Serum Ceramides as Prognostic Biomarkers of Large Thrombus Burden in Patients with STEMI: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study
Abstract
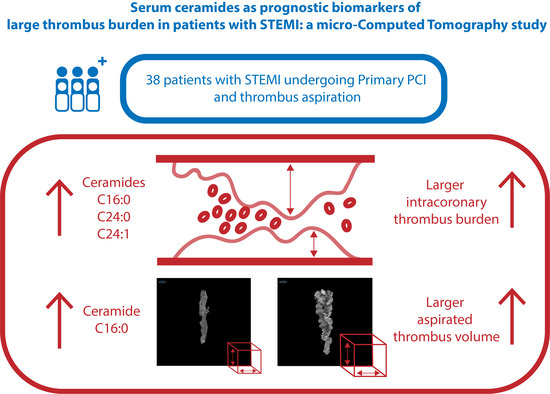
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chalikias, G.; Kikas, P.; Thomaidis, A.; Serif, L.; Georgiadis, G.S. Tziakas, D. A patient with an extensive coronary artery thrombus. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2018, 59, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, H.-K.; Chen, M.-C.; Chang, H.-W.; Hang, C.-L.; Hsieh, Y.-K.; Fang, C.-Y.; Wu, C.-J. Angiographic morphologic features of infarct-related arteries and timely reperfusion in acute myocardial infarction: Predictors of slow-flow and no-reflow phenomenon. Chest 2002, 122, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, J.P.S.; Zijlstra, F.; Ottervanger, J.P.; de Boer, M.-J.; van’t Hof, A.W.J.; Hoorntje, J.C.A.; Suryapranata, H. Incidence and clinical significance of distal embolization during primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2002, 23, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canfield, J.; Totary-Jain, H. 40 years of percutaneous coronary intervention: History and future directions. J. Pers. Med. 2018, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, F.J.; Sousa-Uva, M.; Ahlsson, A.; Alfonso, F.; Banning, A.P.; Benedetto, U.; Byrne, R.A.; Collet, J.P.; Falk, V.; Head, S.J.; et al. 2018 ESC/EACTS guidelines on myocardial revascularization. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 87–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napodano, M.; Dariol, G.; Al Mamary, A.H.; Marra, M.P.; Tarantini, G.; D’Amico, G.; Frigo, A.C.; Buja, P.; Razzolini, R.; Iliceto, S. Thrombus burden and myocardial damage during primary percutaneous coronary in-tervention. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 113, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousoulis, D. Novel risk factors in coronary artery disease: Are they clinically relevant? Hell. J. Cardiol. 2019, 60, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichi, I.; Nakahara, K.; Miyashita, Y.; Hidaka, A.; Kutsukake, S.; Inoue, K.; Maruyama, T.; Miwa, Y.; Harada-Shiba, M.; Tsushima, M.; et al. Association of ceramides in human plasma with risk factors of atherosclerosis. Lipids 2006, 41, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, J.W.; Donato, L.J.; Kopecky, S.L.; Vasile, V.C.; Jaffe, A.S.; Laaksonen, R. Ceramides improve atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk assessment beyond standard risk factors. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 511, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Dong, H.; Sun, R.; Zhao, L.; Sun, M.; Li, L.; Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.; et al. Plasma ceramides in relation to coronary plaque characterization determined by optical coherence tomography. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, C.D.; Siogkas, P.K.; Liga, R.; Benetos, G.; Maaniitty, T.; Sakellarios, A.I.; Koutagiar, I.; Karakitsios, I.; Papafaklis, M.I.; Berti, V.; et al. Characterization of functionally significant coronary artery disease by a coronary computed tomography angiography-based index: A comparison with positron emission tomography. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2019, 20, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafouris, P.P.; Koutagiar, I.P.; Georgakopoulos, A.T.; Spyrou, G.M.; Visvikis, D.; Anagnostopoulos, C.D. Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-based textural features for prediction of event prone carotid atherosclerotic plaques. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavuranakis, M.; Papaioannou, T.G.; Vrachatis, D.; Katsimboulas, M.; Sanidas, E.A.; Vaina, S.; Agrogiannis, G.; Patsouris, E.; Kakadiaris, I.; Stefanadis, C.; et al. Computational imaging of aortic vasa vasorum and neo-vascularization in rabbits using contrast-enhanced intravascular ultrasound: Association with histo-logical analysis. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2018, 20, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papaioannou, T.G.; Manolesou, D.; Dimakakos, E.; Tsoucalas, G.; Vavuranakis, M.; Tousoulis, D. 3D bioprinting methods and techniques: Applications on artificial blood vessel fabrication. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2019, 35, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Karagiannidis, E.; Sofidis, G.; Stalikas, N.; Koletsa, T.; Kartas, A.; Keklikoglou, K.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Kangelidis, I.; Barmpas, A.; Deligiannis, G.; et al. Rationale and design of a prospective, single-arm trial for the evaluation of safety and feasibility of large thrombus burden aspiration in the context of ST elevation myocardial infarction. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannidis, E.; Konstantinidis, N.V.; Sofidis, G.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Sianos, G. Rationale and design of a prospective, observational study for the QUantitative EStimation of Thrombus burden in patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction using micro-computed tomography: The QUEST-STEMI trial. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannidis, E.; Sofidis, G.; Papazoglou, A.S.; Deda, O.; Panteris, E.; Moysidis, D.V.; Stalikas, N.; Kartas, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Stefanopoulos, L.; et al. Correlation of the severity of coronary artery disease with patients’ metabolic profile- rationale, design and baseline patient characteristics of the CorLipid Trial. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sianos, G.; Papafaklis, M.I.; Serruys, P.W. Angiographic thrombus burden classification in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction treated with percutaneous coronary intervention. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2010, 22, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Jolly, S.S.; James, S.K.; Džavík, V.; Cairns, J.A.; Mahmoud, K.D.; Zijlstra, F.; Yusuf, S.; Olivecrona, G.K.; Renlund, H.; Gao, P.; et al. Thrombus aspiration in ST elevation myocardial infarction: An individual patient meta-analysis. Circulation 2016, 135, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröbert, O.; Calais, F.; James, S.K.; Lagerqvist, B. ST-elevation myocardial infarction, thrombus aspiration, and different invasive strategies. A TASTE trial substudy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fröbert, O.; Lagerqvist, B.; Olivecrona, G.K.; Omerovic, E.; Gudnason, T.; Maeng, M.; Aasa, M.; Angerås, O.; Calais, F.; Danielewicz, M.; et al. Thrombus aspiration during ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collet, J.-P.; Thiele, H.; Barbato, E.; Barthélémy, O.; Bauersachs, J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Dendale, P.; Dorobantu, M.; Edvardsen, T.; Folliguet, T.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, G.M.; Landmesser, U. Thrombus aspiration in STEMI revisited: Impact on coronary microcirculation? Open Hear. 2015, 2, e000274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sardella, G.; Stio, R.E. Thrombus aspiration in acute myocardial infarction: Rationale and indication. World J. Cardiol. 2014, 6, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, W.; Li, L.; Sun, M.; Wang, C.; Fang, S.; Yu, B. Plasma ceramides are associated with coronary atherosclerotic burden in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 320, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.M.; Suoniemi, M.; Kardys, I.; Vihervaara, T.; de Boer, S.P.M.; Akkerhuis, K.M.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Ekroos, K.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Oemrawsingh, R.M.; et al. Plasma concentrations of molecular lipid species in relation to coronary plaque characteristics and cardiovascular outcome: Results of the ATHERO-REMO-IVUS study. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Pang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Ling, W. Associations between plasma ceramides and mortality in patients with coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2020, 314, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Sun, M.; Wu, J.; Dong, H.; Liu, J.; Gao, R.; Fang, S.; Xing, L.; Hu, S.; Yu, B. Relationship between elevated plasma ceramides and plaque rupture in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis 2020, 302, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Inclusion Criteria: | Exclusion Criteria: |
