Extracellular Vesicles in Pulmonary Fibrosis Models and Biological Fluids of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients: A Scoping Review
Abstract
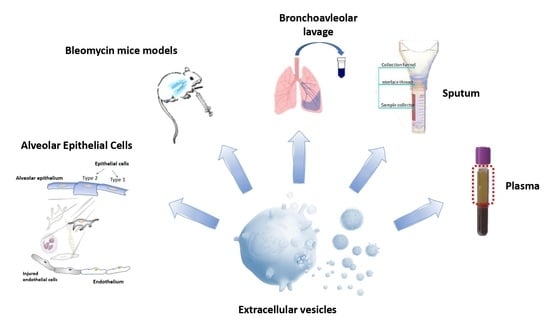
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources and Search
2.3. Selection Process
2.4. Data Charting and Items
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of the Results—Simple Descriptive Data
3.2. Quality Assessment after SANRA
3.3. EVs in Pulmonary Fibrosis Models
3.4. EVs in Bronchoalveolar Lavage from ILD Patients
3.5. EVs in Peripheral Blood from ILD Patients
3.6. EVs in Sputum from ILD Patients
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ILD | interstitial lung disease |
| IPF | idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| EVs | extracellular vesicles |
| miRNA | microRNA |
References
- Antoniou, K.M.; Margaritopoulos, G.A.; Tomassetti, S.; Bonella, F.; Costabel, U.; Poletti, V. Interstitial Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegal, Y.; Kim, D.S.; Shim, T.S.; Lim, C.-M.; Do Lee, S.; Koh, Y.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, W.D.; Lee, J.S.; Travis, W.D.; et al. Physiology Is a Stronger Predictor of Survival than Pathology in Fibrotic Interstitial Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jones, K.D.; Urisman, A.; Elicker, B.M.; Urbania, T.; Johannson, K.A.; Assayag, D.; Lee, J.; Wolters, P.J.; Collard, H.R.; et al. Pathologic Findings and Prognosis in a Large Prospective Cohort of Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. Chest 2017, 152, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, B.; Branagan, P.; Moloney, F.; Haroon, M.; O’Connell, O.J.; O’Connor, T.M.; O’Regan, K.; Harney, S.; Henry, M.T. Biomarkers to Identify ILD and Predict Lung Function Decline in Scleroderma Lung Disease or Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2015, 32, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Snetselaar, R.; van Batenburg, A.A.; van Oosterhout, M.F.M.; Kazemier, K.M.; Roothaan, S.M.; Peeters, T.; van der Vis, J.J.; Goldschmeding, R.; Grutters, J.C.; van Moorsel, C.H.M. Short Telomere Length in IPF Lung Associates with Fibrotic Lesions and Predicts Survival. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chilosi, M.; Doglioni, C.; Murer, B.; Poletti, V. Epithelial Stem Cell Exhaustion in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2010, 27, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, A.U.; Brown, K.K.; Flaherty, K.R.; Kolb, M.; Thannickal, V.J. IPF Consensus Working Group What’s in a Name? That Which We Call IPF, by Any Other Name Would Act the Same. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1800692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chanda, D.; Otoupalova, E.; Hough, K.P.; Locy, M.L.; Bernard, K.; Deshane, J.S.; Sanderson, R.D.; Mobley, J.A.; Thannickal, V.J. Fibronectin on the Surface of Extracellular Vesicles Mediates Fibroblast Invasion. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colquhoun, H.L.; Jesus, T.S.; O’Brien, K.K.; Tricco, A.C.; Chui, A.; Zarin, W.; Lillie, E.; Hitzig, S.L.; Straus, S. Study Protocol for a Scoping Review on Rehabilitation Scoping Reviews. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA-a Scale for the Quality Assessment of Narrative Review Articles. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vancheri, C.; Cottin, V.; Kreuter, M.; Hilberg, O. IPF, Comorbidities and Management Implications. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2015, 32 (Suppl. 1), 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Komura, K.; Yanaba, K.; Horikawa, M.; Ogawa, F.; Fujimoto, M.; Tedder, T.F.; Sato, S. CD19 Regulates the Development of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in a Mouse Model. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2008, 58, 3574–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Sridhar, S.; Tyagi, G.; Phillips, J.E.; Garrido, R.; Harris, P.; Burns, L.; Renteria, L.; Woods, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Bleomycin Induces Molecular Changes Directly Relevant to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Model for “Active” Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Miao, K.; Zhang, L.; Mou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y. Curdione Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Repressing TGF-β-Induced Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Differentiation. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuse, N.; Kamio, K.; Azuma, A.; Matsuda, K.; Inomata, M.; Usuki, J.; Morinaga, A.; Tanaka, T.; Kashiwada, T.; Atsumi, K.; et al. Exosome-Derived MicroRNA-22 Ameliorates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Regulating Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Differentiation in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2020, 87, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Xiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Mishra, A.