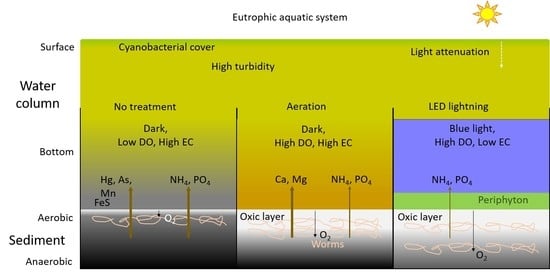
Effects of Light-Emitting Diode Illumination on Sediment Surface Biological Activities and Releases of Nutrients and Metals to Overlying Water in Eutrophic Lake Microcosms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Collection
2.2. Microcosm Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Data Treatments and Analyses
3. Results
3.1. DO and Water Quality Variables
3.2. Nutrient Concentrations in Water
3.3. Metal Concentrations in Water
3.4. Phytoplankton Occurrence in Water
3.5. Nutrient and Organic Content in Sediment
3.6. Oxic Layer and Worm Tunnels in the Sediment
3.7. Composition of the Microbial Community in Water and Sediment
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Aeration and LED on Increasing Oxygen and Biological Activities
4.2. Effects of Aeration and LED on Nutrient Release
4.3. Effects of Aeration and LED on Metal Release
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Taxon | Control | Aeration | LED | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake | River | Lake | River | Lake | River | |
| Cyanobacteria | ||||||
| Arthrospira * | 1 | |||||
| Chroococcus | 4750 | 16 | ||||
| Dactylococcopsis | 11 | |||||
| Pseudanabena * | 1 | |||||
| Green algae | ||||||
| Ankistrodesmus | 1 | |||||
| Cosmarium | 1 | |||||
| Eudrina | 117 | |||||
| Scenedesmus | 8 | |||||
| Oocystaceae | 2 | |||||
| Diatoms | ||||||
| Aulacoseira | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Cyclotella | 20 | 3 | ||||
| Navicula | 1 | |||||
| Nitzschia | 9 | 1 | ||||
| Synedra | 2 | |||||
| Other | ||||||
| Dinoflagellate | 2 | |||||


References
- Harper, D.M. Eutrophication of Freshwaters: Principles, Problems and Restoration; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; p. 327. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, W.K.; Bouska, W.W.; Eitzmann, J.L.; Pilger, T.J.; Pitts, K.L.; Riley, A.J.; Schloesser, J.T.; Thornbrugh, D.J. Eutrophication of US freshwaters: Analysis of potential economic damages. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Diaz, R.J.; Levin, L.A.; Turner, R.E.; Gilbert, D.; Zhang, J. Dynamics and distribution of natural and human-caused hypoxia. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 585–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Zacharias, I. Restoration of eutrophic freshwater by managing internal nutrient loads. A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibuye, F.A.; Zamyadi, A.; Wert, E.C. A critical review on operation and performance of source water control strategies for cyanobacterial blooms: Part I-chemical control methods. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibuye, F.A.; Zamyadi, A.; Wert, E.C. A critical review on operation and performance of source water control strategies for cyanobacterial blooms: Part II-mechanical and biological control methods. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, B.; Andersen, J.M.; Fleischer, S.; Jansson, M. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment-water interface. In Phosphorus in Freshwater Ecosystems; Persson, G., Jansson, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- Beutel, M.W. Inhibition of ammonia release from anoxic profundal sediments in lakes using hypolimnetic oxygenation. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Tian, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, M. Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient levels on heavy metal contents and fractions in river surface sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Long, X.; Chong, Y.; Yu, G. Potential risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments during the denitrification process enhanced by calcium nitrate addition: Effect of AVS residual. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 87, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, A.; Frenzel, P.; Cypionka, H. Life at the oxic–anoxic interface: Microbial activities and adaptations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 691–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Reil, L.A.; Köster, M. Eutrophication of marine waters: Effects on benthic microbial communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 41, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K. The role of periphyton in phosphorus retention in shallow freshwater aquatic systems. J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Wan, J.; Li, J.; Shao, H.; Wu, Y. Periphytic biofilm: A buffer for phosphorus precipitation and release between sediments and water. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Rene, E.R. Periphytic biofilms: A promising nutrient utilization regulator in wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E. Organic matter diagenesis at the oxic/anoxic interface in coastal marine sediments, with emphasis on the role of burrowing animals. In Life at Interfaces and under Extreme Conditions; Liebezeit, G., Dittmann, S., Kröncke, I., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G. (Ed.) The phosphorus cycle. In Limnology, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 239–288. [Google Scholar]
