Risk of Expanded Polystyrene Ingestion by Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Fish Maintenance
2.3. Experimental Design
3. Results
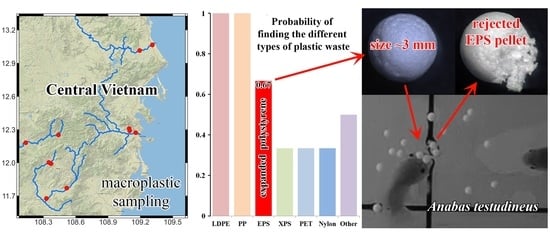
3.1. Qualitative Evaluation of Plastic Contaminations in Water Bodies of Central Vietnam
3.2. Climbing Perch Reaction to the Feed and Polystyrene Pellets
4. Discussion
4.1. The Presence of Macroplastics in Water Bodies of Central Vietnam
4.2. The Risks of the EPS Ingestion by Fish
4.3. Estimation of EPS Grasping by Climbing Perch
4.4. Estimation of EPS Ingestion by Climbing Perch
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akdogan, Z.; Guven, B. Microplastics in the Environment: A Critical Review of Current Understanding and Identification of Future Research Needs. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, T.H.; Vu, H.N. The Crisis of Plastic Waste in Vietnam is Real. Eur. J. Eng. Tech. Res. 2019, 4, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danh, N.T.; Hoi, H.T. Effects of plastic waste to sea environment in Vietnam. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 351, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahens, L.; Strady, E.; Kieu-Le, T.-C.; Dris, R.; Boukerma, K.; Rinnert, E.; Gaspery, G.; Tassin, B. Macroplastic and microplastic contamination assessment of a tropical river (Saigon River Vietnam) transversed by a developing megacity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veerasingam, S.; Mugilarasan, M.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Vethamony, P. Influence of 2015 flood on the distribution and occurrence of microplastic pellets along the Chennai coast India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogdu, S.; Cevik, C.; Ayat, B.; Aydogan, B.; Karaca, S. How microplastics quantities increase with flood events? An example from Mersin Bay NE Levantine coast of Turkey. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laist, D.W. Overview of the biological effects of lost and discarded plastic debris in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1987, 18, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possatto, F.E.; Barletta, M.; Costa, M.F.; Ivar do Sul, J.A.; Dantas, D.V. Plastic debris ingestion by marine catfish: An unexpected fisheries impact. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, H.S.; Nerheim, M.S.; Carroll, K.A.; Eriksen, M. The plastic-associated microorganisms of the North Pacific Gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 75, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, C.D.; Löder, M.G.J.; Fricke, N.F.; Lang, T.; Griebeler, E.-M.; Janke, M.; Gerdts, G. Plastic ingestion by pelagic and demersal fish from the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendel, A.L.; Bessa, F.; Alves, V.E.N.; Amorim, A.L.A.; Patrício, J.; Palma, A.R.T. Widespread microplastic ingestion by fish assemblages in tropical estuaries subjected to anthropogenic pressures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critchell, K.; Hoogenboom, M.O. Effects of microplastic exposure on the body condition and behaviour of planktivorous reef fish (Acanthochromis polyacanthus). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koraltan, I.; Mavruk, S.; Güven, O. Effect of Biological and Environmental Factors on Microplastic Ingestion of Commercial Fish Species. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, B. Ingestion of microplastics by fish and its potential consequences from a physical perspective. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag 2017, 13, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A. Foamed polystyrene in the marine environment: Sources additives transport behavior and impacts. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2020, 54, 10411–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.; Baker, J.; Bamford, H. Proceedings of the International Research Workshop on the Occurrence Effects and Fate of Microplastic Marine Debris; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-30; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2009. Available online: https://marinedebris.noaa.gov/file/2192/download?token=5dvqb-YY (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, P.; Li, M. Adverse physiological and molecular level effects of polystyrene microplastics on freshwater microalgae. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannilli, V.; Di Gennaro, A.; Lecce, F.; Sighicelli, M.; Falconieri, M.; Pietrelli, L.; Poeta, G.; Battisti, C. Microplastics in Talitrus saltator (Crustacea Amphipoda): New evidence of ingestion from natural contexts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28725–28729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazour, M.; Amara, R. Is blue mussel caging an efficient method for monitoring environmental microplastics pollution? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Toxic Effects in Liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, K.; Ekvall, M.T.; Hansson, L.-A.; Linse, S.; Malmendal, A.; Cedervall, T. Altered behavior physiology and metabolism in fish exposed to polystyrene nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaloyianni, M.; Bobori, D.C.; Xanthopoulou, D.; Malioufa, G.; Sampsonidis, I.; Kalogiannis, S.; Feidantsis, K.; Kastrinaki, G.; Dimitriadi, A.; Koumoundouros, G.; et al. Toxicity and functional tissue responses of two freshwater fish after exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Toxics 2021, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery-Gomm, S.; O’Hara, P.D.; Kleine, L.; Bowes, V.; Wilson, L.K.; Barry, K.L. Northern fulmars as biological monitors of trends of plastic pollution in the eastern North Pacific. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1776–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, H.; Lattin, G.L.; Moore, C.J. Incidence mass and variety of plastics ingested by Laysan (Phoebastria immutabilis) and Blackfooted Albatrosses (P. nigripes) recovered as by-catch in the North Pacific Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2190–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Ashe, E.; O’Hara, P.D. Marine mammals and debris in coastal waters of British Columbia Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingh, K.P.; Samuel, P. Food feeding habits and gut contents of Anabas testudineus (Bloch). Matsya 1981, 7, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, E.D.; Ganzha, E.V.; Pavlov, D.S. Climbing perch Anabas testudineus feeding in the darkness: Observation in infrared light. Inland Water Biol. 2021, 14, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, I.L.; Ibrahim, N.; Hamidin, N.; Lutifi, A.L.O.; Ghani, N.A.A. Acute toxicity of endosulfan to Anabas testudineus. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2015, 9, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Kershaw, P.; Turra, A.; Galgani, F. Guidelines for the monitoring and assessment of plastic litter in the ocean. GESAMP Rep. Stud. 2019, 99, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Liem, K.F. Functional design of the air ventilation apparatus and overland escursions by teleosts. Fieldiana Zool. 1987, 37, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kasumyan, A.O.; Pashchenko, N.I.; Oanh, L.T. Morphology of the olfactory organ in the climbing perch (Anabas testudineus Anabantidae Perciformes). Biol. Bull. 2021, 48, 1298–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoca, M.S.; Tyson, C.W.; McGill, M.; Slager, C.J. Odours from marine plastic debris induce food search behaviours in a forage fish. Proc. R. Soc. B 2017, 284, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farrelly, T.A.; Shaw, I.C. Polystyrene as Hazardous Household Waste. In Household Hazardous Waste Management; Mereki, D.M., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, R. Plastic debris in the marine environment: Consequences and solutions. In Marine Nature Conservation in Europe; Krause, J., Von Nordheim, H., Brager, S., Eds.; Bundesamt fur Naturschutz Stralsund: Bonn, Germany, 2006; pp. 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.O.; Bezerra, A.V.A.; Neubauer, T.M.; Ribeiro, L.F.B.; Hotza, D.; Machado, R. Nanocomposites production of polystyrene/silver obtained by embedding silver nanoparticles in situ with styrene polymerization. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratte, H.T. Bioaccumulation and toxicity of silver compounds: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.; Yadav, P.G.; Kumar, S.; Ali, H.; Alarifi, S.; Harrath, A.H. Sensitivity of freshwater pulmonate snail Lymnaea luteola L., to silver nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2014, 104, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramenko, N.; Demidova, T.B.; Krutyakov, Y.A.; Zherebin, P.M.; Krysanov, E.Y.; Kustov, L.M.; Peijnenburg, W. The effect of capping agents on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Danio rerio embryos. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, E.; Nilsson, N.H.; Lithner, D.; Lassen, C. Hazardous Substances in Plastics. Survey of Chemical Substances in Consumer Products No. 132, 2014; Danish Environmental Protection Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014; Available online: https://www2.mst.dk/Udgiv/publications/2014/12/978-87-93283-31-2.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- Kasumyan, A.O.; Døving, K.B. Taste preferences in fishes. Fish Fish. 2003, 4, 289–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasumyan, A.O. The intraoral tactile reception and its interaction with the gustatory system in fish. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2012, 447, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasumyan, A.O.; Sidorov, S.S. Taste properties of free amino acids for Caspian brown trout Salmo trutta caspius. J. Ichthyol. 1994, 34, 831–838. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kasumyan, A.O.; Isaeva, O.M.; Oanh, L.T.K. Taste attractivity of tropical echinoderms for barramundi Lates calcarifer. Aquaculture 2022, 553, 738051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, E.S.; Chess, J.R. Trophic relationships among fishes and plankton in the lagoon at Enewetak Atoll Marshall Islands. Fish Bull. 1977, 76, 133–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, D.; Hu, C.; Jiang, S. Food ingestion consumption and selectivity of pompano Trachinotus ovatus (Linnaeus 1758) under different rotifer densities. Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, M.O.; Armstrong, J.D.; Groothuis, T.G.G.; Metcalfe, N.B. The growth benefits of aggressive behavior vary with individual metabolism and resource predictability. Behav. Ecol. 2013, 24, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, K.P.; Lim, P.E.; Yusoff, S.; Sun, C.; Ding, J.; Loh, K.H. A meta-analysis of the characterisations of plastic ingested by fish globally. Toxics 2022, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Studied Areas | Waterbodies | Province | Sampling Coordinates | Type of Macroplastics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cai River (lower reaches) | Khanh Hoa | 12°16′22″ N 109°09′25″ E | LDPE, PP, EPS, XPS |
| 2. | Am Chua Reservoir | 12°18′35″ N 109°05′46″ E | LDPE, EPS, PET, Other | |
| Am Chua Irrigation channel | 12°17′26″ N 109°06′04″ E | LDPE, PP, EPS, PET, Other | ||
| 3. | Da Rang River (middle reaches) | Phu Yen | 13°00′52″ N 109°11′36″ E | PP, Other |
| Da Rang River (estuary) | 13°03′54″ N 109°18′41″ E | LDPE, PP, EPS, XPS | ||
| 4. | Krong No River (upper reaches) | Lam Dong | 12°15′10″ N 108°26′23″ E | LDPE, PP, Nylon, Other |
| Krong No River (lower reaches) | 12°10′55″ N 108°08′12″ E | LDPE, PP, Other | ||
| 5. | Da Nhim Reservoir | 11°40′38″ N 108°19′41″ E | LDPE, Other | |
| Da Nhim River (middle reaches) | 11°46′16″ N 108°31′00″ E | LDPE, PP, Other | ||
| 6. | Dankia Reservoir | 11°59′31″ N 108°22′17″ E | LDPE, PP, EPS, PET | |
| Ankroet River (connected with Dankia Reservoir) | 12°00′12″ N 108°21′01″ E | LDPE, PP, Nylon |
| Type of Introducing Pellets | Feed Pellets | EPS Pellets | 24th Grasping | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Grasping | 12th Grasping | 1st Grasping | 12th Grasping | ||
| Feed | 12 ± 9.0 0–56 | 63 ± 43.5 7–280 | – | – | 143 ± 63.8 (5) 32–366 |
| Expanded polystyrene | – | – | 35 ± 22.7 2–146 | 75 ± 4.3 62–86 | 817 ± 129.0 (4) 613–1196 |
| Feed and Expanded polystyrene | 2 ± 0.6 0–4 | 49 ± 17.1 12–130 | 14 ± 7.2 1–42 | 193 ± 62.4 53–439 | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ganzha, E.V.; Pavlov, E.D.; Dien, T.D. Risk of Expanded Polystyrene Ingestion by Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus. Water 2023, 15, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071294
Ganzha EV, Pavlov ED, Dien TD. Risk of Expanded Polystyrene Ingestion by Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus. Water. 2023; 15(7):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071294
Chicago/Turabian StyleGanzha, Ekaterina V., Efim D. Pavlov, and Tran Duc Dien. 2023. "Risk of Expanded Polystyrene Ingestion by Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus" Water 15, no. 7: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071294
APA StyleGanzha, E. V., Pavlov, E. D., & Dien, T. D. (2023). Risk of Expanded Polystyrene Ingestion by Climbing Perch Anabas testudineus. Water, 15(7), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071294