Zooplankton as Mercury Repository in Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy): Biomass Composition and Stable Isotope Analysis
Abstract
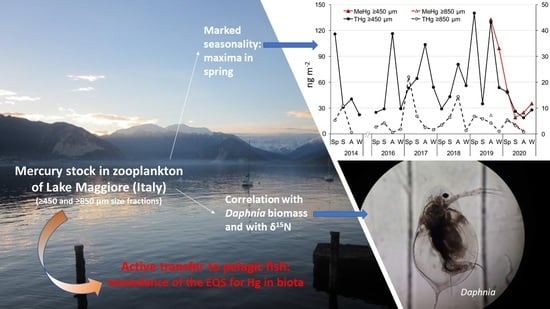
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Brief History of Its Mercury Pollution
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Mercury Analysis
2.4. Stable Isotope Analysis (SIA)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lavoie, R.A.; Jardine, T.D.; Chumchal, M.M.; Kidd, K.A.; Campbell, L.M. Biomagnification of Mercury in Aquatic Food Webs: A Worldwide Meta-Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13385–13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Mercury in Europe’s Environment: A Priority for European and Global Action. Report, No. 11/2018; European Environment Agency: Luxembourg, 2018; ISBN 978-92-9213-984-1. [Google Scholar]
- Marziali, L.; Valsecchi, L.; Schiavon, A.; Mastroianni, D.; Viganò, L. Vertical Profiles of Trace Elements in a Sediment Core from the Lambro River (Northern Italy): Historical Trends and Pollutant Transport to the Adriatic Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustin, M.S.; Bank, M.S.; Bishop, K.; Bowman, K.; Branfireun, B.; Chételat, J.; Eckley, C.S.; Hammerschmidt, C.R.; Lamborg, C.; Lyman, S.; et al. Mercury Biogeochemical Cycling: A Synthesis of Recent Scientific Advances. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Stemberger, R.S.; Klaue, B.; Blum, J.D.; Pickhardt, P.C.; Folt, C.L. Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Food Web Components across a Gradient of Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.; Leermakers, M.; Kurunczi, S.; Bozo, L.; Baeyens, W. Mercury Distribution and Speciation in Lake Balaton, Hungary. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 340, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chételat, J.; Amyot, M.; Garcia, E. Habitat-Specific Bioaccumulation of Methylmercury in Invertebrates of Small Mid-Latitude Lakes in North America. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.K.; Chen, C.; Kamman, N.; Shanley, J.; Chalmers, A.; Jackson, B.; Taylor, V.; Smeltzer, E.; Stangel, P.; Shambaugh, A. Mercury in the Pelagic Food Web of Lake Champlain. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorova, S.; Driscoll, C.T.; Matthews, D.A.; Effler, S.W. Zooplankton Community Changes Confound the Biodilution Theory of Methylmercury Accumulation in a Recovering Mercury-Contaminated Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4066–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, R.; Chen, C.Y.; Folt, C.L. Comparing Nearshore Benthic and Pelagic Prey as Mercury Sources to Lake Fish: The Importance of Prey Quality and Mercury Content. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, S.-X.; Hamilton, P.B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, W.; Chen, C.; Tao, R. Differential Bioaccumulation of Mercury by Zooplankton Taxa in a Mercury-Contaminated Reservoir Guizhou China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chételat, J.; Amyot, M.; Cloutier, L.; Poulain, A. Metamorphosis in Chironomids, More than Mercury Supply, Controls Methylmercury Transfer to Fish in High Arctic Lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9110–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Kainz, M.; Åkerblom, S.; Bravo, A.G.; Sonesten, L.; Branfireun, B.; Deininger, A.; Bergström, A.-K.; Bishop, K. Terrestrial Diet Influences Mercury Bioaccumulation in Zooplankton and Macroinvertebrates in Lakes with Differing Dissolved Organic Carbon Concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lepom, P.; Irmer, U.; Wellmitz, J. Mercury Levels and Trends (1993–2009) in Bream (Abramis brama L.) and Zebra Mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) from German Surface Waters. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguetseng, R.; Fliedner, A.; Knopf, B.; Lebreton, B.; Quack, M.; Rüdel, H. Retrospective Monitoring of Mercury in Fish from Selected European Freshwater and Estuary Sites. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, S.M.; Tanton, T.W.; Abdrashitova, S.A. Mercury in the Aquatic Environment: A Review of Factors Affecting Methylation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 31, 241–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.G.; Cosio, C. Biotic Formation of Methylmercury: A Bio–Physico–Chemical Conundrum. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 1010–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggett, D.B.; Steevens, J.A.; Allgood, J.C.; Lutken, C.B.; Grace, C.A.; Benson, W.H. Mercury in Sediment and Fish from North Mississippi Lakes. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziali, L.; Roscioli, C.; Valsecchi, L. Mercury Bioaccumulation in Benthic Invertebrates: From Riverine Sediments to Higher Trophic Levels. Toxics 2021, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallorini, A.; Loizeau, J.-L. Mercury Methylation in Oxic Aquatic Macro-Environments: A Review. J. Limnol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.R.; Saiki, M.K.; Kuwabara, J.S.; Alpers, C.N.; Marvin-DiPasquale, M.; Krabbenhoft, D.P. Influence of Plankton Mercury Dynamics and Trophic Pathways on Mercury Concentrations of Top Predator Fish of a Mining-Impacted Reservoir. