Mechanochemical Treatment to Remove Arsenic from Copper Ore
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Experimental Conditions
2.2. Analysis Methods
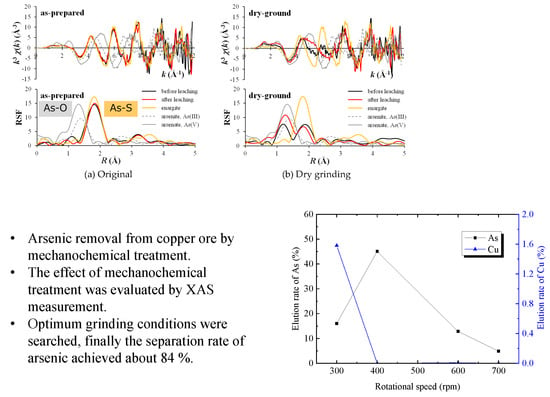
3. Results
3.1. Mechanochemical Effect
3.2. Optimization of Mechanochemical Effect
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leist, M.; Casey, R.J.; Caridi, D. The management of arsenic wastes: Problems and prospects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 76, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintans-Fondo, A.; Fernandez-Calvino, D.; Novoa-Munoz, J.C.; Arias-Estevez, M.; Fernandez-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Alvarez-Rodriguez, E.; Nunez-Delgado, A. As(V) Sorption/Desorption on Different Waste Materials and Soil Samples. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, K.H.; Li, W.H.; Han, J.W.; Liu, W.; Qin, W.Q.; Cai, L.B. Arsenic removal from lead-zinc smelter ash by NaOH-H2O2 leaching. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, V.K.; Mondal, P. Stabilization of arsenic and fluoride bearing spent adsorbent in clay bricks: Preparation, characterization and leaching studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 200, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosmukhamedov, N.; Kaplan, V. Efficient Removal of Arsenic and Antimony during Blast Furnace Smelting of Lead-Containing Materials. JOM 2017, 69, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-H.; Tian, L.; Ilgen, G. Biogenic arsenic volatilisation from an acidic fen. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Zou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Simultaneous volatilization characteristics of arsenic and sulfur during isothermal coal combustion. Fuel 2017, 203, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.; Cruells, M.; Roca, A.; Bergo, R. Treatment of copper flash smelter flue dusts for copper and zinc extraction and arsenic stabilization. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 105, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, W.; Qin, W.; Zhang, T.; Chang, Z.; Xue, K. Effects of sodium salts on the sulfidation of lead smelting slag. Min. Eng. 2017, 108, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwakura, S.; Ohno, H.; Matsubae-Yokoyarna, K.; Kumagai, Y.; Kubo, H.; Nagasaka, T. Removal of arsenic in coal fly ash by acid washing process using dilute H2SO4 solvent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, Z.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; Hu, C.; Wu, W.; Qu, J. Treatment of strongly acidic wastewater with high arsenic concentrations by ferrous sulfide (FeS): Inhibitive effects of S(0)-enriched surfaces. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, S.A.; Sandstrom, A. Selective leaching of arsenic and antimony from a tetrahedrite rich complex sulphide concentrate using alkaline sulphide solution. Min. Eng. 2010, 23, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongamp, W.; Takasaki, Y.; Shibayama, A. Arsenic removal from copper ores and concentrates through alkaline leaching in NaHS media. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.E. Review of metal sulphide precipitation. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G.; Takahashi, K.; Kato, T.; Tokoro, C. Mechanochemical activation of chalcopyrite: Relationship between activation mechanism and leaching enhancement. Min. Eng. 2019, 131, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Granata, G.; Tsunazawa, Y.; Takagi, T.; Tokoro, C. Mechanism and kinetics of enhancement of cerium dissolution from weathered residual rare earth ore by planetary ball milling. Min. Eng. 2019, 134, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadabad, F.K.; Hejazi, S.; Khaki, J.V.; Babakhani, A. Mechanochemical leaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by sulfuric acid. Int. J. Min. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achimovicova, M.; Balaz, P.; Briancin, J. The influence of mechanical activation of chalcopyrite on the selective leaching of copper by sulphuric acid. Metalurgija 2006, 45, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, T.; Harada, J.; Kiku, A.; Tohji, K.; Shinoda, K. Development of a new in-laboratory XAFS apparatus based on new concept. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2001, 8, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankudinov, A.L.; Ravel, B.; Rehr, J.J.; Conradson, S.D. Real-space multiple-scattering calculation and interpretation of x-ray-absorption near-edge structure. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 7565–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ankudinov, A.L.; Bouldin, C.E.; Rehr, J.J.; Sims, J.; Hung, H. Parallel calculation of electron multiple scattering using Lanczos algorithms. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 104107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welham, N.J. Mechanochemical processing of enargite (Cu3AsS4). Hydrometallurgy 2001, 62, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, P.; Da Pelo, S.; Musu, E.; Atzei, D.; Elsener, B.; Fantauzzi, M.; Rossi, A. Enargite oxidation: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2008, 86, 62–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Element | wt % |
|---|---|
| Cu | 30.77 |
| As | 5.76 |
| Fe | 12.90 |
| S | 28.80 |
| Zn | 2.06 |
| Pb | 0.24 |
| Cases | Ball Diameter (mm) | Grinding Time (h) | Rotational Speed (rpm) | Type of Solvent | Elution rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aqueous Concentration (mol/L) | As | Cu | Fe | ||||
| Case 1 | 15 | 8 | 600 | Water | 12.86 | 0.00 | 21.4 |
| - | |||||||
| Case 2 | 15 | 8 | 400 | Water | 45.07 | 0.00 | 14.8 |
| - | |||||||
| Case 3 | 10 | 8 | 600 | Water | 48.18 | 0.00 | 15.96 |
| - | |||||||
| Case 4 | 5 | 8 | 600 | Water | 41.50 | 0.00 | 15.12 |
| - | |||||||
| Case 5 | 15 | 1 | 600 | NaOH | 4.26 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 0.25 | |||||||
| Case 6 | 15 | 1 | 600 | NaOH | 51.73 | 0.00 | 0.03 |
| 0.625 | |||||||
| Case 7 | 15 | 1 | 600 | NaOH | 56.34 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 1.25 | |||||||
| Case 8 | 15 | 1 | 600 | NaOH | 59.86 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| 2.5 | |||||||
| Case 9 | 15 | 1 | 600 | K2S | 32.45 | 0.32 | 0.00 |
| 1.25 | |||||||
| Case 10 | 15 | 1 | 600 | Na2CO3 | 16.31 | 0.00 | 1.71 |
| 1.25 | |||||||
| Case 11 | 15 | 1 | 600 | NaHCO3 | 7.45 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| 1.25 | |||||||
| Case 12 | 10 | 8 | 400 | NaOH | 76.2 | 0.00 | 0.08 |
| 1.25 | |||||||
| Principal Element | Combined Grinding (wt %) | Original Ore (wt %) |
|---|---|---|
| Cu | 42.72 | 30.77 |
| As | 1.37 | 5.76 |
| Fe | 12.5 | 12.90 |
| S | 21.5 | 28.80 |
| Zn | 1.24 | 2.06 |
| Pb | 0.59 | 0.24 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishihara, S.; Shinoda, K.; Kano, J. Mechanochemical Treatment to Remove Arsenic from Copper Ore. Minerals 2019, 9, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9060349
Ishihara S, Shinoda K, Kano J. Mechanochemical Treatment to Remove Arsenic from Copper Ore. Minerals. 2019; 9(6):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9060349
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshihara, Shingo, Kozo Shinoda, and Junya Kano. 2019. "Mechanochemical Treatment to Remove Arsenic from Copper Ore" Minerals 9, no. 6: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9060349
APA StyleIshihara, S., Shinoda, K., & Kano, J. (2019). Mechanochemical Treatment to Remove Arsenic from Copper Ore. Minerals, 9(6), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9060349