Mineralogical Record for Stepwise Hydroclimatic Changes in Lake Qinghai Sediments Since the Last Glacial Period
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Settings
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
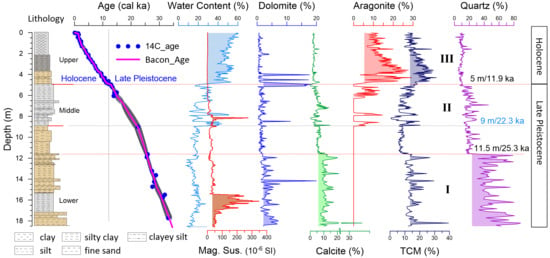
4.1. Lithostratigraphic Units
4.2. Bulk Mineral Composition
5. Discussion
5.1. Hydroclimatic Significance of Minerals
5.1.1. Quartz
5.1.2. Carbonate Minerals
5.2. Stepwise Hydroclimate Dynamics Since the Last Glacial Period
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, Z.S.; Colman, S.M.; Zhou, W.J.; Li, X.Q.; Brown, E.T.; Jull, A.J.T.; Cai, Y.J.; Huang, Y.S.; Lu, X.F.; Chang, H.; et al. Interplay between the Westerlies and Asian monsoon recorded in Lake Qinghai sediments since 32 ka. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.C.G.; Holmes, J.A.; Leng, M.J. Late Holocene isotope hydrology of Lake Qinghai, NE Tibetan Plateau: Effective moisture variability and atmospheric circulation changes. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, A.C.G.; Holmes, J.A. Palaeolimnological evidence for environmental change over the past millennium from Lake Qinghai sediments: A review and future research prospective. Quat. Int. 2009, 194, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, S.M.; Yu, S.Y.; An, Z.S.; Shen, J.; Henderson, A.C.G. Late Cenozoic climate changes in China’s western interior: A review of research on Lake Qinghai and comparison with other records. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2007, 26, 2281–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, M.X.; Song, Y.G.; An, Z.S.; Chang, H.; Li, Y. Clay mineral records of the Erlangjian drill core sediments from the Lake Qinghai Basin, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1846–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.F.; An, Z.S.; Qiang, X.K.; Bloemendal, J.; Song, Y.G.; Chang, H. Magnetostratigraphic determination of the age of ancient Lake Qinghai, and record of the East Asian monsoon since 4.63 Ma. Geology 2013, 41, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, H.; An, Z.; Hu, L. Reevaluation of carbonate concentration and oxygen isotope records from Lake Qinghai, the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 2018, 482, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, W. Lake evolution and hydroclimate variation at Lake Qinghai (China) over the past 32 ka inferred from ostracods and their stable isotope composition. J. Paleolimnol. 2017, 58, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, N.A.; Li, Z.L.; Zhou, X.H.; Zhang, C.Q.; Wang, Y. Carbonate formation and water level changes in a paleo-lake and its implication for carbon cycle and climate change, arid China. Front. Earth Sci. 2013, 7, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Colman, S.M.; Brown, E.T.; An, Z.; Zhou, W.; Jull, A.J.T.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Liu, W.; Xu, H. A climate threshold at the eastern edge of the Tibetan plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5598–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; An, Z.; Cheng, P.; Zhu, Y.; Burr, G.S. Geological record of meltwater events at Qinghai Lake, China from the past 40 ka. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 149, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, G.S.; Kelts, K.R.; Chen, K.Z.; Yu, J.Q.; Niessen, F. Lake Qinghai, China: Closed-basin lake levels and the oxygen isotope record for Ostracoda since the latest Pleistocene. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1991, 84, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Lu, R.; Lyu, Z.; Liu, X. Geochemical characteristics of Holocene aeolian deposits east of Qinghai Lake, China, and their paleoclimatic implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Cong, L.; An, F.; Miao, X.; Chongyi, E. Downwind aeolian sediment accumulations associated with lake-level variations of the Qinghai Lake during the Holocene, Northeastern Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.P.; Lai, Z.P. OSL chronology and palaeoclimatic implications of aeolian sediments in the eastern Qaidam Basin of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2012, 337–338, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhao, S.; Pei, H.; Yang, H. The coupled evolution of mid- to late Holocene temperature and moisture in the southeast Qaidam Basin. Chem. Geol. 2019, 528, 119282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chongyi, E.