- Carlton, R.G.; Wetzel, R.G. Phosphorus flux from lake sediments: Effect of epipelic algal oxygen production. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Mei, X.Y. Effects of benthic algae on release of soluble reactive phosphorus from sediments: A radioisotope tracing study. Water Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kristensen, E.; Penha-Lopes, G.; Delefosse, M.; Valdemarsen, T.; Quintana, C.O.; Banta, G.T. What is bioturbation the need for a precise definition for fauna in aquatic sciences. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, W.; Chen, M.; Liu, L.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xing, X.; Fan, K. Mechanism of phosphorus mobility in sediments with larval (Propsilocerus akamusi) bioturbation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7538–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; van Oosterhout, F. Controlling eutrophication by combined bloom precipitation and sediment phosphorus inactivation. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6527–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, P.M.; Ibelings, B.W.; Bormans, M.; Huisman, J. Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: A review. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Xia, D.; Mi, Q.; Yan, N.; Su, M.; Lin, A.; Zhao, M.; Iseri, Y. Controlling eutrophication via surface aerators in irregular-shaped urban ponds. Water 2021, 13, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Gragnani, A.; Mur, L.R.; van Nes, E.H. On the dominance of filamentous cyanobacteria in shallow, turbid lakes. Ecology 1997, 78, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Cui, B. Performance of macrophyte indicators to eutrophication pressure in ponds. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 96, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Huang, H.; Mi, Q.; Iseri, Y. Effects of substrate and water depth of a eutrophic pond on the physiological status of a submerged plant, Vallisneria natans. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.K.; Oh, S.J.; Yang, H.S. Growth and uptake kinetics of nitrate and phosphate by benthic microalgae for phytoremediation of eutrophic coastal sediments. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, P.S.; Barreira, L.A.; Pereira, H.G.; Perales, J.A.; Varela, J.C. Light emitting diodes (LEDs) applied to microalgal production. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.J.; Kang, G.S.; Kim, A.; Kim, N.E.; Nguyen, T.L.; Kim, D.H. Blue light-emitting diode photoinactivation inhibits edwardsiellosis in fancy carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 2018, 483, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.T.; Kim, A.; Kim, N.; Roh, H.J.; Chun, W.K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.H. Effect of blue light emitting diode on viral hemorrhagic septicemia in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2020, 521, 735019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Yan, N.; Xia, D.; Zhao, M.; Iseri, Y. Improvement of water quality using a circulation device equipped with oxidation carriers and light emitting diodes in eutrophic pond mesocosms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ. U. S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA. 1997–2018. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Spalding, M.H. Photosynthesis and photorespiration in freshwater green algae. Aquat. Bot. 1989, 34, 181–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Vyverman, W. Differences in nutrient uptake capacity of the benthic filamentous algae Cladophora sp., Klebsormidium sp. and Pseudanabaena sp. under varying N/P conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouhsassi, M.; Bouyahya, A.; El Ouahrani, A.; El Harsal, A.; Abrini, J. Evaluation of self-purifying power of cyanobacteria Pseudanabaena galeata: Case of dairy factory effluents. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Matisoff, G. Solute transport in sediments by a large freshwater oligochaete, Branchiura sowerbyi. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matisoff, G.; Wang, X.; McCall, P.L. Biological redistribution of lake sediments by tubificid oligochaetes: Branchiura sowerbyi and Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri/Tubifex tubifex. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 1999, 25, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piot, A.; Rochon, A.; Stora, G.; Desrosiers, G. Experimental study on the influence of bioturbation performed by Nephtys caeca (Fabricius) and Nereis virens (Sars) annelidae on the distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in the sediment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 359, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchet, V.M.; Sauriau, P.G.; Debenay, J.P.; Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Schmidt, S.; Amiard, J.C.; Dupas, B. Influence of the mode of macrofauna-mediated bioturbation on the vertical distribution of living benthic foraminifera: First insight from axial tomodensitometry. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 371, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Ding, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xing, X.; Wang, D.; Gong, M.; Zhang, C. Fine-scale bioturbation effects of tubificid worm (Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri) on the lability of phosphorus in sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.A.; Beeton, A.M. The effect of dissolved oxygen on the burrowing behavior of Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri (Oligochaeta). Hydrobiologia 1975, 47, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Su, F.J.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Huang, T.C.; Wang, Y.S. Embryo Development and Behavior in Sea Urchin (Tripneustes gratilla) Under Different Light Emitting Diodes Condition. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Schubert, C.J.; Fiskal, A.; Dubois, N.; Lever, M.A. Eutrophication as a driver of microbial community structure in lake sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3446–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; He, W.X.; Zhang, D.C. Marinisubtilis pacificus gen. nov., sp. nov., a Member of the Family Microbacteriaceae Isolated from a Deep-Sea Seamount. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 2136–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Fan, J.; Zhao, H.; Cao, M.