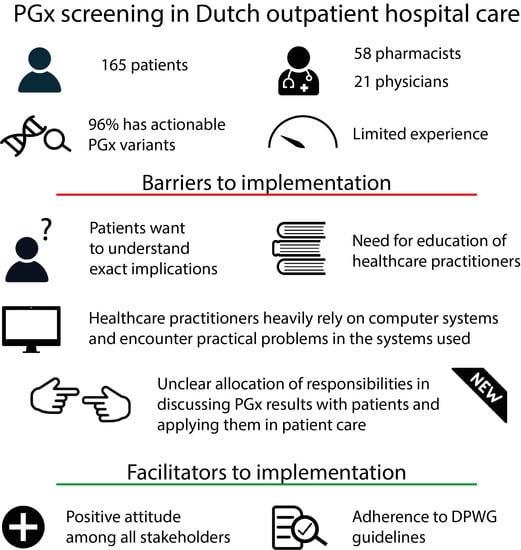
Practical Barriers and Facilitators Experienced by Patients, Pharmacists and Physicians to the Implementation of Pharmacogenomic Screening in Dutch Outpatient Hospital Care—An Explorative Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment of Participants
2.2. Genotyping and Reporting of PGx Screening Results
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Screening Results, Drug Use and DGIs
3.3. CDS Searches and Output during Follow-Up
3.4. Prior Experience of Healthcare Practitioners with PGx
3.5. Knowledge and Education of Healthcare Practitioners
3.6. Patient Attitudes towards PGx Screening after Follow-Up (T2)
3.7. Healthcare Practitioner Attitudes towards PGx Screening
3.8. Practical Application of PGx
3.9. Patients’ Needs for Information about Their PGx Screening Results
3.10. Discussing PGx Screening Results with Patients: Patient Surveys
3.11. Discussing PGx Screening Results with Patients: Healthcare Practitioner Surveys
3.12. Responsibility for Application of PGx Screening Results in Patient Care
3.13. Identified Practical Barriers and Facilitators
4. Discussion
4.1. Frequencies of PGx Variants and DGIs
4.2. Practical Barriers and Facilitators
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartlett, M.J.; Green, D.W.; Shephard, E.A. Pharmacogenetic testing in the UK clinical setting. Lancet 2013, 381, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigter, T.; Jansen, M.E.; de Groot, J.M.; Janssen, S.W.J.; Rodenburg, W.; Cornel, M.C. Implementation of Pharmacogenetics in Primary Care: A Multi-Stakeholder Perspective. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krebs, K.; Milani, L. Translating pharmacogenomics into clinical decisions: Do not let the perfect be the enemy of the good. Hum. Genom. 2019, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swen, J.J.; Wilting, I.; de Goede, A.L.; Grandia, L.; Mulder, H.; Touw, D.J.; de Boer, A.; Conemans, J.M.; Egberts, T.C.; Klungel, O.H.; et al. Pharmacogenetics: From bench to byte. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swen, J.J.; Nijenhuis, M.; de Boer, A.; Grandia, L.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H.; Mulder, H.; Rongen, G.A.; van Schaik, R.H.; Schalekamp, T.; Touw, D.J.; et al. Pharmacogenetics: From bench to byte—An update of guidelines. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, P.C.D.; Swen, J.J.; Guchelaar, H.J. Estimated nationwide impact of implementing a preemptive pharmacogenetic panel approach to guide drug prescribing in primary care in The Netherlands. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Gelder, T.; van Schaik, R.H.N. Pharmacogenetics in daily practice. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 2020, 164, D4191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van der Wouden, C.H.; Paasman, E.; Teichert, M.; Crone, M.R.; Guchelaar, H.-J.; Swen, J.J. Assessing the Implementation of Pharmacogenomic Panel-Testing in Primary Care in the Netherlands Utilizing a Theoretical Framework. JCM 2020, 9, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shuldiner, A.R.; Relling, M.V.; Peterson, J.F.; Hicks, K.; Freimuth, R.R.; Sadee, W.; Pereira, N.L.; Roden, D.M.; Johnson, J.A.; Klein, T.E. The Pharmacogenomics Research Network Translational Pharmacogenetics Program: Overcoming Challenges of Real-World Implementation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanek, E.J.; Sanders, C.L.; Taber, K.A.J.; Khalid, M.; Patel, A.; Verbrugge, R.R.; Agatep, B.C.; Aubert, R.E.; Epstein, R.S.; Frueh, F.W. Adoption of Pharmacogenomic Testing by US Physicians: Results of a Nationwide Survey. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 91, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Driest, S.; Shi, Y.; Bowton, E.; Schildcrout, J.; Peterson, J.; Pulley, J.; Denny, J.; Roden, D. Clinically Actionable Genotypes among 10,000 Patients with Preemptive Pharmacogenomic Testing. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 95, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horgan, D.; Jansen, M.; Leyens, L.; Lal, J.A.; Sudbrak, R.; Hackenitz, E.; Bußhoff, U.; Ballensiefen, W.; Brand, A. An Index of Barriers for the Implementation of Personalised Medicine and Pharmacogenomics in Europe. Public Health Genom. 2014, 17, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunnenberger, H.M.; Crews, K.R.; Hoffman, J.M.; Caudle, K.E.; Broeckel, U.; Howard, S.C.; Hunkler, R.J.; Klein, T.E.; Evans, W.E.; Relling, M.V. Preemptive Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation: Current Programs in Five US Medical Centers. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytema, S.; van der Krieke, L. Routine outcome monitoring: A tool to improve the quality of mental health care? In Improving Mental Health Care; Thornicroft, G., Ruggeri, M., Goldberg, D., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2013; pp. 246–263. ISBN 978-1-118-33798-1. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]



