Temporal and Spatial Variations of Chlorophyll a Concentration and Eutrophication Assessment (1987–2018) of Donghu Lake in Wuhan Using Landsat Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. In Situ Measurements of Water Quality Parameters
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Laboratory Analysis
2.3.2. Image Acquisition and Pre-Processing
- (a)
- Radiometric Calibration
- (b)
- FLAASH Atmospheric Correction
- (c)
- Water Information Extraction
2.3.3. Comprehensive Trophic Level Index
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Landsat Spectral Bands
3.2. Chl-a Algorithm Development
3.3. Validity of the Algorithm
3.4. Validity of the Algorithm Based on Measured Data from 2003–2018
3.5. Application of the Algorithm and Comparison of the Measured Data
4. Discussions
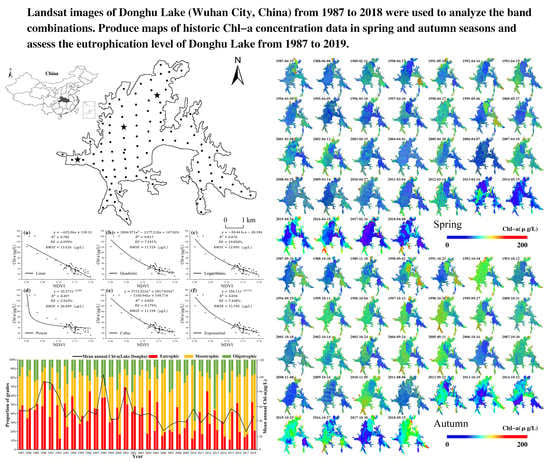
4.1. Seasonal and Inter-Annual Changes of Chl-a Concentration
4.2. Distribution of Chl-a Concentration in Spring and Autumn from 1987 to 2018
4.3. Trophic State Assessment
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- An inversion model of Chl-a concentration was established with remote sensing images and water quality parameter data. The correlation coefficient (R2) of the model was 0.859, the root mean square error (RMSE) was 11.194 μg/L and the relative error (RE) was 9.175%. The R2, RE and RMSE of the verification model were 0.831, 6.509% and 19.846 μg/L respectively. The generated results were reliable for the inversion of Chl-a concentration.
- (2)
- Based on the measured data and meteorological data from 2005 to 2018 in Donghu Lake, it was shown that Chl-a concentration in this lake varied in different seasons and was affected by lake morphology and distribution of surrounding pollution sources, exhibiting obvious spatio-temporal characteristics. The interannual variance analysis indicated that the Chl-a concentration in Donghu Lake was relatively high in warmer years or rainy years, and the seasonal variance analysis showed that Donghu Lake had the highest Chl-a concentration in summer, followed successively by autumn, spring and winter. The pollution levels of water in the sub-lakes were higher than those in the main lake area. Among these sub-lakes, Yujia Hu, Miao Hu and Shuiguo Hu were the three most polluted regions. The comprehensive trophic level index TLI (∑) of Donghu Lake in April 2016 was 63.49, indicating eutrophication at that time.
- (3)
- The accuracy of the model was verified using the data collected over more than ten years in three long-term monitoring points, which were provided by the Donghu Experimental Station of Lake Ecosystems, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The R2, RE and RMSE were 0.641, 2.518% and 22.606 μg/L, respectively. The accuracy is sufficient for conducting a remote sensing inversion, which demonstrates that the Landsat series data can be used for retrieving the long-term Chl-a concentration in inland lakes.
