Inorganic Nitrogen Production and Removal along the Sediment Gradient of a Stormwater Infiltration Basin
Abstract
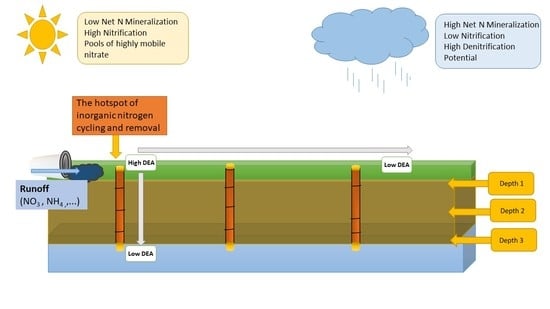
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.4. Biogeochemical Analyses of Soils
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Physiochemical Properties
3.2. Inorganic N Production and Denitrification in SIB Soils
3.2.1. Net N Mineralization
3.2.2. Nitrification
3.2.3. Denitrification
4. Implications for Stormwater Control Measure Efficiency
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.; Bang, K.; Ketchum, L.; Choe, J.; Yu, M. First flush analysis of urban storm runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 293, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.J.; Roy, A.H.; Feminella, J.W.; Cottingham, P.D.; Groffman, P.M.; Morgan, R.P., II. The urban stream syndrome: Current knowledge and the search for a cure. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-Y.; Lusk, M.G. Nutrients in Urban Stormwater Runoff: Current State of the Science and Potential Mitigation Options. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling Eutrophication: Nitrogen and Phosphorus; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, R.; Paerl, H.W. Coastal marine eutrophication: Control of both nitrogen and phosphorus is necessary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, E103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albertin, A.R.; Sickman, J.O.; Pinowska, A.; Stevenson, R.J. Identification of nitrogen sources and transformations within karst springs using isotope tracers of nitrogen. Biogeochemistry 2012, 108, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Song, J.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Duan, L.; Kang, X.; Wang, Q. Fluxes, seasonal patterns and sources of various nutrient species (nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon) in atmospheric wet deposition and their ecological effects on Jiaozhou Bay, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krimsky, L.S.; Lusk, M.G.; Abeels, H.; Seals, L. Sources and concentrations of nutrients in surface runoff from waterfront homes with different landscape practices. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 750, 142320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Groffman, P.M.; Band, L.E.; Elliott, E.M.; Shields, C.A.; Kendall, C. Tracking nonpoint source nitrogen pollution in human-impacted watersheds. Envirom. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8225–8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, M.G.; Toor, G.S.; Inglett, P.W. Organic nitrogen in residential stormwater runoff: Implications for stormwater management in urban watersheds. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-Y.; Toor, G.S. Sources and mechanisms of nitrate and orthophosphate transport in urban stormwater runoff from residential catchments. Water Res. 2017, 112, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.; Lawrence, T.; Stander, E.; Jontos, R.; Kaushal, S.; Newcomer, T.; Grimm, N.; Ekberg, M. Opportunities and challenges for managing nitrogen in urban stormwater: A review and synthesis. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, B.J.; Febria, C.M.; Gevrey, M.; Wainger, L.A. Nitrogen removal by stormwater management structures: A data synthesis. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 1594–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, V.; Marshall, A. Best Management Practices for South Florida Urban Stormwater Management Systems; Technical Publication REG-044; South Florida Water Management District, Everglades Stormwater Program: West Palm Beach, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Clary, J.; Jones, J.; Leisenring, M.; Hobson, P.; Strecker, E. International Stormwater BMP Database: 2016 Summary Statistics; The Water Environment & Reuse Foundation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Badin, A.L.; Monier, A.; Volatier, L.; Geremia, R.A.; Delolme, C.; Bedell, J.-P. Structural stability, microbial biomass and community composition of sediments affected by the hydric dynamics of an urban stormwater infiltration basin. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Zhou, H.; Norton, G.J.; Price, A.H.; Raffan, A.C.; Mooney, S.J.; Peng, X.; Hallett, P.D. Interaction between contrasting rice genotypes and soil physical conditions induced by hydraulic stresses typical of alternate wetting and drying irrigation of soil. Plant. Soil 2018, 430, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikha, M.M.; Rice, C.W.; Milliken, G.A. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization as affected by drying and wetting cycles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, V.B.; Grant, K.; Pritsch, K.; Jentsch, A.; Schloter, M.; Beierkuhnlein, C.; Gschwendtner, S. Seasonal effects of extreme weather events on Potential Extracellular Enzyme Activities in a temperate grassland soil. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A.T.; Yahdjian, L.; Stark, J.M.; Belnap, J.; Porporato, A.; Norton, U.; Ravetta, D.A.; Schaeffer, S.M. Water pulses and biogeochemical cycles in arid and semiarid ecosystems. Oecologia 2004, 141, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzluebbers, A.; Haney, R.; Honeycutt, C.; Schomberg, H.-H.; Hons, F. Flush of carbon dioxide following rewetting of dried soil relates to active organic pools. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, S.A. Soil Nutrient Bioavailability: A Mechanistic Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Vilain, G.; Garnier, J.; Tallec, G.; Tournebize, J. Indirect N2O emissions from shallow groundwater in an agricultural catchment (Seine Basin, France). Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillam, K.; Zebarth, B.; Burton, D. Nitrous oxide emissions from denitrification and the partitioning of gaseous losses as affected by nitrate and carbon addition and soil aeration. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 88, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Peng, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. A field study to evaluate the impact of different factors on the nutrient pollutant concentrations in green roof runoff. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettez, N.D.; Groffman, P.M. Denitrification Potential in Stormwater Control Structures and Natural Riparian Zones in an Urban Landscape. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10909–10917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, N.R.; McPhillips, L.E.; Shapleigh, J.P.; Walter, M.T. The Role of Denitrification in Stormwater Detention Basin Treatment of Nitrogen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7928–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhillips, L.; Walter, M.T. Hydrologic conditions drive denitrification and greenhouse gas emissions in stormwater detention basins. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 85, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Reilly, A.M.; Wanielista, M.P.; Chang, N.-B.; Xuan, Z.; Harris, W.G. Nutrient removal using biosorption activated media: Preliminary biogeochemical assessment of an innovative stormwater infiltration basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenzweig, B.R.; Groffman, P.M.; Zarnoch, C.B.; Branco, B.F.; Hartig, E.K.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Forgione, H.M.; Parris, A. Nitrogen regulation by natural systems in “unnatural” landscapes: Denitrification in ultra-urban coastal ecosystems. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2018, 4, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, C.K.; Kelly, J.J.; Gray, K.A. Effects of variable hydroperiods and water level fluctuations on denitrification capacity, nitrate removal, and benthic-microbial community structure in constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.; Köpp, J.; Gebauer, G.; Horn, M.A. Drying-rewetting and flooding impact denitrifier activity rather than community structure in a moderately acidic fen. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavo, P.; Vidal-Beaudet, L.; Béchet, B.; Lassabatère, L.; Charpentier, S. Spatial distribution of sediments and transfer properties in soils in a stormwater infiltration basin. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, J.L.; Ardón, M.; Bernhardt, E.S. Using environmental variables and soil processes to forecast denitrification potential and nitrous oxide fluxes in coastal plain wetlands across different land uses. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, M.G.; Toor, G.S. Optimizing the hydrologic properties of urban soils. In Urban Soils; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Datry, T.; Malard, F.; Vitry, L.; Hervant, F.; Gibert, J. Solute dynamics in the bed sediments of a stormwater infiltration basin. J. Hydrol. 2003, 273, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassabatere, L.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R.; Goutaland, D.; Letellier, L.; Gaudet, J.; Winiarski, T.; Delolme, C. Effect of the settlement of sediments on water infiltration in two urban infiltration basins. Geoderma 2010, 156, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlin, J.; Kissel, D.; Maddux, L.; Claassen, M.; Long, J. Crop rotation and tillage effects on soil organic carbon and nitrogen. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B. Impact of soil organic matter on soil properties—A review with emphasis on Australian soils. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA, Web Soil Survey. Natural Resources Conservation Service, US Department of Agriculture: Undated. Available online: https://websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov/App/HomePage.htm (accessed on 27 January 2019).