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 2351–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, D.M.; Mayes, B.; Sturup, S.; Folt, C.L.; Chen, C.Y. Assessing Element-Specific Patterns of Bioaccumulation across New England Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poma, G.; Volta, P.; Roscioli, C.; Bettinetti, R.; Guzzella, L. Concentrations and Trophic Interactions of Novel Brominated Flame Retardants, HBCD, and PBDEs in Zooplankton and Fish from Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, R.C.; Gorski, P.R.; Cleckner, L.B.; Hurley, J.P. Mercury Content and Speciation in the Plankton and Benthos of Lake Superior. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 304, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, R.C.; Watras, C.J. Mercury in Zooplankton of Northern Wisconsin Lakes: Taxonomic and Site-Specific Trends. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 80, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kamman, N.; Williams, J.; Bugge, D.; Taylor, V.; Jackson, B.; Miller, E. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Mercury Bioaccumulation by Zooplankton in Lake Champlain (North America). Environ. Pollut. 2012, 161, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leoni, B. Zooplankton Predators and Prey: Body Size and Stable Isotope to Investigate the Pelagic Food Web in a Deep Lake (Lake Iseo, Northern Italy). J. Limnol. 2016, 76, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piscia, R.; Mazzoni, M.; Bettinetti, R.; Caroni, R.; Cicala, D.; Manca, M.M. Stable Isotope Analysis and Persistent Organic Pollutants in Crustacean Zooplankton: The Role of Size and Seasonality. Water 2019, 11, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bettinetti, R.; Quadroni, S.; Manca, M.; Piscia, R.; Volta, P.; Guzzella, L.; Roscioli, C.; Galassi, S. Seasonal Fluctuations of DDTs and PCBs in Zooplankton and Fish of Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy). Chemosphere 2012, 88, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickhardt, P.C.; Folt, C.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Klaue, B.; Blum, J.D. Algal Blooms Reduce the Uptake of Toxic Methylmercury in Freshwater Food Webs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4419–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watras, C.J.; Back, R.C.; Halvorsen, S.; Hudson, R.J.M.; Morrison, K.A.; Wente, S.P. Bioaccumulation of Mercury in Pelagic Freshwater Food Webs. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 219, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, M.; Boggio, E.; Manca, M.; Piscia, R.; Quadroni, S.; Bellasi, A.; Bettinetti, R. Trophic Transfer of Persistent Organic Pollutants through a Pelagic Food Web: The Case of Lake Como (Northern Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, M.; Mazumder, A. Effect of Algal and Bacterial Diet on Methyl Mercury Concentrations in Zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volta, P.; Jeppesen, E.; Sala, P.; Galafassi, S.; Foglini, C.; Puzzi, C.; Winfield, I.J. Fish Assemblages in Deep Italian Subalpine Lakes: History and Present Status with an Emphasis on Non-Native Species. Hydrobiologia 2018, 824, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzella, L.M.; Novati, S.; Casatta, N.; Roscioli, C.; Valsecchi, L.; Binelli, A.; Parolini, M.; Solcà, N.; Bettinetti, R.; Manca, M.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Target Organic and Inorganic Micropollutants in Lake Maggiore and Lake Lugano (Italian-Swiss Water Bodies): Contamination in Sediments and Biota. Hydrobiologia 2018, 824, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poste, A.E.; Hoel, C.S.; Andersen, T.; Arts, M.T.; Færøvig, P.-J.; Borgå, K. Terrestrial Organic Matter Increases Zooplankton Methylmercury Accumulation in a Brown-Water Boreal Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanden, M.J.V.; Rasmussen, J.B. Primary Consumer δ13C and δ15N and the Trophic Position of Aquatic Consumers. Ecology 1999, 80, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilizzoni, P.; Levine, S.N.; Manca, M.; Marchetto, A.; Lami, A.; Ambrosetti, W.; Brauer, A.; Gerli, S.; Carrara, E.A.; Rolla, A.; et al. Ecological Effects of Multiple Stressors on a Deep Lake (Lago Maggiore, Italy) Integrating Neo and Palaeolimnological Approaches. J. Limnol. 2012, 71, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmaso, N.; Mosello, R. Limnological Research in the Deep Southern Subalpine Lakes: Synthesis, Directions and Perspectives. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2010, 1, 29–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetto, A.; Lami, A.; Musazzi, S.; Massaferro, J.; Langone, L.; Guilizzoni, P. Lake Maggiore (N. Italy) Trophic History: Fossil Diatom, Plant Pigments, and Chironomids, and Comparison with Long-Term Limnological Data. Quat. Int. 2004, 113, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziali, L.; Guzzella, L.; Salerno, F.; Marchetto, A.; Valsecchi, L.; Tasselli, S.; Roscioli, C.; Schiavon, A. Twenty-Year Sediment Contamination Trends in Some Tributaries of Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy): Relation with Anthropogenic Factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38193–38208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipino, G. Le Miniere d’oro Dell’Ossola Superiore. 