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Hou, G.; Duan, R. Climate change and anthropogenic activities in Qinghai Lake basin over the last 8500 years derived from pollen and charcoal records in an aeolian section. Catena 2020, 193, 104616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Song, Y.; Sun, H.; Bradák, B.; Orozbaev, R.; Zong, X.; Liu, H. Pronounced changes in paleo-wind direction and dust sources during MIS3b recorded in the Tacheng loess, northwest China. Quat. Int. 2020, 252, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; An, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, F. Lake Qinghai sediment geochemistry linked to hydroclimate variability since the last glacial. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 122, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Vandenberghe, J.; An, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Dong, J.; Sun, Y. Grain size of Lake Qinghai sediments: Implications for riverine input and Holocene monsoon variability. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 449, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.X.; Zhang, B.Z.; Qian, G.M.; Li, H.J.; Xu, L.M. The study of paleoclimatic parameter of Qinghai Lake since Holocene. Quat. Sci. 1994, 14, 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Xingqi, L.; Sumin, W.; Matsumoto, R. Palaeoclimatic changes in the Qinghai Lake area during the last 18,000 years. Quat. Int. 2005, 136, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Q.; Kelts, K.R. Abrupt changes in climatic conditions across the late-glacial/Holocene transition on the N. E. Tibet-Qinghai Plateau: Evidence from Lake Qinghai, China. J. Paleolimnol. 2002, 28, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.L.; Porter, S.C.; An, Z.S.; Kumai, H.; Yoshikawa, S. Grain Size of Quartz as an Indicator of Winter Monsoon Strength on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the Last 130,000 Yr. Quat. Res. 1995, 43, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zeng, M.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Chang, H.; An, Z.; Guo, X. Abrupt climatic events recorded by the Ili loess during the last glaciation in Central Asia: Evidence from grain-size and minerals. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 155, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lin, L.Z.; Yang, B. Clay Mineral in Sediment of Qinghai Lake. Sci. Geol. Sin. 1989, 24, 348–354. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, L. Evaluation of lacustrine organic δ13C as a lake-level indicator: A case study of Lake Qinghai and the satellite lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 532, 109274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Qiang, X.K.; Song, Y.G.; Ao, H.; An, Z.S. Identification of greigite in the late Pleistocene sediments of Lake Qinghai and its environmental implications. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 9, 2309–2316, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.M.; Jin, Z.D.; Wan, D.J.; Zhang, F. Spatial uniformity in the mineralogical and geochemical compositions of surface sediments in Lake Qinghai and their controlling factors. Limnology 2015, 16, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.M.; Yang, X.D.; Tong, G.B.; Zhang, E.L. A 16000-year pollen record of Qinghai Lake and its paleo-climate and paleoenvironment. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2002, 47, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Lake Qinghai: Paleoenvironment and Paleoclimate; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, E.K.; Huang, Y.S.; Morrill, C.; Zhao, J.T.; Wegener, P.; Clemens, S.C.; Colman, S.M.; Gao, L. Abundant C4 plants on the Tibetan Plateau during the Lateglacial and early Holocene. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 87, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, M. Hydrological trend of Qinghai Lake over the last 60 years: Driven by climate variations or human activities? J. Water Clim. Chang. 2019, 10, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; You, C.-F.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Hydrological and solute budgets of Lake Qinghai, the largest lake on the Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 2010, 218, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.P.; Tang, Y.; Xu, Z.Q.; Han, Z.M. A preliminary investigation on chemical evolution of the Lake Qinghai water. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1991, 36, 1172–1174. [Google Scholar]
