Effective Purification of Eutrophic Wastewater from the Beverage Industry by Microbubbles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Apparatus
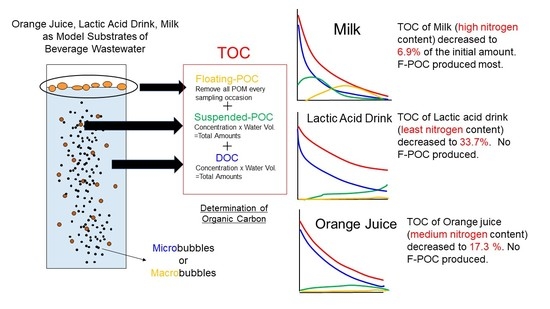
2.2. Model Substrates and Incubations
2.3. Determination of Organic Carbon
2.4. Determination of Other Characteristics
2.5. Statistical Significance
3. Results
3.1. Changes in the Amount of Organic Carbon
3.2. Effects of Microbubbles vs. Macrobubbles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terasaka, K. What is the fine bubble? In Introduction to Fine Bubble Science and Technology; Terasaka, K., Himuro, S., Ando, K., Hata, T., Eds.; Nikkan Kogyou Shinbunsha: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 17–40. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, A.; Oliveira, H.; Rubio, J. Bulk nanobubbles in the mineral and environmental areas: Updating research and applications. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 271, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oya, M. Effect of fine bubbles on removal of linear alkyl benzene sulfonate surfactant during the rinsing stage of laundry washing. J. Surfact. Deterg. 2020, 23, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.; Zhu, W.; Huang, F.; Gao, W.; Khan, N.A. Micro-nanobubble technology and water-related application. Wat. Suppl. 2020, 20, 2021–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaka, K.; Hirabayashi, A.; Nishino, T.; Fujioka, S.; Kobayashi, D. Development of microbubble aerator for waste water treatment using aerobic activated sludge. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 3172–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Takahashi, M.; Chiba, K. Degradation of phenol by the collapse of microbubbles. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, P.E.; Onga, W.Y.J.; Laub, E.V.; Chong, M.N. Investigation on micro-bubble flotation and coagulation for the treatment of anaerobically treated palm oil mill effluent (POME). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M. ξ Potential of microbubbles in aqueous solutions: Electrical properties of the gas-water interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 21858–21864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuntia, S.; Majumder, S.K.; Ghosh, P. Microbubble-aided water and wastewater purification: A review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2012, 28, 191–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, R.; Majumder, S.K. Microbubble generation and microbubble-aided transport process intensification—A state-of-the-art report. Chem. Eng. Process. 2013, 64, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, T.; Bui, T.T.; Han, M.; Kim, T.-I.; Park, H. Micro and nanobubble technologies as a new horizon for water-treatment techniques: A review. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2017, 246, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srithongouthai, S.; Endo, A.; Inoue, A.; Kinoshita, K.; Yoshioka, M.; Sato, A.; Iwasaki, T.; Teshiba, I.; Nashiki, H.; Hama, D.; et al. Control of dissolved oxygen levels of water in net pens for fish farming by a microscopic bubble generating system. Fish. Sci. 2006, 72, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Srithongouthai, S.; Nashiki, H.; Teshiba, I.; Iwasaki, T.; Hama, D.; Tsutsumi, H. DO-increasing effects of a microscopic bubble generating system in a fish farm. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2008, 57, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colt, J.; Kroeger, E.; Rust, M. Characteristics of oxygen flow through fine bubble diffusers used in the aquaculture hauling applications. Aquacul. Eng. 2010, 43, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xie, J. Modeling re-oxygenation performance of fine-bubble–diffusing aeration system in aquaculture ponds. Aquacul. Int. 2019, 27, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joni, I.M.; Subhan, U.; Hanam, E.S.; Azhary, S.Y.; Pratopo, L.H.; Hermawan, W.; Miranti, M.; Panatarani, C. Application of fine bubbles technology in wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) for aquaculture system. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference and Exhibition on Powder Technology (ICePTi) 2019, AIP 2219, Solo, Indonesia, 20–21 August 2019; p. 090001-1-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.