Characterization of Cystatin B Interactome in Saliva from Healthy Elderly and Alzheimer’s Disease Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Sample Collection and Treatment
2.3. Affinity Purification
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Tryptic Digestion
2.6. Nano-HPLC-HR-MS/MS Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Biological Processes and Tissue Enrichment Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Immune-Detection of Cystatin B in IPs
3.2. Identification of the Co-Immunoprecipitated Cystatin B Interactors
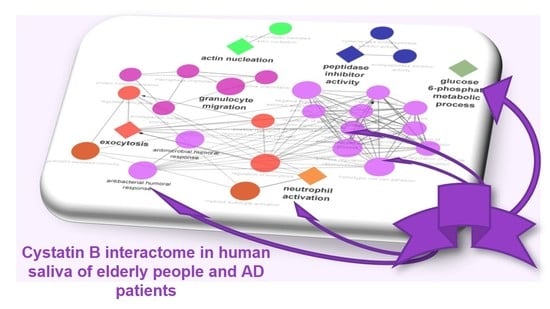
3.3. Biological Pathway and Tissue Analyses
3.4. Preliminary Quantitative Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dickinson, D.P. Cysteine peptidases of mammals: Their biological roles and potential effects in the oral cavity and other tissues in health and disease. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2002, 13, 238–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Žerovnik, E.; Staniforth, R.A.; Turk, D. Amyloid fibril formation by human stefins: Structure, mechanism & putative functions. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soond, S.M.; Kozhevnikova, M.V.; Townsend, P.A.; Zamyatnin, A.A. Cysteine Cathepsin Protease Inhibition: An update on its Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Potential in Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magister, S.; Kos, J. Cystatins in immune system. J. Cancer. 2013, 4, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehtinen, M.K.; Tegelberg, S.; Schipper, H.; Su, H.; Zukor, H.; Manninen, O.; Kopra, O.; Joensuu, T.; Hakala, P.; Bonni, A.; et al. Cystatin B deficiency sensitizes neurons to oxidative stress in progressive myoclonus epilepsy, EPM1. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 5910–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butinar, M.; Prebanda, M.T.; Rajković, J.; Jerič, B.; Stoka, V.; Peters, C.; Reinheckel, T.; Krüger, A.; Turk, V.; Turk, B.; et al. Stefin B deficiency reduces tumor growth via sensitization of tumor cells to oxidative stress in a breast cancer model. Oncogene 2014, 217, 3392–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polajnar, M.; Zavašnik-Bergant, T.; Škerget, K.; Vizovišek, M.; Vidmar, R.; Fonović, M.; Kopitar-Jerala, N.; Petrovič, U.; Navarro, S.; Ventura, S.; et al. Human stefin B role in cell’s response to misfolded proteins and autophagy. PLoS ONE 2014, 21, e102500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Turk, V.; Turk, B.; Kopitar-Jerala, N. Increased expression of stefin B in the nucleus of T98G astrocytoma cells delays caspase activation. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopra, O.; Joensuu, T.; Lehesjoki, A.-E. Mouse Model of Unverricht-Lundborg Disease. In Movement Disorders, 2nd ed.; LeDoux, M.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Chapter 41; pp. 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalioti, M.D.; Mirotsou, M.; Buresi, C.; Peitsch, M.C.; Rossier, C.; Ouazzani, R.; Baldy-Moulinier, M.; Bottani, A.; Malafosse, A.; Antonarakis, S.E. Identification of mutations in cystatin B, the gene responsible for the Unverricht-Lundborg type of progressive myoclonus epilepsy (EPM1). Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 60, 342–351. [Google Scholar]
- Di Matteo, F.; Pipicelli, F.; Kyrousi, C.; Tovecci, I.; Penna, E.; Crispino, M.; Chambery, A.; Russo, R.; Ayo-Martin, A.C.; Giordano, M.; et al. Cystatin B is essential for proliferation and interneuron migration in individuals with EPM1 epilepsy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 8, e11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.; Kahn, M.S.; Bano, B. Mammalian cystatin and protagonists in brain diseases. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 2171–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ii, K.; Ito, H.; Kominami, E.; Hirano, A. Abnormal distribution of cathepsin proteinases and endogenous inhibitors (cystatins) in the hippocampus of patients with Alzheimer’s disease, parkinsonism-dementia complex on Guam, and senile dementia and in the aged. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 1993, 423, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contini, C.; Olianas, A.; Serrao, S.; Deriu, C.; Iavarone, F.; Boroumand, M.; Bizzarro, A.; Lauria, A.; Faa, G.; Castagnola, M.; et al. Top-Down Proteomics of Human Saliva Highlights Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant, and antimicrobial Defense Responses in Alzheimer Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 668852, Erratum in Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 743596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contini, C.; Serrao, S.; Manconi, B.; Olianas, A.; Iavarone, F.; Bizzarro, A.; Masullo, C.; Castagnola, M.; Messana, I.; Diaz, G.; et al. Salivary Proteomics Reveals Significant Changes in Relation to Alzheimer’s Disease and Aging. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 89, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyckaerts, C.; Delatour, B.; Potier, M.-C. Classification and basic pathology of Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 5–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, N.V.; Bugrova, A.E.; Indeykina, M.I.; Fedorova, Y.B.; Kolykhalov, I.V.; Gavrilova, S.I.; Nikolaev, E.N.; Kononikhin, A.S. Proteomic Markers and Early Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biochemistry 2022, 87, 762–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawksworth, J.; Fernández, E.; Gevaert, K. A new generation of AD biomarkers: 2019 to 2021. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 79, 101654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htike, T.T.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, S.; Padmanabhan, P.; Gulyás, B. Peripheral Biomarkers for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2256–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.P.; Sathe, G. Proteomics Landscape of Alzheimer’s Disease. Proteomes 2021, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosp, F.; Vossfeldt, H.; Heinig, M.; Vasiljevic, D.; Arumughan, A.; Wyler, E. Genetic and Environmental Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease GERAD1 Consortium; Landthaler, M.; Hubner, N.; Wanker, E.E.; Lannfelt, L.; et al. Quantitative interaction proteomics of neurodegenerative disease proteins. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1134–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenig, C.; Atias, N.; Taylor, A.K.; Mazza, A.; Schaefer, M.H.; Russ, J.; Riechers, S.P.; Bai, S.; Coughlin, M.; Fontaine, J.F.; et al. Interactome Mapping Provides a Network of Neurodegenerative Disease Proteins and Uncovers Widespread Protein Aggregation in Affected Brains. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, G.; Molzahn, C.; Mayor, T. Protein interaction networks in neurodegenerative diseases: From physiological function to aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipollini, E.; Riccio, M.; Di Giaimo, R.; Dal Piaz, F.; Pulice, G.; Catania, S.; Caldarelli, I.; Dembic, M.; Santi, S.; Melli, M. Cystatin B and its EPM1 mutants are polymeric and aggregate prone in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Škerget, K.; Taler-Vercic, A.; Bavdek, A.; Hodnik, V.; Ceru, S.; Tusek-Znidaric, M.; Kumm, T.; Pitsi, D.; Pompe-Novak, M.; Palumaa, P.; et al. Interaction between oligomers of stefin B and amyloid-β in vitro and in cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 3201–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulbrich, L.; Cozzolino, M.; Marini, E.S.; Amori, I.; De Jaco, A.; Carrì, M.T.; Augusti-Tocco, G. Cystatin B and SOD1: Protein-protein interaction and possible relation to neurodegeneration. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giaimo, R.; Riccio, M.; Santi, S.; Galeotti, C.; Ambrosetti, D.C.; Melli, M. New insights into the molecular basis of progressive myoclonus epilepsy: A multiprotein complex with cystatin B. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 2941–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gleerup, H.S.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Simonsen, A.H. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease in Saliva: A Systematic Review. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 4761054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, N.; Wong, D.T. Saliva: Diagnostics and therapeutic perspectives. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farah, R.; Haraty, H.; Salame, Z.; Fares, Y.; Ojcius, D.M.; Said Sadier, N. Salivary biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, M.; Karpe, A.; Liu, J.W.; Beale, D.; Hor, M.; Hecker, J.; Faunt, J.; Maddison, J.; Johns, S.; Doecke, J.; et al. Salivaomics as a Potential Tool for Predicting Alzheimer’s Disease During the Early Stages of Neurodegeneration. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 82, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Lu, H. Salivary biological biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 105, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gundry, R.L.; White, M.Y.; Murray, C.I.; Kane, L.A.; Fu, Q.; Stanley, B.A.; Van Eyk, J.E. Preparation of proteins and peptides for mass spectrometry analysis in a bottom-up proteomics workflow. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010, 90, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guard, S.E.; Ebmeier, C.C.; Old, W.M. Label-free immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry workflow for large-scale nuclear interactome profiling. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 153, e60432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mellacheruvu, D.; Wright, Z.; Couzens, A.L.; Lambert, J.P.; St-Denis, N.A.; Li, T.; Miteva, Y.V.; Hauri, S.; Sardiu, M.E.; Low, T.Y.; et al. The CRAPome: A contaminant repository for affinity purification-mass spectrometry data. Nat. Methods. 2013, 10, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deutsch, E.W.; Bandeira, N.; Sharma, V.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Carver, J.J.; Kundu, D.J.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Jarnuczak, A.F.; Hewapathirana, S.; Pullman, B.S.; et al. The ProteomeXchange consortium in 2020: Enabling “big data” approaches in proteomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyanova, S.; Cox, J. Perseus: A bioinformatics platform for integrative analysis of proteomics data in cancer research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1711, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabras, T.; Manconi, B.; Iavarone, F.; Fanali, C.; Nemolato, S.; Fiorita, A.; Scarano, E.; Passali, G.C.; Manni, A.; Cordaro, M.; et al. RP-HPLC-ESI-MS evidenced that salivary cystatin B is detectable in adult human whole saliva mostly as S-modified derivatives: S-Glutathionyl, S-cysteinyl and S-S 2-mer. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazgier, M.; Ericksen, B.; Ling, M.; Toth, E.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Galliher-Beckley, A.; Lan, L.; Zou, G.; Zhan, C.; et al. Structural and functional analysis of the pro-domain of human cathelicidin, LL-37. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedrero-Prieto, C.M.; García-Carpintero, S.; Frontiñán-Rubio, J.; Llanos-González, E.; Aguilera García, C.; Alcaín, F.J.; Lindberg, I.; Durán-Prado, M.; Peinado, J.R.; Rabanal-Ruiz, Y. A comprehensive systematic review of CSF proteins and peptides that define Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Proteomics. 2020, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simrén, J.; Ashton, N.J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. An update on fluid biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases: Recent success and challenges ahead. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 61, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, A.L.; Eckhardt, M.; Krogan, N.J. Mass spectrometry-based protein–protein interaction networks for the study of human diseases. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2021, 17, e8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenko Kokalj, S.; Guncar, G.; Stern, I.; Morgan, G.; Rabzelj, S.; Kenig, M.; Staniforth, R.A.; Waltho, J.P.; Zerovnik, E.; Turk, D. Essential Role of Proline Isomerization in Stefin B Tetramer Formation. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 366, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, E.; Cerciello, A.; Chambery, A.; Russo, R.; Cernilogar, F.M.; Pedone, E.M.; Perrone-Capano, C.; Cappello, S.; Di Giaimo, R.; Crispino, M. Cystatin B Involvement in Synapse Physiology of Rodent Brains and Human Cerebral Organoids. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos Remedios, C.G.; Chhabra, D.; Kekic, M.; Dedova, I.V.; Tsubakihara, M.; Berry, D.A.; Nosworthy, N.J. Actin binding proteins: Regulation of cytoskeletal microfilaments. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 433–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.; Sekheri, M.; Filep, J.G. Roles of neutrophil granule proteins in orchestrating inflammation and immunity. FEBS J. 2021, 289, 3932–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, T.; Dahlgren, C.; Stendahl, O.; Andersson, T. Actin assembly and regulation of neutrophil function: Effects of cytochalasin B and tetracaine on chemotactic peptide-induced O2-production and degranulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1991, 49, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, P. Mechanisms of degranulation in neutrophils. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2006, 2, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teahan, C.G.; Totty, N.F.; Segal, A.W. Isolation and characterization of grancalcin, a novel 28 kDa EF-hand calcium-binding protein from human neutrophils. Biochem. J. 1992, 286, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Roes, J.; Segal, A.W.; Radulovic, M. The role of grancalcin in adhesion of neutrophils. Cell Immunol. 2006, 240, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, F.; Umeda, Y.; Shimamoto, S.; Tsuchiya, M.; Tokumitsu, H.; Tokuda, M.; Kobayashi, R. S100 proteins modulate protein phosphatase 5 function: A link between Ca 2+ signal transduction and protein dephosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13787–13798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.Q.; Yamamoto, M.; Mejillano, M.; Yin, H.L. Gelsolin, a multifunctional actin regulatory protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33179–33182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janji, B.; Giganti, A.; De Corte, V.; Catillon, M.; Bruyneel, E.; Lentz, D.; Plastino, J.; Gettemans, J.; Friederich, E. Phosphorylation on Ser5 increases the F-actin-binding activity of L-plastin and promotes its targeting to sites of actin assembly in cells. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryckman, C.; Vandal, K.; Rouleau, P.; Talbot, M.; Tessier, P.A. Proinflammatory Activities of S100: Proteins S100A8, S100A9, and S100A8/A9 Induce Neutrophil Chemotaxis and Adhesion. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Song, R.; Wang, Z.; Jing, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, J. S100A8/A9 in inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Solovjov, D.A.; Ugarova, T.P.; Plow, E.F. Integrin alpha(M)beta(2)-mediated cell migration to fibrinogen and its recognition peptides. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Zhang, K.; Chen, J. Role of integrins in regulating proteases to mediate extracellular matrix remodeling. Cancer Microenviron. 2012, 5, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, S. A critical review on serine protease: Key immune manipulator and pathology mediator. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2017, 45, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, N.; Terlizzi, J.; Aho, S.; Brittingham, R.; Fertala, A.; Oyama, N.; McGrath, J.A.; Uitto, J. Extracellular matrix protein 1 inhibits the activity of matrix metalloproteinase 9 through high-affinity protein/protein interactions. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajes, M.; Eraso-Pichot, A.; Rubio-Moscardo, F.; Guivernau, B.; Ramos-Fernández, E.; Bosch-Morató, M.; Guix, F.X.; Clarimón, J.; Miscione, G.P.; Boada, M.; et al. Methylglyoxal produced by amyloid-β peptide-induced nitrotyrosination of triosephosphate isomerase triggers neuronal death in alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 41, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tajes, M.; Eraso-Pichot, A.; Rubio-Moscardó, F.; Guivernau, B.; Bosch-Morató, M.; Valls-Comamala, V.; Muñoz, F.J. Methylglyoxal reduces mitochondrial potential and activates Bax and caspase-3 in neurons: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 580, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riederer, I.M.; Schiffrin, M.; Kövari, E.; Bouras, C.; Riederer, B.M. Ubiquitination and cysteine nitrosylation during aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.F.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. S-Nitrosylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Harris, P.L.; Sayre, L.M.; Perry, G. Iron accumulation in Alzheimer disease is a source of redox-generated free radicals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9866–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dyer, R.R.; Ford, K.I.; Robinson, R.A.S. The roles of S-nitrosylation and S-glutathionylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Methods Enzymol. 2019, 626, 499–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørklund, G.; Svanberg, E.; Dadar, M.; Card, D.J.; Chirumbolo, S.; Harrington, D.J.; Aaseth, J. The Role of Matrix Gla Protein (MGP) in Vascular Calcification. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 1647–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennartsson, A.; Pieters, K.; Vidovic, K.; Gullberg, U. A murine antibacterial ortholog to human bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI) is expressed in testis, epididymis, and bone marrow. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, R.B.; Hollingsworth, M.A. Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Dhapola, R.; Sarma, P.; Medhi, B.; Reddy, D.H. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease: Current Progress in Molecular Signaling and Therapeutics. Inflammation 2022, 46, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| HC | Sex, Age | μg/μL | AD | Sex, Age | μg/μL | NEG | Sex, Age | μg/μL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #3 | F, 84 | 1.1 | #12 | F, 84 | 0.6 | #2 | M, 85 | 1.8 |
| #5 | F, 81 | 1.4 | #13 | F, 79 | 0.7 | #3 | F, 84 | 1.1 |
| #9 | M, 71 | 1.5 | #14 | F, 82 | 0.9 | #4 | M, 82 | 1.6 |
| #11 | M, 76 | 1.7 | #16 | F, 83 | 0.6 | #5 | F, 81 | 1.4 |
| #12 | F, 77 | 1.2 | #17 | F, 63 | 0.7 | #7 | F, 79 | 1.6 |
