The Impacts of Hydrology and Climate on Hydrological Connectivity in a Complex River–Lake Floodplain System Based on High Spatiotemporal Resolution Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Data Pre-Processing
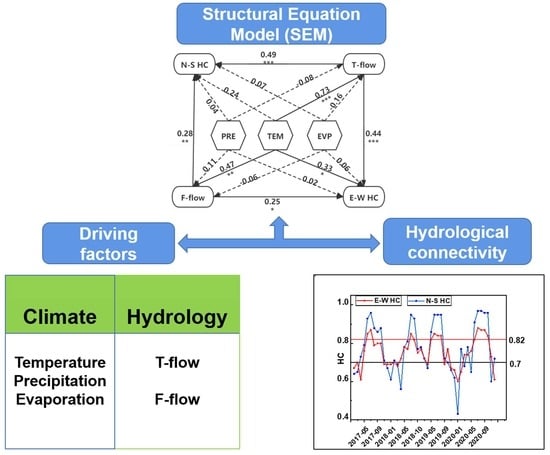
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HC and Temporal and Spatial Inundation Characteristics
3.2. Direct and Indirect Effects of the Hydrological and Meteorological Factors on HC
4. Discussion
4.1. Relative Importance of Hydrological and Meteorological Factors on HC
4.2. The Threshold of HC and Management Implications
4.3. Data Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X. Dramatic inundation changes of China’s two largest freshwater lakes linked to the Three Gorges Dam. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9628–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigg, M.A.; Michaelides, K.; Neal, J.C.; Bates, P.D. Surface water connectivity dynamics of a large scale extreme flood. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, X.; Gong, Z.; Liu, H. Lateral migration of fish between China’s second largest freshwater lake (Dongting Lake) and the mainstem of the Yangtze River. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2019, 102, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Jia, Y.; Liu, G.; Yu, X.; Wen, L. Wintering waterbirds in a large river floodplain: Hydrological connectivity is the key for reconciling development and conservation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G.; Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Wang, S. Seasonal and Diurnal Variations in the Priestley–Taylor Coefficient for a Large Ephemeral Lake. Water 2020, 12, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, G.; Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Wang, S. Testing the Symmetric Assumption of Complementary Relationship: A Comparison between the Linear and Nonlinear Advection-Aridity Models in a Large Ephemeral Lake. Water 2019, 11, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larned, S.T.; Datry, T.; Arscott, D.B.; Tockner, K. Emerging concepts in temporary-river ecology. Freshwat. Biol. 2010, 55, 717–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicente, M.; Ben-Salem, N. Computing structural and functional flow and sediment connectivity with a new aggregated index: A case study in a large Mediterranean catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.L.; Olden, J.D.; Pelland, N.A. Climate change poised to threaten hydrologic connectivity and endemic fishes in dryland streams. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13894–13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, J.; Tan, Z.; Liu, X. Assessment of water storage response to surface hydrological connectivity in a large floodplain system (Poyang Lake, China) using hydrodynamic and geostatistical analysis. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk A 2019, 33, 2071–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, F.; Dutta, D.; Marvanek, S.; Petheram, C.; Ticehurst, C.; Lerat, J.; Kim, S.; Yang, A. Assessing the impacts of climate change and dams on floodplain inundation and wetland connectivity in the wet–dry tropics of northern Australia. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Xue, C.; Lu, J. Assessing effective hydrological connectivity for floodplains with a framework integrating habitat suitability and sediment suspension behavior. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Tan, Z.; Yao, J. New insights on the surface hydrological connectivity of water depth thresholds in a flood-pulse-influenced floodplain system (Poyang Lake, China). Stoch. Env. Res. Risk A 2020, 35, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchioli, R.; Ripple, W.J.; Timmis, K.N.; Azam, F.; Bakken, L.R.; Baylis, M.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boetius, A.; Boyd, P.W.; Classen, A.T.; et al. Scientists’ warning to humanity: Microorganisms and climate change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuma, H.G.; Feyessa, F.F.; Demissie, T.A. Hydrologic responses to climate and land-use/land-cover changes in the Bilate catchment, Southern Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, 3750–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Liang, J.; Guo, S.; Huang, L.; Wu, H.; Hua, S. Quantitative assessment of the contribution of climate variability and human activity to streamflow alteration in Dongting Lake, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Qian, Z.; Lei, M.; Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, S.; Zeng, G. Interactive effects of climate variability and human activities on blue and green water scarcity in rapidly developing watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Hayhoe, K. CMIP5 projected changes in spring and summer drought and wet conditions over North America. Clim. Dynam. 2015, 44, 2737–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Brusseau, M.L.; He, L.; Gorlier, A.; Yao, T.; Tian, P.; Feng, S.; Yu, Q.; Nie, Q.; et al. Interaction of climate change, potentially toxic elements (PTEs), and topography on plant diversity and ecosystem functions in a high-altitude mountainous region of the Tibetan Plateau. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zou, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wu, X. Quantifying the anthropogenic and climatic contributions to changes in water discharge and sediment load into the sea: A case study of the Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.J.; Yin, J.; Paw, U.K.T.; Zhao, S.H.; Qiu, G.Y.; Liu, Z. How the three Gorges Dam affects the hydrological cycle in the mid-lower Yangtze River: A perspective based on decadal water temperature changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Cui, B.; Xie, T.; Yu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ning, Z. Reclamation shifts the evolutionary paradigms of tidal channel networks in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.