Synthesis of Hydronium-Potassium Jarosites: The Effect of pH and Aging Time on Their Structural, Morphological, and Electrical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2SO2−4(aq) + 0.91K+(aq) + 3Fe(OH)3(s) + 0.007(Ag(CN)2)−(aq) + 0.166H2O
0.71NH+4(aq) + (0.04Ag(OH) + 2.85Fe(OH)3 + 0.21Ca(OH)2)(s. amorphous)
3Fe(OH)3(s) + 0.32Pb(OH)2(s) + 0.011Ag(OH)(s) + 0.7H2O
2. Materials and Methods
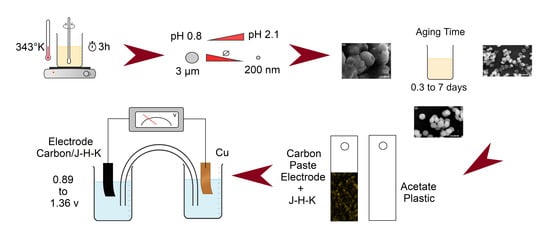
2.1. Synthesis of Hydronium-Potassium Jarosite
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Preparation of Electrodes and Evaluation of Electrical Conductivity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive Spectrometry (EDS) Analysis
3.3. Electrical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, G.K.; Anand, S.; Acharya, S.; Das, R.P. Preparation and decomposition of ammoniumjarosite at elevated temperatures in H2O(NH4)2SO4H2O media. Hydrometallurgy 1995, 38, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouet, C.; Navrotsky, A. Synthesis, characterisation and thermo-chemistry of K-Na-H3O jarosites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 2063–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.L.; Hudson-Edwars, K.A.; Dubbin, W.E.; Wright, K. Dissolution of jarosite [KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6] at pH 2 and 8: Insights from batch experiments and computational modelling. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuñez, C.; Roca, A. Concentration of Iron Oxides by Flotation from Gossan Ore Tailings. Can. Metall. Q. 1984, 23, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, F.; Salinas, E.; Cruells, M.; Roca, A. Alkaline decomposition-cyanidation kinetics of argentian natrojarosite. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 49, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruells, M.; Roca, A.; Patiño, F.; Salinas, E.; Rivera, I. Cyanidation kinetics of argentian jarosite in alkaline media. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 55, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, F.; Cruells, M.; Roca, A.; Salinas, E.; Pérez, M. Kinetics of alkaline decomposition and cyanidation of argentian ammonium jarosite in lime medium. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 70, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, F.; Flores, M.U.; Reyes, I.A.; Islas, H.; Reyes, M.; Juárez, G. Kinetic Modeling of the Alkaline Decomosition and Cyanidation of Argentian Plumbojarosite. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2014, 58, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.L.; Wen, Y.; Chen, C.C.; van Aken, P.A.; Maier, J.; Yu, Y. Nanosheets of earth-abundant jarosite as novel anodes for high-rate and high-life lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10518–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Smith, A.M.L.; Dubbin, W.E.; Bennettt, A.J.; Murphy, P.J.; Wright, K. Comparison of the structures of natural and synthetic Pb-Cu-jarosites-type compounds. Eur. J. Miner. 2008, 20, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, E.; Roca, A.; Cruells, M.; Patiño, F.; Córdoba, D.A. Characterization and alkaline decomposition-cyanidation kinetics of industrial ammonium jarosite in NaOH media. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 60, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Smith, A.M.L.; Dubbin, W.E.; Wright, K. Jarosite in acid mine drainage environments: Formation, mineralogy, stability. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual V. M. Goldschmidt Conference, Moscow, ID, USA, 20–25 May 2005; p. A765. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas, E.; Reyes, M.; Patiño, F.; Méndez, M.T.; Rivera, I.; Martínez, A.; Hernández, L. Factores que afectan el crecimiento de partículas de jarosita de amonio argentífera sintética. Rev. Soc. Quim. Mex. 2002, 46, 67–72. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Farrand, W.H.; Glotch, T.D.; Rice, J.W., Jr.; Hurowitz, J.L.A.; Swayze, G.A. Discovery of jarosite within the Mawrth Vallis region of Mars: Implications for the geologic history of the region. Icarus 2009, 204, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerolli-Mustafa, M.; Fajković, H.; Rončević, S.; Ćurković, L. Assessment of metals risks from different depths of jarosite tailing waste of Trepça Zinc Industry, Kosovo based on BCR procedure. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 148, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireles, I.; Reyes, I.A.; Flores, V.H.; Patiño, F.; Flores, M.U.; Reyes, M.; Acosta, M.; Cruz, R.; Gutierrez, E.J. Kinetics analysis of the decomposition of the KFe3(SO4)2-x(CrO4)xOH)6 jarosite solid solution in Ca(OH)2 medium. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 27, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Chan, C.K. Synthesis of jarosite and Vanadium jarosite analogues using microwave hydrothermal reaction and evaluation of composition-dependent electrochemical properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 9702–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forray, F.L.; Smith, A.M.L.; Navrotsky, A.; Wright, K.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Dibbin, W.E. Synthesis, characterization and thermochemistry of synthetic Pb-As, Pb-Cu and Pb-Zn jarosites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 127, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patiño, F.; Reyes, I.A.; Flores, M.U.; Pandiyan, T.; Roca, A.; Reyes, M.; Hernández, J. Kinetic modeling and experimental design of the sodium aresenojarosite decomposition in alkaline media: Implications. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 137, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouet, C.; Pass, K.L.; Baron, D.; Draucker, S.; Navrotsky, A. Thermochemistry of jarosite-alunite and natrojarosite-natroalunite solid solutions. Geochim. Cossmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A.; Velasco, F. Isótopos Estables en los Minerales de Drenaje Acido del Yacimiento de San Miguel (Faja Pirìtica Ibérica). Rev. Soc. Española Miner. 2008, 9, 27–28. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Salinas, E.; Cerecedo, E.; Ramírez, M.; Patiño, F.; Pérez, M. Kinetics ok alkaline decomposition and cyanidation of argentian rubidium jarosite in NaOH medium. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2012, 43B, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Labra, M.; Romero-Serrano, A.; Salinas-Rodriguez, E.; Avila-Davila, E.O.; Reyes-Perez, M. Synthesis, termo chemistry and kinetics of alkaline decomposition of rubidium jarosite in Ca(OH)2 media. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2012, 43, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunneriusson, L.; Sandström, A.; Holmgren, A.; Kuzmann, E.; Kovacs, K.; Vértes, A. Jarosite inclusion of fluoride and its potential significance to bioleaching of sulphide minerals. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 96, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xie, Z.; Cui, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, L.; Mai, L.; Wang, Y. Direct growth of an economic green energy storage material: Amonocrystalline jarosite-KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6—Nanoplates@rGO hybrid as a superior lithium-ion battery cathode. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 10, 3735–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.L.; Wen, Y.; van Aken, P.A.; Maier, J.; Yu, Y. Jarosite nanosheets fabricated via room-temperature synthesis as cathode materials for high-rate lithium ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inami, T.; Nishiyama, M.; Maegawa, S.; Oka, Y. Magnetic structure of the kagomé lattice antiferromagnet potassium jarosite KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2000, 61, 12181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basciano, L.C.; Peterson, R.C. Crystal chemistry of the natrojarosite-jarosite and natrojarosite-hydronium jarosite solid-solution series: A synthetic study with full Fe site occupancy. Am. Miner. 