Associations between Chronic Kidney Disease and Migraine Incidence: Findings from a Korean Longitudinal Big Data Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
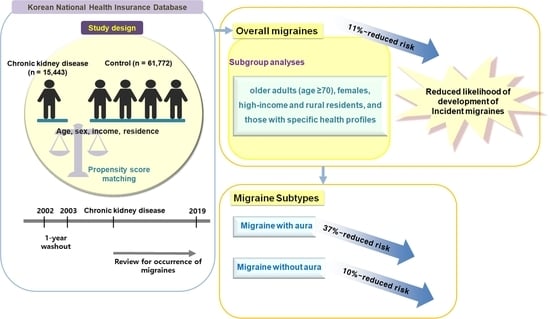
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Exposure (CKD) and Outcome (Migraine)
2.3. Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Newly Occurring Migraine Patients in the CKD and Control Groups
3.2. Relationship between CKD and Migraine in Patients with or without Aura
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delrue, C.; Speeckaert, M.M. Chronic Kidney Disease: Early Detection, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Implications. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Kiernan, M.C. Neurological complications of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 5, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Kim, H.W.; Joo, Y.S.; Park, J.T.; Chang, T.I.; Yoo, T.H.; Park, S.K.; Chae, D.W.; Chung, W.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Association Between Systolic Blood Pressure Variability and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Korean Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: Findings From KNOW-CKD. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e025513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.J.; Song, Y.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, H.S.; Lim, H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, N.Y.; Hong, S.; Choi, Y.; et al. Exploring the Link between Chronic Kidney Disease and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Longitudinal Follow-Up Study Using the Korean National Health Screening Cohort. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillon, J.M.; Massy, Z.A.; Stengel, B. Neurological complications in chronic kidney disease patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Bohm, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiological Insights and Therapeutic Options. Circulation 2021, 143, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.Y.; Park, H.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kronbichler, A.; Koyanagi, A.; Smith, L.; Shin, J.I.; Rhee, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.S.; et al. National trends in the prevalence of chronic kidney disease among Korean adults, 2007–2020. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wu, Y.; Wei, J.; Xia, F.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Miao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Yan, W.; et al. Global, regional, and national time trends in incidence for migraine, from 1990 to 2019: An age-period-cohort analysis for the GBD 2019. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, P.; Kazeminasab, S.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Mohammadinasab, R.; Pourfathi, H.; Araj-Khodaei, M.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Kolahi, A.A.; Safiri, S. Migraine: A Review on Its History, Global Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Comorbidities. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 800605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Yu, H.; Gil Myeong, S.; Park, K.; Kim, D.K. Mid- and Late-Life Migraine Is Associated with an Increased Risk of All-Cause Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease, but Not Vascular Dementia: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.K.; Chu, M.K.; Yu, S.J.; Dell’Agnello, G.; Han, J.H.; Cho, S.J. Burden of migraine and unmet needs from the patients’ perspective: A survey across 11 specialized headache clinics in Korea. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.J.; Stovner, L.J.; Jensen, R.; Uluduz, D.; Katsarava, Z.; on behalf of Lifting The Burden: The Global Campaign against Headache. Migraine remains second among the world’s causes of disability, and first among young women: Findings from GBD2019. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Yeo, J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, S.; Ha, I.H. Trends in healthcare utilization of patients with migraine in South Korea: A retrospective observational study using Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service National Patient Sample data from 2010 to 2018. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e059926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, E.E.; Bergamaschi, C.T.; Campos, R.R. The crosstalk between the kidney and the central nervous system: The role of renal nerves in blood pressure regulation. Exp. Physiol. 2015, 100, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Yan, T.; Chopp, M.; Venkat, P.; Chen, J. Brain-kidney interaction: Renal dysfunction following ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.C.; Wu, C.L.; Kor, C.T.; Chiu, P.F.; Wu, M.J.; Chang, C.C.; Tarng, D.C. Migraine and subsequent chronic kidney disease risk: A nationwide population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e018483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Xiao, C.; Wu, X.; Yan, P.; Cui, H.; Yang, C.; Zhu, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Migraine, chronic kidney disease and kidney function: Observational and genetic analyses. Hum. Genet. 2023, 142, 1185–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, J.I.; Datta, S.; Chiang, C.C.; Garza, I.; Vieira, D.L.; Robertson, C.E. Narrative review of migraine management in patients with renal or hepatic disease. Headache 2023, 63, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.Y.; Lee, E.; Jung, H.W.; Jang, I.Y. Geriatrics Fact Sheet in Korea 2021. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2021, 25, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, S.C.; Kim, Y.Y.; Park, S.K.; Khang, Y.H.; Kim, H.C.; Park, J.H.; Kang, H.J.; Do, C.H.; Song, J.S.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Cohort profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.J.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Rim, H.T.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, J.K.; Chang, I.B.; Song, J.H.; Kim, J.H. A higher probability of subsequent stroke and ischemic heart disease in migraine patients: A longitudinal follow-up study in Korea. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.S.; Choi, H.G.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; Hong, S.; et al. Association between Migraines and Prior Proton Pump Inhibitor Use: A Nested Case–Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.J.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Bang, W.J.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, N.Y.; Hong, S.; Lee, H.K. Risk for Esophageal Cancer Based on Lifestyle Factors-Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, and Body Mass Index: Insight from a South Korean Population Study in a Low-Incidence Area. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, H.; Sundararajan, V.; Halfon, P.; Fong, A.; Burnand, B.; Luthi, J.C.; Saunders, L.D.; Beck, C.A.; Feasby, T.E.; Ghali, W.A. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med. Care 2005, 43, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Thomas, L.E.; Li, F. Addressing Extreme Propensity Scores via the Overlap Weights. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Morgan, K.L.; Zaslavsky, A.M. Balancing Covariates via Propensity Score Weighting. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2018, 113, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat. Med. 2009, 28, 3083–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, M.; Eidlitz Markus, T. Headache in pediatric and adolescent patients with chronic kidney disease, with and without hemodialysis: A comparative cohort study. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fila, M.; Pawlowska, E.; Szczepanska, J.; Blasiak, J. Different Aspects of Aging in Migraine. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 2028–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghdoost, F.; Togha, M. Migraine management: Nonpharmacological points for patients and health care professionals. Open Med. (Wars) 2022, 17, 1869–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godley, F., 3rd; Meitzen, J.; Nahman-Averbuch, H.; O’Neal, M.A.; Yeomans, D.; Santoro, N.; Riggins, N.; Edvinsson, L. How Sex Hormones Affect Migraine: An Interdisciplinary Preclinical Research Panel Review. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.; James, M.T.; Holroyd-Leduc, J.M.; Wilton, S.B.; Seely, E.W.; Wheeler, D.C.; Ahmed, S.B. Sex Hormone Status in Women With Chronic Kidney Disease: Survey of Nephrologists’ and Renal Allied Health Care Providers’ Perceptions. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2017, 4, 2054358117734534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lauro, M.; