Geochronology and Genesis of the Xitian W-Sn Polymetallic Deposit in Eastern Hunan Province, South China: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb and Muscovite Ar-Ar Dating, Petrochemistry, and Wolframite Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
2.1. Sedimentary Rocks
2.2. Structure
2.3. Igneous Rocks
3. Geology of the Ore Deposits
3.1. Longshang
3.2. Hejiangkou
3.3. Heshuxia
3.4. Goudalan
3.5. Shaiheling
4. Sampling and Analytical Methods
4.1. In Situ LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating and Trace Element Compositions
4.2. Muscovite 40Ar-39Ar Dating
4.3. Skarn Major and Trace Elements Analysis
4.4. Wolframite Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopic Composition Analysis
5. Results
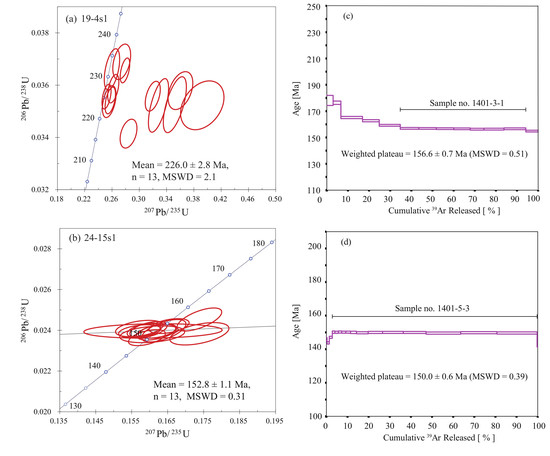
5.1. Zircon U-Pb Dating
5.2. Trace Element Compositions of Zircons
5.3. Muscovite 40Ar-39Ar Dating
5.4. Skarn Major and Trace Elements Analysis Results
5.5. Wolframite Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopic Composition Analysis
6. Discussion
6.1. Timing of Mineralization and Granitic Magmatism
6.2. Physico-Chemical Conditions of the Ore-Forming Fluids
6.3. Source of Ore-Forming Metals
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kempe, U.; Wolf, D. Anomalously high Sc contents in ore minerals from Sn-W deposits: Possible economic significance and genetic implications. Ore Geol. Rev. 2006, 28, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Guo, C.L.; Chen, Y.C. Large-scale tungsten-tin mineralization in the Nanling region, South China: Metallogenic ages and corresponding geodynamic processes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2329–2338. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Guo, C.L.; Yuan, S.D.; Cheng, Y.B.; Chen, Y.C. Spatial-temporal distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in south China and their metallogenic settings. Geol. J. Chin. Univ. 2008, 14, 510–526. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Pirajno, F.; Cook, N. Mesozoic metallogeny in East China and corresponding geodynamic settings-An introduction to the special issue. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiva, A.M.R. Geochemistry of cassiterite and wolframite from tin and tungsten quartz veins in Portugal. Ore Geol. Rev. 2008, 33, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.; Dória, A.; Neiva, A.M.R.; Leal Gomes, C.; Creaser, R.A. Metallogenesis at the Carris W-Mo-Sn deposit (Gerês, Portugal): Constraints from fluid inclusions, mineral geochemistry, Re-Os and He-Ar isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Mao, J.; Liu, P. Geodynamic setting of Late Cretaceous Sn-W mineralization in southeastern Yunnan and northeastern Vietnam. Solid Earth Sci. 2016, 1, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicharro, E.; Boiron, M.; López-García, J.Á.; Barfod, D.N.; Villaseca, C. Origin, ore forming fluid evolution and timing of the Logrosán Sn-(W) ore deposits (Central Iberian Zone, Spain). Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Mao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, W.; Wang, X.; Hao, D. An Early Cretaceous W-Sn deposit and its implications in southeast coastal metallogenic belt: Constraints from U-Pb, Re-Os, Ar-Ar geochronology at the Feie’shan W-Sn deposit, SE China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 81, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloviev, S.G.; Kryazhev, S.G.; Dvurechenskaya, S.S. Geology, mineralization, stable isotope, and fluid inclusion characteristics of the Vostok-2 reduced W-Cu skarn and Au-W-Bi-As stockwork deposit, Sikhote-Alin, Russia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 86, 338–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloviev, S.G.; Kryazhev, S.G.; Dvurechenskaya, S.S. Geology, mineralization, and fluid inclusion characteristics of the Lermontovskoe reduced-type tungsten (Cu, Au, Bi) skarn deposit, Sikhote-Alin, Russia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 89, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Xiang, Y. Petrogenesis of Jurassic tungsten-bearing granites in the Nanling Range, South China: Evidence from whole-rock geochemistry and zircon U-Pb and Hf-O isotopes. Lithos 2017, 278, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.W.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.H.M.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, J. Genetic types, mineralization styles, and geodynamic settings of Mesozoic tungsten deposits in South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 109–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2016; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2016; p. 202.
- Wang, D.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, S.B.; Xu, J.X.; Zhang, J.J.; Zeng, Z.L.; Chen, F.W.; Li, H.Q.; Guo, C.L. Assessment on mineral resource in Nanling region and suggestion for further prospecting. Acta Geol. Sin. 2007, 81, 882–890. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Zhu, J.; Lu, J.; Ma, D. Multiple-aged granitoids and related tungsten-tin mineralization in the Nanling Range, South China. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 2045–2055. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Mao, J.; Bierlein, F.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Zeng, Z. SHRIMP U-Pb (zircon), Ar-Ar (muscovite) and Re-Os (molybdenite) isotopic dating of the Taoxikeng tungsten deposit, South China Block. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 43, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wei, W.; Bi, X.; Peng, J.; Qi, Y.; Wu, L.; Chen, Y. Molybdenite Re-Os and muscovite Ar-40/Ar-39 dating of the Xihuashan tungsten deposit, central Nanling district, South China. Lithos 2012, 150, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Dong, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Fu, J.; Wang, C.; Shan, Y. Zircon U-Pb, molybdenite Re-Os and muscovite Ar-Ar isotopic dating of the Xitian W-Sn polymetallic deposit, eastern Hunan Province, South China and its geological significance. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 78, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, M.; Pirajno, F. Major types and time-space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings. Miner. Deposita 2013, 48, 267–294. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Zhou, M.; Hu, R.; Shen, N.; Yuan, S.; Bi, X.; Du, A.; Qu, W. Precise molybdenite Re-Os and mica Ar-Ar dating of the Mesozoic Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, central Nanling district, South China. Miner. Deposita 2006, 41, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R. Geology and genesis of the Hehuaping magnesian skarn-type cassiterite-sulfide deposit, Hunan Province, Southern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 58, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, W.; Ireland, T.; Tian, X.; Hu, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.; Xu, D. Generation of Late Mesozoic Qianlishan A2-type granite in Nanling Range, South China: Implications for Shizhuyuan W-Sn mineralization and tectonic evolution. Lithos 2016, 266–267, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Peng, J.; Hu, R.; Li, H.; Shen, N.; Zhang, D. A precise U-Pb age on cassiterite from the Xianghualing tin-polymetallic deposit (Hunan, South China). Miner. Deposita 2008, 43, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hua, R.; Wang, R.; Chen, P.; Li, H. New dating of Dajishan granite and related tungsten mineralization, South Jiangxi Province, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2007, 1, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.H.; Bi, X.W.; Hu, R.Z.; Chen, Y.W. Petrogenesis of Yaogangxian granites and inplications for W mineralization, Hunan province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2749–2765. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Lou, F. Petrogenesis of the Xihuashan granites in southeastern China: Constraints from geochemistry and in-situ analyses of zircon U-Pb-Hf-O isotopes. Lithos 2012, 148, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, X.; Wu, S.; Cai, Y.; Liang, X.; Shao, T.; Wang, C.; Fu, J.; Jiang, Y. Isotopic geochemistry, zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of A-type granites from the Xitian W-Sn deposit, SE China: Constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic significance. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Liu, D.Y.; Sun, M.; Li, W.X.; Liang, X.R.; Liu, Y. Precise Sm-Nd and U-Pb isotopic dating of the supergiant Shizhuyuan polymetallic deposit and its host granite, SE China. Geol. Mag. 2004, 141, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.M.; Chen, Z.H.; Shi, G.H.; Li, L.X.; Qu, W.J.; Li, C. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenite from Dajishan tungsten deposit in Jiangxi Province. Miner. Depos. 2011, 30, 1113–1121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, J.; Wang, R.; Yang, P.; Zhu, J.; Yao, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, C.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, W. Constraints of in situ zircon and cassiterite U-Pb, molybdenite Re-Os and muscovite Ar-40-Ar-39 ages on multiple generations of granitic magmatism and related W-Sn mineralization in the Wangxianling area, Nanling Range, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 1021–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.H.; Chen, K.X.; Chen, K.X.; Liu, G.Q.; Fu, J.M.; Yin, J.P. Geological characteristics and Re-Os dating of molybdenites in Hehuaping tin-polymetallic deposit, Southern Hunan Province. Miner. Depos. 2006, 25, 263–268. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Li, X.F.; Feng, Z.H.; Bai, Y. 40Ar/39Ar dating of muscovite from greisenized granite and geological significance in Limu tin deposit. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2009, 29, 21–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Ma, D.S.; Lu, J.J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, R.Q.; Qu, W.J. Re-Os geochronology and S isotope geochemistry of Dengfuxian tungsten deposit, Hunan Province, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 3798–3808. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Chung, S.L.; Zhou, H.W.; Lo, C.H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.W. Jurassic intraplate magmatism in southern Hunan-eastern Guangxi: Ar-40/Ar-39 dating, geochemistry, Sr-Nd isotopes and implications for the tectonic evolution of SE China. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2004, 226, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, R.; Feng, Z.; Chunxia, W.; Tang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, M. Ar-Ar ages of hydrothermal muscovite and igneous biotite at the Guposhan-Huashan district, Northeast Guangxi, South China: Implications for mesozoic W-Sn mineralization. Resour. Geol. 2015, 65, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Peng, J.; Shen, N.; Hu, R.; Dai, T. Ar-40-Ar-39 isotopic dating of the Xianghualing Sn-polymetallic ore field in southern Hunan, China and its geological implications. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. 2007, 81, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Cao, J.; Kong, H.; Shao, Y.; Li, H.; Xi, X.; Deng, X. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the early Mesozoic Xitian granitic pluton in the middle Qin-Hang Belt, South China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb ages and bulk-rock trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 128, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wei, H.; Zhao, R.; Cao, J. Ore-forming mechanism of quartz-vein-type W-Sn deposits of the Xitian district in SE China: Implications from the trace element analysis of wolframite and investigation of fluid inclusions. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 83, 152–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.L.; Li, C.; Wu, S.C.; Xu, Y.M. Molybdenite Re-Os Isotopic Dating of Xitian Deposit in Hunan Province and Its Geological Significance. Rock Miner. Anal. 2014, 33, 142–152. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.Y.; Fu, J.M.; Wu, S.C.; Xu, D.M.; Yang, X.J. 40Ar/39Ar isotopic dating of the Longshang tin-polymetallic deposit, Xitian ore field, eastern Hunan. Geol. Chin. 2008, 35, 706–713. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Bai, X.J.; Hu, R.G.; Cheng, S.B.; Pu, Z.P.; Qiu, H.N. Direct dating of cassiterite in Xitian Tungsten-Tin polymetallic deposit, South-East Hunan, by 40Ar/39Ar Progressive Crushing. Geotecton. Metallog. 2015, 39, 1049–1060. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.W.; Liu, J.X.; Dai, X.L. Geological characteristics and molybdenite Re-Os isotopic age of Hejiangkou tungsten and tin polymetallic deposit, East Hunan, China. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2015, 25, 2883–2897. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.Q.; Shao, Y.J.; Liu, J.P.; Wei, H.T.; Zhao, R.C. Ore-forming fluid of quartz-vein type tungsten deposits, Xitian ore field, eastern Hunan, China. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2016, 26, 1107–1119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, M.; Yan, D.; Zheng, J.; Li, J. Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China: No connection with the Grenvillian orogeny. Geology 2011, 39, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C. The characteristic target-pattern regional ore zonality of the Nanling region, China (I). Geosci. Front. 2011, 2, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Kee, W.; Li, Z.; Ye, H.; Zhao, X.; Liu, K.; Zhou, J. Characteristics and geodynamic evolution of Indosinian magmatism in South China: A case study of the Guikeng pluton. Lithos 2011, 127, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Ye, H.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Takahashi, Y.; Zhao, X.; Kee, W. The Indosinian collision-extension event between the South China Block and the Palaeo-Pacific plate: Evidence from Indosinian alkaline granitic rocks in Dashuang, eastern Zhejiang, South China. Lithos 2013, 172–173, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xue, Q.; Shao, F.; Chen, S.; Duan, M.; Guo, P.; Gong, H.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z. Exotic origin of the Chinese continental shelf: New insights into the tectonic evolution of the western Pacific and eastern China since the Mesozoic. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1598–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, W.; Sun, M.