| Healthcare Practitioner | Self-Graded Knowledge Level | Self-Graded Application Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Community pharmacists | with postgraduate education | 6.5 (4–8) | p = 0.011 | 7 (5–10) | p = 0.005 |
| without postgraduate education | 6 (2–7) | 5 (2–8) | |||
| Hospital pharmacists | with postgraduate education | 7.7 (7–9) | p = 0.01 | 7.5 (7–9) | p = 0.016 |
| without postgraduate education | 6.3 (5–7) | 6 (2–7) | |||
| Physicians | with postgraduate education | 7 (1–9) | p = 0.002 | 7 (6–8) | p = 0.203 |
| without postgraduate education | 4 (6–8) | 6 (3–9) | |||
| Responsible Person | Community Pharmacists | Hospital Pharmacists | Physicians |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmacist | 18 (39%) | 5 (38%) | 2 (9.5%) |
| Prescriber | 10 (22%) | 8 (62%) | 16 (76%) |
| Clinical geneticist | 7 (15%) | - | 2 (9.5%) |
| General practitioner | - | - | - |
| Other | - | ||
| Shared responsibility in general | 5 (11%) | ||
| Pharmacist and prescriber are jointly responsible | 4 (9%) | ||
| Pharmacist, providing sufficient information transfer | 1 (2%) | ||
| Depending on drugs prescribed | - | 1 (5%) | |
| Other | 1 (2%) |
| Perceived by Stakeholder | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | Community Pharmacist | Hospital Pharmacist | Physician | |
| Barriers | ||||
| Practical experience is limited | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Need for further postgraduate education | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Rely on computer systems for application | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Need for education about PGx application | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Practical barriers within computer systems | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Lack of information, specifically about exact implications of PGx screening results | Yes | No | No | No |
| Unclear allocation of responsibilities among healthcare practitioners | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Facilitators | ||||
| Positive attitude towards PGx | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| DPWG guidelines are generally well adhered to | No | No | No | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lanting, P.; Drenth, E.; Boven, L.; van Hoek, A.; Hijlkema, A.; Poot, E.; van der Vries, G.; Schoevers, R.; Horwitz, E.; Gans, R.; et al. Practical Barriers and Facilitators Experienced by Patients, Pharmacists and Physicians to the Implementation of Pharmacogenomic Screening in Dutch Outpatient Hospital Care—An Explorative Pilot Study. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040293
Lanting P, Drenth E, Boven L, van Hoek A, Hijlkema A, Poot E, van der Vries G, Schoevers R, Horwitz E, Gans R, et al. Practical Barriers and Facilitators Experienced by Patients, Pharmacists and Physicians to the Implementation of Pharmacogenomic Screening in Dutch Outpatient Hospital Care—An Explorative Pilot Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(4):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040293
Chicago/Turabian StyleLanting, Pauline, Evelien Drenth, Ludolf Boven, Amanda van Hoek, Annemiek Hijlkema, Ellen Poot, Gerben van der Vries, Robert Schoevers, Ernst Horwitz, Reinold Gans, and et al. 2020. "Practical Barriers and Facilitators Experienced by Patients, Pharmacists and Physicians to the Implementation of Pharmacogenomic Screening in Dutch Outpatient Hospital Care—An Explorative Pilot Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 4: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040293
APA StyleLanting, P., Drenth, E., Boven, L., van Hoek, A., Hijlkema, A., Poot, E., van der Vries, G., Schoevers, R., Horwitz, E., Gans, R., Kosterink, J., Plantinga, M., van Langen, I., Ranchor, A., Wijmenga, C., Franke, L., Wilffert, B., & Sijmons, R. (2020). Practical Barriers and Facilitators Experienced by Patients, Pharmacists and Physicians to the Implementation of Pharmacogenomic Screening in Dutch Outpatient Hospital Care—An Explorative Pilot Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(4), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040293