Highly Functionalized Microporous Activated Biochar from Syagrus coronata Waste: Production, Characterization, and Application in Adsorption Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
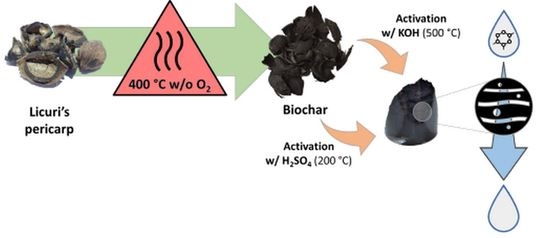
2.1. Adsorbent Preparation
Biochar Activation
2.2. Adsorbent Characterization
2.2.1. Textural Analysis
2.2.2. Boehm Titration
2.2.3. Point of Zero Charge
2.3. Analytical Method for Isoniazid Quantification
2.4. Adsorption Assays
2.4.1. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4.2. Adsorption Isotherms
2.4.3. Influence of the pH on the Adsorption Capacity
2.4.4. Fixed-Bed Column Adsorption Assay
2.5. Desorption and Regeneration Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorbent Preparation
3.2. Adsorbent Characterization
3.2.1. Textural Analysis
3.2.2. Boehm Titration and Point of Zero Charge
3.3. Batch Adsorption Studies
3.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
3.3.2. Isotherm Adsorption
3.3.3. pH Variation Studies
3.4. Fixed Bed Adsorption Studies
3.5. Desorption and Regeneration Studies
3.6. Applicability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jurado, A.; Vàzquez-Suñé, E.; Carrera, J.; de Alda, M.L.; Pujades, E.; Barceló, D. Emerging Organic Contaminants in Groundwater in Spain: A Review of Sources, Recent Occurrence and Fate in a European Context. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 440, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelewska, J.; Kotowska, U.; Karpińska, J.; Kowalczuk, D.; Arciszewska, A.; Świrydo, A. Occurrence, Removal, Mass Loading and Environmental Risk Assessment of Emerging Organic Contaminants in Leachates, Groundwaters and Wastewaters. Microchem. J. 2018, 137, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Baran, N.; Stuart, M.E.; Ward, R.S. Emerging Organic Contaminants in Groundwater: A Review of Sources, Fate and Occurrence. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdallah, M.A.-E.; Nguyen, K.-H.; Ebele, A.J.; Atia, N.N.; Ali, H.R.H.; Harrad, S. A Single Run, Rapid Polarity Switching Method for Determination of 30 Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Waste Water Using Q-Exactive Orbitrap High Resolution Accurate Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1588, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Santiago-Martín, A.; Meffe, R.; Teijón, G.; Hernández, V.M.; López-Heras, I.; Alonso, C.A.; Romasanta, M.A.; de Bustamante, I. Pharmaceuticals and Trace Metals in the Surface Water Used for Crop Irrigation: Risk to Health or Natural Attenuation? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijangos, L.; Ziarrusta, H.; Ros, O.; Kortazar, L.; Fernández, L.A.; Olivares, M.; Zuloaga, O.; Prieto, A.; Etxebarria, N. Occurrence of Emerging Pollutants in Estuaries of the Basque Country: Analysis of Sources and Distribution, and Assessment of the Environmental Risk. Water Res. 2018, 147, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, E.O.; Foureaux, A.F.S.; Rodrigues, J.S.; Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; Santos, L.V.S.; Amaral, M.C.S.; Lange, L.C. Occurrence, Removal and Seasonal Variation of Pharmaceuticals in Brasilian Drinking Water Treatment Plants. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhuka, V.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. Occurrence of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Wastewater and Receiving Waters in South Africa Using LC-OrbitrapTM MS. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrull, J.; Colom, A.; Fabregas, J.; Borrull, F.; Pocurull, E. Presence, Behaviour and Removal of Selected Organic Micropollutants through Drinking Water Treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Adsorptive Removal of Antibiotics from Water and Wastewater: Progress and Challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophia, A.C.; Lima, E.C. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from the Environment by Adsorption. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Costanzo, S.D. Removal of Antibiotics in Conventional and Advanced Wastewater Treatment: Implications for Environmental Discharge and Wastewater Recycling. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4164–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkaystha, J.; Prasher, S.; Afzal, M.T.; Nzediegwu, C.; Dhiman, J. Wheat Straw Biochar Amendment Significantly Reduces Nutrient Leaching and Increases Green Pepper Yield in a Less Fertile Soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Yek, P.N.Y.; Ge, S.; Shi, Y.; Liew, R.K.; Peng, W.; Sonne, C.; Tabatabaei, M.; Aghbashlo, M.; Lam, S.S. Production of Highly Porous Biochar via Microwave Physiochemical Activation for Dechlorination in Water Treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madriaga, V.G.C.; Mattos, J.P.R.; Rossa, V.; Ferreira, L.E.M.; Vasconcelos, S.C.; Silva, D.S.A.; Rocha, P.S.M.; dos Santos, R.D.; Silva, L.P.C.; Araujo, J.R.; et al. Metal-Contaminated Biochars as Cheap and More Sustainable Catalysts for Furfural Conversion to Value-Added Compounds. Mol. Catal. 2022, 531, 112692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, Y.X.; Tan, Y.H.; Mubarak, N.M.; Kansedo, J.; Khalid, M.; Ibrahim, M.L.; Ghasemi, M. A Review on Biochar Production from Different Biomass Wastes by Recent Carbonization Technologies and Its Sustainable Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, G.; Faccini, D.; Zava, M.; Pozzi, A.; Dossi, C.; Monticelli, D.; Spanu, D. Exploring the Adsorption of Pb on Microalgae-Derived Biochar: A Versatile Material for Environmental Remediation and Electroanalytical Applications. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Fang, Y.; Sun, P.; Xie, K.; Zhai, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, H. N-Doped Biochar as a New Metal-Free Activator of Peroxymonosulfate for Singlet Oxygen-Dominated Catalytic Degradation of Acid Orange 7. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhiya, A.K.; Anand, A.; Kaushal, P. Production, Activation, and Applications of Biochar in Recent Times. Biochar 2020, 2, 253–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, P.H.M.; Maia, A.S.; Cordeiro, A.M.T.M.; Gondim, A.D.; Santos, N.A. Catalytic Deoxygenation of the Oil and Biodiesel of Licuri (Syagrus coronata) To Obtain n-Alkanes with Chains in the Range of Biojet Fuels. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15849–15855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepaldi, I.C.; Almeida-Muradian, L.B.D.; Rios, M.D.G.; Penteado, M.D.V.C.; Salatino, A. Composição Nutricional Do Fruto de Licuri (Syagrus coronata (Martius) Beccari). Rev. Bras. Bot. 2001, 24, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- dos Santos, B.S.; Filho, C.M.B.; Junior, J.A.A.D.N.; Brust, F.R.; Bezerra-Silva, P.C.; da Rocha, S.K.L.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Navarro, D.M.D.A.F.; Correia, M.T.D.S.; Napoleão, T.H.; et al. Anti-Staphylococcal Activity of Syagrus coronata Essential Oil: Biofilm Eradication and in Vivo Action on Galleria mellonela Infection Model. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroucha, E.P.T.L.; Aroucha, M.L. Boas Práticas de Manejo para o Extrativismo Sustentável do Licuri; Instituto Sociedade, População e Natureza: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2013; p. 92. Available online: https://ispn.org.br/licuri-boas-praticas-de-manejo-para-o-extrativismo-sustentavel/ (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Sluiter, A.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Extractives in Biomass. NREL Technical Report, NREL/TP-210-42619, 2008, pp. 1–12. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/gen/fy08/42619.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Ash in Biomass. NREL Technical Report, NREL/TP-510-42622, 2008, pp. 1–8. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/gen/fy08/42622.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass. NREL Technical Report, NREL/TP-510-42618, 2012, pp. 1–18. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/gen/fy13/42618.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Al-Qodah, Z.; Shawabkah, R. Production and Characterization of Granular Activated Carbon from Activated Sludge. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, R.V.S.; Gonçalves, A.D.; Vinhal, J.O.; Cassella, R.J.; Santos, R.C.; Sasso, M.A.D.; Peixoto, B.S.; Borba-Santos, L.P.; Rozental, S.; Azevedo, D.A.; et al. Bioproducts from the Pyrolysis of Castor Seed Cake: Basic Dye Adsorption Capacity of Biochar and Antifungal Activity of the Aqueous Phase. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, A.; Do, D.D. The Preparation of Activated Carbon from Macadamia Nutshell by Chemical Activation. Carbon 1997, 35, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkhoda, A.M.; Gyenge, E.; Ellis, N. A Novel Method to Tailor the Porous Structure of KOH-Activated Biochar and Its Application in Capacitive Deionization and Energy Storage. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 87, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The Determination of Pore Volume and Area Distributions in Porous Substances. I. Computations from Nitrogen Isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippens, B. Studies on Pore Systems in Catalysts V. The t Method. J. Catal. 1965, 4, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, H.P. Surface Oxides on Carbon and Their Analysis: A Critical Assessment. Carbon 2002, 40, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönherr, J.; Buchheim, J.; Scholz, P.; Adelhelm, P. Boehm Titration Revisited (Part I): Practical Aspects for Achieving a High Precision in Quantifying Oxygen-Containing Surface Groups on Carbon Materials. C 2018, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prahas, D.; Kartika, Y.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Activated Carbon from Jackfruit Peel Waste by H3PO4 Chemical Activation: Pore Structure and Surface Chemistry Characterization. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 140, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S.K. About the Theory of So-Called Adsorption of Soluble Substances. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handingarl 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of Heavy Metals from Waters by Means of Natural Zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H. Über Die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, R. On the Structure of a Catalyst Surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.C. Heterogeneous Ion Exchange in a Flowing System. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 1664–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.H.; Nelson, J.H. Application of Gas Adsorption Kinetics I. A Theoretical Model for Respirator Cartridge Service Life. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1984, 45, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Viraraghavan, T.; Chen, M. A New Model for Heavy Metal Removal in a Biosorption Column. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2001, 19, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.M.; de Oliveira, P.C.O.; Pina, V.G.S.S.; Peixoto, B.S.; Massante, F.F.; Veloso, M.C.C.; Romeiro, G.A.; de Moraes, M.C.; Ponzio, E.A. Pyrolysis of Syagrus coronata: Transforming Agroindustrial Waste into a New Environmentally Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitor. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, C.; Andrade, J.; Oliveira, P.C.O.; Veloso, M.C.C.; Romeiro, G.A.; das Chagas, E.F. Fumigant Activity of Pyrolysis Fractions Derived from Waste Licuri’s Pericarp (Syagrus coronata—Arecaceae) in the Control the Red Flour Beetle Tribolium Castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R.; Parikh, S.J.; Du, J.; Qi, F.; Willett, I.R. Influences of Feedstock Sources and Pyrolysis Temperature on the Properties of Biochar and Functionality as Adsorbents: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Giorcelli, M.; Jagdale, P.; Rovere, M.; Tagliaferro, A. A Review of Non-Soil Biochar Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cha, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Jung, S.-C.; Ryu, C.; Jeon, J.-K.; Shin, M.-C.; Park, Y.-K. Production and Utilization of Biochar: A Review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Gupta, B.; Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Nimbhorkar, S.K. A Comprehensive Review on the Synthesis, Performance, Modifications, and Regeneration of Activated Carbon for the Adsorptive Removal of Various Water Pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Lua, A.C. Characteristics of Activated Carbons Prepared from Pistachio-Nut Shells by Potassium Hydroxide Activation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 63, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, W.S.; Chen, Y.L.; Lua, A.C. Adsorption of NH3 onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Palm Shells Impregnated with H2SO4. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 281, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Sang, Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Zhan, P.; Huang, J.; Chen, J. Selectable Microporous Carbons Derived from Poplar Wood by Three Preparation Routes for CO2 Capture. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17450–17462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrellas, S.