Cerebrospinal Fluid Penetration and Combination Therapy of Entrectinib for Disseminated ROS1/NTRK-Fusion Positive Pediatric High-Grade Glioma
Abstract
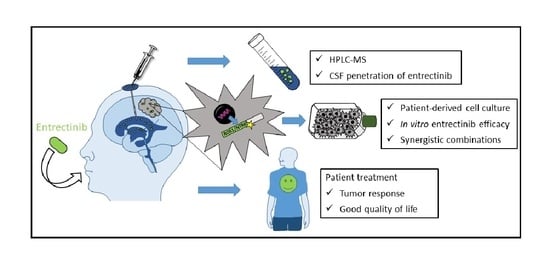
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Patient Samples and Characteristics
2.2. Histopathology
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS) Analysis
2.5. Cell Models
2.6. ATP Assay
2.7. Colony Formation Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics and Response to Entrectinib
3.2. Molecular Diagnostics and Next Generation Sequencing
3.3. CSF Penetration of Entrectinib
3.4. Impact of Entrectinib and Combination with Targeted Therapies on NTRK-Fusion Positive pHGG Cell Viability and Proliferation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celestino, R.; Sigstad, E.; Løvf, M.; Thomassen, G.O.S.; Grøholt, K.K.; Jørgensen, L.H.; Berner, A.; Castro, P.; Lothe, R.A.; Bjøro, T.; et al. Survey of 548 oncogenic fusion transcripts in thyroid tumors supports the importance of the already established thyroid fusions genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012, 51, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.K.; Hong, F.; Vaklavas, C.; Cheng, H.H.; Hammerman, P.; Mitchell, E.P.; Zwiebel, J.A.; Ivy, S.P.; Gray, R.J.; Li, S.; et al. Phase II Study of AZD4547 in Patients with Tumors Harboring Aberrations in the FGFR Pathway: Results From the NCI-MATCH Trial (EAY131) Subprotocol W. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Castillo, M.; Chibon, F.; Arnould, L.; Croce, S.; Ribeiro, A.; Perot, G.; Hostein, I.; Geha, S.; Bozon, C.; Garnier, A.; et al. Secretory Breast Carcinoma: A Histopathologic and Genomic Spectrum Characterized by a Joint Specific ETV6-NTRK3 Gene Fusion. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, R.; Boichard, A.; Kato, S.; Sicklick, J.K.; Bazhenova, L.; Kurzrock, R. Analysis of NTRK Alterations in Pan-Cancer Adult and Pediatric Malignancies: Implications for NTRK-Targeted Therapeutics. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.Y.; Goldman, D.A.; Hechtman, J.F.; Benayed, R.; Schram, A.M.; Cocco, E.; Shifman, S.; Gong, Y.; Kundra, R.; Solomon, J.P.; et al. TRK Fusions Are Enriched in Cancers with Uncommon Histologies and the Absence of Canonical Driver Mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerreiro Stucklin, A.S.; Ryall, S.; Fukuoka, K.; Zapotocky, M.; Lassaletta, A.; Li, C.; Bridge, T.; Kim, B.; Arnoldo, A.; Kowalski, P.E.; et al. Alterations in ALK/ROS1/NTRK/MET drive a group of infantile hemispheric gliomas. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, M.; Mackay, A.; Ismer, B.; Pickles, J.C.; Tatevossian, R.G.; Newman, S.; Bale, T.A.; Stoler, I.; Izquierdo, E.; Temelso, S.; et al. Infant High-Grade Gliomas Comprise Multiple Subgroups Characterized by Novel Targetable Gene Fusions and Favorable Outcomes. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 942–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torre, M.; Vasudevaraja, V.; Serrano, J.; DeLorenzo, M.; Malinowski, S.; Blandin, A.-F.; Pages, M.; Ligon, A.H.; Dong, F.; Meredith, D.M.; et al. Molecular and clinicopathologic features of gliomas harboring NTRK fusions. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C.; Grill, J.; Lellouch-Tubiana, A.; Puget, S.; Chastagner, P.; Frappaz, D.; Doz, F.; Pichon, F.; Plantaz, D.; Gentet, J.C.; et al. High-grade glioma in children under 5 years of age: A chemotherapy only approach with the BBSFOP protocol. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 2006, 42, 2939–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, R.G.; Wilne, S.H.; Robinson, K.J.; Ironside, J.W.; Cox, T.; Chong, W.K.; Michalski, A.; Campbell, R.H.A.; Bailey, C.C.; Thorp, N.; et al. Primary postoperative chemotherapy without radiotherapy for treatment of brain tumours other than ependymoma in children under 3 years: Results of the first UKCCSG/SIOP CNS 9204 trial. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 2010, 46, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.; Perryman, L.; Hargrave, D. Paediatric and adult malignant glioma: Close relatives or distant cousins? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocco, E.; Scaltriti, M.; Drilon, A. NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Ippen, F.M.; Hafeez, U.; Gan, H.K. Emerging Gene Fusion Drivers in Primary and Metastatic Central Nervous System Malignancies: A Review of Available Evidence for Systemic Targeted Therapies. Oncologist 2018, 23, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guntner, A.S.; Peyrl, A.; Mayr, L.; Englinger, B.; Berger, W.; Slavc, I.; Buchberger, W.; Gojo, J. Cerebrospinal fluid penetration of targeted therapeutics in pediatric brain tumor patients. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doebele, R.C.; Drilon, A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Siena, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Farago, A.F.; Blakely, C.M.; Seto, T.; Cho, B.C.; Tosi, D.; et al. Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: Integrated analysis of three phase 1-2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Takeda, M.; Shimizu, S.; Takahama, T.; Yoshida, T.; Watanabe, S.; Iwasa, T.; Yonesaka, K.; Suzuki, S.; Hayashi, H.; et al. A comparative study of curated contents by knowledge-based curation system in cancer clinical sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, D.; Wieland, T.; Solfrank, B.; Grossmann, V.; Steinhard, J.; Frick, A.; Hempel, L.; Eberl, T.; Gaumann, A. Antitumor Activity of Larotrectinib in Esophageal Carcinoma with NTRK Gene Amplification. Oncologist 2020, 25, e881–e886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfaff, E.; El Damaty, A.; Balasubramanian, G.P.; Blattner-Johnson, M.; Worst, B.C.; Stark, S.; Witt, H.; Pajtler, K.W.; van Tilburg, C.M.; Witt, R.; et al. Brainstem biopsy in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma in the era of precision medicine: The INFORM study experience. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 2019, 114, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafay-Cousin, L.; Mabbott, D.J.; Halliday, W.; Taylor, M.D.; Tabori, U.; Kamaly-Asl, I.D.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Bartels, U.; Greenberg, M.; Bouffet, E. Use of ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide chemotherapy in choroid plexus carcinoma. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2010, 5, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavc, I.; Schuller, E.; Falger, J.; Günes, M.; Pillwein, K.; Czech, T.; Dietrich, W.; Rössler, K.; Dieckmann, K.; Prayer, D.; et al. Feasibility of long-term intraventricular therapy with mafosfamide (n = 26) and etoposide (n = 11): Experience in 26 children with disseminated malignant brain tumors. J. Neurooncol. 2003, 64, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajtler, K.W.; Tippelt, S.; Siegler, N.; Reichling, S.; Zimmermann, M.; Mikasch, R.; Bode, U.; Gnekow, A.; Pietsch, T.; Benesch, M.; et al. Intraventricular etoposide safety and toxicity profile in children and young adults with refractory or recurrent malignant brain tumors. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 128, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, S.L.P.; Berg, S.; Ingle, A.M.; Krailo, M.; Adamson, P.C.; Blaney, S.M. Phase 2 clinical trial of intrathecal topotecan in children with refractory leptomeningeal leukemia: A Children’s Oncology Group trial (P9962). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 58, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cairo, M.S.; Sposto, R.; Gerrard, M.; Auperin, A.; Goldman, S.C.; Harrison, L.; Pinkerton, R.; Raphael, M.; McCarthy, K.; Perkins, S.L.; et al. Advanced stage, increased lactate dehydrogenase, and primary site, but not adolescent age (≥15 years), are associated with an increased risk of treatment failure in children and adolescents with mature B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Results of the FAB LMB 96 study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Ullah, M.; de la Cruz, C.C.; Hunsaker, T.; Senn, C.; Wirz, T.; Wagner, B.; Draganov, D.; Vazvaei, F.; Donzelli, M.; et al. Entrectinib, a TRK/ROS1 inhibitor with anti-CNS tumor activity: Differentiation from other inhibitors in its class due to weak interaction with P-glycoprotein. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Siena, S.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Patel, M.; Ahn, M.J.; Lee, J.; Bauer, T.M.; Farago, A.F.; Wheler, J.J.; Liu, S.V.; et al. Safety and Antitumor Activity of the Multitargeted Pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK Inhibitor Entrectinib: Combined Results from Two Phase I Trials (ALKA-372-001 and STARTRK-1). Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farago, A.F.; Le, L.P.; Zheng, Z.; Muzikansky, A.; Drilon, A.; Patel, M.; Bauer, T.M.; Liu, S.V.