- Harris, D.; Horwáth, W.R.; Van Kessel, C. Acid fumigation of soils to remove carbonates prior to total organic carbon or carbon-13 isotopic analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1853–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffman, P.M.; Crawford, M.K. Denitrification potential in urban riparian zones. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Inglett, P.W.; Inglett, K.S. Seasonal patterns of nitrogen cycling in subtropical short-hydroperiod wetlands: Effects of precipitation and restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 556, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Duan, S.; Doody, T.R.; Haq, S.; Smith, R.M.; Johnson, T.A.N.; Newcomb, K.D.; Gorman, J.; Bowman, N.; Mayer, P.M. Human-accelerated weathering increases salinization, major ions, and alkalinization in fresh water across land use. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 83, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummey, D.; Smith, J.; Bolton, H., Jr. Nitrous oxide flux from a shrub-steppe ecosystem: Sources and regulation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 26, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottner, P. Response of microbial biomass to alternate moist and dry conditions in a soil incubated with 14C-and 15N-labelled plant material. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Griffin, D. Water potential and the respiration of microorganisms in the soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1975, 7, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halverson, L.J.; Jones, T.M.; Firestone, M.K. Release of intracellular solutes by four soil bacteria exposed to dilution stress. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gestel, M.; Merckx, R.; Vlassak, K. Soil drying and rewetting and the turnover of 14C-labelled plant residues: First order decay rates of biomass and non-biomass 14C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1993, 25, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, M. Modeling the flush of nitrogen mineralization caused by drying and rewetting soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovieno, P.; Bååth, E. Effect of drying and rewetting on bacterial growth rates in soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.E.; Schimel, J.P.; Meixner, T.; Sickman, J.O.; Melack, J.M. Episodic rewetting enhances carbon and nitrogen release from chaparral soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Schimel, J.P. Effects of drying–rewetting frequency on soil carbon and nitrogen transformations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C. Water quality improvement through bioretention media: Nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrawat, K. Factors affecting nitrification in soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadas, T.M.; Smith, M.; Luan, H. Leaching and retention of dissolved metals in particulate loaded pervious concrete columns. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grella, C.; Wright, I.A.; Findlay, S.J.; Jonasson, O.J. Geochemical contamination of urban water by concrete stormwater infrastructure: Applying an epoxy resin coating as a control treatment. Urban Water J. 2016, 13, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, J.; Toor, G.S. Composition, sources, and bioavailability of nitrogen in a longitudinal gradient from freshwater to estuarine waters. Water Res. 2018, 137, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverey, F.; Grossart, H.