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y. The impact of heterotrophic bacteria on recalcitrant dissolved organic carbon formation in a typical karstic river. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Qi, M.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Kong, D.; Wang, A.; Liang, B. Bioremediation of contaminated urban river sediment with methanol stimulation: Metabolic processes accompanied with microbial community changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Zhao, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Mi, Q.; Hao, A.; Iseri, Y. Effect of remediation reagents on bacterial composition and ecological function in black-odorous water sediments. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G. The role of periphyton in phosphorus retention in shallow lakes with different trophic status, China. Aquat. Bot. 2015, 125, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hölker, F.; Vanni, M.J.; Kuiper, J.J.; Meile, C.; Grossart, H.P.; Stief, P.; Adrian, R.; Lorke, A.; Dellwig, O.; Brand, A.; et al. Tube-dwelling invertebrates: Tiny ecosystem engineers have large effects in lake ecosystems. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 85, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beutel, M.W.; Leonard, T.M.; Dent, S.R.; Moore, B.C. Effects of aerobic and anaerobic conditions on P, N, Fe, Mn, and Hg accumulation in waters overlaying profundal sediments of an oligo-mesotrophic lake. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ding, S.; Wu, Y.; Fan, X.; Jin, Z.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Phosphorus mobilization in lake sediments: Experimental evidence of strong control by iron and negligible influences of manganese redox reactions. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, A.W.; Lamp, W.O. Burrowing macroinvertebrates alter phosphorus dynamics in drainage ditch sediments. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.M.; Ravenscroft, P.; Safiulla, S.; Thirlwall, M.F. Arsenic in groundwater: Testing pollution mechanisms for sedimentary aquifers in Bangladesh. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsic, M.; Teasdale, P.R.; Welsh, D.T.; Johnston, S.G.; Burton, E.D.; Hockmann, K.; Bennett, W.W. Diffusive gradients in thin films reveals differences in antimony and arsenic mobility in a contaminated wetland sediment during an oxic-anoxic transition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem-Nguyen, V.; Skyllberg, U.; Björn, E. Thermodynamic modeling of the solubility and chemical speciation of mercury and methylmercury driven by organic thiols and micromolar sulfide concentrations in boreal wetland soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3678–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caille, N.; Tiffreau, C.; Leyval, C.; Morel, J.L. Solubility of metals in an anoxic sediment during prolonged aeration. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 301, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P.I.; Ng, D.Q.; Li, I.C.; Lin, Y.P. Effects of dissolved oxygen, pH, salinity and humic acid on the release of metal ions from PbS, CuS and ZnS during a simulated storm event. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luquet, G. Biomineralizations: Insights and prospects from crustaceans. Zookeys 2012, 176, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagasawa, H. The crustacean cuticle: Structure, composition and mineralization. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.K.; Oh, S.J.; Yang, H.S.; Kim, P.J. Phytoremediation by benthic microalgae (BMA) and light emitting diode (LED) in eutrophic coastal sediments. Ocean. Sci. J. 2015, 50, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.K.; Jeon, J.Y.; Oh, S.J. Potential for heavy metal (copper and zinc) removal from contaminated marine sediments using microalgae and light emitting diodes. Ocean. Sci. J. 2017, 52, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honglikith, D.; Harada, M.; Hiramatsu, K.; Tabata, T.; Ozaki, A. Anoxification recovery using underwater LED irradiation and influence of its optical spectrum on water quality improvement. Paddy Water Environ. 2022, 20, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.; Su, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Zhao, M.; Iseri, Y. Multiple roles of bamboo as a regulator of cyanobacterial bloom in aquatic systems. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, A.; Yu, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Xia, D.; Zhao, M.; Iseri, Y. Effects of Light-Emitting Diode Illumination on Sediment Surface Biological Activities and Releases of Nutrients and Metals to Overlying Water in Eutrophic Lake Microcosms. Water 2022, 14, 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121839
Hao A, Yu H, Kobayashi S, Xia D, Zhao M, Iseri Y. Effects of Light-Emitting Diode Illumination on Sediment Surface Biological Activities and Releases of Nutrients and Metals to Overlying Water in Eutrophic Lake Microcosms. Water. 2022; 14(12):1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121839
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Aimin, Hong Yu, Sohei Kobayashi, Dong Xia, Min Zhao, and Yasushi Iseri. 2022. "Effects of Light-Emitting Diode Illumination on Sediment Surface Biological Activities and Releases of Nutrients and Metals to Overlying Water in Eutrophic Lake Microcosms" Water 14, no. 12: 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121839
APA StyleHao, A., Yu, H., Kobayashi, S., Xia, D., Zhao, M., & Iseri, Y. (2022). Effects of Light-Emitting Diode Illumination on Sediment Surface Biological Activities and Releases of Nutrients and Metals to Overlying Water in Eutrophic Lake Microcosms. Water, 14(12), 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121839