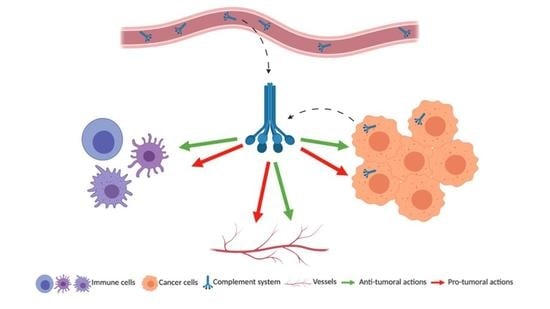
Complement System: Promoter or Suppressor of Cancer Progression?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Complement System
2.1. Complement Activating Pathways
2.2. Complement Effector Pathways
2.3. Complement Regulators
2.4. Complement Complexity
3. Complement and Cancer
3.1. Activation of Complement in the Tumor Microenvironment
3.2. Role of Complement on Tumor Immunity
3.3. Impact of Complement on Tumor Cells
3.3.1. Native Proteins
3.3.2. Activation Fragments
3.4. Role of the Complement on Angiogenesis
3.5. Complement Biomarkers in Patients with Cancer
4. Therapeutic Aspects
4.1. Complement Inhibitors
4.2. Therapeutic Inhibition of C5aR1 on Tumor Cells Versus on Immune Cells
4.3. Complement Activation-Enhancing Therapeutic Antibodies
4.4. Activation Versus Inhibition of Complement in Cancer
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The immune contexture in human tumours: Impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, W.H.; Zitvogel, L.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Kroemer, G. The immune contexture in cancer prognosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roumenina, L.T.; Daugan, M.V.; Petitprez, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Fridman, W.H. Context-dependent roles of complement in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 698–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merle, N.S.; Church, S.E.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement System Part I—Molecular Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merle, N.S.; Noe, R.; Halbwachs-Mecarelli, L.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement System Part II: Role in Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchner: Zur Nomenklatur der schutzenden Eiweisskorper—Google Scholar. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Centr+Bakteriol+Parasitenk.&title=Zur+Nomenklatur+der+schutzenden+Eiweisskorper.&author=H+Buchner&volume=10&publication_year=1891&pages=699-701& (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Sim, R.B.; Schwaeble, W.; Fujita, T. Complement research in the 18th–21st centuries: Progress comes with new technology. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboriaud, C.; Thielens, N.M.; Gregory, L.A.; Rossi, V.; Fontecilla-Camps, J.C.; Arlaud, G.J. Structure and activation of the C1 complex of complement: Unraveling the puzzle. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, T.H.; Boyle, A.L.; Diebolder, C.A.; Kros, A.; Koster, A.J.; Gros, P. Insights into IgM-mediated complement activation based on in situ structures of IgM-C1-C4b. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11900–11905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ugurlar, D.; Howes, S.C.; de Kreuk, B.-J.; Koning, R.I.; de Jong, R.N.; Beurskens, F.J.; Schuurman, J.; Koster, A.J.; Sharp, T.H.; Parren, P.W.H.I.; et al. Structures of C1-IgG1 provide insights into how danger pattern recognition activates complement. Science 2018, 359, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garred, P.; Genster, N.; Pilely, K.; Bayarri-Olmos, R.; Rosbjerg, A.; Ma, Y.J.; Skjoedt, M.-O. A journey through the lectin pathway of complement-MBL and beyond. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 74–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Reis, E.S.; Mastellos, D.C.; Gros, P.; Lambris, J.D. Complement component C3—The “Swiss Army Knife” of innate immunity and host defense. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kemper, C.; Atkinson, J.P.; Hourcade, D.E. Properdin: Emerging roles of a pattern-recognition molecule. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabizadeh, J.A.; Manthey, H.D.; Panagides, N.; Steyn, F.J.; Lee, J.D.; Li, X.X.; Akhir, F.N.M.; Chen, W.; Boyle, G.M.; Taylor, S.M.; et al. C5a receptors C5aR1 and C5aR2 mediate opposing pathologies in a mouse model of melanoma. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 11060–11071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tegla, C.A.; Cudrici, C.; Patel, S.; Trippe, R.; Rus, V.; Niculescu, F.; Rus, H. Membrane Attack by Complement: The Assembly and Biology of Terminal Complement Complexes. Immunol. Res. 2011, 51, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noris, M.; Remuzzi, G. Overview of Complement Activation and Regulation. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, E.E.; Kunz, N.; Kemper, C. Complement and human T cell metabolism: Location, location, location. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 295, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, C.; Togarsimalemath, S.K.; Chauvet, S.; Le Quintrec, M.; Moulin, B.; Buchler, M.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Roumenina, L.T.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Dragon-Durey, M.-A. Anti-factor H autoantibodies in C3 glomerulopathies and in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome: One target, two diseases. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5129–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michailidou, I.; Willems, J.G.P.; Kooi, E.-J.; van Eden, C.; Gold, S.M.; Geurts, J.J.G.; Baas, F.; Huitinga, I.; Ramaglia, V. Complement C1q-C3-associated synaptic changes in multiple sclerosis hippocampus. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 1007–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHarg, S.; Clark, S.J.; Day, A.J.; Bishop, P.N. Age-related macular degeneration and the role of the complement system. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, N.S.; Grunenwald, A.; Rajaratnam, H.; Gnemmi, V.; Frimat, M.; Figueres, M.-L.; Knockaert, S.; Bouzekri, S.; Charue, D.; Noe, R.; et al. Intravascular hemolysis activates complement via cell-free heme and heme-loaded microvesicles. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekar, A.; Bialas, A.R.; de Rivera, H.; Davis, A.; Hammond, T.R.; Kamitaki, N.; Tooley, K.; Presumey, J.; Baum, M.; Van Doren, V.; et al. Schizophrenia risk from complex variation of complement component 4. Nature 2016, 530, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roumenina, L.T.; Daugan, M.V.; Noé, R.; Petitprez, F.; Vano, Y.A.; Sanchez-Salas, R.; Becht, E.; Meilleroux, J.; Clec’h, B.L.; Giraldo, N.A.; et al. Tumor Cells Hijack Macrophage-Produced Complement C1q to Promote Tumor Growth. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1091–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajona, D.; Ortiz-Espinosa, S.; Pio, R. Complement anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a: Emerging roles in cancer progression and treatment. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 85, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajona, D.; Okrój, M.; Pajares, M.J.; Agorreta, J.; Lozano, M.D.; Zulueta, J.J.; Verri, C.; Roz, L.; Sozzi, G.; Pastorino, U.; et al. Complement C4d-specific antibodies for the diagnosis of lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6346–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riihilä, P.; Nissinen, L.; Farshchian, M.; Kallajoki, M.; Kivisaari, A.; Meri, S.; Grénman, R.; Peltonen, S.; Peltonen, J.; Pihlajaniemi, T.; et al. Complement Component C3 and Complement Factor B Promote Growth of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajona, D.; Castaño, Z.; Garayoa, M.; Zudaire, E.; Pajares, M.J.; Martinez, A.; Cuttitta, F.; Montuenga, L.M.; Pio, R. Expression of complement factor H by lung cancer cells: Effects on the activation of the alternative pathway of complement. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6310–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riihilä, P.; Nissinen, L.; Farshchian, M.; Kivisaari, A.; Ala-Aho, R.; Kallajoki, M.; Grénman, R.; Meri, S.; Peltonen, S.; Peltonen, J.; et al. Complement factor I promotes progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravindranath, N.M.H.; Shuler, C. Expression of complement restriction factors (CD46, CD55 & CD59) in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2006, 35, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapka-Skrzypczak, L.; Wolinska, E.; Szparecki, G.; Wilczynski, G.M.; Czajka, M.; Skrzypczak, M. CD55, CD59, factor H and factor H-like 1 gene expression analysis in tumors of the ovary and corpus uteri origin. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 167, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pio, R.; Corrales, L.; Lambris, J.D. The role of complement in tumor growth. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 772, 229–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Netti, G.S.; Lucarelli, G.; Spadaccino, F.; Castellano, G.; Gigante, M.; Divella, C.; Rocchetti, M.T.; Rascio, F.; Mancini, V.; Stallone, G.; et al. PTX3 modulates the immunoflogosis in tumor microenvironment and is a prognostic factor for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Aging 2020, 12, 7585–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, S.D.; Karlsson-Parra, A.; Nilsson, B.; Grimelius, L.; Akerström, G.; Rastad, J.; Juhlin, C. Tumor-specific deposition of immunoglobulin G and complement in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 1996, 27, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.W.; Laskowski, J.; Li, H.Y.; McSharry, M.V.; Sippel, T.R.; Bullock, B.L.; Johnson, A.M.; Poczobutt, J.M.; Neuwelt, A.J.; Malkoski, S.P.; et al. Complement Activation via a C3a Receptor Pathway Alters CD4+ T Lymphocytes and Mediates Lung Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zirakzadeh, A.A.; Sherif, A.; Rosenblatt, R.; Ahlén Bergman, E.; Winerdal, M.; Yang, D.; Cederwall, J.; Jakobsson, V.; Hyllienmark, M.; Winqvist, O.; et al. Tumour-associated B cells in urothelial urinary bladder cancer. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 91, e12830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.