Evolutionary Algorithms for Community Detection in Continental-Scale High-Voltage Transmission Grids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Community Detection
2.1. Community Detection: General Overview
2.2. Community Detection in Power Grids
3. Methodology
- The modularity and improved genetic algorithm (MIGA) [54] takes the modularity (Q) as the objective function, and uses the number of community structures as prior information to improve stability and accuracy of community detection. MIGA also uses simulated annealing [55] as local search strategy. Note that many authors have previously considered the use of local search strategies [56] for solving hard optimisation problems.
- The generational genetic algorithm (GGA+): GGA+ [57] includes efficient and safe initialisation methods in which a maximum node size is assigned to each community. Several operators are applied to migrate or exchange nodes between communities while using the modularity function as the objective function. An important feature of GGA+ is that it is able to rapidly obtain community partitions with different degrees of abstraction.
4. Empirical Study
4.1. Test Cases
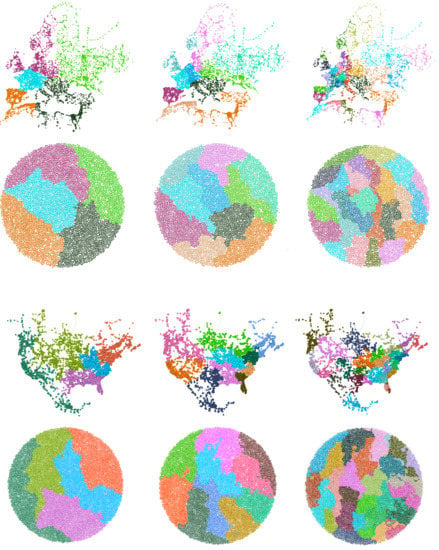
- The European electric network was obtained from the European Network of Transmission System Operators (ENTSO-E) [58]. The ENTSO-E group consists of 43 electricity transmission system operators from 36 countries across Europe who are responsible for the bulk transmission of electric power on the main high-voltage electric networks. This power network, which also includes data from North African and Near Eastern countries, is formed by transmission lines designed for 220 kV voltage and higher and generation stations with a net generation capacity of more than 100 MW.
- The North American electric network was obtained using the GridKit 1.0 toolkit, which was developed in the context of the SciGRID project at the NEXT ENERGY-EWE Research Centre for Energy Technology [59]. GridKit is a power grid extraction tool that converts geographical objects representing elements of power systems in OpenStreetMap to model the electric network. This network covers the United States, Canada, and Mexico and includes transmission lines that operate at relatively high-voltages varying from 69 kV up to 765 kV. The power grid of the United States is probably the best system studied in the literature, due to the particular characteristics of the network. The regions covered receive their bulk electricity from three separate electric grids: the huge Eastern Interconnection, the Western Interconnection, and the relatively small Texas grid [60], which is almost entirely managed by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT).
4.2. Parameter Configuration
4.3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alqurashi, A.; Etemadi, A.H.; Khodaei, A. Treatment of uncertainty for next generation power systems: State-of-the-art in stochastic optimization. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 141, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, L. Distributed optimization approaches for emerging power systems operation: A review. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 144, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.M.; Teng, J.H. Three-phase distribution network fast-decoupled power flow solutions. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2000, 22, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S.; Jurado, F. Power flow analysis with easy modelling of interline power flow controller. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2014, 108, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglini, A.; Komendantova, N.; Brtnik, P.; Patt, A. Perception of barriers for expansion of electricity grids in the European Union. Energy Policy 2012, 47, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codetta-Raiteri, D.; Bobbio, A.; Montani, S.; Portinale, L. A dynamic Bayesian network based framework to evaluate cascading effects in a power grid. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 25, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA; OECD. Security of Supply in Electricity Markets. Evidence and Policy Issues. 2002. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/energy/security-of-supply-in-electricity-markets_9789264174504-en (accessed on 11 November 2019).
- ENTSO-E. Ten-Year Network Development Plan 2010–2020. 2010. Available online: https://www.entsoe.eu/fileadmin/user_upload/_library/SDC/TYNDP/TYNDP-final_document.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2019).