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, D.; Blackburn, M.R.; Henke, C.A.; et al. MicroRNA-101 Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting Fibroblast Proliferation and Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16420–16439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fierro-Fernández, M.; Busnadiego, Ó.; Sandoval, P.; Espinosa-Díez, C.; Blanco-Ruiz, E.; Rodríguez, M.; Pian, H.; Ramos, R.; López-Cabrera, M.; García-Bermejo, M.L.; et al. MiR-9-5p Suppresses pro-Fibrogenic Transformation of Fibroblasts and Prevents Organ Fibrosis by Targeting NOX4 and TGFBR2. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1358–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stolzenburg, L.R.; Wachtel, S.; Dang, H.; Harris, A. MiR-1343 Attenuates Pathways of Fibrosis by Targeting the TGF-β Receptors. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Huang, C.; Senavirathna, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, L. MiR-27b Inhibits Fibroblast Activation via Targeting TGFβ Signaling Pathway. BMC Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, H.; Banerjee, S.; Xie, N.; Ge, J.; Liu, R.-M.; Matalon, S.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, G. MicroRNA-27a-3p Is a Negative Regulator of Lung Fibrosis by Targeting Myofibroblast Differentiation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Chong, S.G.; Upagupta, C.; Yanagihara, T.; Saito, T.; Shimbori, C.; Bellaye, P.-S.; Nishioka, Y.; Kolb, M.R. Fibrotic Extracellular Matrix Induces Release of Extracellular Vesicles with Pro-Fibrotic MiRNA from Fibrocytes. Thorax 2021, 76, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; van den Blink, B.; Hamblin, M.J.; Brown, A.W.; Golden, J.A.; Ho, L.A.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Vasakova, M.; Pesci, A.; Antin-Ozerkis, D.E.; et al. Long-Term Treatment with Recombinant Human Pentraxin 2 Protein in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Open-Label Extension Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, S.H.; Woeller, C.F.; Thatcher, T.H.; Pollock, S.J.; Small, E.M.; Sime, P.J.; Phipps, R.P. Activated Human Lung Fibroblasts Produce Extracellular Vesicles with Antifibrotic Prostaglandins. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiot, J.; Cambier, M.; Boeckx, A.; Henket, M.; Nivelles, O.; Gester, F.; Louis, E.; Malaise, M.; Dequiedt, F.; Louis, R.; et al. Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Fibrosis in Airway Epithelial Cells through Delivery of Antifibrotic MiR-142-3p. Thorax 2020, 75, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Chen, S.; Fang, Y.; Zuo, W.; Cui, J.; Xie, S. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Suppress the Fibroblast Proliferation by Downregulating FZD6 Expression in Fibroblasts via MicrRNA-29b-3p in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 8613–8625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, J.; Peraza, J.; Padilla, M.; Capaccione, K.; Salvatore, M.M. Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Disease of Alveolar Collapse and Collagen Deposition. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Hou, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, L. Exosomes Derived from Three-Dimensional Cultured Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Pulmonary Fibrosis in a Mouse Silicosis Model. Stem Cell Res. 2020, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargagli, E.; Monaci, F.; Bianchi, N.; Bucci, C.; Rottoli, P. Analysis of Trace Elements in Bronchoalveolar Lavage of Patients with Diffuse Lung Diseases. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 124, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, E.; Cameli, P.; Carleo, A.; Refini, R.M.; Bergantini, L.; D’alessandro, M.; Vietri, L.; Perillo, F.; Volterrani, L.; Rottoli, P.; et al. The Effect of Cigarette Smoking on Bronchoalveolar Lavage Protein Profiles from Patients with Different Interstitial Lung Diseases. Panminerva Med. 2019, 62, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capelozzi, V.L.; Faludi, E.P.; Balthazar, A.B.; Fernezlian, S.d.M.; Filho, J.V.B.; Parra, E.R. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Improves Diagnostic Accuracy in Patients with Diffuse Lung Disease. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2013, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Carleo, A.; Cameli, P.; Perrone, A.; Fossi, A.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Bronchoalveolar Lavage from IPF Patients: A Novel Prognostic Biomarker? Minerva Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottoli, P.; Bargagli, E. Is Bronchoalveolar Lavage Obsolete in the Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease? Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2003, 9, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Alessandro, M.; Carleo, A.; Cameli, P.; Bergantini, L.; Perrone, A.; Vietri, L.; Lanzarone, N.; Vagaggini, C.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. BAL Biomarkers’ Panel for Differential Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, T.; Tavanti, L.; De Magistris, S.; Lombardi, S.; Romei, C.; Falaschi, F.; Paggiaro, P.; Celi, A. Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers in Chronic Interstitial Lung Diseases. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 49, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Novelli, F.; Neri, T.; Tavanti, L.; Armani, C.; Noce, C.; Falaschi, F.; Bartoli, M.L.; Martino, F.; Palla, A.; Celi, A.; et al. Procoagulant, Tissue Factor-Bearing Microparticles in Bronchoalveolar Lavage of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients: An Observational Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Medina, A.; Lehmann, M.; Burgy, O.; Hermann, S.; Baarsma, H.A.; Wagner, D.E.; De Santis, M.M.; Ciolek, F.; Hofer, T.P.; Frankenberger, M.; et al. Increased Extracellular Vesicles Mediate WNT5A Signaling in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, B.; Mattson, J.; Paintal, H.; Nathan, M.; Shen, F.; Beaumont, M.; Malinao, M.-C.; Li, Y.; Canfield, J.; Basham, B.; et al. Differential Expression of Monocyte/Macrophage- Selective Markers in Human Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Exp. Lung Res. 2011, 37, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.; Gilpin, S.E.; Ask, K.; Cox, G.; Cook, D.; Gauldie, J.; Margetts, P.J.; Farkas, L.; Dobranowski, J.; Boylan, C.; et al. Circulating Fibrocytes Are an Indicator of Poor Prognosis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlund, C.J.E.; Gucluler Akpinar, G.; Steiner, L.; Ibrahim, A.; Bandeira, E.; Lepzien, R.; Lukic, A.; Smed-Sörensen, A.; Kullberg, S.; Eklund, A.; et al. Sarcoidosis Exosomes Stimulate Monocytes to Produce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and CCL2. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, A.; Navratilova, Z.; Kolek, V.; Novosadova, E.; Čépe, K.; du Bois, R.M.; Petrek, M. Expression Analysis of Extracellular MicroRNA in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid from Patients with Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Respirology 2018, 23, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Bravo, M.-J.; Wahlund, C.J.E.; Qazi, K.R.; Moulder, R.; Lukic, A.; Rådmark, O.; Lahesmaa, R.; Grunewald, J.; Eklund, A.; Gabrielsson, S. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis Is Associated with Exosomal Vitamin D-Binding Protein and Inflammatory Molecules. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qazi, K.R.; Torregrosa Paredes, P.; Dahlberg, B.; Grunewald, J.; Eklund, A.; Gabrielsson, S. Proinflammatory Exosomes in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Patients with Sarcoidosis. Thorax 2010, 65, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wahlund, C.J.E.; Eklund, A.; Grunewald, J.; Gabrielsson, S. Pulmonary Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Local and Systemic Inflammation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayock, R.L.; Bertrand, P.; Morrison, C.E.; Scott, J.H. Manifestations of sarcoidosis. Analysis of 145 patients, with a review of nine series selected from the literature. Am. J. Med. 1963, 35, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeffler, H.P.; Reichel, H.; Bishop, J.E.; Norman, A.W. Gamma-Interferon Stimulates Production of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 by Normal Human Macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 127, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Alessandro, M.; Soccio, P.; Bergantini, L.; Cameli, P.; Scioscia, G.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Lacedonia, D.; Bargagli, E. Extracellular Vesicle Surface Signatures in IPF Patients: A Multiplex Bead-Based Flow Cytometry Approach. Cells 2021, 10, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, K.M.; Alexandrakis, M.; Tzanakis, N.; Tsiligianni, I.; Tzortzaki, E.G.; Siafakas, N.M.; Bouros, D.E. Induced Sputum versus Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid in the Evaluation of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respiration 2005, 72, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiot, J.; Henket, M.; Corhay, J.L.; Moermans, C.; Louis, R. Sputum Biomarkers in IPF: Evidence for Raised Gene Expression and Protein Level of IGFBP-2, IL-8 and MMP-7. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Njock, M.-S.; Guiot, J.; Henket, M.A.; Nivelles, O.; Thiry, M.; Dequiedt, F.; Corhay, J.-L.; Louis, R.E.; Struman, I. Sputum Exosomes: Promising Biomarkers for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Thorax 2019, 74, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kadota, T.; Fujita, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Araya, J.; Kuwano, K.; Ochiya, T. Emerging role of extracellular vesicles as a senescence-associated secretory phenotype: Insights into the pathophysiology of lung diseases. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 60, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No. | Title, Author, Year, (Reference) | Justification of the Article’s Importance for the Readership | Statement of Concrete Aims or Formulation of Questions | Description of the Literature Search | Referencing | Scientific Reasoning | Appropriate Presentation of Data | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fibrotic extracellular matrix induces release of extracellular vesicles with pro-fibrotic miRNA from fibrocytes. Sato S, Thorax, 2021 [1] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 9 |
