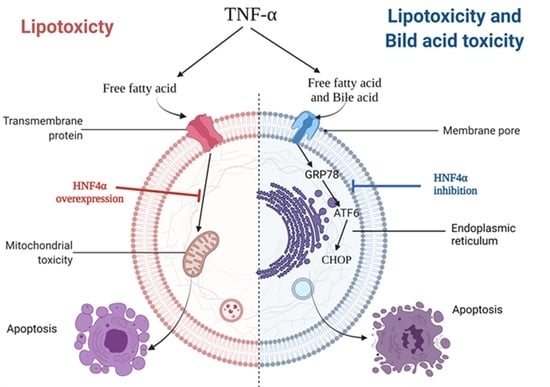
Regulation of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Attenuated Lipotoxicity but Increased Bile Acid Toxicity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hepatic HNF4α Expression in NAFLD Patients
2.2. Hepatic HNF4α Expression NAFLD Animal Models
2.3. Histology Assessment
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. shHNF4α Construction and Animal Study
2.6. HNF4α Overexpression in In Vitro System
2.7. siRNA Knockdown
2.8. Cell Culture
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. TUNEL Assay
2.11. MTT Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hepatic HNF4α Expression Increased in NAFLD
3.2. HNF4α Overexpression Attenuated Lipotoxicity
3.3. HNF4α Overexpression Increased NFκB via Activating Bile Acid Synthesis
3.4. Inhibition of HNF4α Attenuated Bile Acid Toxicity
3.5. Inhibition of HNF4α Attenuated Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in NAFLD Animal Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, X.; Lee, D.H.; Fujii, H.; Wu, Y.; Kam, L.Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999–2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayhurst, G.P.; Lee, Y.H.; Lambert, G.; Ward, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (nuclear receptor 2A1) is essential for maintenance of hepatic gene expression and lipid homeostasis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watt, A.J.; Garrison, W.D.; Duncan, S.A. HNF4: A central regulator of hepatocyte differentiation and function. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.Y. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha regulation of bile acid and drug metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, H.H.; Ng, N.H.J.; Loo, L.S.W.; Jasmen, J.B.; Teo, A.K.K. The molecular functions of hepatocyte nuclear factors—In and beyond the liver. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, J.Y. Regulation of bile acid synthesis: Pathways, nuclear receptors, and mechanisms. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Ma, H.; Ge, X.; Edwards, P.A.; Zhang, Y. Hepatic hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha is essential for maintaining triglyceride and cholesterol homeostasis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamagata, K.; Furuta, H.; Oda, N.; Kaisaki, P.J.; Menzel, S.; Cox, N.J.; Fajans, S.S.; Signorini, S.; Stoffel, M.; Bell, G.I. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY1). Nature 1996, 384, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baciu, C.; Pasini, E.; Angeli, M.; Schwenger, K.; Afrin, J.; Humar, A.; Fischer, S.; Patel, K.; Allard, J.; Bhat, M. Systematic integrative analysis of gene expression identifies HNF4A as the central gene in pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Chen, G.; Pan, M.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; Liu, Y.; Nian, X.; Sheng, L.; Xu, B. High fat diet-induced oxidative stress blocks hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha and leads to hepatic steatosis in mice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 4770–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebke-Wheeler, J.; Zhang, K.; Battle, M.; Si-Tayeb, K.; Garrison, W.; Chhinder, S.; Li, J.; Kaufman, R.J.; Duncan, S.A. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha is implicated in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced acute phase response by regulating expression of cyclic adenosine monophosphate responsive element binding protein H. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Zhang, Y.; Klaassen, C.D. Dose-response of five bile acids on serum and liver bile Acid concentrations and hepatotoxicty in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, M.; Coxito, P.M.; Sardao, V.A.; Palmeira, C.M.; Oliveira, P.J. Bile acids are toxic for isolated cardiac mitochondria: A possible cause for hepatic-derived cardiomyopathies? Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2005, 5, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashby, K.; Navarro Almario, E.E.; Tong, W.; Borlak, J.; Mehta, R.; Chen, M. Review article: Therapeutic bile acids and the risks for hepatotoxicity. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1623–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, H. Crosstalk of HNF4alpha with extracellular and intracellular signaling pathways in the regulation of hepatic metabolism of drugs and lipids. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Zalzala, M.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y. A metabolic stress-inducible miR-34a-HNF4alpha pathway regulates lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Lu, H. Novel mechanisms of regulation of the expression and transcriptional activity of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmucker, D.L.; Ohta, M.; Kanai, S.; Sato, Y.; Kitani, K. Hepatic injury induced by bile salts: Correlation between biochemical and morphological events. Hepatology 1990, 12, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranha, M.M.