Anti gC1qR/p32/HABP1 Antibody Therapy Decreases Tumor Growth in an Orthotopic Murine Xenotransplant Model of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
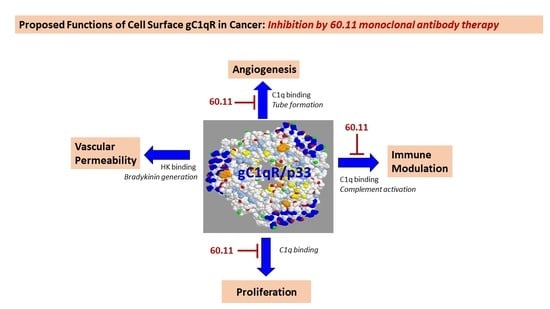
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibody Production
2.2. Murine Xenotransplantation Model
2.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.3.1. Ki 67 Immunostaining
2.3.2. Cleaved Caspase 3 Immunostaining
2.3.3. TUNEL Immunostaining
2.3.4. CD31 Immunostaining
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of Target Staining
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B


References
- Shah, S.P.; Roth, A.; Goya, R.; Oloumi, A.; Ha, G.; Zhao, Y.; Turashvili, G.; Ding, J.; Tse, K.; Haffari, G. The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple-negative breast cancers. Nature 2012, 486, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, S.; Broglio, K.; Esteva, F.J.; Yang, W.; Kau, S.W.; Islam, R.; Albarracin, C.; Yu, T.K.; Green, M.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; et al. Survival among women with triple receptor-negative breast cancer and brain metastases. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffty, B.G.; Yang, Q.; Reiss, M.; Kearney, T.; Higgins, S.A.; Weidhaas, J.; Harris, L.; Hait, W.; Toppmeyer, D. Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5652–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianan, A.; Franzese, E.; Centonze, S.; Carlino, F.; Della Corte, C.M.; Ventriglia, J.; Petrillo, A.; De Vita, F.; Alfano, R.; Ciardiello, F.; et al. Triple-negative breast cancers: Systematic review of the literature on molecular and clinical features with a focus on treatment with innovative drugs. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tray, N.; Adams, S.; Esteva, F.J. Antibody-drug conjugates in triple negative breast cancer. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 2651–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtzelis, I.; Rafail, S. The dual role of complement in cancer and its implication in anti-tumor therapy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulla, R.; Tripodo, C.; Rami, D.; Ling, G.S.; Agostinis, C.; Guarnotta, C.; Zorzet, S.; Durigutto, P.; Botto, M.; Tedesco, F. C1q acts in the tumor microenvironment as a cancer-promoting factor independently of complement activation. Nature Commun. 2016, 7, 10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bossi, F.; Tripodo, C.; Rizzi, L.; Bulla, R.; Agostinis, C.; Guarnotta, C.; Munaut, C.; Baldassarre, G.; Papa, G.; Zorzet, S.; et al. C1q as a unique player in angiogenesis with therapeutic implication in wound healing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4209–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Hosszu, K.K.; Valentino, A.; Peerschke, E.I.B. The C1q family of proteins: Insights into the emerging non-traditional functions. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peerschke, E.I.B.; Ghebrehiwet, B. cC1qR/CR and gC1qR/p33: Observations in cancer. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 61, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Datta, K. Multifunction, multicompartmental hyaluronan-binding protein 1 (HABP1/p32/gC1qR: Implication in cancer progression and metastasis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 10784–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kandov, E.; Kaur, A.; Kishore, U.; Ji, P.; Williams, J.; Peerschke, E.I.B.; Ghebrehiwet, B. C1q and C1q receptors (gC1qR and cC1qR) as potential novel targets for therapy against breast cancer. Cur. Trends Immunol. 2018, 19, 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Lim, B.L.; Peerschke, E.I.; Willis, A.C.; Reid, K.B. Isolation, cDNA cloning, and overexpression of a 33-kDa cell surface glycoprotein that binds to the globular “heads” of C1q. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 1809–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubinstein, D.B.; Stortchevoi, A.; Boosalis, M.; Ashfaq, R.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Peerschke, E.I.; Calvo, F.; Guillaume, T. Receptor for the globular heads of C1q [gC1q-R, p33, hyaluronan binding protein) is preferentially expressed by adenocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 110, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembitzer, F.R.; Kinoshita, Y.; Burstein, D.; Phelps, R.G.; Beasley, M.B.; Garcia, R.; Harpaz, N.; Jaffer, S.; Thung, S.N.; Unger, P.D.; et al. gC1qR expression in normal and pathologic human tissues: Differential expression in tissues of epithelial and mesenchymal origin. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2012, 60, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.B.; Jiang, C.T.; Zhang, G.Q.; Wang, J.S.; Pang, D. Increased expression of hyaluronic acid binding protein 1 is correlated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 100, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, D. Increased breast cancer risk with HABP1/p32/gC1qR genetic polymorphism rs2285747 and its upregulation in northern Chinese women. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13932–13941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amamoto, R.; Yagi, M.; Song, Y.; Oda, Y.; Tsuneyoshi, M.; Naito, S.; Yokomizo, A.; Kuroiwa, K.; Tokunaga, S.; Kato, S.; et al. Mitochondrial p32/C1QBP is highly expressed in prostate cancer and is associated with shorter prostate-specific antigen relapse time after radical prostatectomy. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, J. Significance of hyaluronan binding protein [HABP1/P32/gC1qR] expression in advanced serous ovarian cancer patients. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, T.; Yu, G.; Wang, J. Overexpression of HABP1 correlated with clinicopathological characteristics and unfavorable prognosis in endometrial cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogal, V.; Zhang, L.; Krajewski, S.; Ruoslahti, E. Mitochondria/cell surface protein p32/gC1qR as a molecular target in tumor cells and tumor stroma. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7210–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paasonen, L.; Sharma, S.; Braun, G.B.; Katamraju, V.R.; Chung, T.D.Y.; She, Z.; Sugahara, K.N.; Yliperttula, M.; Wu, B.; Pellecchia, M.; et al. New p32/gC1qR ligands for targeted drug delivery. Chembiochemistry 2016, 17, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Jesty, J.; Peerschke, E.I.B. gC1qR/p33: Structure-function predictions from the crystal structure. Immunobiology 2002, 205, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.K.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, H. Mouse models of breast cancer in preclinical research. Lab. Anim. Res. 2018, 34, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.-C.; Hwang, H.-J.; An, H.-T.; Lee, H.; Partk, J.-S.; Hong, J.; Ko, J.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.-S.; Ko, Y.-G. Antibody neutralization of cell-surface gC1qR/HABP1/SF2-p32 prevents lamellipodia formation and tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 49972–49985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, A.M.; Douglas, D.L.; Liang, Y.; Hyder, S.M.; Baines, C.P. The mitochondrial protein C1qbp promotes cell proliferation, migration and resistance to cell death. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 4119–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Lu, P.D.; Zhang, W.; Lim, B.-L.; Eggleton, P.; Leigh, L.E.A.; Reid, K.B.M.; Peerschke, E.I.B. Identification of functional domins on gC1q-R, a cell surface protein, which binds to the globular heads of C1q, using monoclonal antibodies and synthetic peptides. Hybridoma 1996, 15, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Geisbrecht, B.V.; Xu, X.; Savitt, A.G.; Peerschke, E.I.B. The C1q receptors: Focus on gC1qR [C1qBP, p32, HABP-1]. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 45, 101338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.L.; White, R.A.; Hummel, G.S.; Mak, S.C.; Schwaeble, W.J.; Reid, K.B.M.; Peerschke, E.I.B.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Characterization of the murine gene for gC1q-BP [gC1q-R], a novel cell protein that binds the globular heads of C1q, vitronectin, high molecular weight kinogen and factor XII. Gene 1998, 209, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, N.J.; Reid, K.B.M.; van den Berg, R.H.; Daha, M.R.; Leigh, L.E.A.; Lim, B.L.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Schwaeble, W.J. The murine homologues of gC1qBP, a 33kDa protein that binds to the globular ‘heads’ of C1q. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savitt, A.G.; Mena-Taboada, P.; Monsalve, G.; Benach, J.L. Francisella tularensis infection-derived monoclonal antibodies provide detection, protection and therapy. Clin. Vacc. Immunol. 2009, 16, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Q.; Bournazou, E.; Sansone, P.; Berishaj, M.; Gao, S.P.; Daly, L.; Wels, J.; Theilen, T.; Granitto, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. The IL-6/JAK/STAT3 feed-forward loop drives tumorigenesis and metastasis. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.P.; Chang, Q.; Mao, N.; Daly, L.A.; Vogel, R.; Chan, T.; Liu, S.H.; Bournazou, E.; Schori, E.; Zhang, H.; et al. JAK2 inhibition sensitizes resistant EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer 2016, 9, 421–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moroz, M.A.; Kochetkov, T.; Cai, S.; Wu, J.; Shamis, M.; Nair, J.; de Stanchina, E.; Serganova, I.; Schwartz, G.K.; Banerjee, D.; et al. Imaging colon cancer response following treatment with AZD1152: A preclinical analysis of [18F]Fluoro-2-deoxuglucose and 3′-deoxy-3′-[18F]Fluorothymidine imaging. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peerschke, E.I.B.; Bayer, A.S.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Xiong, Y.Q. gC1qR/p33 blockade reduces Staphylococcus aureus colonization of target tissues in an animal model of infective endocarditis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4418–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.S.; Okaniwa, M.; Yao, Z.; Novotny, C.J.; McWhirter, C.; Banaji, A.; Won, H.; Wong, W.; Berger, M.; de Stanchina, E.; et al. Overcoming mTOR resistance mutations with a new-generation mTOR inhibitor. Nature 2016, 534, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaffer, D.R.; Viale, A.; Ishiwata, R.; Leversha, M.; Olgac, S.; Manova, K.; Satagopan, J.; Scher, H.; Koff, A. Evidence for a p27 tumor suppressive function independent of its role regulating cell proliferation in the prostate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peerschke, E.I.B.; Reid, K.B.M.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Identification of a novel 33-kDa C1q binding site on human blood platelets. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 5896–5901. [Google Scholar]
- Eggleton, P.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Sastry, K.N.; Coburn, J.P.; Zaner, K.S.; Reid, K.B.M.; Tauber, A.I. Identification of a gC1q-bindin protein [gC1q-R] on the surface of human neutrophils. Subcellular localization and binding properties in comparison with cC1q-R. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuna, P.; Iyer, M.; Peerschke, E.I.; Kaplan, A.P.; Reid, K.B.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Human C1q induces eosinophil migration. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 81, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, P.; Szekeres, A.; Wille, S.; Stockl, J.; Selenko, N.; Prager, E.; Staffler, G.; Madic, O.; Stockinger, H.; Knapp, W. Identification of human CD93 as the phagocytic C1q receptor [C1qRP] by expression cloning. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 33–140. [Google Scholar]
