A First Step towards a Comprehensive Approach to Harmonic Analysis of Synchronous Peripheral Volume Pulses: A Proof-of-Concept Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Grouping of Middle-Aged Healthy and Diabetic Subjects
2.2. Study Procedure
2.2.1. Clinic Visit for Type 2 Diabetes
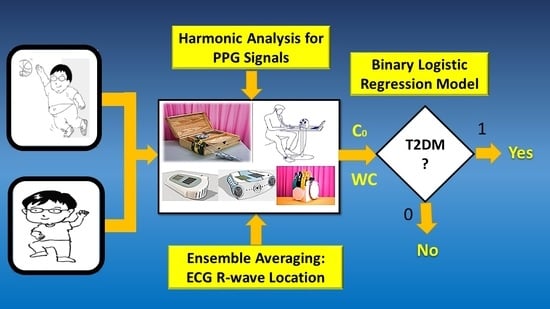
2.2.2. Data Measurement
2.3. Harmonic Analysis of Synchronous Peripheral Volume Pulses
2.3.1. Radial Arterial Waveform and Digital Volume Pulse for the Same Subject
2.3.2. Data Acquisition and Harmonic Analysis in the Study
- Data acquisition for peripheral volume pulses
- 2.
- Harmonic analysis for peripheral volume pulses
2.4. Statistical Methods for the Study
2.4.1. Bland–Altman Analysis
2.4.2. Statistical Analysis and Logistic Regression
3. Results
3.1. C0 from Synchronous Peripheral Volume Pulse Signals
3.2. Assessment of Agreement between Radial Arterial Waveform and Digital Volume Pulse on C0
3.3. Choosing A Sufficient Number for Ensembled Averaging for C0 Computation
3.3.1. Coordination for CPU Time vs. Ensembled Averaging Number
3.3.2. Reproducibility of C0 Using Digital Volume Pulse Measured from Left Index Finger
3.4. Reliability of C0 in Differentiating Type 2 Diabetic Patients
3.4.1. C0 Is associated with Type 2 Diabetics
3.4.2. Correlation of Type 2 Diabetic Risk Factors with C0
3.5. Discrimination of Binary Logistic Regression Model Using SPSS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wang, Y.-Y.L.; Hsu, T.-L.; Jan, M.-Y.; Wang, W.-K. Review: Theory and applications of the harmonic analysis of arterial pressure pulse waves. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2010, 30, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Jindal, G.D.; Jain, R.K.; Bhat, S.N.; Pande, J.A.; Sawant, M.S.; Jindal, S.K.; Deshpande, A.K. Harmonic analysis of peripheral pulse for screening subjects at high risk of diabetes. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2017, 41, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.M.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, S.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, G.C. The first harmonic of radial pulse wave predicts major adverse cardiovascular and microvascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2019, 3, 107420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melis, M.; Morbiducci, U.; Rietzschel, E.R.; De Buyzere, M.; Qasem, A.; Van Bortel, L.; Claessens, T.; Montevecchi, F.M.; Avolio, A.; Segers, P. Blood pressure waveform analysis by means of wavelet transform. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2009, 47, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.T.; Lee, C.H.; Liu, A.B.; Chung, W.S.; Tang, C.J.; Sun, C.K.; Yip, H.K. Arterial stiffness using radial arterial waveforms measured at the wrist as an indicator of diabetic control in the elderly. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.W.; Wang, W.K. Reliability assessment for pulse wave measurement using artificial pulse generator. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2015, 39, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, W.K. Development of a good standard protocol for the harmonic analysis of radial pulse wave and assessing its reliability in healthy humans. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2015, 3, 2900206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, L.C.; Machado, J.P.; Monteiro, F.J.; Greten, H.J. Can traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis be parameterized and standardized? a narrative review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Luo, C.H.; Nilotpal, S.; Tai, C.C.; Xie, X.; Xie, H. Fourier series analysis for novel spatiotemporal pulse waves: Normal, taut, and slippery pulse images. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 5734018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, Y.N.; Huang, Y.C.; Lin, J.S.; Lee, S.M.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Su, Y.C. Different harmonic characteristics were found at each location on TCM radial pulse diagnosis by spectrum analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 3, 9018271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, Z.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Xu, J.T.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.F. Radial pulse wave signals combined with ba-PWV for the risk prediction of hypertension and the monitoring of its accompanying metabolic risk factors. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 3926851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Cheng, S.M.; Lin, J.S.; Lin, C.J.; Su, Y.C. Applying pulse spectrum analysis to facilitate the diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 2709486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, K.M.