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Costa, A.; da Silva, I.B.; Camilo, M.E.; de Moura, M.C.; Rodrigues, C.M. Bile acid levels are increased in the liver of patients with steatohepatitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 20, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, S.; Yang, Y.; McCullough, A.J.; Marczewski, S.; Bennett, C.; Kalhan, S.C. Elevated hepatic fatty acid oxidation, high plasma fibroblast growth factor 21, and fasting bile acids in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 23, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, J.Y. Bile acid regulation of gene expression: Roles of nuclear hormone receptors. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crestani, M.; Sadeghpour, A.; Stroup, D.; Galli, G.; Chiang, J.Y. Transcriptional activation of the cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A) by nuclear hormone receptors. J. Lipid Res. 1998, 39, 2192–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, N.; Baker, S.S.; Chapa-Rodriguez, A.; Liu, W.; Nugent, C.A.; Tsompana, M.; Mastrandrea, L.; Buck, M.J.; Baker, R.D.; Genco, R.J.; et al. Suppressed hepatic bile acid signalling despite elevated production of primary and secondary bile acids in NAFLD. Gut 2018, 67, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y.; Stroup, D. Identification and characterization of a putative bile acid-responsive element in cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17502–17507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusl, T.; Wild, N.; Vennegeerts, T.; Wimmer, R.; Goke, B.; Brand, S.; Rust, C. Free fatty acids sensitize hepatocytes to bile acid-induced apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechmann, L.P.; Kocabayoglu, P.; Sowa, J.P.; Sydor, S.; Best, J.; Schlattjan, M.; Beilfuss, A.; Schmitt, J.; Hannivoort, R.A.; Kilicarslan, A.; et al. Free fatty acids repress small heterodimer partner (SHP) activation and adiponectin counteracts bile acid-induced liver injury in superobese patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1394–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, M.; Jambon, S.; Depauw, S.; David-Cordonnier, M.H. Targeting Transcription Factors for Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2018, 23, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henley, M.J.; Koehler, A.N. Advances in targeting ‘undruggable’ transcription factors with small molecules. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 669–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Characteristics | Control (n = 16) | NAFLD (n = 33) | * p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (Men, %) | 18.8% | 48.5% | 0.011 |
| Age (year) | 45.2 ± 13.2 | 45.3 ± 14.7 | 0.983 |
| Height (cm) | 160.7 ± 6.1 | 165.7 ± 10.5 | 0.044 |
| Weight (kg) | 59.6 ± 10.7 | 72.7 ± 12.6 | <0.001 |
| AST (IU) | 29.9 ± 1.2 | 36.3 ± 18.9 | <0.001 |
| ALT (IU) | 17.1 ± 7.1 | 51.9 ± 41.0 | <0.001 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.7 | 0.423 |
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 0.067 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 97.8 ± 17.7 | 109.6 ± 52.7 | 0.295 |
| GGT (mg/dL) | 30.4 ± 23.2 | 57.5 ± 44.4 | 0.011 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 190.3 ±32.9 | 189.8 ± 46.1 | 0.964 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 91.6 ± 44.7 | 165.3 ± 121.3 | 0.006 |
| HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 61.6 ± 14.6 | 45.1 ± 9.8 | <0.001 |
| LDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 114.5 ± 31.8 | 118.4 ± 43.8 | 0.725 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roh, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Yoon, E.L.; Lee, S.R.; Jun, D.W. Regulation of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Attenuated Lipotoxicity but Increased Bile Acid Toxicity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Life 2022, 12, 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12111682
Roh YJ, Kim Y, Lee JS, Oh JH, Lee SM, Yoon EL, Lee SR, Jun DW. Regulation of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Attenuated Lipotoxicity but Increased Bile Acid Toxicity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Life. 2022; 12(11):1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12111682
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoh, Yoon Jin, Yun Kim, Jae Sun Lee, Ju Hee Oh, Seung Min Lee, Eileen Laurel Yoon, Sung Ryol Lee, and Dae Won Jun. 2022. "Regulation of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Attenuated Lipotoxicity but Increased Bile Acid Toxicity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease" Life 12, no. 11: 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12111682
APA StyleRoh, Y. J., Kim, Y., Lee, J. S., Oh, J. H., Lee, S. M., Yoon, E. L., Lee, S. R., & Jun, D. W. (2022). Regulation of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Attenuated Lipotoxicity but Increased Bile Acid Toxicity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Life, 12(11), 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12111682