-W. The Complement Receptors C3aR and C5aR Are a New Class of Immune Checkpoint Receptor in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajona, D.; Zandueta, C.; Corrales, L.; Moreno, H.; Pajares, M.J.; Ortiz-Espinosa, S.; Martínez-Terroba, E.; Perurena, N.; de Miguel, F.J.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; et al. Blockade of the Complement C5a/C5aR1 Axis Impairs Lung Cancer Bone Metastasis by CXCL16-mediated Effects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewski, M.M.; DeAngelis, R.A.; Benencia, F.; Ricklin-Lichtsteiner, S.K.; Koutoulaki, A.; Gerard, C.; Coukos, G.; Lambris, J.D. Modulation of the antitumor immune response by complement. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabizadeh, J.A.; Manthey, H.D.; Steyn, F.J.; Chen, W.; Widiapradja, A.; Md Akhir, F.N.; Boyle, G.M.; Taylor, S.M.; Woodruff, T.M.; Rolfe, B.E. The Complement C3a Receptor Contributes to Melanoma Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting Neutrophil and CD4+ T Cell Responses. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 4783–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zheng, X.; Yi, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, K. Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells (HSCs) Exert Immunosuppressive Effects in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Producing Complement C3. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, S.; Efremova, M.; Riedel, A.; Mahata, B.; Pramanik, J.; Huuhtanen, J.; Kar, G.; Vento-Tormo, R.; Hagai, T.; Chen, X.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals a Dynamic Stromal Niche That Supports Tumor Growth. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, W.D.; Gulino, A.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Seoane, R.C.; Tian, K.; Best, K.; Köhl, J.; Belmonte, B.; Strid, J.; Botto, M. C3 Drives Inflammatory Skin Carcinogenesis Independently of C5. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Lv, X.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Xu, E.; Dai, W.; et al. C5aR1 is a master regulator in Colorectal Tumorigenesis via Immune modulation. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8619–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Han, X.; Yang, F.; Gao, J.; Hu, C.; Shu, C.; Feng, Y.; et al. Intracellular Activation of Complement C3 Leads to PD-L1 Antibody Treatment Resistance by Modulating Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelle, V.; Langlois, M.-P.; Tarrab, E.; Lapierre, P.; Poliquin, L.; Lamarre, A. Transient complement inhibition promotes a tumor-specific immune response through the implication of natural killer cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadrevu, S.K.; Chintala, N.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, P.; Cleveland, C.; Riediger, L.; Manne, S.; Fairlie, D.P.; Gorczyca, W.; Almanza, O.; et al. Complement C5a Receptor Facilitates Cancer Metastasis by Altering T-Cell Responses in the Metastatic Niche. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3454–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrales, L.; Ajona, D.; Rafail, S.; Lasarte, J.J.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Lambris, J.D.; Rouzaut, A.; Pajares, M.J.; Montuenga, L.M.; Pio, R. Anaphylatoxin C5a creates a favorable microenvironment for lung cancer progression. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4674–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavita, E.; Gentile, S.; Rubino, M.; Maina, V.; Papait, R.; Kunderfranco, P.; Greco, C.; Feruglio, F.; Molgora, M.; Laface, I.; et al. PTX3 is an extrinsic oncosuppressor regulating complement-dependent inflammation in cancer. Cell 2015, 160, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surace, L.; Lysenko, V.; Fontana, A.O.; Cecconi, V.; Janssen, H.; Bicvic, A.; Okoniewski, M.; Pruschy, M.; Dummer, R.; Neefjes, J.; et al. Complement is a central mediator of radiotherapy-induced tumor-specific immunity and clinical response. Immunity 2015, 42, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunn, L.; Ding, C.; Liu, M.; Ma, Y.; Qi, C.; Cai, Y.; Hu, X.; Aggarwal, D.; Zhang, H.-G.; Yan, J. Opposing roles for complement component C5a in tumor progression and the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2985–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liao, J.-Y.; Song, E.; Xia, Q.; Pan, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, B.; Ye, Y.; et al. Complement Signals Determine Opposite Effects of B Cells in Chemotherapy-Induced Immunity. Cell 2020, 180, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Sze, C.-I.; Lin, S.-R.; Lee, M.-H.; He, R.-Y.; Schultz, L.; Chang, J.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; Boackle, R.J.; Hsu, L.-J.; et al. Complement C1q activates tumor suppressor WWOX to induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bandini, S.; Macagno, M.; Hysi, A.; Lanzardo, S.; Conti, L.; Bello, A.; Riccardo, F.; Ruiu, R.; Merighi, I.F.; Forni, G.; et al. The non-inflammatory role of C1q during Her2/neu-driven mammary carcinogenesis. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, A.; Sultan, S.H.A.; Murugaiah, V.; Pathan, A.A.; Alhamlan, F.S.; Karteris, E.; Kishore, U. Human C1q Induces Apoptosis in an Ovarian Cancer Cell Line via Tumor Necrosis Factor Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulla, R.; Tripodo, C.; Rami, D.; Ling, G.S.; Agostinis, C.; Guarnotta, C.; Zorzet, S.; Durigutto, P.; Botto, M.; Tedesco, F. C1q acts in the tumour microenvironment as a cancer-promoting factor independently of complement activation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riihilä, P.M.; Nissinen, L.M.; Ala-Aho, R.; Kallajoki, M.; Grénman, R.; Meri, S.; Peltonen, S.; Peltonen, J.; Kähäri, V.-M. Complement factor H: A biomarker for progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, J.; Renner, B.; Pickering, M.C.; Serkova, N.J.; Smith-Jones, P.M.; Clambey, E.T.; Nemenoff, R.A.; Thurman, J.M. Complement factor H-deficient mice develop spontaneous hepatic tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbore, G.; Kemper, C.; Kolev, M. Intracellular complement—The complosome—In immune cell regulation. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 89, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrehiwet, B. Complement proteins in unexpected places: Why we should be excited, not concerned! F1000Research 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Hu, X.-B. C5a stimulates the proliferation of breast cancer cells via Akt-dependent RGC-32 gene activation. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2817–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.S.; Vasquez, H.G.; Rupaimoole, R.; Pradeep, S.; Wu, S.; Zand, B.; Han, H.-D.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Bottsford-Miller, J.; Huang, J.; et al. Autocrine effects of tumor-derived complement. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piao, C.; Cai, L.; Qiu, S.; Jia, L.; Song, W.; Du, J. Complement 5a Enhances Hepatic Metastases of Colon Cancer via Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1-mediated Inflammatory Cell Infiltration. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 10667–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nitta, H.; Wada, Y.; Kawano, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Irie, A.; Taniguchi, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Yamada, G.; Suzuki, K.; Honda, J.; et al. Enhancement of human cancer cell motility and invasiveness by anaphylatoxin C5a via aberrantly expressed C5a receptor (CD88). Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2004–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozanov, D.V.; Sikora, S.; Godzik, A.; Postnova, T.I.; Golubkov, V.; Savinov, A.; Tomlinson, S.; Strongin, A.Y. Non-proteolytic, receptor/ligand interactions associate cellular membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase with the complement component C1q. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 50321–50328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlaicu, S.I.; Tegla, C.A.; Cudrici, C.D.; Danoff, J.; Madani, H.; Sugarman, A.; Niculescu, F.; Mircea, P.A.; Rus, V.; Rus, H. Role of C5b-9 complement complex and response gene to complement-32 (RGC-32) in cancer. Immunol. Res. 2013, 56, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez-Cruz, S.; Gimotty, P.A.; Guerra, M.W.; Connolly, D.C.; Wu, Y.-Q.; DeAngelis, R.A.; Lambris, J.D.; Coukos, G.; Scholler, N. Genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of complement impairs endothelial cell function and ablates ovarian cancer neovascularization. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, R.; Yamaoka, K.; Sawamukai, N.; Shimajiri, S.; Oshita, K.; Yukawa, S.; Tokunaga, M.; Iwata, S.; Saito, K.; Chiba, K.; et al. C5a promotes migration, proliferation, and vessel formation in endothelial cells. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandini, S.; Curcio, C.; Macagno, M.; Quaglino, E.; Arigoni, M.; Lanzardo, S.; Hysi, A.; Barutello, G.; Consolino, L.; Longo, D.L.; et al. Early onset and enhanced growth of autochthonous mammary carcinomas in C3-deficient Her2/neu transgenic mice. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, L.; Zhang, F.; Pan, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, N.; Jin, J.; Wu, J.; Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Jin, H.; et al. Complement component 7 (C7), a potential tumor suppressor, is correlated with tumor progression and prognosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86536–86546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozenberg, P.; Ziporen, L.; Gancz, D.; Saar-Ray, M.; Fishelson, Z. Cooperation between Hsp90 and mortalin/GRP75 in resistance to cell death induced by complement C5b-9. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwens, T.A.M.; Trouw, L.A.; Veerhuis, R.; Dirven, C.M.F.; Lamfers, M.L.M.; Al-Khawaja, H. Complement activation in Glioblastoma multiforme pathophysiology: Evidence from serum levels and presence of complement activation products in tumor tissue. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 278, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.; Wu, J.; Lu, F.; Peng, X.; Liu, C.; Zhou, N.; Ying, M. The imbalance in the complement system and its possible physiological mechanisms in patients with lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grzmil, M.; Voigt, S.; Thelen, P.; Hemmerlein, B.; Helmke, K.; Burfeind, P. Up-regulated expression of the MAT-8 gene in prostate cancer and its siRNA-mediated inhibition of expression induces a decrease in proliferation of human prostate carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2004, 24, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oner, F.; Savaş, I.; Numanoğlu, N. Immunoglobulins and complement components in patients with lung cancer. Tuberk Toraks 2004, 52, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.-L.; Chen, Y.-J.; Jing, X.-Y.; Wang, N.-N.; Zhang, T.; Hu, C.-J. Detection and Identification of Serum Peptides Biomarker in Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2018, 24, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajona, D.; Razquin, C.; Pastor, M.D.; Pajares, M.J.; Garcia, J.; Cardenal, F.; Fleischhacker, M.; Lozano, M.D.; Zulueta, J.J.; Schmidt, B.; et al. Elevated levels of the complement activation product C4d in bronchial fluids for the diagnosis of lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, P.Y.; Tan, O.; Diakiw, S.M.; Carter, D.; Sekerye, E.O.; Wasinger, V.C.; Liu, T.; Kavallaris, M.; Norris, M.D.; Haber, M.; et al. Identification of plasma complement C3 as a potential biomarker for neuroblastoma using a quantitative proteomic approach. J. Proteom. 2014, 96, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wu, W.; Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, R.; Hu, L. Expression and clinical significance of AHSG and complement C3 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2014, 94, 2175–2179. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, W.; Zhen, C.; Zhou, H.; Yang, R.; Chen, L.; Hu, L. Expression and clinical significance of complement C3, complement C4b1 and apolipoprotein E in pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, L. Anaphylatoxin C3a: A potential biomarker for esophageal cancer diagnosis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 8, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, L.; Moore, K.; Phillips, L.; Boyle, F.M.; Marsh, D.J.; Baxter, R.C. Novel serum protein biomarker panel revealed by mass spectrometry and its prognostic value in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2014, 16, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, G.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Tang, M.; Cao, X.; Xu, G.-L.; Wu, Y.-Z. Complement C5a/C5aR pathway potentiates the pathogenesis of gastric cancer by down-regulating p21 expression. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmig, S.; Lochnit, G.; Schneider, J. Comparative proteomic analysis in serum of former uranium miners with and without radon induced squamous lung cancer. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. Lond. Engl. 2019, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pio, R.; Garcia, J.; Corrales, L.; Ajona, D.; Fleischhacker, M.; Pajares, M.J.; Cardenal, F.; Seijo, L.; Zulueta, J.J.; Nadal, E.; et al. Complement factor H is elevated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and sputum from patients with lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2010, 19, 2665–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Z.-Z.; Corey, M.J.; Pärepalo, M.; Majno, S.; Hellwage, J.; Zipfel, P.F.; Kinders, R.J.; Raitanen, M.; Meri, S.; Jokiranta, T.S. Complement factor H as a marker for detection of bladder cancer. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heicappell, R.; Müller, M.; Fimmers, R.; Miller, K. Qualitative determination of urinary human complement factor H-related protein (hcfHrp) in patients with bladder cancer, healthy controls, and patients with benign urologic disease. Urol. Int. 2000, 65, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy, A.; Ahn, J.-M.; Sung, H.-J.; Kong, D.-H.; Ha, K.-S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Cho, J.-Y. Fucosylated glycoproteomic approach to identify a complement component 9 associated with squamous cell lung cancer (SQLC). J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 2948–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Chai, N.; Gu, Y.; Ding, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ren, G.; Hao, X.; Fan, D.; Wu, K.; et al. Systematic immunohistochemical analysis of the expression of CD46, CD55, and CD59 in colon cancer. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swierzko, A.S.; Szala, A.; Sawicki, S.; Szemraj, J.; Sniadecki, M.; Sokolowska, A.; Kaluzynski, A.; Wydra, D.; Cedzynski, M. Mannose-Binding Lectin (MBL) and MBL-associated serine protease-2 (MASP-2) in women with malignant and benign ovarian tumours. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2014, 63, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ytting, H.; Jensenius, J.C.; Christensen, I.J.; Thiel, S.; Nielsen, H.J. Increased activity of the mannan-binding lectin complement activation pathway in patients with colorectal cancer. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Liang, B.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Tong, X.; Lou, W.; Le, L.; Tang, X.; Fu, F. Identification of core genes in ovarian cancer by an integrative meta-analysis. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Hwan, J.D.; Bae, S.; Bae, D.-H.; Shick, W.A. Identification of differentially expressed genes using an annealing control primer system in stage III serous ovarian carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Liu, B.; Xin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, Y. Down-regulated expression of complement factor I: A potential suppressive protein for gastric cancer identified by serum proteome analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2007, 377, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.C.; Looi, M.L.; Zakaria, S.Z.S.; Sagap, I.; Rose, I.M.; Chin, S.-F.; Jamal, R. Identification of Differentially Expressed Proteins in the Serum of Colorectal Cancer Patients Using 2D-DIGE Proteomics Analysis. Pathol. Oncol. Res. POR 2016, 22, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricklin, D.; Mastellos, D.C.; Reis, E.S.; Lambris, J.D. The renaissance of complement therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ajona, D.; Ortiz-Espinosa, S.; Moreno, H.; Lozano, T.; Pajares, M.J.; Agorreta, J.; Bértolo, C.; Lasarte, J.J.; Vicent, S.; Hoehlig, K.; et al. A Combined PD-1/C5a Blockade Synergistically Protects against Lung Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diebolder, C.A.; Beurskens, F.J.; de Jong, R.N.; Koning, R.I.; Strumane, K.; Lindorfer, M.A.; Voorhorst, M.; Ugurlar, D.; Rosati, S.; Heck, A.J.R.; et al. Complement is activated by IgG hexamers assembled at the cell surface. Science 2014, 343, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zha, H.; Han, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, B.; Zhu, B. Blocking C5aR signaling promotes the anti-tumor efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1349587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massard, C.; Cassier, P.; Bendell, J.C.; Marie, D.B.; Blery, M.; Morehouse, C.; Ascierto, M.; Zerbib, R.; Mitry, E.; Tolcher, A.W. Preliminary results of STELLAR-001, a dose escalation phase I study of the anti-C5aR, IPH5401, in combination with durvalumab in advanced solid tumours. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar-Kharghan, V. The role of the complement system in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Q.; Li, T.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Role of the complement system in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbore, G.; West, E.E.; Rahman, J.; Le Friec, G.; Niyonzima, N.; Pirooznia, M.; Tunc, I.; Pavlidis, P.; Powell, N.; Li, Y.; et al. Complement receptor CD46 co-stimulates optimal human CD8+ T cell effector function via fatty acid metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, R.P.; Lindorfer, M.A. Cytotoxic mechanisms of immunotherapy: Harnessing complement in the action of anti-tumor monoclonal antibodies. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiffier, B.; Haioun, C.; Ketterer, N.; Engert, A.; Tilly, H.; Ma, D.; Johnson, P.; Lister, A.; Feuring-Buske, M.; Radford, J.A.; et al. Rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) for the treatment of patients with relapsing or refractory aggressive lymphoma: A multicenter phase II study. Blood 1998, 92, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar]
- Zent, C.S.; Secreto, C.R.; LaPlant, B.R.; Bone, N.D.; Call, T.G.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Jelinek, D.F.; Tschumper, R.C.; Kay, N.E. Direct and complement dependent cytotoxicity in CLL cells from patients with high-risk early-intermediate stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treated with alemtuzumab and rituximab. Leuk. Res. 2008, 32, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Janmaat, M.L.; Mutis, T.; Lammerts van Bueren, J.J.; Ahmadi, T.; Sasser, A.K.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Parren, P.W.H.I. Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD38 in hematological malignancies and beyond. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 270, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.