| #13 | M, 74 | 1.2 | #18 | F, 80 | 0.9 | #8 | M, 74 | 2.2 |
| #14 | M, 87 | 2.7 | #19 | F, 80 | 0.4 | #9 | M, 71 | 1.5 |
| #16 | F, 81 | 0.9 | #20 | M, 87 | 0.5 | #10 | M, 78 | 1.5 |
| #17 | F, 82 | 1.5 | #22 | M, 87 | 0.8 | #11 | M, 76 | 1.7 |
| #19 | F, 86 | 1.8 | #23 | F, 75 | 0.4 | #12 | F, 77 | 1.2 |
| #20 | F, 73 | 3.2 | #24 | F, 75 | 0.3 | #13 | M, 74 | 1.2 |
| #21 | M, 79 | 2.2 | #25 | F, 83 | 0.2 | #15 | M, 73 | 1.7 |
| #22 | F, 78 | 1.7 | #26 | F, 84 | 0.4 | #16 | F, 81 | 0.9 |
| #24 | F, 78 | 1.2 | #27 | F, 81 | 0.3 | #18 | F, 72 | 1.7 |
| #25 | F, 75 | 2.1 | #30 | M, 86 | 0.2 | #20 | F, 73 | 3.2 |
| #26 | F, 75 | 0.8 | #32 | F, 88 | 0.3 | #21 | M, 79 | 2.2 |
| #30 | F, 76 | 0.4 | #33 | F, 81 | 0.3 | #22 | F, 78 | 1.7 |
| #28 | F, 78 | 0.5 | #34 | F, 77 | 0.4 | #23 | F, 79 | 2.1 |
| #31 | F, 81 | 0.4 | #35 | M, 87 | 0.8 | #24 | F, 78 | 1.2 |
| #34 | F, 72 | 0.2 | #36 | M, 84 | 1.0 | #25 | F, 75 | 2.1 |
| #35 | M, 80 | 1.2 | #37 | F, 77 | 0.6 | #26 | F, 75 | 0.8 |
| #37 | F, 78 | 3.6 | #38 | F, 78 | 1.2 | #28 | F, 78 | 0.5 |
| #38 | F, 78 | 2.2 | #39 | M, 76 | 0.8 | #29 | M, 73 | 0.3 |
| #39 | F, 83 | 1.7 | #40 | M, 85 | 1.6 | #35 | M, 80 | 1.2 |
| #36 | F, 73 | 2.9 | ||||||
| #38 | F, 78 | 2.2 |
| UniProt-KB Code | Protein Name | MW | AD and HC (NR Samples) > 150 kDa |
|---|---|---|---|
| P52209 | 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylating | 53.1 | ● |
| O15144 | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 2 | 34.3 | ● |
| P59998 | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 4 | 19.7 | |
| P61158 | Actin-related protein 3 | 47.3 | ● |
| Q9HDC9 | Adipocyte plasma membrane-associated protein | 46.5 | |
| P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | 46.7 | |
| A8K2U0 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin-like protein 1 | 161.0 | ● |
| P0DTE7 | Alpha-amylase 1B | 57.7 | ● |
| P04083 | Annexin A1 | 38.7 | ● |
| P50995 | Annexin A11 | 54.4 | |
| P12429 | Annexin A3 | 36.4 | |
| P08758 | Annexin A5 | 35.9 | |
| P20292 | Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein | 18.1 | |
| P17213 | Bactericidal permeability-increasing protein | 53.9 | ● |
| Q96DR5 | BPI fold-containing family A member 2 | 27.0 | |
| Q8TDL5 | BPI fold-containing family B member 1 | 52.4 | ● |
| Q8N4F0 | BPI fold-containing family B member 2 | 49.1 | |
| P23280 | Carbonic anhydrase 6 | 35.3 | ● |
| P06731 | Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 | 76.7 | |
| P49913 | Cathelin-like domain | 11.3 | |
| P08311 | Cathepsin G | 28.8 | ● |
| P08962 | CD63 antigen | 25.6 | |
| P29373 | Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2 | 15.7 | ● |
| P0C0L4 | Complement C4-A | 192.7 | |
| O75131 | Copine-3 | 60.1 | |
| Q9UBG3 | Cornulin | 53.5 | ● |
| P31146 | Coronin-1A | 51.0 | ● |
| P04080 | Cystatin-B | 11.1 | ● |
| P01034 | Cystatin-C | 15.8 | ● |
| P28325 | Cystatin-D | 16.1 | ● |
| P09228 | Cystatin-SA | 16.4 | |
| P01037 | Cystatin-SN | 16.4 | ● |
| P54108 | Cysteine-rich secretory protein 3 | 27.6 | |
| P31930 | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 1 | 52.6 | |
| P32926 | Desmoglein-3 | 107.5 | ● |
| Q96HE7 | ERO1-like protein alpha | 54.4 | ● |
| Q16610 | Extracellular matrix protein 1 | 60.6 | ● |
| Q01469 | Fatty acid-binding protein 5 | 15.2 | ● |
| P02671 | Fibrinogen alpha chain | 94.9 | ● |
| P02675 | Fibrinogen beta chain | 55.9 | ● |
| P02679 | Fibrinogen gamma chain | 51.5 | ● |
| P17931 | Galectin-3 | 26.1 | ● |
| P47929 | Galectin-7 | 15.1 | ● |
| P06396 | Gelsolin | 85.6 | ● |
| P11413 | Glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase | 59.2 | ● |
| P06744 | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase | 63.1 | ● |
| P15104 | Glutamine synthetase | 42.0 | |
| P09211 | Glutathione S-transferase P | 23.3 | ● |
| P28676 | Grancalcin | 24.0 | |