-Q.; Jiang, C.; Long, Y.; Deng, B.; Yan, S. Hydrological Drought in Dongting Lake Area (China) after the Running of Three Gorges Dam and a Possible Solution. Water 2020, 12, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yi, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Lei, M.; Meng, Q.; Zhai, Y. Detecting changes in water level caused by climate, land cover and dam construction in interconnected river-lake systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epting, S.M.; Hosen, J.D.; Alexander, L.C.; Lang, M.W.; Armstrong, A.W.; Palmer, M.A. Landscape metrics as predictors of hydrologic connectivity between Coastal Plain forested wetlands and streams. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Tan, Z.; Werner, A.D. Satellite image-based investigation of the seasonal variations in the hydrological connectivity of a large floodplain (Poyang Lake, China). J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arheimer, B.; Lindström, G. Detecting Changes in River Flow Caused by Wildfires, Storms, Urbanization, Regulation, and Climate Across Sweden. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 8990–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Connolly, J.; Liang, M.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S. Mechanistic links between biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and stability in a multi-site grassland experiment. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 3370–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Qian, B.; Niu, L.; Wang, P.; Gu, J.; Yang, N. How fluvial inputs directly and indirectly affect the ecological status of different lake regions: A bio-assessment framework. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Meng, Q.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, M. The influence of hydrological variables, climatic variables and food availability on Anatidae in interconnected river-lake systems, the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River floodplain. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, P.; Gui, Z.; Ming, B.; Yang, Z.; Xie, K.; Zhang, X. Reducing lake water-level decline by optimizing reservoir operating rule curves: A case study of the Three Gorges Reservoir and the Dongting Lake. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Huang, L.; Lai, X.; Lu, L.; Wu, H.; et al. Effects of landscape structure, habitat and human disturbance on birds: A case study in East Dongting Lake wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 67, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Baiyinbaoligao; Wu, Y. Maintaining the connected river-lake relationship in the middle Yangtze River reaches after completion of the Three Gorges Project. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 32, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-H.; Yue, T.; Xin-sheng, C.; Feng, L.; Zheng-miao, D. The impact of Three Gorges Dam on the downstream eco-hydrological environment and vegetation distribution of East Dongting Lake. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, D.; Simwanda, M.; Salekin, S.; Nyirenda, V.; Murayama, Y.; Ranagalage, M. Sentinel-2 Data for Land Cover/Use Mapping: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, G.; Cawkwell, F.; Wingler, A. Status of Phenological Research Using Sentinel-2 Data: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granero-Belinchon, C.; Adeline, K.; Lemonsu, A.; Briottet, X. Phenological Dynamics Characterization of Alignment Trees with Sentinel-2 Imagery: A Vegetation Indices Time Series Reconstruction Methodology Adapted to Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.; Shi, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Fan, X. Co-seismic landslide mapping using Sentinel-2 10-m fused NIR narrow, red-edge, and SWIR bands. Landslides 2021, 18, 2017–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Surface water connectivity of seasonal isolated lakes in a dynamic lake-floodplain system. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, M. Comparison of thresholding methods for shoreline extraction from Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 imagery: Extreme Lake Salda, track of Mars on Earth. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Shi, L.; Guan, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jing, L.; Lei, G. Potential Impacts of Proposed Chenglingji Hydraulic Project on Wetlands in Dongting Lake. Wetl. Sci. 2018, 16, 377. [Google Scholar]
- Guojing Gan, Y.L.; Chen, D.; Zheng, C. Investigation of a non-linear complementary relationship model for monthly evapotranspiration estimation at global flux sites. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 2645–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardo-Igúzquiza, E.; Dowd, P.A. CONNEC3D: A computer program for connectivity analysis of 3D random set models. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgaard, C. Spatio-Temporal Structural Equation Modeling in a Hierarchical Bayesian Framework: What Controls Wet Heathland Vegetation? Ecosystems 2019, 22, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefcheck, J.S. piecewiseSEM: Piecewise structural equation modelling in r for ecology, evolution, and systematics. Methods Ecol. Evolution. 2016, 7, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertes, L.A.K. Documentation and significance of the perirheic zone on inundated floodplains. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1749–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforge, D.; De Viron, O.; Vanclooster, M.; Van Camp, M.; Watlet, A. Detecting hydrological connectivity using causal inference from time series: Synthetic and real karstic case studies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sc. 2022, 26, 2181–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Tan, Z.; Yao, J. The role of a seasonal lake groups in the complex Poyang Lake-floodplain system (China): Insights into hydrological behaviors. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; He, G.; Wang, G.; Cao, H. Surface Water Changes in Dongting Lake from 1975 to 2019 Based on Multisource Remote-Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Fang, Y.; Cui, B. A model to evaluate spatiotemporal variations of hydrological connectivity on a basin-scale complex river network with intensive human activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E. Characterizing channel-floodplain connectivity using satellite altimetry: Mechanism, hydrogeomorphic control, and sediment budget. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 243, 111783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Aminjafari, S.; Yang, W.; Cui, B.; Yan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Jaramillo, F. Using InSAR to identify hydrological connectivity and barriers in a highly fragmented wetland. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 4417–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hawley-Howard, J.; Pitt, A.L.; Wang, J.J.; Baldwin, R.F.; Chow, A.T. Water quality of small seasonal wetlands in the Piedmont ecoregion, South Carolina, USA: Effects of land use and hydrological connectivity. Water Res. 2015, 73, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, Y.; Tan, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Yao, J. Hydrodynamic investigation of surface hydrological connectivity and its effects on the water quality of seasonal lakes: Insights from a complex floodplain setting (Poyang Lake, China). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amezcua, F.; Rajnohova, J.; Flores-de-Santiago, F.; Flores-Verdugo, F.; Amezcua-Linares, F. The Effect of Hydrological Connectivity on Fish Assemblages in a Floodplain System From the South-East Gulf of California, Mexico. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, V.; Schmitt, R.J.P.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Zarfl, C.; King, H.; Schipper, A.M. Impacts of current and future large dams on the geographic range connectivity of freshwater fish worldwide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3648–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naia, M.; Hermoso, V.; Carvalho, S.B.; Brito, J.C. Promoting connectivity between priority freshwater sites for conservation in intermittent hydrological systems. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshwat. Ecosyst. 2021, 31, 1886–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fraser, J.D.; Chen, J. Wintering waterbirds in the middle and lower Yangtze River floodplain: Changes in abundance and distribution. Bird Conserv. Int. 2016, 27, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Lei, J.; Zuo, A.; Zhang, H.; Lei, G.; Wen, L. Optimizing the timing of water level recession for conservation of wintering geese in Dongting Lake, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrial, E.; Espínola, L.A.; Rabuffetti, A.P.; Eurich, M.F.; Paira, A.R.; Blettler, M.C.M.; Amsler, M.L. Variability of hydrological connectivity and fish dynamics in a wide subtropical–temperate floodplain. River Res. Appl. 2019, 35, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, T.; Pinceel, T.; De Necker, L.; Wepener, V.; Lemmens, P.; Brendonck, L. Lateral hydrological connectivity differentially affects the community characteristics of multiple groups of aquatic invertebrates in tropical wetland pans in South Africa. Freshwat. Biol. 2019, 64, 2189–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gu, Q.; Liu, G.; Shen, J.; Tang, X. Hydrological Condition Constrains Vegetation Dynamics for Wintering Waterfowl in China’s East Dongting Lake Wetland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ombadi, M.; Nguyen, P.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.L. Evaluation of Methods for Causal Discovery in Hydrometeorological Systems. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lai, G.; Li, L. Predicting the Hydrological Impacts of the Poyang Lake Project Using an EFDC Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 5015009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Yi, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Zhai, Y.; Pei, Z. The Impacts of Hydrology and Climate on Hydrological Connectivity in a Complex River–Lake Floodplain System Based on High Spatiotemporal Resolution Images. Water 2022, 14, 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121836
Yang S, Liang J, Li X, Yi Y, Zhu Z, Li X, Chen X, Li S, Zhai Y, Pei Z. The Impacts of Hydrology and Climate on Hydrological Connectivity in a Complex River–Lake Floodplain System Based on High Spatiotemporal Resolution Images. Water. 2022; 14(12):1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121836
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Suhang, Jie Liang, Xiaodong Li, Yuru Yi, Ziqian Zhu, Xin Li, Xuwu Chen, Shuai Li, Yeqing Zhai, and Ziming Pei. 2022. "The Impacts of Hydrology and Climate on Hydrological Connectivity in a Complex River–Lake Floodplain System Based on High Spatiotemporal Resolution Images" Water 14, no. 12: 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121836
APA StyleYang, S., Liang, J., Li, X., Yi, Y., Zhu, Z., Li, X., Chen, X., Li, S., Zhai, Y., & Pei, Z. (2022). The Impacts of Hydrology and Climate on Hydrological Connectivity in a Complex River–Lake Floodplain System Based on High Spatiotemporal Resolution Images. Water, 14(12), 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121836