-H.; Romain, G.; Yan, W.; Watanabe, M.; Charab, W.; Todorova, B.; Lee, J.; Triplett, K.; Donkor, M.; Lungu, O.I.; et al. IgG Fc domains that bind C1q but not effector Fcγ receptors delineate the importance of complement-mediated effector functions. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, O.; Cosimo, E.; Dobbin, E.; McCaig, A.M.; Clarke, C.; Brant, A.M.; Leach, M.T.; Michie, A.M.; Wheadon, H. Complement deficiencies limit CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment efficacy in CLL. Leukemia 2015, 29, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dzietczenia, J.; Wróbel, T.; Mazur, G.; Poreba, R.; Jaźwiec, B.; Kuliczkowski, K. Expression of complement regulatory proteins: CD46, CD55, and CD59 and response to rituximab in patients with CD20+ non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Med. Oncol. Northwood Lond. Engl. 2010, 27, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluczkowycz, A.W.; Beurskens, F.J.; Beum, P.V.; Lindorfer, M.A.; van de Winkel, J.G.J.; Parren, P.W.H.I.; Taylor, R.P. Binding of submaximal C1q promotes complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) of B cells opsonized with anti-CD20 mAbs ofatumumab (OFA) or rituximab (RTX): Considerably higher levels of CDC are induced by OFA than by RTX. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cook, E.M.; Lindorfer, M.A.; van der Horst, H.; Oostindie, S.; Beurskens, F.J.; Schuurman, J.; Zent, C.S.; Burack, R.; Parren, P.W.H.I.; Taylor, R.P. Antibodies That Efficiently Form Hexamers upon Antigen Binding Can Induce Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity under Complement-Limiting Conditions. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostindie, S.C.; van der Horst, H.J.; Lindorfer, M.A.; Cook, E.M.; Tupitza, J.C.; Zent, C.S.; Burack, R.; VanDerMeid, K.R.; Strumane, K.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; et al. CD20 and CD37 antibodies synergize to activate complement by Fc-mediated clustering. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, D.V.; Rösner, T.; Hansen, A.G.; Andersen, K.R.; Thiel, S.; Andersen, G.R.; Valerius, T.; Laursen, N.S. Recruitment of properdin by bi-specific nanobodies activates the alternative pathway of complement. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 124, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderman, K.A.; Lam, S.; Sier, C.F.; Gorter, A. Cross-linking tumor cells with effector cells via CD55 with a bispecific mAb induces beta-glucan-dependent CR3-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, J.W.; Damko, E.; Modi, B.; Tu, N.; Meagher, K.; Voronina, V.; Gartner, H.; Ehrlich, G.; Rafique, A.; Babb, R.; et al. A novel bispecific antibody platform to direct complement activity for efficient lysis of target cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajona, D.; Hsu, Y.-F.; Corrales, L.; Montuenga, L.M.; Pio, R. Down-regulation of human complement factor H sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to complement attack and reduces in vivo tumor growth. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5991–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitprez, F.; de Reyniès, A.; Keung, E.Z.; Chen, T.W.-W.; Sun, C.-M.; Calderaro, J.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Hsiao, L.-P.; Lacroix, L.; Bougoüin, A.; et al. B cells are associated with survival and immunotherapy response in sarcoma. Nature 2020, 577, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajona, D.; Pajares, M.J.; Corrales, L.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Agorreta, J.; Lozano, M.D.; Torre, W.; Massion, P.P.; de-Torres, J.P.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; et al. Investigation of complement activation product c4d as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Regulated Steps | Regulators | Soluble or Membranous |
|---|---|---|
| C1 complex/MBL complex | C1 inhibitors | Soluble |
| C3 convertases C5 convertases | Factor H (FH) | Soluble |
| CFHRs (1 to 5) | Soluble | |
| Properdin (FP) | Soluble | |
| C4 Binding Protein (C4BP) | Soluble | |
| Factor I (FI) | Soluble | |
| Membrane cofactor proteins (MCP/CD46) | Membranous | |
| Decay acceleration factor (DAF/CD55) | Membranous | |
| Complement receptor 1 (CR1) | Membranous | |
| MAC | CD59 | Membranous |
| Clusterin | Soluble | |
| Vitronectin | Soluble |
| Overexpression | |||
| Molecule | Type of Cancer | Mechanism of Action | Ref. |
| C1q | Glioblastoma | Plasma: increased C1q in the sera of patients in comparison with healthy controls. | [72] |
| C1s | Lung cancer | Plasma: increased levels of C1s in plasma of lung cancer patient in comparison with controls | [73] |
| Prostate cancer | Tumor: Up-regulation of C1s expression in prostate tumors compared to matched normal prostate tissues | [74] | |
| C4 | Lung cancer | Plasma: elevated C4 levels in cancer patients in comparison to control group | [75] |
| C4a | Papillary thyroid cancer | Plasma: increased C4a in the sera of patients in comparison with healthy controls. | [76] |