Á.; Lovera, R.G.; Escalona, N.; Sepúlveda, C.; Sotelo, J.L.; García, J. Chemical-Activated Carbons from Peach Stones for the Adsorption of Emerging Contaminants in Aqueous Solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revellame, E.D.; Fortela, D.L.; Sharp, W.; Hernandez, R.; Zappi, M.E. Adsorption Kinetic Modeling Using Pseudo-First Order and Pseudo-Second Order Rate Laws: A Review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Kinetic Models: Physical Meanings, Applications, and Solving Methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedia, J.; Peñas-Garzón, M.; Gómez-Avilés, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Belver, C. A Review on the Synthesis and Characterization of Biomass-Derived Carbons for Adsorption of Emerging Contaminants from Water. C—J. Carbon Res. 2018, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fungaro, D.A.; Bruno, M. Remoção de azul de metileno de solução aquosa usando zeólitas sintetizadas com amostras de cinzas de carvão diferentes. Quím. Nova 2009, 32, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Cooperative Adsorption on Solid Surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portinho, R.; Zanella, O.; Féris, L.A. Grape Stalk Application for Caffeine Removal through Adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsawy, T.; Rashad, E.; El-Qelish, M.; Mohammed, R.H. A Comprehensive Review on the Chemical Regeneration of Biochar Adsorbent for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. NPJ Clean Water 2022, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, J.N. The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation Revisited. Biochem. Educ. 1983, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorand, L.; Campbell, L.K.; Robertson, B.J. Enzymic Coupling of Isoniazid to Proteins. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, V.; Erto, A.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Piraján, J. Effect of Solution pH on the Adsorption of Paracetamol on Chemically Modified Activated Carbons. Molecules 2017, 22, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo, J.L.; Ovejero, G.; Rodríguez, A.; Álvarez, S.; García, J. Removal of Atenolol and Isoproturon in Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption in a Fixed-Bed Column. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 5045–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavola, A.; D’Amato, E.; Baciocchi, R. Ion Exchange Treatment of Groundwater Contaminated by Arsenic in the Presence of Sulphate. Breakthrough Experiments and Modeling. Water Air Soil Pollut 2012, 223, 2373–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Akar, S.T.; Akar, T. From Green Biowaste to Water Treatment Applications: Utilization of Modified New Biochar for the Efficient Removal of Ciprofloxacin. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 24, 100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyà, J.J. Pyrolysis for Biochar Purposes: A Review to Establish Current Knowledge Gaps and Research Needs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7939–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salihi, E.Ç.; Aydın, E. Adsorptive Characteristics of Isoniazid on Powdered Activated Carbon: π–π Dispersion Interactions at the Solid–Solution Interface. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihi, E.Ç.; Gündüz, Z.; Baştuğ, A.S. Fast Retention of Isoniazid on Organobentonite Prepared Using Green Chemistry Approach: Contribution of the π Interactions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2695–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zheng, C.; Hou, H. Preparation of Granular Activated Carbon and Its Mechanism in the Removal of Isoniazid, Sulfamethoxazole, Thiamphenicol, and Doxycycline from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, C.; Tandlich, R.; Wilhelmi, B. Adsorptive Removal of Ciprofloxacin and Isoniazid from Aqueous Solution. Nova Biotechnol. Chim. 2018, 17, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihi, E.Ç.; Wang, J.; Kabacaoğlu, G.; Kırkulak, S.; Šiller, L. Graphene Oxide as a New Generation Adsorbent for the Removal of Antibiotics from Waters. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Franco, M.A.E.; de Carvalho, C.B.; Bonetto, M.M.; Soares, R.; Féris, L.A. Diclofenac Removal from Water by Adsorption Using Activated Carbon in Batch Mode and Fixed-Bed Column: Isotherms, Thermodynamic Study and Breakthrough Curves Modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Acronym | Material Description |
|---|---|
| BC | Biochar prepared from the S. coronata fruit husks |
| AAC | Biochar BC treated with H2SO4 at 200 °C |
| BAC | Activated biochar from BC treated with KOH at 500 °C |
| CAC | Commercial activated carbon |
| Materials | Biomass Components (Dry Basis) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extractives | Lignin | Holocellulose | Insoluble Ash | |