-P.; Premke, K.; Lischeid, G. Carbon and nutrient cycling in kettle hole sediments depending on hydrological dynamics: A review. Hydrobiologia 2016, 775, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Location and Season | Zone | Gravimetric Moisture (%) | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Texture | pH | Inorganic C, g/kg | Total C (g/kg) | Total N (g/kg) | C:N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIB 1-wet season | 1 | 21.6 (1.5) | 34 (24) | Sand | 8.0 (0.4) | 0.69 (1.03) | 2.8 (3.8) | 0.2 (0.1) | 8.4 (8.2) |
| 2 | 21.5 (1.6) | 33 (25) | Sand | 6.4 (0.2) | 0.02 (0.03) | 1.2 (1.4) | 0.2 (0.1) | 4.6 (3.5) | |
| 3 | 18.3 (11.0) | 28 (23) | Sand | 6.4 (0.2) | 0.04 (0.04) | 0.9 (0.8) | 0.2 (0.1) | 4.4 (2.5) | |
| SIB 1-dry season | 1 | 0.8 (0.4) | 21 (3) | Sand | 8.6 (0.2) | 1.25 (0.61) | 4.8 (2.1) | 0.3 (0.1) | 13.3 (3.2) |
| 2 | 1.7 (0.9) | 16 (6) | Sand | 7.5 (0.7) | 0.18 (0.04) | 1.0 (0.7) | 0.2 (0.1) | 4.6 (2.6) | |
| 3 | 3.2 (2.2) | 11 (5) | Sand | 6.4 (0.3) | 0.17 (0.02) | 0.4 (0.5) | 0.2 (0.1) | 2.1 (2.2) | |
| SIB 2-wet season | 1 | 20.4 (1.3) | 24 (5) | Sandy clay | 7.5 (0.9) | 0.18 (0.17) | 3.7 (1.9) | 0.4 (0.1) | 8.6 (2.6) |
| 2 | 21.9 (2.1) | 24 (4) | Sand | 5.9 (0.4) | 0.09 (0.05) | 4.4 (1.0) | 0.4 (0.1) | 11.1 (2.8) | |
| 3 | 19.5 (3.9) | 22 (73) | Sand | 6.0 (0.7) | 0.04 (0.02) | 4.8 (20.4) | 0.4 (0.1) | 12.7 (2.8) | |
| SIB 2-dry season | 1 | 24.3 (4.1) | 116 (71) | Sandy clay | 8.6 (0.8) | 1.82 (1.23) | 25.1 (21.1) | 2.2 91.7) | 9.7 (3.4) |
| 2 | 18.7 (2.9) | 38 (29) | Sand | 6.4 (0.4) | 0.35 (0.20) | 1.9 (1.7) | 0.3 (0.1) | 5.6 (2.5) | |
| 3 | 15.2 (3.8) | 37 (27) | Sand | 6.2 (0.9) | 0.31 (0.28) | 2.0 (6.2) | 0.4 (0.3) | 5.1 (6.0) |
| Location and Season | Zone | Exchangeable NO3-N (mg/kg) | Exchangeable NH4-N (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIB 1-wet season | 1 | 0.8 (0.4) | 2.0 (1.2) |
| 2 | 0.8 (0.3) | 2.1 (1.2) | |
| 3 | 0.5 (0.5) | 1.6 (0.2) | |
| SIB 1-dry season | 1 | 0.7 (0.0) | 7.4 (0.4) |
| 2 | 0.7 (0.1) | 8.1 (2.8) | |
| 3 | 0.5 (0.0) | 7.8 (1.2) | |
| SIB 2-wet season | 1 | 1.1 (0.7) | 6.3 (4.0) |
| 2 | 0.4 (0.1) | 10.0 (3.7) | |
| 3 | 0.5 (0.1) | 5.1 (1.5) | |
| SIB 2-dry season | 1 | 12.4 (11.8) | 14.7 (2.3) |
| 2 | 0.7 (0.1) | 8.9 (0.6) | |
| 3 | 1.0 (0.2) | 8.6 (1.4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Si, Q.; Lusk, M.G.; Inglett, P.W. Inorganic Nitrogen Production and Removal along the Sediment Gradient of a Stormwater Infiltration Basin. Water 2021, 13, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030320
Si Q, Lusk MG, Inglett PW. Inorganic Nitrogen Production and Removal along the Sediment Gradient of a Stormwater Infiltration Basin. Water. 2021; 13(3):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030320
Chicago/Turabian StyleSi, Qianyao, Mary G. Lusk, and Patrick W. Inglett. 2021. "Inorganic Nitrogen Production and Removal along the Sediment Gradient of a Stormwater Infiltration Basin" Water 13, no. 3: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030320
APA StyleSi, Q., Lusk, M. G., & Inglett, P. W. (2021). Inorganic Nitrogen Production and Removal along the Sediment Gradient of a Stormwater Infiltration Basin. Water, 13(3), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13030320