2008, 93, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, H.; Taniguchi, I. Synthesis of Li2FeP2O7/Carbon nanocomposite as cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 298, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Tian, W.; Shen, J.; Qiao, X.; Sun, T.; Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Facile fabrication of a jarosite ultrathin KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6@rGO nanosheet hybrid composite with pseudocapacitive contribution as a robust anode for lithium-ion batteries. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Lui, L.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, H.; Lu, Y. Electrochemical surface passivation of LiCoO2 particles at ultrahigh voltage and its applications in lithium-based batteries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Qin, C.; Yan, P.; Sui, M. Origins of capacity and voltage fading of LiCoO2 upon high voltage cycling. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20824–20831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandineni, P.; Asl, H.Y.; Choudhury, A. Kagomé lattices as cathode: Effect of particle size and fluoride substitution on electrochemical lithium insertion in sodium and ammonium jarosites. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 242, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J.E.; Kaiman, S. Synthesis and properties of jarosite type-compounds. Can. Miner. 1976, 14, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.W. A chemical study of some synthetic potassium-hydronium jarosites. Can. Miner. 1970, 10, 696–703. [Google Scholar]
- Kunda, W.; Veltman, H. Decomposition of Jarosite. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1979, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, F.; Ramírez, J. Síntesis y caracterización de argentojarosita y plumbojarosita. Rev. Soc. Quím. Mex. 1993, 37, 51–62. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Dutrizac, J.E.; Hardy, D.J. The behaviour of thiocyanate and the cyanate during jarosite precipitation. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 45, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, J.L.; Chimeros, J.M.; Queralt, I.; Viladevall, M.; Pérez, K.F.Y.F. Efecto del mineral de ganga en la síntesis de jarosita de potasio y su distribución de tamaños de partículas. Boletín Miner. 2006, 17, 21–28. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Roca, A.; Patiño, F.; Rivera, I.; Hernández, L.; Pérez, M.; Salinas, E.; Reyes, M. Decomposition and Cyanidation Kinetics of the Argentian Ammonium Jarosite in NaOH Media. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2007, 51, 47–54. [Google Scholar]






| Sample Name | pH | Aging Time |
|---|---|---|
| Jar-0.8-0 | 0.8 | 0 |
| Jar-1.1-0 | 1.1 | 0 |
| Jar-2.1-0 | 2.1 | 0 |
| Jar-2.1-3 | 2.1 | 3 |
| Jar-2.1-7 | 2.1 | 7 |
| Sample Name | Average Crystallite Size (nm) | a (nm) | c (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jar-0.8-0 | 14.5 | 7.316 | 17.15 |
| Jar-1.1-0 | 12.2 | 7.2995 | 17.12 |
| Jar-2.1-0 | 9.48 | 7.2748 | 17.10 |
| Jar-2.1-3 | 10.67 | 7.2837 | 17.12 |
| Jar-2.1-7 | 7.83 | 7.2684 | 17.07 |
| ICDDPDF 22-0827 | - | 7.29 | 17.13 |
| Sample Name | Potassium Jarosite (JK) (%) | Lattice Parameters | Hydronium Jarosite (JH) (%) | Lattice Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (nm) | c (nm) | a (nm) | c (nm) | |||
| Original | - | 7.2900 | 17.1600 | - | 7.3238 | 17.005 |
| Jar-0.8-0 | 22.29 | 7.3840 | 17.0320 | 77.71 | 7.3238 | 17.005 |
| Jar-1.1-0 | 17.56 | 7.3105 | 17.2731 | 82.44 | 7.3287 | 17.005 |
| Jar-2.1-0 | 10.02 | 7.2913 | 17.1744 | 89.98 | 7.3052 | 16.9700 |
| Jarosite Component | Theoretical (%) | Synthetic (%) | Jar-0.8-0 (%) | Jar-1.1-0 (%) | Jar-2.1-0 (%) | Jar-2.1-3 (%) | Jar-2.1-7 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 7.81 | 7.17 | 5.50 | 6.20 | 6.72 | 7.02 | 7.15 |
