Controlling Eutrophication via Surface Aerators in Irregular-Shaped Urban Ponds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Field Survey
2.3. Statistical Analysis
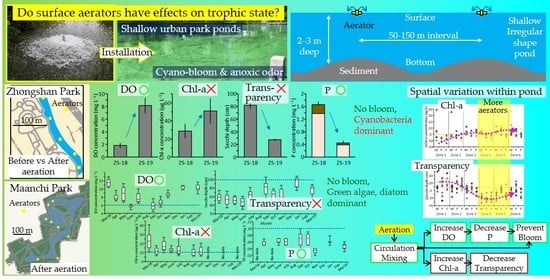
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Water Quality in ZS Pond
3.2. Temporal Changes of Water Quality in MA Pond
3.3. Spatial Variation of Water Quality in MA
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Water Quality by Aerators in ZS
4.2. Water Quality through Year in MA
4.3. Spatial Variation of Water Quality in MA
4.4. Limitations and Possibilities of Surface Aerators
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassall, C. The ecology and biodiversity of urban ponds. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2014, 1, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waajen, G.W.A.M.; Faassen, E.J.; Lürling, M. Eutrophic urban ponds suffer from cyanobacterial blooms: Dutch examples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9983–9994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertli, B.; Parris, K.M. Toward management of urban ponds for freshwater biodiversity. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Chorus, I. Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater “seafood” and its consequences for public health: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.Y.; Liang, S.; Lee, J. Toxin-producing cyanobacteria in freshwater: A review of the problems, impact on drinking water safety, and efforts for protecting public health. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousso, B.Z.; Bertone, E.; Stewart, R.; Hamilton, D.P. A systematic literature review of forecasting and predictive models for cyanobacteria blooms in freshwater lakes. Wat. Res. 2020, 182, 115959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helminen, H.; Karjalainen, J.; Kurkilahti, M.; Rask, M.; Sarvala, J. Eutrophication and fish biodiversity in Finnish lakes. SIL Proc. 1922–2010 2000, 27, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Xie, P. Impact of eutrophication on biodiversity of the macrozoobenthos community in a Chinese shallow lake. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2001, 16, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glibert, P.M. Eutrophication, harmful algae and biodiversity—Challenging paradigms in a world of complex nutrient changes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Zanden, M.J.V.; Schierup, H.H.; Christoffersen, K.; Lodge, D.M. From Greenland to green lakes: Cultural eutrophication and the loss of benthic pathways in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Z.; Cui, B. Performance of macrophyte indicators to eutrophication pressure in ponds. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 96, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masseret, E.; Amblard, C.; Bourdier, G. Changes in the structure and metabolic activities of periphytic communities in a stream receiving treated sewage from a waste stabilization pond. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2299–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Biswas, D.K.; Nian, Y.; Jiang, G. Potential of constructed wetlands in treating the eutrophic water: Evidence from Taihu Lake of China. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Huang, S.; Scholz, M.; Li, J. Nutrient removal in pilot-scale constructed wetlands treating eutrophic river water: Assessment of plants, intermittent artificial aeration and polyhedron hollow polypropylene balls. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 197, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Zacharias, I. Restoration of eutrophic freshwater by managing internal nutrient loads. A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Bai, S.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Z.; Yu, G. Dredging project caused short-term positive effects on lake ecosystem health: A five-year follow-up study at the integrated lake ecosystem level. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; van Oosterhout, F. Controlling eutrophication by combined bloom precipitation and sediment phosphorus inactivation. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6527–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waajen, G.; van Oosterhout, F.; Douglas, G.; Lürling, M. Geo-engineering experiments in two urban ponds to control eutrophication. Water Res. 2016, 97, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, R.; Wu, Y.; Lürling, M.; Cai, H.; Jiang, H.-L.; Liu, X. Bioavailable phosphorus (P) reduction is less than mobile P immobilization in lake sediment for eutrophication control by inactivating agents. Water Res. 2017, 109, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Xi, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Gu, B.; He, Z. Purifying eutrophic river waters with integrated floating island systems. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorok, R.A.; Ginn, T.C.; Lorenzen, M.W. Evaluation of Aeration/Circulation as a Lake Restoration Technique; Environmental Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Beutel, M.W.; Horne, A.J. A review of the effects of hypolimnetic oxygenation on lake and reservoir water quality. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1999, 15, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visser, P.M.; Ibelings, B.W.; Bormans, M.; Huisman, J. Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: A review. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastorok, R.A.; Grieb, T.M. Prediction of lake response to induced circulation. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1984, 1, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyd, C.E. Pond water aeration systems. Aquac. Eng. 1998, 18, 9–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Mishra, S.K.; Shrivastav, A.; Park, M.S.; Yang, J.W. Recent trends in the mass cultivation of algae in raceway ponds. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2015, 51, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Mucci, M. Mitigating eutrophication nuisance: In-lake measures are becoming inevitable in eutrophic waters in the Netherlands. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 4447–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Xenopoulos, M.A.; Buttle, J.M.; Marsalek, J.; Wagner, N.D.; Pick, F.R.; Frost, P.C. Thermal stratification patterns in urban ponds and their relationships with vertical nutrient gradients. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 127, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Pang, X.; Long, L.; Xu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Deng, S.; He, J.; et al. Dynamics of sediment phosphorus affected by mobile aeration: Pilot-scale simulation study in a hypereutrophic pond. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Moulick, S.; Mal, B.C. Selection of aerators for intensive aquacultural pond. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 56, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, T.; Inagaki, T.; Nakamura, C.; Hashimoto, R.; Negoro, N.; Hyodo, J.; Honda, S. Water circulation induced by mechanical aerators in a rectangular vessel for shrimp aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2019, 85, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, R.; Anderson, M.A. Stratification and mixing in Lake Elsinore, California: An assessment of axial flow pumps for improving water quality in a shallow eutrophic lake. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4457–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zębek, E. Response of cyanobacteria to the fountain-based water aeration system in Jeziorak Mały urban lake. Limnol. Rev. 2014, 14, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Tang, H.; Han, Y.; Li, M. Two-year moving aeration controls cyanobacterial blooms in an extremely eutrophic shallow pond: Variation in phytoplankton community and Microcystis colony size. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.L.; Tao, S.; Dawson, R.W.; Li, B.G. A GIS-based method of lake eutrophication assessment. Ecol. Model. 2001, 144, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Chen, Z.; Mao, G.; Chen, L.; Crittenden, J.; Li, R.Y.M.; Chai, L. Evaluation of eutrophication in freshwater lakes: A new non-equilibrium statistical approach. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Huang, H.; Mi, Q.; Iseri, Y. Effects of substrate and water depth of a eutrophic pond on the physiological status of a submerged plant, Vallisneria natans. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, B.; Andersen, J.M.; Fleischer, S.; Jansson, M. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment-water interface. In Phosphorus in Freshwater Ecosystems. Developments in Hydrobiologia; Persson, G., Jansson, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 48, pp. 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- Bormans, M.; Maršálek, B.; Jančula, D. Controlling internal phosphorus loading in lakes by physical methods to reduce cyanobacterial blooms: A review. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, Y.; Ura, H.; Kimura, T.; Shiono, M.; Seo, S.K. Factors controlling hypolimnetic ammonia accumulation in a lake. Limnology 2002, 3, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beutel, M.W. Inhibition of ammonia release from anoxic profundal sediments in lakes using hypolimnetic oxygenation. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Yan, N.; Xia, D.; Zhao, M.; Iseri, Y. Improvement of water quality using a circulation device equipped with oxidation carriers and light emitting diodes in eutrophic pond mesocosms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xie, P.; Li, S.; Tang, H.; Liu, H. The low TN:TP ratio, a cause or a result of Microcystis blooms? Water Res. 2003, 37, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y. The effects of temperature and nutrient ratios on Microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China: An 11-year investigation. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Zhou, B.; Song, L.; Shang, M. Use statistical machine learning to detect nutrient thresholds in Microcystis blooms and microcystin management. Harmful Algae 2020, 94, 101807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, Z.; Qiao, H.; Liu, F. Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Use of conductivity to indicate long-term changes in pollution processes in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21376–21385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Shi, X. Temperature triggers the annual cycle of Microcystis, comparable results from the laboratory and a large shallow lake. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEnroe, N.A.; Buttle, J.M.; Marsalek, J.; Pick, F.R.; Xenopoulos, M.A.; Frost, P.C. Thermal and chemical stratification of urban ponds: Are they ‘completely mixed reactors’? Urban Ecosyst. 2013, 16, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzer, D.P.; Jackson, C.R.; Mosner, M. Influences of riparian logging on plants and invertebrates in small, depressional wetlands of Georgia, USA. Hydrobiologia 2000, 441, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.O.; Likens, G.E.; Malcom, H.M. Trophic basis of invertebrate production in 2 streams at the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2001, 20, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.P.; Singh, P. Effect of CO2 concentration on algal growth: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsetchine, V.; Schernewski, G. The influence of spatial wind inhomogeneity on flow patterns in a small lake. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3348–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçyigit, M.B.; Falconer, R.A. Three-dimensional numerical modelling of wind-driven circulation in a homogeneous lake. Adv. Water Resour. 2004, 27, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, J.H.; Stretch, D.D.; Tirok, K. Wind-driven circulation patterns in a shallow estuarine lake: St Lucia, South Africa. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 146, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Mean across All Months | LME Model Results (F 2, p 3) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone | Position | Factors 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Mid. | Peri. | M | Z | P | M × Z | M × P | Z × P | |||
| T (°C) | 22.4 | 22.2 | 22.0 | 22.2 | 22.5 | 22.3 | 22.4 | 22.2 | >99 | 2.58 | 2.52 | 1.80 | 2.81 | 1.45 | ||
| EC (μS cm−1) | 463 | 454 | 450 | 450 | 448 | 449 | 452 | 453 | >99 | >99 | 5.37 | 17 | 1.42 | 0.49 | ||
| DO (mg L−1) | 7.49 | 8.28 | 8.51 | 8.07 | 9.04 | 9.00 | 8.90 | 8.15 | >99 | 6.08 | 11 | 6.35 | 7.17 | 1.23 | ||
| pH | 7.89 | 8.02 | 8.09 | 8.08 | 8.18 | 8.13 | 8.11 | 8.04 | >99 | 8.01 | 4.61 | 2.96 | 2.34 | 0.67 | ||
| Chl-a (μg L−1) | 9.6 | 12.6 | 17.2 | 14.0 | 17.9 | 19.1 | 18.2 | 13.5 | 35 | 4.83 | 11 | 5.80 | 5.57 | 0.69 | ||
| Turbidity (NTU) | 18.9 | 16.4 | 16.0 | 23.1 | 16.6 | 17.8 | 18.2 | 18.1 | 53 | 10 | 0.01 | 12 | 5.41 | 2.61 | ||
| ORP (mV) | 426 | 425 | 440 | 456 | 442 | 442 | 416 | 450 | 17 | 3.66 | 33 | 2.06 | 3.32 | 2.63 | ||
| SD (cm) | 85 | 82 | 70 | 46 | 61 | 67 | 66 | 70 | 20 | 10 | 1.48 | 1.31 | 1.76 | 0.41 | ||
| Mean across All Months | ANOVA Results (F 2, p 3) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone | Layer | Factors 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Surf. | Bott. | M | Z | L | M × Z | M × L | Z × L | |||
| TN | 1.769 | 1.749 | 1.637 | 1.544 | 1.524 | 1.611 | 1.657 | 1.621 | 28 | 1.34 | 0.25 | 1.58 | 2.11 | 2.18 | ||
| NH4+-N | 0.173 | 0.231 | 0.165 | 0.152 | 0.179 | 0.152 | 0.163 | 0.188 | 11 | 5.08 | 5.55 | 4.23 | 0.36 | 1.31 | ||
| NO2−-N | 0.025 | 0.030 | 0.028 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.027 | 0.028 | >99 | 11 | 3.03 | 5.34 | 1.80 | 1.69 | ||
| NO3−-N | 0.619 | 0.576 | 0.549 | 0.516 | 0.548 | 0.543 | 0.550 | 0.567 | >99 | 4.63 | 1.61 | 2.58 | 1.95 | 1.30 | ||
| TP | 0.068 | 0.061 | 0.057 | 0.053 | 0.050 | 0.063 | 0.059 | 0.058 | 3.50 | 2.36 | 0.08 | 1.05 | 2.20 | 0.68 | ||
| SRP | 0.055 | 0.043 | 0.037 | 0.034 | 0.038 | 0.048 | 0.043 | 0.041 | 5.58 | 4.05 | 0.43 | 0.96 | 1.77 | 0.76 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Xia, D.; Mi, Q.; Yan, N.; Su, M.; Lin, A.; Zhao, M.; Iseri, Y. Controlling Eutrophication via Surface Aerators in Irregular-Shaped Urban Ponds. Water 2021, 13, 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233360
Hao A, Kobayashi S, Xia D, Mi Q, Yan N, Su M, Lin A, Zhao M, Iseri Y. Controlling Eutrophication via Surface Aerators in Irregular-Shaped Urban Ponds. Water. 2021; 13(23):3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233360
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Aimin, Sohei Kobayashi, Dong Xia, Qi Mi, Ning Yan, Mengyao Su, Aishou Lin, Min Zhao, and Yasushi Iseri. 2021. "Controlling Eutrophication via Surface Aerators in Irregular-Shaped Urban Ponds" Water 13, no. 23: 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233360
APA StyleHao, A., Kobayashi, S., Xia, D., Mi, Q., Yan, N., Su, M., Lin, A., Zhao, M., & Iseri, Y. (2021). Controlling Eutrophication via Surface Aerators in Irregular-Shaped Urban Ponds. Water, 13(23), 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233360