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, T. Geochronological, geochemical and geothermal constraints on petrogenesis of the Indosinian peraluminous granites in the South China Block: A case study in the Hunan Province. Lithos 2007, 96, 475–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China Block: Key observations and controversies. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1273–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Shi, X.; Castillo, P.R. The late Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the South China Sea: A petrologic perspective. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 85, 178–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Guo, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Dong, Y.; Liu, S.; He, D.; Cheng, S.; Lu, R.; Yao, A. Tectonics of South China continent and its implications. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 1804–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.M.; Chen, P.R.; Zhang, W.L.; Liu, X.D.; Lu, J.J.; Lin, J.F.; Yao, J.M.; Ql, H.W.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, S.Y. Metallogenic systems related to Mesozoic and Cenozoic granitoids in South China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2003, 46, 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.M.; Zhang, W.L.; Gu, S.Y.; Chen, P.R. Comparison between REE granites and W-Sn granite in the Nanling region, South China, and their mineralizations. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2321–2328. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Guo, F.; Peng, T.P. Mesozoic mafic magmatism in Hunan-Jiangxi province and the lithospheric extension. Earth Sci. Front. 2003, 10, 159–169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.G.; Li, J.K.; Wang, D.H.; Liu, J.; He, H.H. The deep tectonic features of Qitianling ore-concentrated area in Southern Hunan province and its contrains to the regional ore-forming process. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 695–703. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Lu, J.; Ma, D.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R. The Late Triassic Dengfuxian A-type granite, Hunan Province: Age, petrogenesis, and implications for understanding the late Indosinian tectonic transition in South China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2015, 57, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zeng, L.; Li, Q.; Fu, J.; Ding, T. Hybrid genesis of Jurassic fayalite-bearing felsic subvolcanic rocks in South China: Inspired by petrography, geochronology, and Sr-Nd-O-Hf isotopes. Lithos 2016, 264, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Long, Z.Q.; Xu, H.H.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, C.C. Structural characteristics and prospecting significance of the Xitian tin-tungsten polymetallic deposit, Hunan province, China. Geotecton. Metallog. 2012, 36, 217–226. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Hunan Province. Regional Geology of the Hunan Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1988; p. 507. (In Chinese)
- Wang, Y.J.; Fan, W.M.; Guo, F.; Peng, T.P.; Li, C.W. Geochemistry of Mesozoic mafic rocks adjacent to the Chenzhou-Linwu fault, South China: Implications for the lithospheric boundary between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks. Int. Geol. Rev. 2003, 45, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ma, A.J.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.R.; Ni, Y.J. Research on U-Pb Chronology in Xitian pluton of Hunan province. Geoscience 2013, 27, 819–830. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Alle, P.; Corfu, F.; Griffin, W.L.; Meier, M.; Ober, F.; Von Quadt, A.; Roddick, J.C.; Speigel, W. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace-element and REE analyses. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 1995, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhlou, S.; Belousova, E.; Griffin, W.L.; Pearson, N.J.; O Reilly, S.Y. Trace element and isotopic composition of GJ-red zircon standard by laser ablation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, A158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Hu, Z.; Gao, C.; Zong, K.; Wang, D. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-north china orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in Zircons from mantle xenoliths. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 537–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem. Geol. 2002, 192, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.S. Age determinations of 40Ar-40K, 40Ar-40Ar and radiogenic 40Ar released characteristics on K-Ar geostandards of China. Chin. J. Geol. 1983, 4, 315–323. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.N.; Bai, X.J.; Liu, W.G.; Mei, L.F. Automatic 40Ar/39Ar dating technique using multicollector ArgusVI MS with home-made apparatus. Geochimica 2015, 44, 477–484. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Koppers, A. ArArCALC-software for Ar-40/Ar-39 age calculations. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Siebel, W.; Satir, M.; Lu, M.T.; Saka, K. Geochronology of the Karadere basement (NW Turkey) and implications for the geological evolution of the Istanbul zone. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2002, 91, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.; Schaltegger, U. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2003, 53, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution: An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks; Blackwell Scientific: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985; p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Hoskin, P. Trace-element composition of hydrothermal zircon and the alteration of Hadean zircon from the Jack Hills, Australia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle compositions and processes. In Magmatism in the Ocean Basins; Saunders, A.D., Norry, M.J., Eds.; Geological Society, London Special Publication: London, UK, 1989; Volume 32, pp. 313–345. [Google Scholar]
- Zartman, R.E.; Doe, B.R. Plumbotectonics-The model. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Q.; Wu, S.C.; Du, A.D.; Fu, J.M.; Yang, X.J.; Tang, Z.H.; Wei, J.Q. Metallogenic ages of the Xitian tungsten-tin deposit, Eastern Hunan Province. Geotecton. Metallog. 2008, 32, 63–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hua, R.M.; Mao, J.W. A preliminary discussion on the Mesozoic metallogenic explosion in East China. Miner. Depos. 1999, 18, 300–308. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ferry, J.M.; Watson, E.B. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2007, 154, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irber, W. The lanthanide tetrad effect and its correlation with K/Rb, Eu/Eu*, Sr/Eu, Y/Ho, and Zr Hf of evolving peraluminous granite suites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlik, M.; Raith, J.G.; Gerdes, A. U-Pb, Lu-Hf and trace element characteristics of zircon from the Felbertal scheelite deposit (Austria): New constraints on timing and source of W mineralization. Chem. Geol. 2016, 421, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trail, D.; Watson, E.B.; Tailby, N.D. Ce and Eu anomalies in zircon as proxies for the oxidation state of magmas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 97, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trail, D.; Watson, E.B.; Tailby, N.D. The oxidation state of Hadean magmas and implications for early Earth’s atmosphere. Nature 2011, 480, 79–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Watanabe, K.; Yonezu, K. Zircon morphology, geochronology and trace element geochemistry of the granites from the Huangshaping polymetallic deposit, South China: Implications for the magmatic evolution and mineralization processes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 60, 14–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, A.D.; Berry, A.J. An experimental study of trace element partitioning between zircon and melt as a function of oxygen fugacity. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 95, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Oxygen isotope and trace element geochemistry of zircons from porphyry copper system: Implications for Late Triassic metallogenesis within the Yidun Terrane, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Chem. Geol. 2016, 441, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, P.; Holtz, F.; Linnen, R.L.; Behrens, H. Solubility of cassiterite in evolved granitic melts: Effect of T, fO2, and additional volatiles. Lithos 2005, 80, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B. Metallogeny of Tin; Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences Berlin Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1990; Volume 32, p. 211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chi, G.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, T.; Zhang, J. Oxygen fugacity of Yanshanian granites in South China and implications for metallogeny. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnen, R.L.; Pichavant, M.; Holtz, F. The combined effects of fO2 and melt composition on SnO2 solubility and tin diffusivity in haplo-granitic melts. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4965–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 1996, 123, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veksler, I.V.; Dorfman, A.M.; Kamenetsky, M.; Dulski, P.; Dingwell, D.B. Partitioning of lanthanides and Y between immiscible silicate and fluoride melts, fluorite and cryolite and the origin of the lanthanide tetrad effect in igneous rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2847–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, E.; Grevesse, N. Abundances of the elements: Meteoritic and solar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M. Rare-earth element mobility during hydrothermal and metamorphic fluid-rock interaction and the significance of the oxidation state of europium. Chem. Geol. 1991, 93, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulvais, P.; Fourcade, S.; Moine, B.; Gruau, G.; Cuney, M. Rare-earth elements distribution in granulite-facies marbles: A witness of fluid-rock interaction. Lithos 2000, 53, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qin, K.Z.; Li, G.M.; Xiao, B.; Li, J.X.; Jiang, H.Z.; Chen, J.B.; Zhao, J.X.; Fan, X.; Han, F.J. Geochemical characteristics and origin of skarn rocks in the Nuri Cu-Mo-W deposit, Southern Tibet. Geol. Explor. 