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Jackman, D.; et al. Durable Clinical Response to Entrectinib in NTRK1-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2015, 10, 1670–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, D.S.; Bauer, T.M.; Lee, J.J.; Dowlati, A.; Brose, M.S.; Farago, A.F.; Taylor, M.; Shaw, A.T.; Montez, S.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Larotrectinib in adult patients with solid tumours: A multi-centre, open-label, phase I dose-escalation study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.; Miller, J.J.; Nayyar, N.; Gill, C.M.; Kaneb, A.; D’Andrea, M.; Le, L.P.; Lee, J.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Clinical and radiographic response following targeting of BCAN-NTRK1 fusion in glioneuronal tumor. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, A.W.; Kandula, V.V.R.; Shah, N. Larotrectinib imaging response in low-grade glioma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, D.S.; Wong, M.; Mayoh, C.; Kumar, A.; Tsoli, M.; Mould, E.; Tyrrell, V.; Khuong-Quang, D.-A.; Pinese, M.; Gayevskiy, V.; et al. Brief Report: Potent clinical and radiological response to larotrectinib in TRK fusion-driven high-grade glioma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabler, L.; Lötsch, D.; Kirchhofer, D.; van Schoonhoven, S.; Schmidt, H.M.; Mayr, L.; Pirker, C.; Neumayer, K.; Dinhof, C.; Kastler, L.; et al. TERT expression is susceptible to BRAF and ETS-factor inhibition in BRAFV600E/TERT promoter double-mutated glioma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Li, G.; Dogan, S.; Gounder, M.; Shen, R.; Arcila, M.; Wang, L.; Hyman, D.M.; Hechtman, J.; Wei, G.; et al. What hides behind the MASC: Clinical response and acquired resistance to entrectinib after ETV6-NTRK3 identification in a mammary analogue secretory carcinoma (MASC). Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2016, 27, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Nagasubramanian, R.; Blake, J.F.; Ku, N.; Tuch, B.B.; Ebata, K.; Smith, S.; Lauriault, V.; Kolakowski, G.R.; Brandhuber, B.J.; et al. A Next-Generation TRK Kinase Inhibitor Overcomes Acquired Resistance to Prior TRK Kinase Inhibition in Patients with TRK Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russo, M.; Misale, S.; Wei, G.; Siravegna, G.; Crisafulli, G.; Lazzari, L.; Corti, G.; Rospo, G.; Novara, L.; Mussolin, B.; et al. Acquired Resistance to the TRK Inhibitor Entrectinib in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion-Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neftel, C.; Laffy, J.; Filbin, M.G.; Hara, T.; Shore, M.E.; Rahme, G.J.; Richman, A.R.; Silverbush, D.; Shaw, M.L.; Hebert, C.M.; et al. An Integrative Model of Cellular States, Plasticity, and Genetics for Glioblastoma. Cell 2019, 178, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.-S.; McKay, R.M.; Burns, D.K.; Kernie, S.G.; Parada, L.F. A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature 2012, 488, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gojo, J.; Pavelka, Z.; Zapletalova, D.; Schmook, M.T.; Mayr, L.; Madlener, S.; Kyr, M.; Vejmelkova, K.; Smrcka, M.; Czech, T.; et al. Personalized Treatment of H3K27M-Mutant Pediatric Diffuse Gliomas Provides Improved Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.P.; Tirosh, I.; Trombetta, J.J.; Shalek, A.K.; Gillespie, S.M.; Wakimoto, H.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Curry, W.T.; Martuza, R.L.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 2014, 344, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cocco, E.; Schram, A.M.; Kulick, A.; Misale, S.; Won, H.H.; Yaeger, R.; Razavi, P.; Ptashkin, R.; Hechtman, J.F.; Toska, E.; et al. Resistance to TRK inhibition mediated by convergent MAPK pathway activation. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Bendell, J.C.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Burris, H.A.; Patnaik, A.; Jones, S.F.; Rasco, D.; Cox, D.S.; Durante, M.; Bellew, K.M.; et al. A phase IB trial of the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib (GSK1120212) in combination with everolimus in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2015, 26, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usta, D.; Sigaud, R.; Buhl, J.L.; Selt, F.; Marquardt, V.; Pauck, D.; Jansen, J.; Pusch, S.; Ecker, J.; Hielscher, T.; et al. A Cell-Based MAPK Reporter Assay Reveals Synergistic MAPK Pathway Activity Suppression by MAPK Inhibitor Combination in BRAF-Driven Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma Cells. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 1736–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvasaravanan, K.D.; Wiederspohn, N.; Hadzalic, A.; Strobel, H.; Payer, C.; Schuster, A.; Karpel-Massler, G.; Siegelin, M.D.; Halatsch, M.-E.; Debatin, K.-M.; et al. The limitations of targeting MEK signalling in Glioblastoma therapy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, S.; Zhao, L.; Hanson, M.; Kanas, G.; Davis, C.; Robinson, D.; Turnure, M.; Clark, O. Treatment of Advanced/Metastatic Melanoma in the United States and Western Europe: Results of the CancerMPact Survey. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5633–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón-Orjuela, N.; Prieto-Pinto, L.; Lasalvia, P.; Herrera, D.; Castrillón, J.; González-Bravo, D.; Castañeda-Cardona, C.; Rosselli, D. Efficacy and safety of dabrafenib-trametinib in the treatment of unresectable advanced/metastatic melanoma with BRAF-V600 mutation: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Derm. Ther. 2020, 33, e13145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, R.; Hauschild, A.; Santinami, M.; Atkinson, V.; Mandalà, M.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Chiarion Sileni, V.; Larkin, J.; Nyakas, M.; Dutriaux, C.; et al. Five-Year Analysis of Adjuvant Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Stage III Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Tolcher, A.W.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Beeram, M.; Rasco, D.W.; Smith, L.S.; Gunn, S.; Smetzer, L.; Mays, T.A.; Kaiser, B.; et al. The clinical effect of the dual-targeting strategy involving PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAS/MEK/ERK pathways in patients with advanced cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2316–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rangaraju, S.; Farago, A.; Heym, K.M.; Ahn, M.; Drilon, A.; Potts, S.; Hornby, Z.; Multani, P.; Li, G. P14.19 Preclinical and clinical efficacy of entrectinib in primary and metastatic brain tumors harboring NTRK, ROS1, or ALK gene fusions. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, iii106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Case | Disease Status | Location | Histology | Gene-Fusion | Mutations | MGMT | Chromosomal Deletions | Molecular Findings | Cell Line |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1st recurrence | right hemisphere | IHG | ROS/ARCN1 | PTEN | unmeth. | 10 | MAPK-activation | - |
| 2 | primary tumor | left occipital | gliosarcoma | EML4-NTRK3 | MRE11A (VUS) | unmeth. | CDKN2A/B | - | VBT247 |
| 2 | 3rd recurrence | left fronto-median | gliosarcoma | EML4-NTRK3 | INSR, NF2 | unmeth. | 5 p, 8 p, 20, 22, CDKN2A/B | AURKC, IGF1, TGFB3 overexpression | VBT363 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayr, L.; Guntner, A.S.; Madlener, S.; Schmook, M.T.; Peyrl, A.; Azizi, A.A.; Dieckmann, K.; Reisinger, D.; Stepien, N.M.; Schramm, K.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Penetration and Combination Therapy of Entrectinib for Disseminated ROS1/NTRK-Fusion Positive Pediatric High-Grade Glioma. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040290
Mayr L, Guntner AS, Madlener S, Schmook MT, Peyrl A, Azizi AA, Dieckmann K, Reisinger D, Stepien NM, Schramm K, et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Penetration and Combination Therapy of Entrectinib for Disseminated ROS1/NTRK-Fusion Positive Pediatric High-Grade Glioma. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(4):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040290
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayr, Lisa, Armin S. Guntner, Sibylle Madlener, Maria T. Schmook, Andreas Peyrl, Amedeo A. Azizi, Karin Dieckmann, Dominik Reisinger, Natalia M. Stepien, Kathrin Schramm, and et al. 2020. "Cerebrospinal Fluid Penetration and Combination Therapy of Entrectinib for Disseminated ROS1/NTRK-Fusion Positive Pediatric High-Grade Glioma" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 4: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040290
APA StyleMayr, L., Guntner, A. S., Madlener, S., Schmook, M. T., Peyrl, A., Azizi, A. A., Dieckmann, K., Reisinger, D., Stepien, N. M., Schramm, K., Laemmerer, A., Jones, D. T. W., Ecker, J., Sahm, F., Milde, T., Pajtler, K. W., Blattner-Johnson, M., Strbac, M., Dorfer, C., ... Gojo, J. (2020). Cerebrospinal Fluid Penetration and Combination Therapy of Entrectinib for Disseminated ROS1/NTRK-Fusion Positive Pediatric High-Grade Glioma. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(4), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040290