2015. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/19622039/Le_miniere_doro_dellOssola_Superiore (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Manca, M.; Cavicchioni, N.; Morabito, G. First Observations on the Effect of a Complete, Exceptional Overturn of Lake Maggiore on Plankton and Primary Productivity. Internat. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2000, 85, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benndorf, J. A Manual on Methods for the Assessment of Secondary Productivity in Fresh Waters. Int. Revue Ges. Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1986, 71, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US-EPA. Method 7473—Mercury in Solids and Solutions by Thermal Decomposition, Amalgamation, and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Valsecchi, L.; Roscioli, C.; Schiavon, A.; Marziali, L. Methylmercury Determination in Freshwater Biota and Sediments: Static Headspace GC-MS Compared to Direct Mercury Analyzer. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascariello, S.; Mazzoni, M.; Bettinetti, R.; Manca, M.; Patelli, M.; Piscia, R.; Valsecchi, S.; Polesello, S. Organic Contaminants in Zooplankton of Italian Subalpine Lakes: Patterns of Distribution and Seasonal Variations. Water 2019, 11, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.Y.; Folt, C.L. High Plankton Densities Reduce Mercury Biomagnification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisanello, F.; Marziali, L.; Rosignoli, F.; Poma, G.; Roscioli, C.; Pozzoni, F.; Guzzella, L. In Situ Bioavailability of DDT and Hg in Sediments of the Toce River (Lake Maggiore Basin, Northern Italy): Accumulation in Benthic Invertebrates and Passive Samplers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10542–10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziali, L.; Valsecchi, L. Mercury Bioavailability in Fluvial Sediments Estimated Using Chironomus riparius and Diffusive Gradients in Thin-Films (DGT). Environments 2021, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, M.G. Size-Selective Predation on Daphnia by Rainbow Trout and Yellow Perch. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1967, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.; Vijverberg, J.; Polishchuk, L.V.; Voronov, D.A. Daphnia Body Size and Population Dynamics under Predation by Invertebrate and Fish Predators in Lago Maggiore: An Approach Based on Contribution Analysis. J. Limnol. 2008, 67, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polishchuk, L.V.; Vijverberg, J.; Voronov, D.A.; Mooij, W.M. How to Measure Top-down vs Bottom-up Effects: A New Population Metric and Its Calibration on Daphnia. Oikos 2013, 122, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpowicz, M.; Sługocki, Ł.; Kozłowska, J.; Ochocka, A.; López, C. Body Size of Daphnia cucullata as an Indicator of the Ecological Status of Temperate Lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. A Maturation Size Threshold and Phenotypic Plasticity of Age and Size at Maturity in Daphnia magna. Oikos 1994, 69, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroni, R.; Free, G.; Visconti, A.; Manca, M. Phytoplankton Functional Traits and Seston Stable Isotopes Signature: A Functional-Based Approach in a Deep, Subalpine Lake, Lake Maggiore (N. Italy). J. Limnol. 2012, 71, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visconti, A.; Manca, M. Seasonal Changes in the Δ13C and Δ15N Signatures of the Lago Maggiore Pelagic Food Web. J. Limnol. 2011, 70, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visconti, A.; Volta, P.; Fadda, A.; Di Guardo, A.; Manca, M. Seasonality, Littoral versus Pelagic Carbon Sources, and Stepwise 15N-Enrichment of Pelagic Food Web in a Deep Subalpine Lake: The Role of Planktivorous Fish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 71, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marziali, L.; Piscia, R.; Valsecchi, L.; Roscioli, C.; Manca, M. Zooplankton as Mercury Repository in Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy): Biomass Composition and Stable Isotope Analysis. Water 2022, 14, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050680
Marziali L, Piscia R, Valsecchi L, Roscioli C, Manca M. Zooplankton as Mercury Repository in Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy): Biomass Composition and Stable Isotope Analysis. Water. 2022; 14(5):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050680
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarziali, Laura, Roberta Piscia, Lucia Valsecchi, Claudio Roscioli, and Marina Manca. 2022. "Zooplankton as Mercury Repository in Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy): Biomass Composition and Stable Isotope Analysis" Water 14, no. 5: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050680
APA StyleMarziali, L., Piscia, R., Valsecchi, L., Roscioli, C., & Manca, M. (2022). Zooplankton as Mercury Repository in Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy): Biomass Composition and Stable Isotope Analysis. Water, 14(5), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050680