2011, 47, 78–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zamanian, H.; Radmard, K. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the baba Ali magnetite skarn deposit, western Iran-a key to determine conditions of mineralisation. Geologos 2016, 22, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, B.; Valui, G.; Kruk, N.; Gonevchuk, V.; Usuki, M.; Wu, J.T.J. Emplacement ages, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic characterization of Mesozoic to early Cenozoic granitoids of the Sikhote-Alin Orogenic Belt, Russian Far East: Crustal growth and regional tectonic evolution. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 111, 872–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, M.J.; Vernon, R.H.; Turner, S.P.; Schaefer, B.F.; Foden, J.D. Contrasting Sr and Nd isotopic behaviour during magma mingling; new insights from the Mannum A-type granite. Lithos 2011, 126, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkert, R.A.; Feigenson, M.D.; Mana, S.; Bolge, L. Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic constraints on the mantle source of Neoproterozoic mafic dikes of the rifted eastern Laurentian margin, north-central Appalachians, USA. Lithos 2015, 212–215, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.X.; Sun, X.M.; Shi, G.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Gao, J.F.; Xu, T. Trace elements, rare earth elements (REE) and Nd-Sr isotopic compositions in scheelites and their implications for the mineralization in Daping gold mine in Yunnan province, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 733–741. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zuo, R. Sr-Nd-Pb isotope systematics of magnetite: Implications for the genesis of Makeng Fe deposit, southern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindle, A.G.; Webb, P.C. Niobian wolframite from Glen Gairn in the Eastern Highland of Scotland-A microprobe investigation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhou, X.M.; Chen, P.R.; Li, H.M.; Zhou, H.Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Shen, W.Z. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic strongly peraluminous granites in the Nanling, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2003, 33, 1209–1218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.Q.; Li, X.H.; Dai, T.M. Theory and Application of Isotope Systematics in Earth Sciences; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; p. 333. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y. Magnesian and Calcic Skarn Type Tin-Polymetallic Mineralization in the Nanling Range: Case Study from Hehuaping and Xitian. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2012. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]














© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Wu, Q.; Yang, X.; Kong, H.; Li, H.; Xi, X.; Huang, Q.; Liu, B. Geochronology and Genesis of the Xitian W-Sn Polymetallic Deposit in Eastern Hunan Province, South China: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb and Muscovite Ar-Ar Dating, Petrochemistry, and Wolframite Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopes. Minerals 2018, 8, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8030111
Cao J, Wu Q, Yang X, Kong H, Li H, Xi X, Huang Q, Liu B. Geochronology and Genesis of the Xitian W-Sn Polymetallic Deposit in Eastern Hunan Province, South China: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb and Muscovite Ar-Ar Dating, Petrochemistry, and Wolframite Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopes. Minerals. 2018; 8(3):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8030111
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jingya, Qianhong Wu, Xiaoyong Yang, Hua Kong, Huan Li, Xiaoshuang Xi, Qianfeng Huang, and Biao Liu. 2018. "Geochronology and Genesis of the Xitian W-Sn Polymetallic Deposit in Eastern Hunan Province, South China: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb and Muscovite Ar-Ar Dating, Petrochemistry, and Wolframite Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopes" Minerals 8, no. 3: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8030111
APA StyleCao, J., Wu, Q., Yang, X., Kong, H., Li, H., Xi, X., Huang, Q., & Liu, B. (2018). Geochronology and Genesis of the Xitian W-Sn Polymetallic Deposit in Eastern Hunan Province, South China: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb and Muscovite Ar-Ar Dating, Petrochemistry, and Wolframite Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopes. Minerals, 8(3), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8030111