Olfactory Laterality Is Valence-Dependent in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
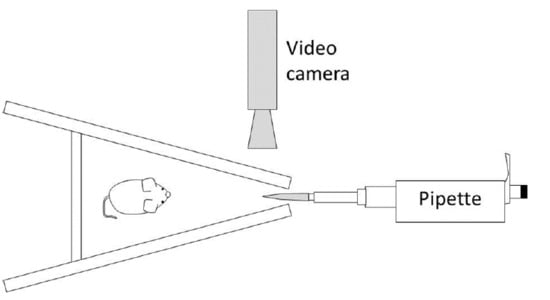
2.2. Apparatus and Odour Stimuli
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knaden, M.; Hansson, B.S. Mapping odor valence in the brain of flies and mice. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 24, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, F. Wiring olfaction: The cellular and molecular mechanisms that guide the development of synaptic connections from the nose to the cortex. Front. Neurosci. 2009, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.L. The central olfactory and accessory olfactory system. In Neurobiology of Taste and Smell; Finger, T.E., Silver, W.L., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 179–203. [Google Scholar]
- Schwob, J.E.; Price, J.L. The development of axonal connections in the central olfactory system of rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 223, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberly, L.B.; Price, J.L. Association and commissural fiber systems of the olfactory cortex of the rat. I. Systems originating in the piriform cortex and adjacent areas. J. Comp. Neurol. 1978, 178, 711–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayakawa, K.; Kobayakawa, R.; Matsumoto, H.; Oka, Y.; Imai, T.; Ikawa, M.; Okabe, M.; Ikeda, T.; Itohara, S.; Kikusui, T.; et al. Innate versus learned odour processing in the mouse olfactory bulb. Nature 2007, 450, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadziola, M.A.; Tylicki, K.A.; Christian, D.L.; Wesson, D.W. The olfactory tubercle encodes odor valence in behaving mice. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4515–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampin, O.; Bellier, C.; Maurin, Y. Electrophysiological responses of rat olfactory tubercle neurons to biologically relevant odours. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, K.; Bhalla, U.S. Laterality and symmetry in rat olfactory behavior and in physiology of olfactory input. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5750–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.A. Binaral interactions in the rat piriform cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 1997, 78, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Hall, W.G. New routes to early memories. Science 1987, 238, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.; Arnold, H.M.; Hall, W.G. Unilateral conditioning of an odor aversion in 6-day-old rat pups. Behav. Neurosci. 1995, 109, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaudon, P.; Bouillot, C.; Zimmer, L.; Costes, N.; Ravel, N. Activity in the rat olfactory cortex is correlated with behavioral response to odor: A microPET study. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R.; Tazi, A.; Bluthé, R.M. Cerebral lateralization of olfactory-mediated affective processes in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1990, 40, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olds, J.L.; Bhalla, U.S.; McPhie, D.L.; Lester, D.S.; Bower, J.M.; Alkon, D.L. Lateralization of membrane-associated protein kinase C in rat piriform cortex: Specific to operant training cues in the olfactory modality. Behav. Brain. Res. 1994, 61, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Putrino, D.; Wilson, D.A. Dynamic cortical lateralization during olfactory discrimination learning. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Wilson, D.A. Task-correlated cortical asymmetry and intra-and inter-hemispheric separation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Greevy, P.D.; Rogers, L.J. Motor and sensory laterality in thoroughbred horses. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2005, 92, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalchi, M.; Sasso, R.; Pepe, A.M.; Dimatteo, S.; Vallortigara, G.; Quaranta, A. Sniffing with the right nostril: Lateralization of response to odour stimuli by dogs. Anim. Behav. 2011, 82, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boyer des Roches, A.; Richard-Yris, M.A.; Henry, S.; Ezzaouïa, M.; Hausberger, M. Laterality and emotions: Visual laterality in the domestic horse (Equus caballus) differs with objects’ emotional value. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalchi, M.; Padalino, B.; Aubé, L.; Quaranta, A. Right-nostril use during sniffing at arousing stimuli produces higher cardiac activity in jumper horses. Laterality 2015, 20, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalchi, M.; d’Ingeo, S.; Quaranta, A. The dog nose “KNOWS” fear: Asymmetric nostril use during sniffing at canine and human emotional stimuli. Behav. Brain. Res. 2016, 304, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G.; Andrew, R.J. Divided Brains: The Biology and Behaviour of Brain Asymmetries; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Royet, J.P.; Plailly, J. Lateralization of olfactory processes. Chem. Senses 2004, 29, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikusui, T.; Kajita, M.; Otsuka, N.; Hattori, T.; Kumazawa, K.; Watarai, A.; Nagasawa, M.; Inutsuka, A.; Yamanaka, A.; Matsuo, N. Sex differences in olfactory-induced neural activation of the amygdala. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 346, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karenina, K.; Giljov, A.; Ingram, J.; Rowntree, V.J.; Malashichev, Y. Lateralization of mother–infant interactions in a diverse range of mammal species. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisman, H.; Hayley, S.; Kelly, O.; Borowski, T.; Merali, Z. Psychogenic, neurogenic, and systemic stressor effects on plasma corticosterone and behavior: Mouse strain-dependent outcomes. Behav. Neurosci. 2001, 115, 443–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquenot, D.; Ruscoe, W.A. Mouse population eruptions in New Zealand forests: The role of population density and seedfall. J. Anim. Ecol. 2000, 69, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caut, S.; Casanovas, J.G.; Virgos, E.; Lozano, J.; Witmer, G.W.; Courchamp, F. Rats dying for mice: Modelling the competitor release effect. Austr. Ecol. 2007, 32, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leliveld, L.M.; Langbein, J.; Puppe, B. The emergence of emotional lateralization: Evidence in non-human vertebrates and implications for farm animals. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 145, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.M.; Dufresne, M.M.; Waldron, J. Lateralized sex differences in stress-induced dopamine release in the rat. NeuroReport 2009, 20, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.C.; Blanchard, R.J. Innate and conditioned reactions to threat in rats with amygdaloid lesions. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1972, 81, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, R.E.; Blundell, J.; Collins, A. Neural plasticity and stress induced changes in defense in the rat. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2001, 25, 721–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, R.E.; Blundell, J.; Burton, P. Phosphorylated cyclic AMP response element binding protein expression induced in the periaqueductal gray by predator stress: Its relationship to the stress experience, behavior and limbic neural plasticity. Prog Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 1243–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, R.; Blundell, J.; Burton, P. Role of NMDA receptors in the lateralized potentiation of amygdala afferent and efferent neural transmission produced by predator stress. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 86, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.N.; Fitzgerald, L.W.; Keller, R.W., Jr.; Glick, S.D. Side and region dependent changes in dopamine activation with various durations of restraint stress. Brain Res. 1991, 550, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohl, F.; Roedel, A.; Binder, E.; Holsboer, F. Impact of high and low anxiety on cognitive performance in a modified hole board test in C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.W.; Kerr, L.E.; Kelly, J.S.; Marston, H.M.; Spratt, C.; Finlayson, K.; Sharkey, J. The odour span task: A novel paradigm for assessing working memory in mice. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.J. Emotion and affective style: Hemispheric substrates. Psychol. Sci. 1992, 3, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Species/Strain/Sex | Brain Structure | Side | Measure | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rats/Long Evans males | anterior PC | LEFT | Enhanced beta frequency band oscillations during the first stages of odour discrimination learning Performance-and context-dependent asymmetry | [16] |
| Rats/Long Evans males | anterior PC orbitofrontal cortex | LEFT RIGHT | Enhanced odour-evoked activity during initial stages of odour discrimination learning | [17] |
| Rats/Sprague Dawley females | PC | LEFT | Olfactory-learning specific lateralisation of translocation of enzyme protein kinase C from cytosol to membrane | [15] |
| Rats/Wistar males | OB | LEFT | Absence of adaptive response to the odour of a stressed conspecific when lesioned | [14] |
| Rats/Wistar males | anterior PC lateral amygdala | LEFT | Activation correlated with behavioural responsiveness | [13] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jozet-Alves, C.; Percelay, S.; Bouet, V. Olfactory Laterality Is Valence-Dependent in Mice. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091129
Jozet-Alves C, Percelay S, Bouet V. Olfactory Laterality Is Valence-Dependent in Mice. Symmetry. 2019; 11(9):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091129
Chicago/Turabian StyleJozet-Alves, Christelle, Solenn Percelay, and Valentine Bouet. 2019. "Olfactory Laterality Is Valence-Dependent in Mice" Symmetry 11, no. 9: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091129
APA StyleJozet-Alves, C., Percelay, S., & Bouet, V. (2019). Olfactory Laterality Is Valence-Dependent in Mice. Symmetry, 11(9), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11091129