- (4)
- Historically, Donghu Lake was connected with the Yangtze River. The sub-lakes of Donghu Lake had high fluidity, good water quality and abundant aquatic plants. However, urbanization and human intervention have exerted enormous impacts on Donghu Lake. The lake’s biodiversity has been destroyed and its water quality has declined sharply. The situation has been somewhat improved through a variety of engineering measures and ecological management, showing that the building of the eco-water network of Donghu Lake has been effective for the restoration of its ecological structure and the improvement of its water quality.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Q.; Huang, M.; Tang, X. Eutrophication assessment of seasonal urban lakes in China Yangtze River Basin using Landsat 8-derived Forel-Ule index: A six-year (2013–2018) observation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.; Liao, W. Spatiotemporal change patterns of urban lakes in China’s major cities between 1990 and 2015. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 11, 1085–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, A.J.; Parris, K.M. Local and landscape determinants of amphibian communities in urban ponds. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, E.S.; Alameddine, I.; El-Fadel, M. Monitoring water quality in a hypereutrophic reservoir using Landsat ETM+ and OLI sensors: How transferable are the water quality algorithms? Environ. Monit. Assess 2018, 190, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yi, C.; Xie, P.; Xing, Y.; Ni, L. Sedimentation rates, nitrogen and phosphorus retentions in the largest urban Lake Donghu, China. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2005, 267, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durovic, B.; Durovic, I.; Joksimovic, A.; Crnojevic, V.; Dukanovic, S.; Pestoric, B. Monitoring the eutrophication using Landsat 8 in the Boka Kotorska Bay. Acta Adriat. 2018, 59, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wen, Z.; Lyu, L.; Du, Y.; Sha, L.; Fang, C. Quantification of lake clarity in China using Landsat OLI imagery data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Xie, P.; Hong, L. Changes in the Phytoplankton Community of Lake Donghu Since the 1980s. J. Freshwater Ecol. 2005, 20, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Yesou, H. MERIS observations of chlorophyll-a dynamics in Erhai Lake between 2003 and 2009. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 8309–8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wu, X.; Bing, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. Study on Retrieval of Chlorophyll-a Concentration Based on Landsat OLI Imagery in the Haihe River, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bocharov, A.V.; Tikhomirov, O.A.; Khizhnyak, S.D.; Pakhomov, P.M. Monitoring of Chlorophyll in Water Reservoirs Using Satellite Data. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 84, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, H.D.; Johansson, J.; Hudson, J.J. A 29-year assessment of the water clarity and chlorophyll-a concentration of a large reservoir: Investigating spatial and temporal changes using Landsat imagery. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y. Spatial downscaling of MODIS Chlorophyll-a using Landsat 8 images for complex coastal water monitoring. Estuari. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 209, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markogianni, V.; Kalivas, D.; Petropoulos, G.; Dimitriou, E. An Appraisal of the Potential of Landsat 8 in Estimating Chlorophyll-a, Ammonium Concentrations and Other Water Quality Indicators. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poddar, S.; Chacko, N.; Swain, D. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in Northern Coastal Bay of Bengal Using Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-2 MSI Sensors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, M.G.; Hamilton, D.P.; Hicks, B.; Brabyn, L. Empirical and semi-analytical chlorophyll a algorithms for multi-temporal monitoring of New Zealand lakes using Landsat. Environ. Monit. Assess 2015, 187, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.A.; Gitelson, A.A.; Zhou, J.; Gurlin, D.; Moses, W.; Ioannou, I.; Ahmed, S.A. Algorithms for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in coastal and inland waters using red and near infrared bands. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 24109–24125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Schalles, J.F.; Hladik, C.M. Remote chlorophyll-a retrieval in turbid, productive estuaries: Chesapeake Bay case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacobi, Y.Z.; Moses, W.J.; Kaganovsky, S.; Sulimani, B.; Leavitt, B.C.; Gitelson, A.A. NIR-red reflectance-based algorithms for chlorophyll-a estimation in mesotrophic inland and coastal waters: Lake Kinneret case study. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2428–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, G.; Loiselle, S.A.; Yang, D.; Ma, R.; Su, W.; Gao, C. Remote estimation of chlorophyll a concentrations over a wide range of optical conditions based on water classification from VIIRS observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y. Extraction of Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Concentrations of Chlorophyll-a and Total Suspended Matter in Poyang Lake Using GF-1 Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Han, X.; Chen, X.; Qi, L. Long-Term Distribution Patterns of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in China’s Largest Freshwater Lake: MERIS Full-Resolution Observations with a Practical Approach. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Chen, J.; Fukushima, T.; Ma, R. An Enhanced Three-Band Index for Estimating Chlorophyll-a in Turbid Case-II Waters: Case Studies of Lake Kasumigaura, Japan, and Lake Dianchi, China. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, W.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Feng, S. A 30-Year Assessment of Phytoplankton Blooms in Erhai Lake Using Landsat Imagery: 1987 to 2016. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Loiselle, S.; Xue, K.; Liang, Q. Satellite-Based Estimation of Column-Integrated Algal Biomass in Nonalgae Bloom Conditions: A Case Study of Lake Chaohu, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, K.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J. A comparison of factors influencing the summer phytoplankton biomass in China’s three largest freshwater lakes: Poyang, Dongting, and Taihu. Hydrobiologia 2016, 792, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Kong, L.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Z. Release characteristics of sediment P in all fractions of Donghu Lake, Wuhan, China. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 25572–25580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Berezina, N.A.; Golubkov, S.M.; Cao, X.; Golubkov, M.S.; Song, C.; Umnova, L.P.; Zhou, Y. Phosphorus flux by macrobenthic invertebrates in a shallow eutrophic lake Donghu: Spatial change. Know. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Hou, J.; Cao, X.; Song, C.; Zhou, Y. Sediment–water interaction in phosphorus cycling as affected by trophic states in a Chinese shallow lake (Lake Donghu). Hydrobiologia 2016, 776, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Gu, S. Thin-layer fine-sand capping of polluted sediments decreases nutrients in overlying water of Wuhan Donghu Lake in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 7156–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Stegen, J.C.; Yu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Nearly a decade-long repeatable seasonal diversity patterns of bacterioplankton communities in the eutrophic Lake Donghu (Wuhan, China). Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 3839–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, Q.; Yu, Y.; Dai, L. Spatiotemporal pattern of bacterioplankton in Donghu Lake. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 32, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Xie, P. Budgets and Dynamics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in a Shallow, Hypereutrophic Lake in China. J. Freshwater Ecol. 2000, 15, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Hansson, L.-A.; Zhao, X.; Xie, P. Eco-chemical mechanisms govern phytoplankton emissions of dimethylsulfide in global surface waters. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, E.; Aguado, S.; García, G. Monitoring Coastal Lagoon Water Quality Through Remote Sensing: The Mar Menor as a Case Study. Water 2019, 11, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Song, K.; Liu, G.; Wen, Z.; Fang, C.; Shang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Q.; Du, J.; Zhang, B. Quantifying total suspended matter (TSM) in waters using Landsat images during 1984–2018 across the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeni, A.O.; Adesalu, T.A. Validating chlorophyll-a concentrations in the Lagos Lagoon using Remote Sensing extraction and laboratory fluorometric methods. MethodsX 2018, 5, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.T.T.; Koike, K.; Nhuan, M.T.; Canh, B.D.; Thao, N.T.P.; Parsons, M. Landsat 8/OLI Two Bands Ratio Algorithm for Chlorophyll-A Concentration Mapping in Hypertrophic Waters: An Application to West Lake in Hanoi (Vietnam). IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4919–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Alcantara, E.; Rodrigues, T.; Rotta, L.; Bernardo, N.; Imai, N. Remote Sensing of the chlorophyll-a based on OLI/Landsat-8 and MSI/Sentinel-2A (Barra Bonita reservoir, Brazil). Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias 2018, 90, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhan, W.; Sun, C.; Duan, Y. Landsat 8 OLI image based terrestrial water extraction from heterogeneous backgrounds using a reflectance homogenization approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, D.; Frazier, A. Automated Method for Monitoring Water Quality Using Landsat Imagery. Water 2016, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murugan, P.; Sivakumar, R.; Pandiyan, R.; Annadurai, M. Comparison of in-situ Hyperspectral and Landsat ETM+ Data for Chlorophyll-a Mapping in Case-II Water (Krishnarajapuram Lake, Bangalore). J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Perk, R.L.; Gurlin, D.; Rundquist, D.C.; Leavitt, B.C.; Barrow, T.M.; Brakhage, P. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters using airborne hyperspectral data. Water Res. 2012, 46, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Othman, Y.; Steele, C.; Hilaire, R.S. Surface Reflectance Climate Data Records (CDRs) is a Reliable Landsat ETM+ Source to Study Chlorophyll Content in Pecan Orchards. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2017, 46, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, M.F.O.; Merkel, B.J. Application of Landsat 5 and Landsat 7 images data for water quality mapping in Mosul Dam Lake, Northern Iraq. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 7, 3557–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Pascual, J.E.; Almonacid-Caballer, J.; Ruiz, L.A.; Palomar-Vázquez, J. Automatic extraction of shorelines from Landsat TM and ETM+ multi-temporal images with subpixel precision. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, J.; Wang, G.; Xue, B.; Wang, P.; Hao, F.; Xie, G.; Peng, Y. Assessment of lake eutrophication using a novel multidimensional similarity cloud model. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Li, R.; Oyama, Y.; Fukushima, T. Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in Inland Waters by a NIR-Red-Based Algorithm: Validation in Asian Lakes. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3492–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzar Abbas, M.; Melesse, A.M.; Scinto, L.J.; Rehage, J.S. Satellite Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Sensor in Shallow Coastal Water Bodies: Validation and Improvement. Water 2019, 11, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Xu, X.; Kong, F.; Zhang, S.; Kong, W.; Hao, J.; Shang, L. Two-decade reconstruction of algal blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3522–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbick, N.; Hu, F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Qi, J.G.; Zhang, H.J.; Becker, B. Mapping Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in West Lake, China using Landsat 7 ETM+. J. Great Lakes Res. 2008, 34, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Dokulil, M.T. Imbalance of plankton community metabolism in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. J. Great Lakes Res. 2011, 37, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, M.; Duan, H.; Loiselle, S.; Xu, J. Fourteen-Year Record (2000–2013) of the Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Floating Algae Blooms in Lake Chaohu, Observed from Time Series of MODIS Images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10523–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonansea, M.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Pinotti, L.; Ferrero, S. Using multi-temporal Landsat imagery and linear mixed models for assessing water quality parameters in Río Tercero reservoir (Argentina). Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Landsat Date | Sensor | Landsat Date | Sensor | Landsat Date | Sensor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19April 1987 | Landsat-5/TM | 23 October 1997 | Landsat-5/TM | 28 April 2008 | Landsat-5/TM |
| 26 September 1987 | Landsat-5/TM | 17 April 1998 | Landsat-5/TM | 8 November 2008 | Landsat-5/TM |
| 8 June 1988 | Landsat-5/TM | 26 October 1998 | Landsat-5/TM | 14 March 2009 | Landsat-5/TM |
| 30 October 1988 | Landsat-5/TM | 6 May 1999 | Landsat-5/TM | 24 October 2009 | Landsat-5/TM |
| 11 February 1989 | Landsat-5/TM | 27 September 1999 | Landsat-5/TM | 27 April 2010 | Landsat-5/TM |
| 18 November 1989 | Landsat-5/TM | 27 May 2000 | Landsat-5/TM | 5 November 2010 | Landsat-5/TM |
| 27 April 1990 | Landsat-5/TM | 31 October 2000 | Landsat-5/TM | 4 March 2011 | Landsat-5/TM |
| 2 September 1990 | Landsat-5/TM | 8 March 2001 | Landsat-5/TM | 8 August 2011 | Landsat-5/TM |
| 16 May 1991 | Landsat-5/TM | 18 October 2001 | Landsat-5/TM | 14 March 2012 | Landsat-7/ETM+ |