| 2 | Extracellular Vesicle Surface Signatures in IPF Patients: A Multiplex Bead-Based Flow Cytometry Approach. d’Alessandro M, Cells, 2021 [2] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| 3 | Exosome-Derived microRNA-22 Ameliorates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Regulating Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Differentiation in Vitro and in Vivo. Kuse N, J Nippon Med Sch, 2020 [3] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 4 | Exosomes derived from three-dimensional cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse silicosis model. Xu C, Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020 [4] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 6 |
| 5 | Sarcoidosis exosomes stimulate monocytes to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and CCL2. Wahlund CJE, Sci Rep, 2020 [5] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| 6 | Pulmonary Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Local and Systemic Inflammation. Wahlund C, Front Cell Dev Biol, 2017 [6] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 9 |
| 7 | Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Fibrosis in Airway Epithelial Cells through Delivery of Antifibrotic miR-142-3p. Guiot J, Thorax, 2020 [7] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 |
| 8 | Sputum Exosomes: Promising Biomarkers for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Njock MS, Thorax, 2019 [8] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| 9 | Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Suppress the Fibroblast Proliferation by Downregulating FZD6 Expression in Fibroblasts via Micrrna-29b-3p in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Wan X, J Cell Physiol, 2020 [9] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| 10 | Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers in Chronic Interstitial Lung Diseases. Neri T, Ann Clin Lab Sci, 2019 [10] | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| 11 | Activated Human Lung Fibroblasts Produce Extracellular Vesicles with Antifibrotic Prostaglandins. Lacy SH, Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2019 [11] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 9 |
| 12 | Increased Extracellular Vesicles Mediate WNT5A Signaling in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Martin-Medina A, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2018 [12] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| 13 | Expression Analysis of Extracellular Microrna in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid from Patients with Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Kirshore A, Respirology, 2018 [13] | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| 14 | Pulmonary Sarcoidosis is Associated with Exosomal Vitamin D-Binding Protein and Inflammatory Molecules. Martinez-Bravo MJ, J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017 [14] | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 15 | Procoagulant, Tissue Factor-Bearing Microparticles in Bronchoalveolar Lavage of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients: An Observational Study. Novelli F, Plos One, 2014 [15] | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| 16 | Proinflammatory Exosomes in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Patients with Sarcoidosis. Qazi K, Thorax, 2010 [16] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 17 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
d’Alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Bargagli, E.; Vidal, S. Extracellular Vesicles in Pulmonary Fibrosis Models and Biological Fluids of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients: A Scoping Review. Life 2021, 11, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121401
d’Alessandro M, Bergantini L, Bargagli E, Vidal S. Extracellular Vesicles in Pulmonary Fibrosis Models and Biological Fluids of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients: A Scoping Review. Life. 2021; 11(12):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121401
Chicago/Turabian Styled’Alessandro, Miriana, Laura Bergantini, Elena Bargagli, and Silvia Vidal. 2021. "Extracellular Vesicles in Pulmonary Fibrosis Models and Biological Fluids of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients: A Scoping Review" Life 11, no. 12: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121401
APA Styled’Alessandro, M., Bergantini, L., Bargagli, E., & Vidal, S. (2021). Extracellular Vesicles in Pulmonary Fibrosis Models and Biological Fluids of Interstitial Lung Disease Patients: A Scoping Review. Life, 11(12), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121401