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, S.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, G.C. Risk assessment of macrovascular and microvascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes by analyzing the amplitude variation of the fourth harmonic component of radial pulse wave. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.M.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, S.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, G.C. Assessment of cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes patients by insight into radial pulse wave harmonic index. Acta Physiol. 2020, 228, e13398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.K.; Tsai, J.S.; Lin, L.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Lai, C.F.; Ho, T.W.; Lai, F. Characteristics of harmonic indexes of the arterial blood pressure waveform in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.W.; Liao, K.M.; Chang, Y.T.; Wang, S.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, G.C. The first harmonic of radial pulse as an early predictor of silent coronary artery disease and adverse cardiac events in type 2 diabetic patients. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 5128626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.A.; Chen, Y.S.; Kuo, C.D. Increased first and second pulse harmonics in Tai Chi Chuan practitioners. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaisti, M.; Panula, T.; Leppänen, J.; Punkkinen, R.; Tadi, M.J.; Vasankari, T.; Jaakkola, S.; Kiviniemi, T.; Airaksinen, J.; Kostiainen, P. Clinical assessment of a non-invasive wearable MEMS pressure sensor array for monitoring of arterial pulse waveform, heart rate and detection of atrial fibrillation. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castaneda, D.; Esparza, A.; Ghamari, M.; Soltanpur, C.; Nazeran, H. A review on wearable photoplethysmography sensors and their potential future applications in health care. Int. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 4, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millasseau, S.C.; Guigui, F.G.; Kelly, R.P.; Prasad, K.; Cockcroft, J.R.; Ritter, J.M.; Chowienczyk, P.J. Noninvasive assessment of the digital volume pulse. Comparison with the peripheral pressure pulse. Hypertension 2000, 36, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- John, A.; Dingchang, Z.; Panicos, A.K.; Mohamed, E. Photoplethysmography, 1st ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021; In press. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, J.L.; Rocha, M.X.; Vasconcelos, G.G.; Vasconcelos Filho, J.E.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Alexandria, A.R. Advances in photopletysmography signal analysis for biomedical applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jindal, G.D.; Bhat, S.N.; Sawant, M.S.; Deshpande, A.K. Role of harmonics and subharmonics in peripheral pulse analysis. MGM J. Med. Sci. 2020, 7, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Hsu, P.C.; Lin, C.F.; Wang, H.J.; Sun, C.K.; Liu, A.B.; Lo, M.T.; Tang, C.J. Multiscale entropy analysis of pulse wave velocity for assessing atherosclerosis in the aged and diabetic. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 2978–2981. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, P.C.; Wu, H.T.; Sun, C.K. Assessment of subtle changes in diabetes-associated arteriosclerosis using photoplethysmographic pulse wave from index finger. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.C.; Ta, N.; Hu, W.R.; Wang, S.Y.; Xiao, M.X.; Tang, X.J.; Chen, J.J.; Wu, H.T. Percussion Entropy Analysis of Synchronized ECG and PPG Signals as a Prognostic Indicator for Future Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Traverso, G.; Ciccarelli, G.; Schwartz, S.; Hughes, T.; Boettcher, T.; Barman, R.; Langer, R.; Swiston, A. Physiologic Status Monitoring via the Gastrointestinal Tract. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rangayyanr, R.M. Biomedical Signal Analysis, 2nd ed.; Wiley-IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 397–401. [Google Scholar]