-B.; Xing, X.-H.; Yu, A.-F.; Zhou, Y.-N.; Sun, X.-L.; Jurcik, B. Enhanced ozonation of simulated dyestuff wastewater by microbubbles. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamoto, C.; Fujiwara, N.; Shigekawa, Y.; Tada, K.; Yano, J.; Yokoyama, T.; Minamoto, Y.; Nakayama, S. Effect of acidic conditions on decomposition of methylene blue in aqueous solution by air microbubbles. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, H.; Hong, X.; Han, H.; Shan, S. Effect of pure oxygen fine bubbles on the organic matter removal and bacterial community evolution treating coal gasification wastewater by membrane bioreactor. Biores. Technol. 2016, 221, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Liu, Y. Enhanced microbubbles assisted cleaning of diesel contaminated sand. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2017, 124, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Xia, Z. Application of ozone micro-nano-bubbles to groundwater remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, H.; Qian, H.; Yao, W. Effects of ozone-microbubble treatment on the removal of residual pesticides and the adsorption mechanism of pesticides onto the apple matrix. Food Cont. 2021, 120, 107548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghia, N.H.; Van, P.T.; Giang, P.T.; Hanh, N.T.; St-Hilaire, S.; Domingos, J.A. Control of Vibrio parahaemolyticus (AHPND strain) and improvement of water quality using nanobubble technology. Aquacul. Res. 2021, 52, 2727–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.R.H.; Granvilleb, A.M.; Brownec, C.I.; Dagastinec, R.R.; Yapa, R.; Jeffersone, B.; Henderson, R.K. Determining how polymer-bubble interactions impact algal separation using the novel “Posi”-dissolved air flotation process. Sep. Pur. Technol. 2018, 201, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurita, Y.; Chiba, I.; Kijima, A. Physical eradication of small planktonic crustaceans from aquaculture tanks with cavitation treatment. Aquacul. Int. 2017, 25, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, I.; Inaba, N.; Yamamoto, K. Harmful algal blooms and environmentally friendly control strategies in Japan. Fish. Sci. 2021, 87, 437–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangdej, U.; Fukami, K. Stimulation of photosynthesis and consequent oxygen production in anoxic bottom water environment by supplying low light through an optical fiber. Fish. Sci. 2004, 70, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzaki, N.; Kai, M.; Aoyama, H.; Suzuki, T. Changes in mortality rate and glycogen content of the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum during the development of oxygen-deficient waters. Fish. Sci. 2003, 69, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, E.W.; Nicodemus, P.; Spooner, E.; Heath, A. The effectiveness of an artificial floating wetland to remove nutrients in an urban stream: A pilot-study in the Chicago River, Chicago, IL USA. Hydrology 2021, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsine, E.A.; Benhammou, A.; Pons, M.-N. Water resources management in soft drink industry-water use and wastewater generation. Environ. Technol. 2005, 26, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valta, K.; Kosanovic, T.; Malamis, D.; Moustakas, K.; Loizidou, M. Overview of water usage and wastewater management in the food and beverage industry. Desal. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3335–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.L.; dos Santos, E.C.L.; Lopez, A.M.Q. Sugar-alcohol industry: Quality of its biotreated washing water for reuse in fertigation. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2020, 27, 10275–10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitouras, A.; Basu, O.; Al-Ghussain, N.; Delatolla, R. Kinetic effects of anaerobic staging and aeration rates on sequencing batch moving bed biofilm reactors: Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus treatment of cheese production wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharupaneedi, S.P.; Nataraj, S.K.; Nadagouda, M.; Reddy, K.R.; Shukla, S.