| 23 October 1991 | Landsat-5/TM | 12 April 2002 | Landsat-5/TM | 16 April 2013 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 16 April 1992 | Landsat-5/TM | 14 October 2002 | Landsat-5/TM | 19 October 2013 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 18 October 1992 | Landsat-5/TM | 15 April 2003 | Landsat-5/TM | 15 May 2014 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 19 April 1993 | Landsat-5/TM | 24 October 2003 | Landsat-5/TM | 22 October 2014 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 12 October 1993 | Landsat-5/TM | 1 April 2004 | Landsat-5/TM | 16 April 2015 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 5 March 1994 | Landsat-5/TM | 24 September 2004 | Landsat-5/TM | 25 October 2015 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 29 September 1994 | Landsat-5/TM | 20 April 2005 | Landsat-5/TM | 18 April 2016 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 9 April 1995 | Landsat-5/TM | 11 September 2005 | Landsat-5/TM | 27 October 2016 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 11 October 1995 | Landsat-5/TM | 07 April 2006 | Landsat-5/TM | 16 February 2017 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 10 March 1996 | Landsat-5/TM | 16 October 2006 | Landsat-5/TM | 30 October 2017 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 4 October 1996 | Landsat-5/TM | 10 April 2007 | Landsat-5/TM | 8 April 2018 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| 30 April 1997 | Landsat-5/TM | 30 October 2007 | Landsat-5/TM | 15 September 2018 | Landsat-8 OLI |
| Parameter | Chl-a | TP | TN | SD | CODMn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rij | 1 | 0.84 | 0.82 | −0.83 | 0.83 |
| 1 | 0.7056 | 0.6724 | 0.6889 | 0.6889 |
| Spectral Channel | Landsat-8 OLI | Landsat-7/ETM+ | Landsat-5/TM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bands | Wavelength (μm) | Bands | Wavelength (μm) | Bands | Wavelength (μm) | |
| Band 1 | Coastal | 0.43–0.45 | Blue | 0.45–0.52 | Blue | 0.45–0.52 |
| Band 2 | Blue | 0.45–0.51 | Green | 0.52–0.60 | Green | 0.52–0.60 |
| Band 3 | Green | 0.53–0.59 | Red | 0.63–0.69 | Red | 0.63–0.69 |
| Band 4 | Red | 0.64–0.67 | Near-Infrared | 0.77–0.90 | Near-Infrared | 0.76–0.90 |
| Band 5 | Near-Infrared | 0.85–0.88 | Near-Infrared | 1.55–1.75 | Near-Infrared | 1.55–1.75 |
| Band 6 | SWIR 1 | 1.57–1.65 | Thermal | 10.40–12.50 | Thermal | 10.40–12.50 |
| Band 7 | SWIR 2 | 2.11–2.29 | Mid-Infrared | 2.08–2.35 | Mid-Infrared | 2.08–2.35 |
| Band 8 | Panchromatic | 0.50–0.68 | Panchromatic | 0.52–0.90 | ||
| Band 9 | Cirrus | 1.36–1.38 | ||||
| Band 10 | TIRS 1 | 10.60–11.19 | ||||
| Band 11 | TIRS 2 | 11.50–12.51 | ||||
| Band | r | p | Band | r | p | Band | r | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | −0.458 ** | 0.0000 | B3/B2 | −0.288 * | 0.0111 | B3/(B1 + B4) | −0.607 ** | 0.0000 |
| B2 | −0.458 ** | 0.0000 | B3/B4 | −0.609 ** | 0.0000 | B3/(B2 + B4) | −0.532 ** | 0.0000 |
| B3 | −0.500 ** | 0.0000 | B4/B1 | −0.265 * | 0.0197 | B3/(B1 + B2 + B4) | −0.582 ** | 0.0000 |
| B4 | −0.414 ** | 0.0002 | B4/B2 | 0.400 ** | 0.0003 | B4/(B1 + B2) | −0.065 | 0.5755 |
| B5 | −0.166 | 0.1494 | B4/B3 | 0.605 ** | 0.0000 | B4/(B1 + B3) | 0.214 | 0.0615 |
| B6 | −0.087 | 0.4542 | B1/(B2 + B3) | 0.526 ** | 0.0000 | B4/(B2 + B3) | 0.606 ** | 0.0000 |
| B7 | −0.062 | 0.5941 | B1/(B2 + B4) | 0.391 ** | 0.0004 | B4/(B1 + B2 + B3) | 0.313 ** | 0.0056 |
| B1/B2 | 0.444 ** | 0.0001 | B1/(B3 + B4) | 0.475 ** | 0.0000 | (B1 − B2)/(B1 + B2) | 0.462 ** | 0.0000 |
| B1/B3 | 0.546 ** | 0.0000 | B1/(B2 + B3 + B4) | 0.479 ** | 0.0000 | (B1 − B3)/(B1 + B3) | −0.263 * | 0.0210 |
| B1/B4 | 0.284 * | 0.0122 | B2/(B1 + B3) | −0.240 * | 0.0352 | (B1 − B4)/(B1 + B4) | 0.268 * | 0.0183 |
| B2/B1 | 0.465 ** | 0.0000 | B2/(B1 + B4) | −0.500 ** | 0.0000 | (B2 − B3)/(B2 + B3) | −0.321 ** | 0.0044 |
| B2/B3 | 0.342 ** | 0.0023 | B2/(B3 + B4) | 0.003 | 0.9770 | (B2 − B4)/(B2 + B4) | 0.401 ** | 0.0003 |
| B2/B4 | −0.399 ** | 0.0003 | B2/(B1 + B3 + B4) | −0.312 ** | 0.0057 | (B3 − B4)/(B3 + B4) | −0.826 ** | 0.0000 |
| B3/B1 | −0.534 ** | 0.0000 | B3/(B1 + B2) | −0.523 ** | 0.0000 | (B4 − B3)/(B4 + B3) | −0.826 ** | 0.0000 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yue, Z. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Chlorophyll a Concentration and Eutrophication Assessment (1987–2018) of Donghu Lake in Wuhan Using Landsat Images. Water 2020, 12, 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082192
Yang X, Jiang Y, Deng X, Zheng Y, Yue Z. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Chlorophyll a Concentration and Eutrophication Assessment (1987–2018) of Donghu Lake in Wuhan Using Landsat Images. Water. 2020; 12(8):2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082192
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xujie, Yan Jiang, Xuwei Deng, Ying Zheng, and Zhiying Yue. 2020. "Temporal and Spatial Variations of Chlorophyll a Concentration and Eutrophication Assessment (1987–2018) of Donghu Lake in Wuhan Using Landsat Images" Water 12, no. 8: 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082192
APA StyleYang, X., Jiang, Y., Deng, X., Zheng, Y., & Yue, Z. (2020). Temporal and Spatial Variations of Chlorophyll a Concentration and Eutrophication Assessment (1987–2018) of Donghu Lake in Wuhan Using Landsat Images. Water, 12(8), 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082192