Environmental Antimicrobial Resistance in a Small Urban Mediterranean River: A Focus on Endemic Beta-Lactamases in Clinically Relevant Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
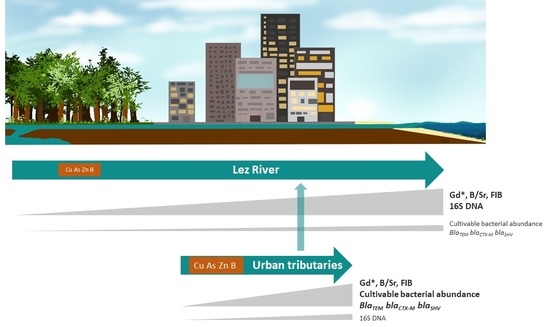
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Strategy
2.3. Physico-Chemical and Chemical Characterization of Water
2.3.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters
2.3.2. Major Ions Analysis
2.3.3. Metals and Organotin Analysis
2.3.4. Dissolved Organic Carbon
2.4. Bacterial Enumeration
2.4.1. Fecal Indicator Bacteria (FIB) Quantification
2.4.2. Heterotrophic Cultivable Bacteria and Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria Enumeration
2.4.3. Multidrug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria Enumeration
2.5. Isolation and Characterization of Multidrug Resistant Bacteria
2.6. Gene Quantification by Real-Time PCR (qPCR) in Water Samples
2.6.1. DNA Extraction from Water Samples
2.6.2. Quantifications
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Description of the System
3.1.1. Hydrological Characteristics
3.1.2. Bacterial Counts
3.1.3. Human Source Contamination
3.1.4. Chemical Contamination
3.2. Characteristics of Environmental AMR with Cultural Approach
3.3. Focus on Clinically Relevant Resistance during the Winter Campaign (C2)
3.3.1. Genetic Quantification
3.3.2. Characterization of Multidrug Resistant Enterobacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO | Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics. Available online: http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/global-priority-list-antibiotic-resistant-bacteria/en/ (accessed on 22 February 2021).
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Europe 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Un Premier État Des Connaissances Sur l’antibiorésistance et Les Antibiotiques Dans l’environnement | Anses - Agence Nationale de Sécurité Sanitaire de l’alimentation, de l’environnement et Du Travail. Available online: https://www.anses.fr/fr/content/un-premier-%C3%A9tat-des-connaissances-sur-l%E2%80%99antibior%C3%A9sistance-et-les-antibiotiques-dans-l (accessed on 22 February 2021).
- Antibiorésistance et Environnement - État et Causes Possibles de La Contamination Des Milieux En France Par Les Antibiotiques et Par Les Bactéries Résistantes Aux Antibiotiques et Supports Génétiques de La Résistance | Anses - Agence Nationale de Sécurité Sanitaire de l’alimentation, de l’environnement et Du Travail. Available online: https://www.anses.fr/fr/content/antibior%C3%A9sistance-et-environnement-%C3%A9tat-et-causes-possibles-de-la-contamination-des-milieu-0 (accessed on 22 February 2021).
- Matheu, J.; Aidara-Kane, A.; Andremont, A. The ESBL Tricycle AMR Surveillance Porject: A Simple, One Health Approach to Global Surveillance. Available online: http://resistancecontrol.info/2017/the-esbl-tricycleamr-surveillance-project-a-simple-one-health-approach-toglobal-surveillance/ (accessed on 19 July 2021).
- Almakki, A.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Marchandin, H.; Licznar-Fajardo, P. Antibiotic Resistance in Urban Runoff. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almakki, A.; Maure, A.; Pantel, A.; Romano-Bertrand, S.; Masnou, A.; Marchandin, H.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Licznar-Fajardo, P. NDM-5-Producing Escherichia Coli in an Urban River in Montpellier, France. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girlich, D.; Bonnin, R.A.; Naas, T. Occurrence and Diversity of CTX-M-Producing Escherichia Coli From the Seine River. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 603578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroche, E.; Pawlak, B.; Berthe, T.; Skurnik, D.; Petit, F. Occurrence of Antibiotic Resistance and Class 1, 2 and 3 Integrons in Escherichia Coli Isolated from a Densely Populated Estuary (Seine, France). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 68, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kang, H.Y.; Lee, Y. The Identification of CTX-M-14, TEM-52, and CMY-1 Enzymes in Escherichia Coli Isolated from the Han River in Korea. J. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanji, H.; Murphy, N.M.; Akhigbe, C.; Doumith, M.; Hope, R.; Livermore, D.M.; Woodford, N. Isolation of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant O25b:H4-ST131 Escherichia Coli with CTX-M-14 Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase from UK River Water. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pantanella, F.; Lekunberri, I.; Gagliardi, A.; Venuto, G.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Fabiani, M.; Balcázar, J.L.; Schippa, S.; De Giusti, M.; Borrego, C.; et al. Effect of Urban Wastewater Discharge on the Abundance of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia Coli in Two Italian Rivers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakali, O.; Tandukar, S.; Brooks, J.P.; Sherchan, S.P.; Sherchand, J.B.; Haramoto, E. The Occurrence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in an Urban River in Nepal. Water 2020, 12, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabiet, M.; Brissaud, F.; Seidel, J.L.; Pistre, S.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F. Positive Gadolinium Anomalies in Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents and Aquatic Environment in the Hérault Watershed (South France). Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, P.; Vaishampayan, P. Editorial: MALDI-TOF MS Application in Microbial Ecology Studies. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdouchakour, F.; Dupont, C.; Grau, D.; Aujoulat, F.; Mournetas, P.; Marchandin, H.; Parer, S.; Gibert, P.; Valcarcel, J.; Jumas-Bilak, E. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Achromobacter Sp. Clonal Selection Leads to Successive Waves of Contamination of Water in Dental Care Units. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7509–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koeuth, T.; Versalovic, J.; Lupski, J.R. Differential Subsequence Conservation of Interspersed Repetitive Streptococcus Pneumoniae BOX Elements in Diverse Bacteria. Genome Res. 1995, 5, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercier, E.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Allardet-Servent, A.; O’Callaghan, D.; Ramuz, M. Polymorphism in Brucella Strains Detected by Studying Distribution of Two Short Repetitive DNA Elements. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CA-SFM CA-SFM - EUCAST, Comité de l’antibiogramme de la Société Française de Microbiologie. In: CASFM / EUCAST: Société Française de Microbiologie Ed. 2016. Available online: https://www.sfm-microbiologie.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/CASFM2016_V1.0_FEVRIER.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2021).
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Indexing of Escherichia Coli to Identify High-Risk Sources of Fecal Contamination of Foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drieux, L.; Brossier, F.; Sougakoff, W.; Jarlier, V. Phenotypic Detection of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Production in Enterobacteriaceae: Review and Bench Guide. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14 (Suppl S1), 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lartigue, M.-F.; Zinsius, C.; Wenger, A.; Bille, J.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases of the CTX-M Type Now in Switzerland. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2855–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Shazly, S.; Dashti, A.; Vali, L.; Bolaris, M.; Ibrahim, A.S. Molecular Epidemiology and Characterization of Multiple Drug-Resistant (MDR) Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter Baumannii. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 41, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, H.; Fujimoto, C.; Haruki, Y.; Maeda, T.; Kokeguchi, S.; Petelin, M.; Arai, H.; Tanimoto, I.; Nishimura, F.; Takashiba, S. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Using TaqMan and SYBR Green for Actinobacillus Actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas Gingivalis, Prevotella Intermedia, TetQ Gene and Total Bacteria. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 39, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Marrs, C.F.; Ye, W.; Simon, C.; Foxman, B.; Nriagu, J. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance in Drinking Water Treatment and Distribution Systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5714–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marti, E.; Jofre, J.; Balcazar, J.L. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Bacterial Community Composition in a River Influenced by a Wastewater Treatment Plant. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, A.E.; Field, K.G. A PCR Assay To Discriminate Human and Ruminant Feces on the Basis of Host Differences in Bacteroides-Prevotella Genes Encoding 16S RRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4571–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernhard, A.E.; Field, K.G. Identification of Nonpoint Sources of Fecal Pollution in Coastal Waters by Using Host-Specific 16S Ribosomal DNA Genetic Markers from Fecal Anaerobes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seurinck, S.; Defoirdt, T.; Verstraete, W.; Siciliano, S.D. Detection and Quantification of the Human-Specific HF183 Bacteroides 16S RRNA Genetic Marker with Real-Time PCR for Assessment of Human Faecal Pollution in Freshwater. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, L.K.; Simonich, M.T.; Field, K.G. Microplate Subtractive Hybridization to Enrich for Bacteroidales Genetic Markers for Fecal Source Identification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3179–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Santo Domingo, J.W.; Lamendella, R.; Edge, T.; Hill, S. Phylogenetic Diversity and Molecular Detection of Bacteria in Gull Feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3969–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Wang, X.C.; Dzakpasu, M. Genetic Characterization of Fecal Impacts of Seagull Migration on an Urban Scenery Lake. Water Res. 2017, 117, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubiana, M.; Salles, C.; Tournoud, M.-G.; Licznar-Fajardo, P.; Zorgniotti, I.; Tremelo, M.-L.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Robert, S.; Monfort, P. Monitoring Urban Beach Quality on a Summer Day: Determination of the Origin of Fecal Indicator Bacteria and Antimicrobial Resistance at Prophète Beach, Marseille (France). Front. Microbiol. 2021. Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luthy, R.G.; Sedlak, D.L.; Plumlee, M.H.; Austin, D.; Resh, V.H. Wastewater-Effluent-Dominated Streams as Ecosystem-Management Tools in a Drier Climate. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arrêté Du 27 Juillet 2015 Modifiant l’arrêté Du 25 Janvier 2010 Relatif Aux Méthodes et Critères d’évaluation de l’état Écologique, de l’état Chimique et Du Potentiel Écologique Des Eaux de Surface Pris En Application Des Articles R. 212-10, R. 212-11 et R. 212-18 Du Code de l’environnement – Légifrance. Available online: https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/jorf/id/JORFTEXT000031107256 (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Müller, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. The Pollution Conveyed by Urban Runoff: A Review of Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proia, L.; Anzil, A.; Subirats, J.; Borrego, C.; Farrè, M.; Llorca, M.; Balcázar, J.L.; Servais, P. Antibiotic Resistance along an Urban River Impacted by Treated Wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Jia, J.; Wu, L.; Xue, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z. Analysis of Bacterial Community Characteristics, Abundance of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes Along a Pollution Gradient of Ba River in Xi’an, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, W.-Y.; Huang, F.