- Bangladesh Rural Advancement Committee. Two Studies on the Impact of Meghna-Dhonagada Flood Control, Drainage and Irrigation Project; BRAC-ICDDR, B Joint Research Project: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Carrel, M.; Voss, P.; Streatfield, P.K.; Yunus, M.; Emch, M. Protection from annual flooding is correlated with increased cholera prevalence in Bangladesh: A zero-inflated regression analysis. Environ. Health 2010, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haque, E.A.; Brander, L.; Brouwer, R.; Akter, S.; Mahmud, S. The environmental and social impacts of flood defences in rural Bangladesh. In Nature’s Wealth: The Rconomics of Ecosystem Services and Poverty; Beukering, P., Papyrakis, E., Bouma, J., Brouwer, R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 296–314. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning (Information Science and Statistics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Szeliski, R. Computer Vision Algorithms and Applications; Springer: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C. Machine Learning, a Probabilistic Perspective. CHANCE 2014, 27, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, D.A. Machine Learning for Healthcare Technologies; Institution of Engineering and Technology Press: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambrisge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Beckel, C.; Sadamori, L.; Santini, S. Automatic Socio-economic Classification of Households Using Electricity Consumption Data. In Proceedings of the E-Energy ’13: Fourth International Conference on Future Energy Systems, Berkeley, CA, USA, 21–24 May 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumenstock, J.; Cadamuro, G.; On, R. Predicting poverty and wealth from mobile phone metadata. Science 2015, 350, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jean, N.; Burke, M.; Xie, M.; Davis, W.M.; Lobell, D.B.; Ermon, S. Combining satellite imagery and machine learning to predict poverty. Science 2016, 353, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolnick, D.; Donti, P.L.; Kaack, L.H.; Kochanski, K.; Lacoste, A.; Sankaran, K.; Ross, A.S.; Milojevic-Dupont, N.; Jaques, N.; Waldman-Brown, A.; et al. Tackling Climate Change with Machine Learning. CoRR 2019, arXiv:1906.05433. [Google Scholar]
- Cordier, T.; Esling, P.; Lejzerowicz, F.; Visco, J.; Ouadahi, A.; Martins, C.; Cedhagen, T.; Pawlowski, J. Predicting the Ecological Quality Status of Marine Environments from eDNA Metabarcoding Data Using Supervised Machine Learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9118–9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Zhang, Z.; Krasnuk, D.; Lathrop, R.G. Evaluating the impact of land uses on stream integrity using machine learning algorithms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperotto, A.; Molina, J.; Torresan, S.; Critto, A.; Pulido-Velazquez, M.; Marcomini, A. A Bayesian Networks approach for the assessment of climate change impacts on nutrients loading. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 100, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhong, N.; Tu, X.; Jia, J.; Wang, J. Tackle environmental challenges in pollution controls using artificial intelligence: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 134279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Falah, F.; Dayal, K.S.; Deo, R.C.; Mohammadi, F.; Biggs, T.; Moghaddam, D.D.; Naghibi, S.A.; Bui, D.T. Machine learning approaches for spatial modeling of agricultural droughts in the south-east region of Queensland Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tipping, M.E. The Relevance Vector Machine. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 652–658. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.E. Gaussian Processes in Machine Learning. In Advanced Lectures on Machine Learning, ML Summer Schools 2003, Canberra, Australia, 2–14 February 2003, Tübingen, Germany, 4–16 August 2003, Revised Lectures; Bousquet, O., von Luxburg, U., Rätsch, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, 2004; pp. 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benavoli, A.; Mangili, F. Gaussian Processes for Bayesian hypothesis tests on regression functions. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics; San Diego, CA, USA, 9–12 May 2015, Lebanon, G., Vishwanathan, S.V.N., Eds.; Proceedings of Machine Learning Research PMLR: London, UK; Volume 38, pp. 74–82.
- Saleh, A.; Ahmed, S.; Mirjahan, M.; Rahman, M.; Salehin, M.; Mondal, M. Performance Evaluation of FCD/FCDI Projects During the 1998 Flood. In Engineering Concerns of Flood, Institute of Flood Control and Drainage Research; BUET: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1998; pp. 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S. The use of normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, B.; Shamsuddin, D. Environmental Impacts of Flood Control Drainage and Irrigation (FCDI) Projects in a Non-Irrigated Area of Bangladesh: A Case Study. J. Transdiscipl. Environ. Stud. 2012, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar]





| Year | AUC | SE | |Year−1982| | SE of Diff | Z Score | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1982 | 0.564 | 0.0056 | ||||
| 1996 | 0.616 | 0.0055 | 0.052 | 0.0078 | −6.6611 | |
| 2005 | 0.567 | 0.0056 | 0.003 | 0.0079 | −0.3803 | 0.7 |
| 2014 | 0.557 | 0.0056 | 0.007 | 0.0079 | 0.8862 | 0.38 |
| Pre-Embankment | Post-Embankment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event | (x, = 7) | p Value | (x, = 24) | p Value |
| Internal Movement | 10.63 | 0.31 | 102.57 | <0.01 * |
| In-Migration | 1.82 | 1.94 | 14.19 | 1.88 |
| Mortality | 2.88 | 1.79 | 17.43 | 1.66 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manandhar, A.; Fischer, A.; Bradley, D.J.; Salehin, M.; Islam, M.S.; Hope, R.; Clifton, D.A. Machine Learning to Evaluate Impacts of Flood Protection in Bangladesh, 1983–2014. Water 2020, 12, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020483
Manandhar A, Fischer A, Bradley DJ, Salehin M, Islam MS, Hope R, Clifton DA. Machine Learning to Evaluate Impacts of Flood Protection in Bangladesh, 1983–2014. Water. 2020; 12(2):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020483
Chicago/Turabian StyleManandhar, Achut, Alex Fischer, David J. Bradley, Mashfiqus Salehin, M. Sirajul Islam, Rob Hope, and David A. Clifton. 2020. "Machine Learning to Evaluate Impacts of Flood Protection in Bangladesh, 1983–2014" Water 12, no. 2: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020483
APA StyleManandhar, A., Fischer, A., Bradley, D. J., Salehin, M., Islam, M. S., Hope, R., & Clifton, D. A. (2020). Machine Learning to Evaluate Impacts of Flood Protection in Bangladesh, 1983–2014. Water, 12(2), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020483