- Cochran, J.; Denholm, P.; Speer, B.; Miller, M. Grid Integration and the Carrying Capacity of the U.S. Grid to Incorporate Variable Renewable Energy; Technical Report NREL/TP-6A20-62607; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bornholdt, S.; Schuster, H.G. Handbook of Graphs and Networks: From the Genome to the Internet; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Espejo, R.; Lumbreras, S.; Ramos, A. Analysis of transmission-power-grid topology and scalability, the European case study. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 509, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, B.D.; Sánchez-García, R.J.; Anderson, J.W. Symmetry in complex networks. Discret. Appl. Math. 2008, 156, 3525–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortunato, S. Community detection in graphs. Phys. Rep. 2010, 486, 75–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortunato, S.; Hric, D. Community detection in networks: A user guide. Phys. Rep. 2016, 659, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, M.E. Communities, modules and large-scale structure in networks. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Zhou, Z. Complex network measurement and optimization of Chinese domestic movies with internet of things technology. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Cao, B.; Zhou, G.; Sun, J. The monitoring and research of unstable locations in eco-industrial networks. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 105, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Dong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wei, G.; Xing, L.; Yan, J. Structure analysis and core community detection of embodied resources networks among regional industries. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 479, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, G.A.; Aiello, M. The Power Grid as a complex network: A survey. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2013, 392, 2688–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pahwa, S.; Youssef, M.; Schumm, P.; Scoglio, C.; Schulz, N. Optimal intentional islanding to enhance the robustness of power grid networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2013, 392, 3741–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-García, R.J.; Fennelly, M.; Norris, S.; Wright, N.; Niblo, G.; Brodzki, J.; Bialek, J.W. Hierarchical Spectral Clustering of Power Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 29, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Q. Community detection based on local topological information and its application in power grid. Neurocomputing 2015, 170, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.; Girvan, M. Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 026113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IEA. Large-Scale Electricity Interconnection. Technology and Prospects for Cross-Regional Networks. 2016. Available online: https://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/Interconnection.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2019).
- Reihanian, A.; Feizi-Derakhshi, M.R.; Aghdasi, H.S. Community detection in social networks with node attributes based on multi-objective biogeography based optimization. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 62, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.A.; Younis, M.S.; Latif, S.; Qadir, J.; Baig, A. Community detection in networks: A multidisciplinary review. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 108, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanavos, A.; Perikos, I.; Hatzilygeroudis, I.; Tsakalidis, A. Emotional community detection in social networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 65, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.P.; Dinh, T.N.; Shen, Y.; Thai, M.T. Dynamic social community detection and its applications. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, S.S.; El-Sayed, M.F.; Hassan, Y.F. Semantic clustering of search engine results. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 931258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kicsi, A.; Csuvik, V.; Vidács, L.; Horváth, F.; Beszédes, Á.; Gyimóthy, T.; Kocsis, F. Feature analysis using information retrieval, community detection and structural analysis methods in product line adoption. J. Syst. Softw. 2019, 155, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atay, Y.; Koc, I.; Babaoglu, I.; Kodaz, H. Community detection from biological and social networks: A comparative analysis of metaheuristic algorithms. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 50, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozylowicz, L.; Nita, A.; Manolache, S.; Popescu, V.D.; Hartel, T. Navigating protected areas networks for improving diffusion of conservation practices. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soofi, S.; Ahmed, S.; Fox, M.P.; MacLeod, W.B.; Thea, D.M.; Qazi, S.A.; Bhutta, Z.A. Effectiveness of community case management of severe pneumonia with oral amoxicillin in children aged 2–59 months in Matiari district, rural Pakistan: A cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Núñez, A.J.; Batagelj, V.; Vargas-Quesada, B.; Moya-Anegón, F.; Chinchilla-Rodríguez, Z. Optimizing SCImago Journal & Country Rank classification by community detection. J. Informetr. 2014, 8, 369–383. [Google Scholar]