- Ingle, V.K. Digital Signal Processing Using MATLAB, 3rd ed.; Cengage Learning Stamford: Stamford, CT, USA, 2011; pp. 121–188. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, E.C.; Dowd, B.E.; Maciejewski, M.L. Marginal effects—Quantifying the effect of changes in risk factors in logistic regression models. JAMA 2019, 321, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.W.; Guo, S.W.; Cao, S.S.; Lin, N.; Ye, Z.S.; Wei, S.C.; Zheng, X.Y.; Guo, M.M.; Meng, X.R.; Huang, F.M. The Construction of Unsmooth Pulse Images in Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on Wave Intensity Technology. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 2468254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosch, P.; Al Abdulgader, A. Unappreciated Contributions of Arabic Physicians to Cardiology and Why the Heart Is Truly the “King of Organs”. Cardiol. Vasc. Res. 2021, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Cho, J.; Kim, C. Motion artifact removal techniques for wearable EEG and PPG sensor systems. Front. Electron. 2021, 2, 685513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, H.H.; Shaltis, P.; Reisner, A.; Rhee, S.; Hutchinson, R.C. Mobile monitoring with wearable photoplethysmographic biosensors. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2003, 22, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanello, N.; Landini, L. Introduction to Complex Systems Analysis with Wavelets; Barbieri, R., Scilingo, E., Valenza, G., Eds.; Complexity and Nonlinearity in Cardiovascular Signals; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Group 1 | Group 2 | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD or N (%) | Mean ± SD or N (%) | ||
| Gender (male/female) | 63 (29/34) | 78 (44/34) | N/A |
| Age, year | 54.59 ± 10.06 | 63.54 ± 8.33 ** | <0.001 |
| Body height, cm | 162.58 ± 8.19 | 162.45 ± 8.54 | 0.927 |
| Body weight, kg | 64.32 ± 11.29 | 71.07 ± 11.11 * | 0.001 |
| WC, cm | 83.25 ± 10.85 | 93.87 ± 9.78 ** | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.28 ± 3.68 | 26.88 ± 3.81 ** | <0.001 |
| SBP, mmHg | 120.89 ± 14.58 | 123.99 ± 23.38 | 0.361 |
| DBP, mmHg | 74.86 ± 9.44 | 74.35 ± 13.77 | 0.802 |
| PP, mmHg | 46.03 ± 11.75 | 49.88 ± 15.51 | 0.105 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 124.95 ± 41.12 | 120.87 ± 38.22 | 0.543 |
| Cholesterol, mg/dL | 184.52 ± 66.30 | 185.28 ± 47.23 | 0.937 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.83 ± 0.35 | 8.35 ± 1.77 ** | <0.001 |
| FPG, mg/dL | 99.48 ± 16.42 | 161.83 ± 35.71 ** | <0.001 |
| Location for PVP Measurement | Subject A | Subject B | Subject C | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | C1 | C2 | C0 | C1 | C2 | C0 | C1 | C2 | |
| Left ear | 429.5 | 32.3 | 21.3 | 410.8 | 13.7 | 5.8 | 403.2 | 40.5 | 14.8 |
| Right ear | 429.5 | 10.6 | 5.8 | 410.8 | 3.2 | 1.4 | 403.2 | 6.7 | 2.3 |
| Left index finger | 429.5 | 14.8 | 10.4 | 410.8 | 8.2 | 4.6 | 403.2 | 2.2 | 1.0 |
| Right index finger | 429.5 | 13.1 | 10.0 | 410.8 | 10.0 | 5.8 | 403.2 | 2.3 | 1.2 |
| Left index toe | 429.5 | 4.8 | 2.9 | 410.8 | 13.6 | 8.1 | 403.2 | 12.6 | 7.8 |
| Right index toe | 429.5 | 8.6 | 4.8 | 410.8 | 18.9 | 10.1 | 403.2 | 5.4 | 3.4 |
| Coefficient | Group 1 | Group 2 | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||
| C0 | 417.62 ± 44.80 | 363.05 ± 60.93 ** | <0.001 |
| C1 | 8.53 ± 5.47 | 8.15 ± 6.19 | 0.707 |
| C2 | 3.55 ± 2.43 | 3.30 ± 2.41 | 0.545 |
| C3 | 1.62 ± 1.12 | 1.46 ± 1.20 | 0.426 |
| C4 | 0.86 ± 0.69 | 0.80 ± 0.64 | 0.568 |
| C5 | 0.76 ± 0.56 | 0.68 ± 0.62 | 0.438 |
| C6 | 0.45 ± 0.35 | 0.41 ± 0.44 | 0.532 |
| C7 | 0.25 ± 0.23 | 0.25 ± 0.26 | 0.909 |
| C8 | 0.18 ± 0.16 | 0.18 ± 0.21 | 0.987 |
| C9 | 0.12 ± 0.10 | 0.13 ± 0.18 | 0.578 |
| C10 | 0.07 ± 0.06 | 0.09 ± 0.12 | 0.138 |
| Parameter | Coef. | Sign. | Exp(B) | 95% CI for OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | −0.015 | 0.001 | 0.986 | 0.977–0.994 |
| WC | 0.122 | 0.002 | 1.130 | 1.045–1.222 |
| Constant | −6.573 | 0.046 | 0.001 | – |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.-T.; Haryadi, B.; Chen, J.-J. A First Step towards a Comprehensive Approach to Harmonic Analysis of Synchronous Peripheral Volume Pulses: A Proof-of-Concept Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121263
Wu H-T, Haryadi B, Chen J-J. A First Step towards a Comprehensive Approach to Harmonic Analysis of Synchronous Peripheral Volume Pulses: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(12):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121263
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Hsien-Tsai, Bagus Haryadi, and Jian-Jung Chen. 2021. "A First Step towards a Comprehensive Approach to Harmonic Analysis of Synchronous Peripheral Volume Pulses: A Proof-of-Concept Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 12: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121263
APA StyleWu, H. -T., Haryadi, B., & Chen, J. -J. (2021). A First Step towards a Comprehensive Approach to Harmonic Analysis of Synchronous Peripheral Volume Pulses: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(12), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121263