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Su, J.-Q. Increased Levels of Antibiotic Resistance in Urban Stream of Jiulongjiang River, China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5697–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gothwal, R.; Thatikonda, S. Role of Environmental Pollution in Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Aquatic Environment of River: Case of Musi River, South India. Water Environ. J. 2017, 31, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Site | Strain | Species | M-rep-PCR Profile | Antibiotic’s Family Resistance | MAR Index | ESBL | blaSHV | blaTEM | blaCTX-M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L2 | 2 L2E 14 | E. coli | Ec1 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides | 0.42 | + | - | - | - |
| L6 | 2 L6 E5 | E. coli | Ec2 | β-lactams/quinolones | 0.38 | + | - | - | + |
| 2 L6 E7 | E. coli | Ec2 | β-lactams/quinolones | 0.38 | + | - | - | + | |
| FA1 | 2 FA1 E1A | K. pneumoniae | Kp1 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides/ sulfamides | 0.67 | + | + | + | + |
| 2FA1 E5 | K. pneumoniae | Kp2 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides/ sulfamides | 0.71 | + | + | - | + | |
| 2FA1 E1B | E. coli | Ec3 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides/ sulfamides | 0.71 | + | - | - | + | |
| 2 FA1 E2 | E. coli | Ec3 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides/ sulfamides | 0.63 | + | - | - | + | |
| FA2 | 2 FA2 E1 | K. pneumoniae | Kp3 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides/ sulfamides | 0.58 | + | + | + | + |
| 2 FA2 E4bB | K. pneumoniae | Kp4 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides/ sulfamides | 0.63 | + | + | + | + | |
| 2 FA2 E6 | K. pneumoniae | Kp5 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides/ sulfamides | 0.67 | + | + | + | + | |
| 2 FA2 E3 | E. coli | Ec3 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides/ sulfamides | 0.71 | + | - | - | + | |
| 2 FA2 E4a | E. coli | Ec4 | β-lactams/sulfamides/amphenicols | 0.38 | + | - | + | - | |
| 2 FA2 E5 | E. coli | Ec5 | β-lactams/aminoglycosides/sulfamides/ amphenicols | 0.46 | + | - | + | + | |
| V3 | 2 V3 E1 | K. aerogenes | Ka1 | β-lactams | 0.58 | - | ND | ND | ND |
| 2 V3 E7 | K. aerogenes | Ka1 | β-lactams/amphenicols | 0.63 | - | ND | ND | ND | |
| 2 V3 E4 | K. aerogenes | Ka2 | β-lactams/amphenicols | 0.63 | - | ND | ND | ND | |
| 2 V3 E8 | K. aerogenes | Ka2 | β-lactams/amphenicols | 0.63 | - | ND | ND | ND | |
| 2 V3 E5 | K. aerogenes | Ka3 | β-lactams/amphenicols | 0.63 | - | ND | ND | ND | |
| 2 V3 E6 | K. aerogenes | Ka4 | β-lactams | 0.58 | - | ND | ND | ND | |
| Lant | 2 Lant E4 | E. coli | Ec6 | β-lactams/quinolones | 0.50 | + | - | + | + |
| 2 Lant E10 | E. coli | Ec6 | β-lactams/quinolones | 0.50 | + | - | + | + | |
| M2 | 2 M2 E5 | K. pneumoniae | Kp6 | β-lactams/quinolones/aminoglycosides/ amphenicols | 0.63 | + | + | + | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aujoulat, F.; Ragot, R.; Toubiana, M.; Bancon-Montigny, C.; Monfort, P.; Salles, C.; Masnou, A.; Delpoux, S.; Rio, M.; Tournoud, M.-G.; et al. Environmental Antimicrobial Resistance in a Small Urban Mediterranean River: A Focus on Endemic Beta-Lactamases in Clinically Relevant Bacteria. Water 2021, 13, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152010
Aujoulat F, Ragot R, Toubiana M, Bancon-Montigny C, Monfort P, Salles C, Masnou A, Delpoux S, Rio M, Tournoud M-G, et al. Environmental Antimicrobial Resistance in a Small Urban Mediterranean River: A Focus on Endemic Beta-Lactamases in Clinically Relevant Bacteria. Water. 2021; 13(15):2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152010
Chicago/Turabian StyleAujoulat, Fabien, Rose Ragot, Mylène Toubiana, Chrystelle Bancon-Montigny, Patrick Monfort, Christian Salles, Agnès Masnou, Sophie Delpoux, Marlène Rio, Marie-George Tournoud, and et al. 2021. "Environmental Antimicrobial Resistance in a Small Urban Mediterranean River: A Focus on Endemic Beta-Lactamases in Clinically Relevant Bacteria" Water 13, no. 15: 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152010
APA StyleAujoulat, F., Ragot, R., Toubiana, M., Bancon-Montigny, C., Monfort, P., Salles, C., Masnou, A., Delpoux, S., Rio, M., Tournoud, M. -G., Marchand, P., Jumas-Bilak, E., & Licznar-Fajardo, P. (2021). Environmental Antimicrobial Resistance in a Small Urban Mediterranean River: A Focus on Endemic Beta-Lactamases in Clinically Relevant Bacteria. Water, 13(15), 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152010