- Carusi, C.; Bianchi, G. Scientific community detection via bipartite scholar/journal graph co-clustering. J. Informetr. 2019, 13, 354–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.O. An overview of social networks and economic applications. In Handbook of Social Economics; North-Holland (Elsevier): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 511–585. [Google Scholar]
- Arcia-Garibaldi, G.; Cruz-Romero, P.; Gómez-Expósito, A. Future power transmission: Visions, technologies and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarco, C.L.; Baone, C.A. Control of Power Systems with High Penetration Variable Generation. In Renewable Energy Integration: Practical Management of Variability, Uncertainty, and Flexibility in Power Grids, 2nd ed.; Academic Press (Elsevier): San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Krad, I.; Florita, A.; Hodge, B.M.; Ibanez, E.; Zhang, J.; Ela, E. Stochastic multi-timescale power system operations with variable wind generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 32, 3325–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlachtberger, D.; Brown, T.; Schramm, S.; Greiner, M. The benefits of cooperation in a highly renewable European electricity network. Energy 2017, 134, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teichler, S.L.; Levitine, I. HVDC transmission: A path to the future? Electr. J. 2010, 23, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzivasileiadis, S.; Ernst, D.; Andersson, G. The global grid. Renew. Energy 2013, 57, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, M. Spatial Networks. Phys. Rep. 2011, 499, 1–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrero, M.; Montoya, F.G.; Baños, R.; Alcayde, A.; Gil, C. Community detection in national-scale high voltage transmission networks using genetic algorithms. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 38, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Min, X. Vulnerability analysis and critical areas identification of the power systems under terrorist attacks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 473, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.C.; Pitsoulis, L. Community detection by modularity maximization using GRASP with path relinking. Comput. Oper. Res. 2013, 40, 3121–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandes, U.; Delling, D.; Gaertler, M.; Gorke, R.; Hoefer, M.; Nikoloski, Z.; Wagner, D. On modularity clustering. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2008, 20, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DasGupta, B.; Desai, D. On the complexity of Newman’s community finding approach for biological and social networks. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2013, 79, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fogel, D.B. Evolutionary Computation: Toward a New Philosophy of Machine Intelligence, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; 384p. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems: An Introductory Analysis with Applications to Biology, Control, and Artificial Intelligence; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975; 183p. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, P.; Montoya, F.G.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F.; Gil, C. Genetic algorithm for S-transform optimisation in the analysis and classification of electrical signal perturbations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 6766–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Han, B.; Ni, M. A topology analysis and genetic algorithm combined approach for power network intentional islanding. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 71, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Kumar, A. Optimal coordination of directional over current relays using a modified real coded genetic algorithm: A comparative study. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 82, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Bai, J.; Jiao, L.; Jinm, C. Community detection based on modularity and an improved genetic algorithm. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2013, 392, 1215–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Vecchi, M.P.; Gelatt, C.D. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 1983, 220, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizys, R.; Juan, A.A.; Sawik, B.; Calvet, L. A biased-randomized iterated local search algorithm for rich portfolio optimization. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrero, M.; Montoya, F.G.; Baños, R.; Alcayde, A.; Gil, C. Adaptive community detection in complex networks using genetic algorithms. Neurocomputing 2017, 266, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENTSO-E. ENTSO-E Transmission System Map. 2019. Available online: https://www.entsoe.eu/map/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 11 November 2019).
- Wiegmans, B. GridKit 1.0 ’for Scientists’ (Version v1.0). Zenodo. 2016. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/47263#.XeT6e2ZumiM (accessed on 11 November 2019).
- Mazur, A.; Metcalfe, T. America’s three electric grids: Are efficiency and reliability functions of grid size? Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2012, 89, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacomy, M.; Venturini, T.; Heymann, S.; Bastian, M. ForceAtlas2, a continuous graph layout algorithm for handy network visualization designed for the Gephi software. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TresAmigas. Tres Amigas Superstation Project. 2019. Available online: http://www.tresamigasllc.com/ (accessed on 11 November 2019).