| P04899 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-2 | 40.4 | ● |
| P04792 | Heat shock protein beta-1 | 22.8 | ● |
| P11215 | Integrin alpha-M | 127.1 | |
| P05107 | Integrin beta-2 | 84.7 | |
| P22079 | Lactoperoxidase | 80.2 | ● |
| P30740 | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor | 42.7 | ● |
| P08493 | Matrix γ-carboxyglutamic acid (GLA)–rich protein | 12.3 | ● |
| P14780 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | 78.4 | |
| Q9HC84 | Mucin-5B | 596.0 | ● |
| Q8TAX7 | Mucin-7 | 39.1 | ● |
| P24158 | Myeloblastin | 27.8 | |
| P41218 | Myeloid cell nuclear differentiation antigen | 45.8 | ● |
| P05164 | Myeloperoxidase | 83.8 | ● |
| P59665 | Neutrophil defensin 1 | 10.2 | ● |
| P08246 | Neutrophil elastase | 28.5 | ● |
| O15162 | Phospholipid scramblase 1 | 35.0 | |
| P13796 | Plastin-2 | 70.2 | ● |
| P12273 | Prolactin-inducible protein | 16.6 | ● |
| P06703 | Protein S100-A6 | 10.2 | ● |
| P05109 | Protein S100-A8 | 10.8 | ● |
| P06702 | Protein S100-A9 | 13.2 | ● |
| Q08188 | Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase E | 76.6 | ● |
| P50395 | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta | 50.6 | ● |
| P60763 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 3 | 21.4 | |
| P51159 | Ras-related protein Rab-27A | 24.9 | |
| P52566 | Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 2 | 23.0 | ● |
| P48594 | Serpin B4 | 44.8 | |
| P36952 | Serpin B5 | 42.1 | ● |
| Q9UBC9 | Small proline-rich protein 3 | 18.1 | ● |
| P29401 | Transketolase | 67.8 | ● |
| P60174 | Triosephosphate isomerase | 26.7 | ● |
| Q16851 | UTP--glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase | 56.9 | |
| Q96DA0 | Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B | 22.7 | ● |
| Log2 LFQ Abundance, Mean ± SD | AD VS HC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UniProt-KB Code | Protein Name | AD | HC | −Log10 p Value (p Value) | Log2 Fold Change (Fold Change) | |
| P17213 | BPI | 24.8 ± 0.1 | 23.5 ± 0.3 | 2.7 (0.002) | 1.2 (2.3) | ↑AD |
| P08493 | Matrix Gla protein | 22.2 ± 0.4 | 20.6 ± 0.4 | 2.1 (0.008) | 1.6 (3.0) | ↑AD |
| Q8TAX7 | Mucin-7 | 24.7 ± 0.5 | 23.6 ± 0.2 | 1.9 (0.01) | 1.2 (2.3) | ↑AD |
| P60174 | TPI | 18.3 ± 0.6 | 19.7 ± 0.4 | 1.6 (0.02) | −1.4 (0.4) | ↓AD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contini, C.; Serrao, S.; Manconi, B.; Olianas, A.; Iavarone, F.; Guadalupi, G.; Messana, I.; Castagnola, M.; Masullo, C.; Bizzarro, A.; et al. Characterization of Cystatin B Interactome in Saliva from Healthy Elderly and Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Life 2023, 13, 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030748
Contini C, Serrao S, Manconi B, Olianas A, Iavarone F, Guadalupi G, Messana I, Castagnola M, Masullo C, Bizzarro A, et al. Characterization of Cystatin B Interactome in Saliva from Healthy Elderly and Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Life. 2023; 13(3):748. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030748
Chicago/Turabian StyleContini, Cristina, Simone Serrao, Barbara Manconi, Alessandra Olianas, Federica Iavarone, Giulia Guadalupi, Irene Messana, Massimo Castagnola, Carlo Masullo, Alessandra Bizzarro, and et al. 2023. "Characterization of Cystatin B Interactome in Saliva from Healthy Elderly and Alzheimer’s Disease Patients" Life 13, no. 3: 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030748
APA StyleContini, C., Serrao, S., Manconi, B., Olianas, A., Iavarone, F., Guadalupi, G., Messana, I., Castagnola, M., Masullo, C., Bizzarro, A., Turck, C. W., Maccarrone, G., & Cabras, T. (2023). Characterization of Cystatin B Interactome in Saliva from Healthy Elderly and Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Life, 13(3), 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030748