| S. coronata waste | 3.3% ± 1.3% | 35.9% ± 0.9% | 60.2% ± 2.7% | 0.6% ± 0.5% |
| Textural Analysis | Adsorbent | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | AAC | BAC | CAC | |
| SBET [m2·g−1] | 13 | 6 | 1006 | 745 |
| P.V. [cm3·g−1] | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.436 | 0.673 |
| P.D. [Å] | 464 | 704 | 27 | 59 |
| µP Area | 79% | 17% | 79% | 51% |
| µP Volume | 50% | 24% | 72% | 23% |
| BAC | CAC | AAC | BC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first order | ||||
| R2adj | 0.9304 | 0.9960 | 0.9954 | 0.9854 |
| qe [mg·g−1] | 80.55 | 58.74 | 8.55 | 2.47 |
| k1 [min−1] | 0.18 | 0.28 | 0.089 | 1.30 |
| Δqe | 3.41% | 0.18% | 2.38% | 33.20% |
| Pseudo-second order | ||||
| R2adj | 0.9178 | 0.9957 | 0.9965 | 0.9772 |
| qe [mg·g−1] | 96.31 | 62.68 | 9.26 | 2.57 |
| k2 [g·mg−1·min−1] | 0.0016 | 0.0044 | 0.017 | 0.70 |
| Δqe | 15.48% | 6.51% | 5.56% | 30.54% |
| BAC | CAC | AAC | BC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | ||||
| R2adj | 0.9858 | 0.9982 | 0.9981 | 0.8972 |
| Qmax [mg·g−1] | 712.42 | 136.02 | 94.36 | 1,337,202 |
| Kl [L·mg−1] | 0.00057 | 0.1 | 0.0053 | 9.6 × 10−8 |
| Freundlich | ||||
| R2adj | 0.9995 | 0.9859 | 0.9973 | 0.9984 |
| Kf [mg·g−1·(mg·L−1]−1/n] | 15.65 | 33.89 | 3.23 | 0.017 |
| n | 1.73 | 3.91 | 1.97 | 0.75 |
| Sips | ||||
| R2adj | 0.9995 | 0.9986 | 0.9979 | 0.9978 |
| Qmax [mg·g−1] | 728.05 | 151.39 | 125.29 | 15,350.18 |
| Ks [(L·mg−1)ms] | 7.6 × 10−5 | 7.2 × 10−2 | 2.8 × 10−3 | 3.4 × 10−5 |
| ms | 0.61 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 1.33 |
| Model | BAC | CAC | AAC | BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thomas | ||||
| R2adj | 0.9592 | 0.9475 | 0.949 | 0.9474 |
| Kt [mL·min−1·mg−1] | 0.0049 | 0.0049 | 0.03 | 0.25 |
| qt [mg·g−1] | 107.36 | 57.02 | 14.54 | 2.67 |
| ΔQmax | −2.20% | −6.30% | −10.80% | −38.70% |
| Yan | ||||
| R2adj | 0.9935 | 0.9856 | 0.9967 | 0.9979 |
| qY [mg·g−1] | 98.82 | 51.77 | 12.67 | 1.87 |
| aY | 2.53 | 2.69 | 2.05 | 1.42 |
| ΔQmax | 5.90% | 3.50% | 3.50% | 2.80% |
| Yoon & Nelson | ||||
| R2 adj | 0.9592 | 0.9557 | 0.949 | 0.9474 |
| Z [min] | 10.74 | 5.7 | 1.45 | 0.27 |
| KYN [min−1] | 0.25 | 0.49 | 1.48 | 12.54 |
| Condition | Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Methanol | 38.8% (isoniazid desorption) |
| Ethanol | 18.3% (isoniazid desorption) |
| Basic water (pH 10) | 17.6% (isoniazid desorption) |
| 300 °C | 67% (recovery of adsorption capacity) |
| 400 °C | 0% (material decomposition) |
| Product | Mass |
|---|---|
| Licuri fruit husk | 10 kg |
| Condensable gases | 4 kg |
| Non-condensable gases | 2.4 kg |
| Biochar (BC) | 3.6 kg |
| Biochar + KOH | 14.4 kg |
| Activated carbon (BAC) | 2.3 kg |
| Material | Qmax [mg·g−1] | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| BAC | 712.42 | This study |
| Powdered activated carbon | 169.49–178.57 | [69] |
| Bentonite | 21.10 | [70] |
| Organobentonite | 33.90 | |
| Granular activated carbon from the cornstalk | 27.0172 | [71] |
| Kaolinite | 0.824 | [72] |
| Perlite | 0.130 | |
| Talc | 2.481 | |
| Vermiculite | 0.099 | |
| Coal fly ash | 7.092 | |
| Graphene oxide | 13.89 | [73] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peixoto, B.S.; Mota, L.S.d.O.; Oliveira, P.C.O.d.; Veloso, M.C.d.C.; Romeiro, G.A.; Moraes, M.C.d. Highly Functionalized Microporous Activated Biochar from Syagrus coronata Waste: Production, Characterization, and Application in Adsorption Studies. Water 2022, 14, 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213525
Peixoto BS, Mota LSdO, Oliveira PCOd, Veloso MCdC, Romeiro GA, Moraes MCd. Highly Functionalized Microporous Activated Biochar from Syagrus coronata Waste: Production, Characterization, and Application in Adsorption Studies. Water. 2022; 14(21):3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213525
Chicago/Turabian StylePeixoto, Bruno Salarini, Larissa Silva de Oliveira Mota, Pamella Christina Ortega de Oliveira, Márcia Cristina da Cunha Veloso, Gilberto Alves Romeiro, and Marcela Cristina de Moraes. 2022. "Highly Functionalized Microporous Activated Biochar from Syagrus coronata Waste: Production, Characterization, and Application in Adsorption Studies" Water 14, no. 21: 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213525
APA StylePeixoto, B. S., Mota, L. S. d. O., Oliveira, P. C. O. d., Veloso, M. C. d. C., Romeiro, G. A., & Moraes, M. C. d. (2022). Highly Functionalized Microporous Activated Biochar from Syagrus coronata Waste: Production, Characterization, and Application in Adsorption Studies. Water, 14(21), 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213525