- An, Z.S.; Wang, P.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, P.Z.; Wang, S.M.; Li, X.Q.; Sun, Q.L.; Song, Y.G.; Al, L.; et al. Geophysical survey on the tectonic and sediment distribution of Qinghai Lake basin. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Cheng, P.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Jull, A.J.T.; Wu, Z. 14C Chronostratigraphy for Qinghai Lake in China. Radiocarbon 2014, 56, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaauw, M.; Christen, J.A.; Bennett, K.D.; Reimer, P.J. Double the dates and go for Bayes—Impacts of model choice, dating density and quality on chronologies. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 188, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaauw, M.; Christen, J.A. Flexible paleoclimate age-depth models using an autoregressive gamma process. Bayesian Anal. 2011, 6, 457–474. [Google Scholar]
- Reimer, P.J.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Beck, J.W.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Buck, C.E.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M. IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0–50,000 years cal BP. Radiocarbon 2013, 55, 1869–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, M.X.; Song, Y.G. Application of the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm to X-ray diffraction quantitative phase analysis. Earth Sci. 2013, 38, 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.X.; Song, Y.G. Study on the Influencing Factors of the Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm for X-ray Diffraction Quantitative Phase Analysis. Rock Miner. Anal. 2012, 31, 798–806. [Google Scholar]
- Last, F.M.; Last, W.M. Lacustrine carbonates of the northern Great Plains of Canada. Sediment. Geol. 2012, 277, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; You, C.-F.; Yu, T.-L.; Wang, B.-S. Sources and flux of trace elements in river water collected from the Lake Qinghai catchment, NE Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y. Geochemistry of eolian dust and its elemental contribution to Lake Qinghai sediment. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; You, C.-F. Constraints on water chemistry by chemical weathering in the Lake Qinghai catchment, northeastern Tibetan Plateau (China): Clues from Sr and its isotopic geochemistry. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomonaga, Y.; Brennwald, M.S.; Livingstone, D.M.; Kwiecien, O.; Randlett, M.-È.; Stockhecke, M.; Unwin, K.; Anselmetti, F.S.; Beer, J.; Haug, G.H.; et al. Porewater salinity reveals past lake-level changes in Lake Van, the Earth’s largest soda lake. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHenry, L.J.; Kodikara, G.R.L.; Stanistreet, I.G.; Stollhofen, H.; Njau, J.K.; Schick, K.; Toth, N. Lake conditions and detrital sources of Paleolake Olduvai, Tanzania, reconstructed using X-ray Diffraction analysis of cores. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 556, 109855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrier, A.K.; Pednekar, H.; Mahesh, B.S.; Mohan, R.; Gazi, S. Sediment grain size and surface textural observations of quartz grains in late quaternary lacustrine sediments from Schirmacher Oasis, East Antarctica: Paleoenvironmental significance. Polar Sci. 2016, 10, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; An, Z.; Lu, F. Quantitively partition of eolian and hydromorphic components in lacustrine sediments: An example from lake Qinghai. J. Geomech. 2010, 16, 402–411. [Google Scholar]