| C4d | Lung cancer | Bronchial fluid: Higher levels of C4d in cancer patients than patients with control group. | [77] |
| Lung cancer | Plasma: Higher levels of C4d in cancer patients than patients with benign nodules. | [25] | |
| C3 | Lung cancer | Plasma: elevated C3 levels in cancer patients in comparison to control group | [75] |
| Neuroblastoma | Plasma: elevated C3 levels in cancer patients in comparison to healthy donors | [78] | |
| Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Tumor: Higher levels of C3 protein in cancerous tissues than in adjacent normal pancreatic tissues | [79] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | Tumor: Higher levels of C3 protein in cancerous tissues than in normal pancreatic tissues | [80] | |
| C3a | Esophageal cancer | Plasma: Higher C3a levels in patients than healthy donors | [81] |
| C3a desArg | Breast cancer | Plasma: Higher C3a desArg level in patients than healthy donors | [82] |
| C5a | Non-small cell lung cancer | Plasma: Higher C3a levels in patients than healthy donors | [47] |
| C5aR1 | Gastric cancer | Tumor: higher expression of C5aR1 in gastric tumoral tissues than in adjacent non-tumoral tissues | [83] |
| FH | Squamous lung cancer | Plasma: Up-regulation of FH in uranium exposed miners in comparison with exposed miners without lung disease | [84] |
| Lung cancer | Bronchoalveolar lavage: Higher concentration of factor H in lung cancer patients than controls | [85] | |
| Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma | Tumor: FH is more expressed in invasive cSCC than normal skin or in situ cSCC. | [56] | |
| Bladder cancer | Urines: FH and FH related protein are markers for bladder cancer | [86,87] | |
| FI | Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma | Tumor: FI is more expressed in invasive cSCC than normal skin or in situ cSCC. | [28] |
| C9 | Squamous cell lung cancer | Plasma: C9 and its fucosylated form are significantly higher in SQLC patients, as compared to healthy control | [88] |
| CD46 | Colon cancer | Tumor: CD46 is higher in colon cancer tissues compared with normal adjacent colon tissues | [89] |
| CD55 | Colon cancer | Tumor: CD55 is higher in colon cancer tissues compared with normal adjacent colon tissues | [89] |
| CD59 | Colon cancer | Tumor: CD59 is higher in colon cancer tissues compared with normal adjacent colon tissues | [89] |
| MASP2 | Ovarian tumor | Tumor: MASP2 gene expression is higher with ovarian cancer compared with controls | [90] |
| MBL | Colon tumor | Plasma: MBL2 levels increases in patients compared to healthy blood donors. | [91] |
| Ovarian tumor | Tumor: MBL2 gene expression is higher with ovarian cancer compared with controls | [90] | |
| Underexpression | |||
| C1s | Ovarian cancer | Tumor: Down-regulation of C1s mRNA in ovarian tumor vs healthy control | [92] |
| Ovarian cancer | Tumor: Down-regulation of C1s expression in stage III serous ovarian carcinoma compared to normal tissue | [93] | |
| Lung cancer | Tumor: decrease expression in lung tumor tissues in comparison with peritumoral tissues | [73] | |
| C4BP | Ovarian cancer | Tumor: Down-regulation of C4BPA mRNA in ovarian tumor vs healthy control | [92] |
| C7 | Ovarian cancer | Tumor: Down-regulation of C7 mRNA in ovarian tumor vs healthy control | [92] |
| FB | Glioblastoma | Plasma: decreased level of FB in GBM | [72] |
| FI | Gastric cancer | Plasma: FI is significantly lower in gastric cancer sera compared to normal sera. Declining expression with the advanced pTNM stage from stage I to IV of gastric cancer patients | [94] |
| FH | Colon cancer | Plasma: Decrease in FH protein level in the serum of colorectal cancer patients vs. normal control | [95] |
| Ovarian cancer | Tumor: Down-regulation of FH mRNA in ovarian tumor vs healthy control | [92] | |
| CD55 | Ovarian cancer | Tumor: Lower expression of CD55 in ovarian cancer than in control | [30] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Revel, M.; Daugan, M.V.; Sautés-Fridman, C.; Fridman, W.H.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement System: Promoter or Suppressor of Cancer Progression? Antibodies 2020, 9, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040057
Revel M, Daugan MV, Sautés-Fridman C, Fridman WH, Roumenina LT. Complement System: Promoter or Suppressor of Cancer Progression? Antibodies. 2020; 9(4):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleRevel, Margot, Marie V. Daugan, Catherine Sautés-Fridman, Wolf H. Fridman, and Lubka T. Roumenina. 2020. "Complement System: Promoter or Suppressor of Cancer Progression?" Antibodies 9, no. 4: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040057
APA StyleRevel, M., Daugan, M. V., Sautés-Fridman, C., Fridman, W. H., & Roumenina, L. T. (2020). Complement System: Promoter or Suppressor of Cancer Progression? Antibodies, 9(4), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9040057