|---|---|
| 1. STEMI diagnosis | 1. Patients receiving fibrinolytic therapy |
| 2. Patients undergoing both primary PCI and MATh within 12 h from symptom onset | 2. Patients with known intolerance to heparin or anti-platelet medication |
| 3. Fasting plasma for at least 8 h |
| A. Baseline Clinical and Demographic Patient Characteristics | |
| Age [years(± SD)] | 58.4 ± 12.5 |
| Male gender [n (%)] | 30 (78.9%) |
| Smoking [n (%)] | 27 (71.1%) |
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 13 (34.2%) |
| Dyslipidemia [n (%)] | 7 (18.4%) |
| Diabetes mellitus [n (%)] | 3 (7.9%) |
| BMI [kg/m2 (± SD)] | 32.1 ± 23.2 |
| Pain-to-balloon time [min (± SD)] | 305 ± 250.5 |
| Prior Medication [n (%)]: | |
| I. aspirin | 5 (13.8%) |
| II. clopidogrel | 2 (5.3%) |
| III. statin | 8 (21.1%) |
| anticoagulant(s) | 2 (5.3%) |
| Peri-procedural Medication [n (%)]: | |
| I. heparin | 1 (2.6%) |
| II. clopidogrel | 7 (18.4%) |
| III. prasugrel | 1 (2.6%) |
| IV. ticagrelor | 32 (84.2%) |
| GP2B/3A | 17 (44.7%) |
| B. Outcomes of Interest | |
| Aspirated thrombus volume [m3 (± SD)] Pre-procedural TIMI flow | 16.6 ± 18.3 |
| 0 | 24 (63.2%) |
| I | 6 (15.8%) |
| II | 2 (5.3%) |
| III | 6 (15.8%) |
| Post-procedural TIMI flow | |
| 0 | 1 (2.6%) |
| I | 1 (2.6%) |
| II | 5 (13.2%) |
| III | 31 (81.6%) |
| Modified TIMI thrombus grade classification | |
| Grade 2 | 6 (15.8%) |
| Grade 3 | 10 (26.3%) |
| Grade 4 | 22 (57.9%) |
| Volume/RVD | TIMI Thrombus Classification | Pre-Procedural TIMI Flow | Post-Procedural TIMI Flow | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C16:0 | r = 0.326 p = 0.046 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.236 p = 0.030 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.210 p = 0.049 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.277 p = 0.039 |
| C18:0 | r = 0.299 p = 0.069 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.119 p = 0.188 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.129 p = 0.208 | Nagelkerke R2= 0.329 p = 0.017 |
| C24:0 | r = 0.214 p = 0.197 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.311 p = 0.008 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.055 p = 0.601 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.218 p = 0.092 |
| C24:1 | r = 0.309 p = 0.059 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.423 p = 0.001 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.177 p = 0.095 | Nagelkerke R2 = 0.075 p = 0.556 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karagiannidis, E.; Papazoglou, A.S.; Stalikas, N.; Deda, O.; Panteris, E.; Begou, O.; Sofidis, G.; Moysidis, D.V.; Kartas, A.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; et al. Serum Ceramides as Prognostic Biomarkers of Large Thrombus Burden in Patients with STEMI: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11020089
Karagiannidis E, Papazoglou AS, Stalikas N, Deda O, Panteris E, Begou O, Sofidis G, Moysidis DV, Kartas A, Chatzinikolaou E, et al. Serum Ceramides as Prognostic Biomarkers of Large Thrombus Burden in Patients with STEMI: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(2):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11020089
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaragiannidis, Efstratios, Andreas S. Papazoglou, Nikolaos Stalikas, Olga Deda, Eleftherios Panteris, Olga Begou, Georgios Sofidis, Dimitrios V. Moysidis, Anastasios Kartas, Evangelia Chatzinikolaou, and et al. 2021. "Serum Ceramides as Prognostic Biomarkers of Large Thrombus Burden in Patients with STEMI: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 2: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11020089
APA StyleKaragiannidis, E., Papazoglou, A. S., Stalikas, N., Deda, O., Panteris, E., Begou, O., Sofidis, G., Moysidis, D. V., Kartas, A., Chatzinikolaou, E., Keklikoglou, K., Bompoti, A., Gika, H., Theodoridis, G., & Sianos, G. (2021). Serum Ceramides as Prognostic Biomarkers of Large Thrombus Burden in Patients with STEMI: A Micro-Computed Tomography Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(2), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11020089