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Membrane-based separation of potential emerging pollutants. Sep. Pur. Tech. 2019, 210, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağtaş, M.; Dilaver, M.; Koyuncu, I. Ceramic membrane overview and applications in textile industry: A review. Wat. Sci. Tech. 2021, 84, 1059–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugham, T.; Kaleekkal, N.J.; Gopal, S.; Nambikkattu, J.; Rambabu, K.; Aboulella, A.M.; Wicjramasingha, S.R.; Banat, F. Recent developments in porous ceramic membranes for wastewater treatment and desalination: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Nam, S.-N.; Jang, A.; Jang, M.; Park, C.M.; Son, A.; Her, N.; Heo, J. Review of adsorption-membrane hybrid systems for water and wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleka, E.N.; Gallios, G.P.; Matis, K.A. A perspective on flotation: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotech. 2018, 93, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, M.; Gamberi, M.; Mora, C.; Pilati, F.; Regattieri, A. Design, prototyping, and assessment of a wastewater closed-loop recovery and purification system. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikasa, Y.; Yamawaki, N.; Shida, H.; Okumura, H.; Akamatu, S.; Yusuke Nishiuchi, Y.; Hata, T. Study on fixed salt removal effect by fine bubbles. In Proceedings of the 18th Asian Pacific Confederation of Chemical Engineering Congress (APCChE 2019), Sapporo, Japan, 23–27 September 2019; Volume 333, p. 02009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, K.; Meier, B.; Overbeck, J. Vertical and temporal changes in bacterial production and its consumption by heterotrophic nanoflagellates in a north German eutrophic lake. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1991, 122, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahat, S.B.; Omar, R.; Man, H.C.; Idris, A.I.; Kamal, S.M.M.; Adbullah, L.C.; Shreeshivadasan, C. Dynamic anaerobic membrane bioreactor (DAnMBR) with phase separation for food processing wastewater treatment at mesophilic temperature: Characterization of cake layer. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.; Etchepare, R.; Calgaroto, S.; Rubio, J. Aqueous dispersions of nanobubbles: Generation, properties and features. Min. Eng. 2016, 94, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of the Environment. Industrial Wastewater Management in Japan. Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/en/focus/docs/files/20120801-51.pdf (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- Yamamoto, K. (Sakamoto-Giken Inc., Nankoku, Kochi, Japan). Personal communication, 2021. [Google Scholar]






| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| MiB | microbubble |
| MaB | macrobubble |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| DOM | dissolved organic matter |
| POM | particulate organic matter |
| TOC | total organic carbon |
| DOC | dissolved organic carbon |
| POC | particulate organic carbon |
| S-POC | POC suspended in the water |
| F-POC | POC floating on the water surface |
| C/N ratio | carbon/nitrogen ratio |
| COD | chemical oxygen demand |
| C (g-C L−1) | N (g-N L−1) | C/N | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | (±SD) | Mean | (±SD) | ||
| Orange Juice | 42.7 a | 1.59 | 1.34 a | 0.08 | 31.9 a |
| Lactic Acid Drink | 43.0 a | 1.56 | 0.67 b | 0.06 | 64.7 b |
| Milk | 63.6 b | 1.99 | 5.23 c | 0.17 | 12.2 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukami, K.; Oogi, T.; Motomura, K.; Morita, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Hata, T. Effective Purification of Eutrophic Wastewater from the Beverage Industry by Microbubbles. Water 2021, 13, 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243661
Fukami K, Oogi T, Motomura K, Morita T, Sakamoto M, Hata T. Effective Purification of Eutrophic Wastewater from the Beverage Industry by Microbubbles. Water. 2021; 13(24):3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243661
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukami, Kimio, Tatsuro Oogi, Kohtaro Motomura, Tomoka Morita, Masaoki Sakamoto, and Takashi Hata. 2021. "Effective Purification of Eutrophic Wastewater from the Beverage Industry by Microbubbles" Water 13, no. 24: 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243661
APA StyleFukami, K., Oogi, T., Motomura, K., Morita, T., Sakamoto, M., & Hata, T. (2021). Effective Purification of Eutrophic Wastewater from the Beverage Industry by Microbubbles. Water, 13(24), 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13243661