| Feature | EU Grid | NA Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Nodes | 7893 | 16,063 |
| Edges | 10,346 | 20,169 |
| Average degree | 2.62 | 2.51 |
| Network diameter | 108 | 158 |
| Avg. path length | 41.27 | 48.99 |
| Avg. clustering coefficient | 0.07 | 0.01 |
| Eigenvector centrality | 1.70 | 1.87 |
| Grid | Method | Metric | c = 2 | c = 3 | c = 4 | c = 5 | c = 10 | c = 20 | c = 30 | c = 40 | c = 50 | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | Max(Q) | 0.496 | 0.660 | 0.740 | 0.785 | 0.877 | 0.911 | 0.921 | 0.924 | 0.922 | 0.804 | |
| Mean(Q) | 0.495 | 0.654 | 0.736 | 0.781 | 0.872 | 0.909 | 0.918 | 0.922 | 0.921 | 0.801 | ||
| MIGA | Min(Q) | 0.491 | 0.612 | 0.730 | 0.777 | 0.866 | 0.907 | 0.916 | 0.920 | 0.919 | 0.793 | |
| SD(Q) | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | ||
| Mean time | 515 | 632 | 404 | 409 | 289 | 296 | 205 | 237 | 246 | 359 | ||
| Max(Q) | 0.498 | 0.665 | 0.746 | 0.793 | 0.889 | 0.929 | 0.941 | 0.943 | 0.948 | 0.817 | ||
| Mean(Q) | 0.498 | 0.663 | 0.744 | 0.793 | 0.887 | 0.927 | 0.938 | 0.942 | 0.947 | 0.815 | ||
| GGA+ | Min(Q) | 0.496 | 0.661 | 0.742 | 0.791 | 0.885 | 0.925 | 0.937 | 0.940 | 0.946 | 0.814 | |
| SD(Q) | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | ||
| Mean time | 661 | 614 | 556 | 417 | 443 | 462 | 314 | 228 | 244 | 438 | ||
| Louvain | (Q) | 0.291 | 0.599 | 0.677 | 0.699 | 0.874 | 0.929 | 0.939 | 0.944 | 0.945 | 0.766 | |
| NA | Max(Q) | 0.498 | 0.663 | 0.743 | 0.788 | 0.882 | 0.924 | 0.939 | 0.945 | 0.948 | 0.814 | |
| Mean(Q) | 0.498 | 0.659 | 0.740 | 0.789 | 0.878 | 0.922 | 0.937 | 0.944 | 0.947 | 0.813 | ||
| MIGA | Min(Q) | 0.497 | 0.656 | 0.736 | 0.785 | 0.872 | 0.921 | 0.936 | 0.943 | 0.946 | 0.810 | |
| SD(Q) | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | ||
| Mean time | 1228 | 770 | 708 | 747 | 425 | 317 | 423 | 559 | 244 | 602 | ||
| Max(Q) | 0.499 | 0.670 | 0.753 | 0.804 | 0.900 | 0.943 | 0.956 | 0.963 | 0.967 | 0.828 | ||
| Mean(Q) | 0.499 | 0.669 | 0.753 | 0.802 | 0.898 | 0.940 | 0.955 | 0.962 | 0.966 | 0.827 | ||
| GGA+ | Min(Q) | 0.498 | 0.667 | 0.751 | 0.801 | 0.893 | 0.936 | 0.954 | 0.961 | 0.965 | 0.825 | |
| SD(Q) | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | ||
| Mean time | 1909 | 1335 | 1221 | 568 | 521 | 764 | 593 | 552 | 298 | 862 | ||
| Louvain | (Q) | 0.478 | 0.608 | 0.652 | 0.754 | 0.881 | 0.935 | 0.952 | 0.959 | 0.963 | 0.798 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guerrero, M.; Baños, R.; Gil, C.; Montoya, F.G.; Alcayde, A. Evolutionary Algorithms for Community Detection in Continental-Scale High-Voltage Transmission Grids. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11121472
Guerrero M, Baños R, Gil C, Montoya FG, Alcayde A. Evolutionary Algorithms for Community Detection in Continental-Scale High-Voltage Transmission Grids. Symmetry. 2019; 11(12):1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11121472
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuerrero, Manuel, Raul Baños, Consolación Gil, Francisco G. Montoya, and Alfredo Alcayde. 2019. "Evolutionary Algorithms for Community Detection in Continental-Scale High-Voltage Transmission Grids" Symmetry 11, no. 12: 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11121472
APA StyleGuerrero, M., Baños, R., Gil, C., Montoya, F. G., & Alcayde, A. (2019). Evolutionary Algorithms for Community Detection in Continental-Scale High-Voltage Transmission Grids. Symmetry, 11(12), 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11121472