- Vegh, Z.; Goyarts, E.C.; Rozengarten, K.; Mazumder, A.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Maturation-dependent expression of C1q-binding proteins on the cell surface of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, D.E.; Mikkola, A.M.; Stepanek, A.M.; Vernet, A.; Hall, C.D.; Sun, C.C.; Yildririm, E.; Starpoli, J.F.; Lee, J.T.; Brown, D.E. Practical murine hematopathology: A comparative review and implications for research. Comp. Med. 2015, 65, 96–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Peerschke, E.I.B. Structure and function of gC1qR: A multiligand binding cellular protein. Immunobiology 1998, 199, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, P.D.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Peerschke, E.I.; Ghebrehiwet, B. The C1q-binding cell membrane proteins cC1qR and gC1qR are released from activated cells: Subcellular distribution and immunochemical characterization. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 84, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Martin, D.; Cuesta, A.M.; Fogal, V.; Ruoslahti, E.; Alvarez-Vallin, L. The multicompartmental p32/gC1qR as a new target for antibody-based tumor targeting strategies. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5197–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishida, N.; Yano, H.; Nishida, T.; Kamura, T.; Kojiro, M. Angiogenesis in Cancer. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, B.E.; Cebon, J. Cancer exploiting complement: A clue or an exception? Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1205–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, S.; Leandersson, K.; Edsjo, A.; Larssen, C. Prognostic stromal gene signatures in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Vehicle | 60.11 Treatment (Group 2) | 60.11 Treatment (Group 3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor Volume (mm3) | 894 ± 143 | 401 ± 48 | 700 ± 104 |
| (p = 8.34 × 10−5) | (p = 0.040) | ||
| Mouse Weight (g) | 24.80 ± 2.16 | 25.00 ± 2.00 | 23.60 ± 1.67 |
| (p = 0.883) | (p = 0.356) | ||
| Serum 60.11 (μg/mL) | undetectable | 52 ± 40 | 49 ± 25 |
| (median 34; range 31–124) | (median 47; range 28–89) |
| Treatment Groups | Reference Values * | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Count | Vehicle Control (Group 1) | 60.11 Treatment (Group2) | |
| RBC (1012/L) | 9.77 ± 0.05 | 9.68 ± 0.41 (p = 0.779) | 7.4–10.1 |
| Hgb (g/dL) | 15.95 ± 0.81 | 15.58 ± 0.54 (p = 0.441) | 13.2–18.0 |
| Platelets (109/L) | 769 ± 133 | 778 ± 137 (p = 0.923) | 659–1372 |
| WBC (109/L) | 7.38 ± 3.50 | 5.09 ± 1.40 (p = 0.005) | 2.1–11.3 |
| Neutrophils (109/L) | 2.10 ± 0.93 | 1.42 ± 0.44 (p = 0.064) | 0.4–2.1 |
| Lymphocytes (109/L) | 4.98 ± 2.54 | 3.46 ± 1.07 (p = 0.002) | 0.7–9.3 |
| Monocytes (109/L) | 0.20 ± 0.10 | 0.106 ± 0.052 (p = 0.42) | 0.01–0.43 |
| Eosinophils (109/L) | 0.090 ± 0.24 | 0.094 ± 0.017 (p = 7 × 10−5) | 0–0.4 |
| Basophils (109/L) | 0.010 ± 0.005 | 0.006 ± 0.005 (p = 2 × 10−5) | 0–0.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peerschke, E.I.; Stanchina, E.d.; Chang, Q.; Manova-Todorova, K.; Barlas, A.; Savitt, A.G.; Geisbrecht, B.V.; Ghebrehiwet, B. Anti gC1qR/p32/HABP1 Antibody Therapy Decreases Tumor Growth in an Orthotopic Murine Xenotransplant Model of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Antibodies 2020, 9, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040051
Peerschke EI, Stanchina Ed, Chang Q, Manova-Todorova K, Barlas A, Savitt AG, Geisbrecht BV, Ghebrehiwet B. Anti gC1qR/p32/HABP1 Antibody Therapy Decreases Tumor Growth in an Orthotopic Murine Xenotransplant Model of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Antibodies. 2020; 9(4):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040051
Chicago/Turabian StylePeerschke, Ellinor I., Elisa de Stanchina, Qing Chang, Katia Manova-Todorova, Afsar Barlas, Anne G. Savitt, Brian V. Geisbrecht, and Berhane Ghebrehiwet. 2020. "Anti gC1qR/p32/HABP1 Antibody Therapy Decreases Tumor Growth in an Orthotopic Murine Xenotransplant Model of Triple Negative Breast Cancer" Antibodies 9, no. 4: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040051
APA StylePeerschke, E. I., Stanchina, E. d., Chang, Q., Manova-Todorova, K., Barlas, A., Savitt, A. G., Geisbrecht, B. V., & Ghebrehiwet, B. (2020). Anti gC1qR/p32/HABP1 Antibody Therapy Decreases Tumor Growth in an Orthotopic Murine Xenotransplant Model of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Antibodies, 9(4), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040051