- Kalińska-Nartiša, E.; Stivrins, N.; Grudzinska, I. Quartz grains reveal sedimentary palaeoenvironment and past storm events: A case study from eastern Baltic. Estuar Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 200, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morellón, M.; Valero-Garcés, B.; Moreno, A.; González-Sampériz, P.; Mata, P.; Romero, O.; Maestro, M.; Navas, A. Holocene palaeohydrology and climate variability in northeastern Spain: The sedimentary record of Lake Estanya (Pre-Pyrenean range). Quat. Int. 2008, 181, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Guo, G.; Yu, S. Quartz content of core SX97 in Zhoujiang River Estuary and its indication for climatic and environmental changes. J Trop. Ocenogr. 2001, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gierlowski-Kordesch, E.H. Lacustrine carbonates. Dev. Sedimentol. 2010, 61, 1–101. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Colman, S.M.; Brown, E.T.; Henderson, A.C.G.; Werne, J.P.; Holmes, J.A. Abrupt deglaciation on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from Lake Qinghai. J. Paleolimnol. 2014, 51, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, J.; Nehrke, G.; Jöns, N.; Immenhauser, A.; Kwiecien, O. Refining the interpretation of lacustrine carbonate isotope records: Implications of a mineralogy-specific Lake Van case study. Chem. Geol. 2019, 513, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LZBCAS. Evolution of Recent Environment in Qinghai Lake and Its Prediction, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, M.; Kelts, K. Primary and diagenetic carbonates in the anoxic sediments of Lake Bosumtwi, Ghana. Geology 1986, 14, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzschuh, U. Palaeo-moisture evolution in monsoonal Central Asia during the last 50,000 years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2006, 25, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.B.; Liu, X.Q.; Herzschuh, U. Asynchronous evolution of the Indian and East Asian Summer Monsoon indicated by Holocene moisture patterns in monsoonal central Asia. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 103, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.P.; Scuderi, L.; Paillou, P.; Liu, Z.T.; Li, H.W.; Ren, X.Z. Quaternary environmental changes in the drylands of China—A critical review. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2011, 30, 3219–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Herzschuh, U.; Shumilovskikh, L.S.; Mischke, S.; Birks, H.J.B.; Wischnewski, J.; Böhner, J.; Schlütz, F.; Lehmkuhl, F.; Diekmann, B. Quantitative reconstruction of precipitation changes on the NE Tibetan Plateau since the Last Glacial Maximum-extending the concept of pollen source-area to pollen-based climate reconstructions from large lakes. Clim. Past Discuss. 2014, 10, 536–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dykoski, C.A.; Edwards, R.L.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, D.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, M.L.; Lin, Y.S.; Qing, J.M.; An, Z.S.; Revenaugh, J. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 233, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Kong, X.; Shao, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; An, Z. Millennial- and orbital-scale changes in the East Asian monsoon over the past 224,000 years. Nature 2008, 451, 1090–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Sinha, A.; Spotl, C.; Yi, L.; Chen, S.; Kelly, M.; Kathayat, G.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; et al. The Asian monsoon over the past 640,000 years and ice age terminations. Nature 2016, 534, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.G.; Lai, Z.P.; Han, L.; An, Z.S. Rapid and Cyclic Dust Accumulation during MIS 2 in Central Asia Inferred from Loess OSL Dating and Grainsize Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Railsback, L.B.; Brook, G.A.; Chen, J.; Kalin, R.; Fleisher, C.J. Environmental controls on the petrology of a Late Holocene speleothem from Botswana with annual layers of aragonite and calcite. J. Sediment. Res. 1994, 64, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.X.; Zhang, B.Z.; Yang, W.B. On the model of post-glacial palaeoclimatic fluctuation in Qinghai lake region. Quat. Sci. 1989, 9, 66–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Fu, M.; An, Z. A new approach for reconstructing Holocene temperatures from a multi-species long chain alkenone record from Lake Qinghai on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Org. Geochem. 2015, 88, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Lab Code | Depth (cm) | Date Material | Measured 14C Age (yr BP) | Calibrated Age (Cal yr BP) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14C Age | Error | Lower | Upper | Median | |||
