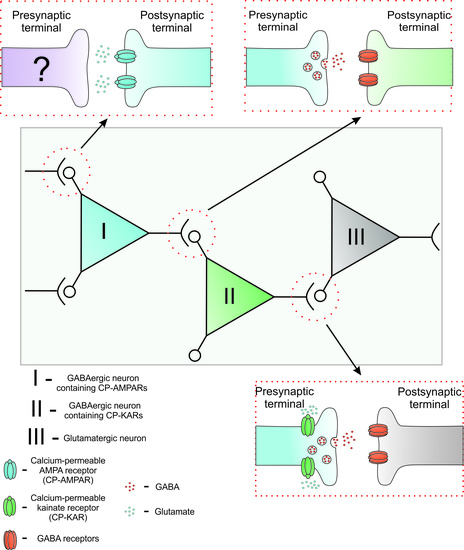
Properties of GABAergic Neurons Containing Calcium-Permeable Kainate and AMPA-Receptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. [Ca2+]i Measurements. Handling of Image Data
2.3. Spontaneous Synchronous Activity
2.4. Immunocytochemistry
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Reagents
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Neurons Expressing CP-KARs
3.2. Identification of Neurons Containing CP-AMPARs
3.3. Neurons Expressing CP-AMPARs Are GABAergic
3.4. Calcium-Binding Proteins in Neurons Expressing CP-AMPARs and CP-KARs
3.5. GABAergic Neurons Expressing CP-AMPARs Inhibit GABAergic Neurons Expressing CP-KARs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chávez, A.E.; Singer, J.H.; Diamond, J.S. Fast neurotransmitter release triggered by Ca influx through AMPA-type glutamate receptors. Nature 2006, 443, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerma, J. Roles and rules of kainate receptors in synaptic transmission. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Bartley, A.F.; Dobrunz, L.E. Calcium-permeable presynaptic kainate receptors involved in excitatory short-term facilitation onto somatostatin interneurons during natural stimulus patterns. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 101, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bahn, S.; Volk, B.; Wisden, W. Kainate receptor gene expression in the developing rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 5525–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, I.; Bischoff, S.; Heinemann, S.F.; Mulle, C. Kainate Receptor-Mediated Responses in the CA1 Field of Wild-Type and GluR6-Deficient Mice. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternain, A.V.; Herrera, M.T.; Nieto, M.A.; Lerma, J. GluR5 and GluR6 Kainate Receptor Subunits Coexist in Hippocampal Neurons and Coassemble to Form Functional Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyeth, M.S.; Pelkey, K.A.; Yuan, X.; Vargish, G.; Johnston, A.D.; Hunt, S.; Fang, C.; Abebe, D.; Mahadevan, V.; Fisahn, A.; et al. Neto Auxiliary Subunits Regulate Interneuron Somatodendritic and Presynaptic Kainate Receptors to Control Network Inhibition. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2156–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caiati, M.D.; Sivakumaran, S.; Cherubini, E. In the developing rat hippocampus, endogenous activation of presynaptic kainate receptors reduces GABA release from mossy fiber terminals. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakha, P.; Vesikansa, A.; Orav, E.; Heikkinen, J.; Kukko-Lukjanov, T.-K.; Shintyapina, A.; Franssila, S.; Jokinen, V.; Huttunen, H.J.; Lauri, S.E. Axonal Kainate Receptors Modulate the Strength of Efferent Connectivity by Regulating Presynaptic Differentiation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.-Y. Neuroprotection of GluR5-containing kainate receptor activation against ischemic brain injury through decreasing tyrosine phosphorylation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors mediated by Src kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 29355–29366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, Q.; Liu, Y.; Han, D.; Xu, J.; Zong, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.-Y. Neuroprotection of GluK1 kainate receptor agonist ATPA against ischemic neuronal injury through inhibiting GluK2 kainate receptor-JNK3 pathway via GABA(A) receptors. Brain Res. 2012, 1456, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononov, A.V.; Bal’, N.V.; Zinchenko, V.P. Control of spontaneous synchronous Ca2+ oscillations in hippocampal neurons by GABAergic neurons containing kainate receptors without desensitization. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 2012, 6, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, D.R.; Huang, X.-P.; Wells, J.W.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Interaction of domoic acid and several derivatives with kainic acid and AMPA binding sites in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 218, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.L.; McIlhinney, R.A. Effects of acromelic acid A on the binding of 3H-kainic acid and 3H-AMPA to rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 105, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosenkov, A.M.; Teplov, I.Y.; Sergeev, A.I.; Maiorov, S.A.; Zinchenko, V.P.; Gaidin, S.G. Domoic acid suppresses hyperexcitation in the network due to activation of kainate receptors of GABAergic neurons. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 671, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossart, R.; Esclapez, M.; Hirsch, J.C.; Bernard, C.; Ben-Ari, Y. GluR5 kainate receptor activation in interneurons increases tonic inhibition of pyramidal cells. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogoshi, F.; Weiss, J.H. Heterogeneity of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA/Kainate Channel Expression in Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons: Fluorescence Imaging and Immunocytochemical Assessment. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10521–10530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, J.K.; Paternain, A.V.; Selak, S.; Ahring, P.K.; Lerma, J. A mosaic of functional kainate receptors in hippocampal interneurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8986–8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isaac, J.T.R.; Ashby, M.C.; McBain, C.J. The role of the GluR2 subunit in AMPA receptor function and synaptic plasticity. Neuron 2007, 54, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.J.; Zukin, R.S. Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity and neuronal death. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, J.R.P.; Melcher, T.; Koh, D.-S.; Sakmann, B.; Seeburg, P.H.; Jonas, P.; Monyer, H. Relative abundance of subunit mRNAs determines gating and Ca2+ permeability of AMPA receptors in principal neurons and interneurons in rat CNS. Neuron 1995, 15, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, J.H.; Yuste, R.; Tamas, G. Ca2+ imaging of mouse neocortical interneurone dendrites: Contribution of Ca2+-permeable AMPA and NMDA receptors to subthreshold Ca2+dynamics. J. Physiol. 2003, 551, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochet, P.; Audinat, E.; Lambolez, B.; Crépel, F.; Rossier, J.; Iino, M.; Tsuzuki, K.; Ozawa, S. Subunit composition at the single-cell level explains functional properties of a glutamate-gated channel. Neuron 1994, 12, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini-Giampietro, D. The GluR2 (GluR-B) hypothesis: Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in neurological disorders. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.; Weiss, J.H. Calcium-permeable AMPA channels in neurodegenerative disease and ischemia. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2006, 16, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liao, M.; Mielke, J.G.; Ning, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; El-Hayek, Y.H.; Gomez, E.; Zukin, R.S.; Fehlings, M.G.; et al. Ischemic insults direct glutamate receptor subunit 2-lacking AMPA receptors to synaptic sites. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5309–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cull-Candy, S.; Kelly, L.; Farrant, M. Regulation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors: Synaptic plasticity and beyond. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2006, 16, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusa, R.; Zimmermann, F.; Koh, D.S.; Feldmeyer, D.; Gass, P.; Seeburg, P.H.; Sprengel, R. Early-onset epilepsy and postnatal lethality associated with an editing-deficient GluR-B allele in mice. Science 1995, 270, 1677–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, K.-M.; Yokota, H.; Mashiko, T.; Castillo, P.E.; Zukin, R.S.; Bennett, M.V.L. Blockade of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors protects hippocampal neurons against global ischemia-induced death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12230–12235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spaethling, J.M.; Klein, D.M.; Singh, P.; Meaney, D.F. Calcium-permeable AMPA receptors appear in cortical neurons after traumatic mechanical injury and contribute to neuronal fate. J. Neurotrauma 2008, 25, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossart, R.; Tyzio, R.; Dinocourt, C.; Esclapez, M.; Hirsch, J.C.; Ben-Ari, Y.; Bernard, C. Presynaptic Kainate Receptors that Enhance the Release of GABA on CA1 Hippocampal Interneurons. Neuron 2001, 29, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cepeda-Prado, E.A.; Khodaie, B.; Quiceno, G.D.; Beythien, S.; Edelmann, E.; Lessmann, V. Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Mediate Timing-Dependent LTP Elicited by Low Repeat Coincident Pre- and Postsynaptic Activity at Schaffer Collateral-CA1 Synapses. Cereb. Cortex 2021. [CrossRef]
- Lalanne, T.; Oyrer, J.; Farrant, M.; Sjöström, P.J. Synapse Type-Dependent Expression of Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2018, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zinchenko, V.P.; Gaidin, S.G.; Teplov, I.Y.; Kosenkov, A.M.; Sergeev, A.I.; Dolgacheva, L.P.; Tuleuhanov, S.T. Visualization, Properties, and Functions of GABAergic Hippocampal Neurons Containing Calcium-Permeable Kainate and AMPA Receptors. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 2020, 14, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidin, S.G.; Zinchenko, V.P.; Kosenkov, A.M. Mechanisms of ammonium-induced neurotoxicity. Neuroprotective effect of alpha-2 adrenergic agonists. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 693, 108593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiorov, S.A.; Zinchenko, V.P.; Gaidin, S.G.; Kosenkov, A.M. Potential mechanism of GABA secretion in response to the activation of GluK1-containing kainate receptors. Neurosci. Res. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Gaidin, S.G.; Zinchenko, V.P.; Sergeev, A.I.; Teplov, I.Y.; Mal’tseva, V.N.; Kosenkov, A.M. Activation of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors stimulates GABA release by astrocytes. Glia 2020, 68, 1114–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, A.; Verderio, C.; Pravettoni, E.; Matteoli, M. Synaptic and intrinsic mechanisms shape synchronous oscillations in hippocampal neurons in culture. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplov, I.Y.; Zinchenko, V.P.; Kosenkov, A.M.; Gaidin, S.G.; Nenov, M.N.; Sergeev, A.I. Involvement of NMDA and GABA(A) receptors in modulation of spontaneous activity in hippocampal culture: Interrelations between burst firing and intracellular calcium signal. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 553, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosenkov, A.M.; Gaidin, S.G.; Sergeev, A.I.; Teplov, I.Y.; Zinchenko, V.P. Fast changes of NMDA and AMPA receptor activity under acute hyperammonemia in vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 686, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turovsky, E.A.; Zinchenko, V.P.; Gaidin, S.G.; Turovskaya, M.V. Calcium-Binding Proteins Protect GABAergic Neurons of the Hippocampus from Hypoxia and Ischemia in vitro. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 2018, 12, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchenko, V.P.; Gaidin, S.G.; Teplov, I.Y.; Kosenkov, A.M. Inhibition of spontaneous synchronous activity of hippocampal neurons by excitation of GABAergic neurons. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 2017, 11, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosoi, C.R.; Rose, C.F. Identifying the direct effects of ammonia on the brain. Metab. Brain Dis. 2009, 24, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oja, S.S.; Saransaari, P.; Korpi, E.R. Neurotoxicity of Ammonia. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C.-S.; Ferrea, S.; Quasthoff, K.; Walter, J.; Görg, B.; Häussinger, D.; Schnitzler, A.; Hartung, H.-P.; Dihné, M. Ammonium chloride influences in vitro-neuronal network activity. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 235, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larm, J.A.; Beart, P.M.; Cheung, N.S. Neurotoxin domoic acid produces cytotoxicity via kainate- and ampa-sensitive receptors in cultured cortical neurones. Neurochem. Int. 1997, 31, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, K.; Iwahori, Y.; Ozaki, S.; Ohta, H. Regulation of spontaneous Ca(2+) spikes by metabotropic glutamate receptors in primary cultures of rat cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 2252–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisabella, B.; Bolshakov, V.Y.; Benes, F.M. Kainate receptor-mediated modulation of hippocampal fast spiking interneurons in a rat model of schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celio, M.R.; Heizmann, C.W. Calcium-binding protein parvalbumin as a neuronal marker. Nature 1981, 293, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyás, A.I.; Tóth, K.; Dános, P.; Freund, T.F. Subpopulations of GABAergic neurons containing parvalbumin, calbindin D28k, and cholecystokinin in the rat hippocampus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 312, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeulemeester, H.; Arckens, L.; Vandesande, F.; Orban, G.A.; Heizmann, C.W.; Pochet, R. Calcium binding proteins and neuropeptides as molecular markers of GABAergic interneurons in the cat visual cortex. Exp. Brain Res. 1991, 84, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, E.O.; Paulsen, O. Role of GABAergic inhibition in hippocampal network oscillations. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Engberink, A.H.O.; Meijer, J.H.; Michel, S. Chloride cotransporter KCC2 is essential for GABAergic inhibition in the SCN. Neuropharmacology 2018, 138, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goutierre, M.; Al Awabdh, S.; Donneger, F.; François, E.; Gomez-Dominguez, D.; Irinopoulou, T.; La Menendez de Prida, L.; Poncer, J.C. KCC2 Regulates Neuronal Excitability and Hippocampal Activity via Interaction with Task-3 Channels. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 91–103.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asrar, S.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, W.; Jia, Z. Ca(2+) permeable AMPA receptor induced long-term potentiation requires PI3/MAP kinases but not Ca/CaM-dependent kinase II. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, T.F.; Gulyás, A.I. Inhibitory control of GABAergic interneurons in the hippocampus. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1997, 75, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.J. Regulation of calcium homoeostasis in neurons: The role of calcium-binding proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1995, 23, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wondolowski, J.; Frerking, M. Subunit-dependent postsynaptic expression of kainate receptors on hippocampal interneurons in area CA1. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pressey, J.C.; Woodin, M.A. Kainate receptor regulation of synaptic inhibition in the hippocampus. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zinchenko, V.P.; Kosenkov, A.M.; Gaidin, S.G.; Sergeev, A.I.; Dolgacheva, L.P.; Tuleukhanov, S.T. Properties of GABAergic Neurons Containing Calcium-Permeable Kainate and AMPA-Receptors. Life 2021, 11, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121309
Zinchenko VP, Kosenkov AM, Gaidin SG, Sergeev AI, Dolgacheva LP, Tuleukhanov ST. Properties of GABAergic Neurons Containing Calcium-Permeable Kainate and AMPA-Receptors. Life. 2021; 11(12):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121309
Chicago/Turabian StyleZinchenko, Valery Petrovich, Artem Mikhailovich Kosenkov, Sergei Gennadevich Gaidin, Alexander Igorevich Sergeev, Ludmila Petrovna Dolgacheva, and Sultan Tuleukhanovich Tuleukhanov. 2021. "Properties of GABAergic Neurons Containing Calcium-Permeable Kainate and AMPA-Receptors" Life 11, no. 12: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121309
APA StyleZinchenko, V. P., Kosenkov, A. M., Gaidin, S. G., Sergeev, A. I., Dolgacheva, L. P., & Tuleukhanov, S. T. (2021). Properties of GABAergic Neurons Containing Calcium-Permeable Kainate and AMPA-Receptors. Life, 11(12), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121309