| Fe | 33.45 | 29.50 | 20.20 | 20.90 | 21.20 | 21.48 | 21.43 |
| SO4 | 38.36 | 40.70 | 39.84 | 38.95 | 40.14 | 43.44 | 44.70 |
| H3O + OH * | 20.38 | 22.63 | 34.56 | 33.95 | 31.94 | 28.06 | 26.72 |
| Electrode | Registry (V) | Reverse (V) |
|---|---|---|
| Cu coin | 0.52 | - |
| Graphite-0.1g (G1) | 0.89 | −0.90 |
| G1/Jar-0.8-0 (0.1 g) | 0.90 | −0.95 |
| G1/Jar)-0.8-0 (0.05 g) | 0.90 | −1.01 |
| G1/Jar-1.1-0 (0.1 g) | 0.96 | −0.99 |
| G1/Jar-1.1-0 (0.05 g) | 0.89 | −0.90 |
| G1/Jar-2.1-0 (0.1 g) | 0.94 | −0.95 |
| G1/Jar-2.1-0 (0.05 g) | 0.90 | −0.96 |
| G1/Jar)-2.1-3 (0.1 g) | 1.00 | −1.00 |
| G1/Jar-2.1-3 (0.05 g) | 1.35 | −1.42 |
| G1/Jar-2.1-7 (0.1 g) | 1.36 | −0.98 |
| G1/Jar-2.1-7 (0.05 g) | 1.00 | −1.05 |
| Jarosite | Synthesis Conditions/Results |
|---|---|
| K | 25 °C, 1 atm, pH 0.9–2.22, time 6 weeks–6 months/potassium jarosite [35] |
| NH3-Na | 180–190 °C, 350 KPa, 0.75 h retention time/agglomerates >10 μm [36] |
| Ag-Pb | 98 °C, 24 h, 500 s−1/rhombohedral crystals, semispherical particles 80–100 μm [37] |
| K | 99 °C, 24 h, 500 s−1, pH 1.6/agglomerates [38] |
| Ag | 98 °C, 24 h, jarosite seeds/semispherical particles >30 μm [6] |
| K-Na-H3O | 96 °C, 4 h, dehydrated overnight at 111 °C/ICDD PDF 220827 [15] |
| K | 100 °C, 24 h, 500 s−1, pH 1.5, dried at 283 K for 24 h/cauliflower particles >30 μm [39] |
| NH4-H3O-Ag | 95 °C, 24 h, pH 1.8, using seeds to increase particle size/spherical particles of 37–44 μm [40] |
| K-F | 70 °C, 48 h, dried 3 days at room temperature, pH 1.6/agglomerates of particles ~1 μm [24] |
| Ag-Rb | 95 °C, 24 h, pH 1.2/particles 20–30 μm [22] |
| K-based GO | Graphene oxide layers, 81 °C, 12 h, stirred for 10 h at 25 °C/bulks of JK >10 μm, with nanoplates width ~800 nm and thickness ~100 nm, reversible capacity of 70.7 mAh g−1 [25] |
| K-rGO nanosheets | Dissolution of KNO3-FeSO47H2O-GO, 111 °C (autoclave) during 12 h/particle size over 4 μm, 545 mAh g−1 at the end of 1000 cycles at 500 mAh g−1 [30] |
| H3O-K | 70 °C, 3 h, pH (0.8, 1.1 and 2.1), aging time 0, 3, and 7 days/particle sizes varying from agglomerates 5 to 10 μm to individual particles from 0.2 to 1 μm. Morphologies from quasi spherical, elliptical, spherical, and euhedral. With electrical properties generating from 0.86 to 1.36 V in the Daniell’s cell (this work) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Lazcano, E.; Cerecedo-Sáenz, E.; Hernández-Ávila, J.; Toro, N.; Karthik, T.V.K.; Mendoza-Anaya, D.; Fernández-García, M.E.; Rodríguez-Lugo, V.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E. Synthesis of Hydronium-Potassium Jarosites: The Effect of pH and Aging Time on Their Structural, Morphological, and Electrical Properties. Minerals 2021, 11, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010080
Hernández-Lazcano E, Cerecedo-Sáenz E, Hernández-Ávila J, Toro N, Karthik TVK, Mendoza-Anaya D, Fernández-García ME, Rodríguez-Lugo V, Salinas-Rodríguez E. Synthesis of Hydronium-Potassium Jarosites: The Effect of pH and Aging Time on Their Structural, Morphological, and Electrical Properties. Minerals. 2021; 11(1):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010080
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Lazcano, Elías, E. Cerecedo-Sáenz, J. Hernández-Ávila, Norman Toro, T. V. K. Karthik, D. Mendoza-Anaya, M. E. Fernández-García, V. Rodríguez-Lugo, and E. Salinas-Rodríguez. 2021. "Synthesis of Hydronium-Potassium Jarosites: The Effect of pH and Aging Time on Their Structural, Morphological, and Electrical Properties" Minerals 11, no. 1: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010080
APA StyleHernández-Lazcano, E., Cerecedo-Sáenz, E., Hernández-Ávila, J., Toro, N., Karthik, T. V. K., Mendoza-Anaya, D., Fernández-García, M. E., Rodríguez-Lugo, V., & Salinas-Rodríguez, E. (2021). Synthesis of Hydronium-Potassium Jarosites: The Effect of pH and Aging Time on Their Structural, Morphological, and Electrical Properties. Minerals, 11(1), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11010080