| AA78739 | 1 | TOC | 30 | 30 | 30 | 140 | 60 |
| AA78740 | 5 | TOC | 200 | 35 | 80 | 310 | 180 |
| XA2718 | 8 | TOC | 1210 | 40 | 1060 | 1260 | 1140 |
| XA1748 | 9 | TOC | 1430 | 30 | 1290 | 1380 | 1330 |
| XA2730 | 21 | TOC | 1550 | 20 | 1390 | 1520 | 1470 |
| XA2771 | 44 | TOC | 1220 | 40 | 1060 | 1270 | 1150 |
| XA2770 | 62 | TOC | 1780 | 40 | 1570 | 1820 | 1700 |
| XA2769 | 83 | TOC | 2000 | 40 | 1870 | 2060 | 1950 |
| XA2721 | 86 | TOC | 2310 | 30 | 2190 | 2360 | 2340 |
| XA2711 | 104 | TOC | 2180 | 20 | 2130 | 2310 | 2240 |
| XA2768 | 128 | TOC | 2470 | 40 | 2360 | 2710 | 2560 |
| XA2766 | 171 | TOC | 3565 | 40 | 3720 | 3970 | 3865 |
| XA2713 | 194 | TOC | 3740 | 20 | 3990 | 4220 | 4110 |
| XA2765 | 215 | TOC | 4340 | 40 | 4840 | 5040 | 4920 |
| XA2764 | 238 | TOC | 4380 | 40 | 4860 | 5050 | 4940 |
| XA2763 | 257 | TOC | 4990 | 50 | 5610 | 5890 | 5720 |
| XA2700 | 282 | TOC | 5570 | 20 | 6310 | 6400 | 6350 |
| AA77753 * | 284 | TOC | 5708 | 40 | 6380 | 6620 | 6498 |
| XA2762 | 316 | TOC | 6270 | 40 | 7030 | 7270 | 7210 |
| XA2759 | 344 | TOC | 6780 | 55 | 7520 | 7720 | 7630 |
| XA2758 | 368 | TOC | 7510 | 40 | 8200 | 8400 | 8335 |
| XA2716 | 391 | TOC | 8450 | 30 | 9440 | 9530 | 9485 |
| XA2757 | 412 | TOC | 8600 | 50 | 9500 | 9680 | 9560 |
| XA1756 * | 413 | TOC | 8580 | 45 | 9485 | 9665 | 9540 |
| AA77711 | 416 | seed | 8540 | 50 | 9470 | 9580 | 9520 |
| XA2756 | 434 | TOC | 9430 | 50 | 10,520 | 11,060 | 10,660 |
| AA77712 | 454 | seed | 9280 | 50 | 10,280 | 10,580 | 10,460 |
| XA2755 | 455 | TOC | 9370 | 50 | 10,430 | 10,720 | 10,590 |
| AA77760 | 456 | TOC | 9410 | 60 | 10,430 | 11,060 | 10,640 |
| XA3200 | 463 | TOC | 10,235 | 30 | 11,830 | 12,080 | 11,990 |
| XA1586 * | 475 | seed | 9720 | 47 | 10,917 | 11,230 | 11,148 |
| AA78019 | 477 | TOC | 9755 | 60 | 10,880 | 11,270 | 11,190 |
| XA2701 | 480 | TOC | 9900 | 45 | 11,210 | 11,590 | 11,290 |
| AA77761 | 481 | TOC | 9890 | 50 | 11,200 | 11,600 | 11,290 |
| XA3195 | 485 | TOC | 10,290 | 30 | 11,840 | 12,230 | 12,070 |
| XA3194 | 490 | TOC | 10,310 | 30 | 11,990 | 12,350 | 12,100 |
| XA1752 | 497 | seed | 11,020 | 35 | 12,880 | 13,050 | 12,940 |
| XA2754 | 514 | TOC | 11,280 | 60 | 13,080 | 13,270 | 13,170 |
| XA3210 | 521 | TOC | 11,510 | 30 | 13,270 | 13,430 | 13,350 |
| XA3226 | 572 | TOC | 12,630 | 40 | 14,670 | 15,130 | 14,910 |
| XA2752 | 577 | TOC | 12,230 | 50 | 13,920 | 14,250 | 14,090 |
| AA77765 | 605 | TOC | 12,010 | 60 | 13,750 | 14,000 | 13,870 |
| AA78823 | 901 | TOC | 18,820 | 130 | 22,130 | 22,590 | 22,360 |
| XA3229 | 1162 | TOC | 21,680 | 70 | 25,370 | 26,420 | 25,880 |
| XA3963 | 1189 | TOC | 21,190 | 70 | 25,390 | 26,000 | 25,570 |
| XA2777 | 1323 | TOC | 22,620 | 100 | 26,960 | 27,730 | 27,370 |
| XA2705 | 1363 | TOC | 23,900 | 90 | 28,380 | 29,150 | 28,730 |
| XA2776 | 1425 | TOC | 23,350 | 160 | 27,910 | 28,330 | 28,130 |
| XA2775 | 1473 | TOC | 22,810 | 100 | 27,070 | 27,880 | 27,540 |
| AA77785 | 1550 | TOC | 27,250 | 335 | 31,690 | 32,200 | 31,940 |
| XA2774 | 1574 | TOC | 26,330 | 150 | 30,810 | 31,510 | 31,210 |
| AA77790 | 1773 | TOC | 28,670 | 300 | 32,665 | 33,605 | 33,150 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Zong, X.; Qian, L.; Liu, H.; Dong, J.; Chang, H.; Zhang, M. Mineralogical Record for Stepwise Hydroclimatic Changes in Lake Qinghai Sediments Since the Last Glacial Period. Minerals 2020, 10, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10110963
Song Y, Zong X, Qian L, Liu H, Dong J, Chang H, Zhang M. Mineralogical Record for Stepwise Hydroclimatic Changes in Lake Qinghai Sediments Since the Last Glacial Period. Minerals. 2020; 10(11):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10110963
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yougui, Xiulan Zong, Linbo Qian, Huifang Liu, Jibao Dong, Hong Chang, and Mingyu Zhang. 2020. "Mineralogical Record for Stepwise Hydroclimatic Changes in Lake Qinghai Sediments Since the Last Glacial Period" Minerals 10, no. 11: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10110963
APA StyleSong, Y., Zong, X., Qian, L., Liu, H., Dong, J., Chang, H., & Zhang, M. (2020). Mineralogical Record for Stepwise Hydroclimatic Changes in Lake Qinghai Sediments Since the Last Glacial Period. Minerals, 10(11), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10110963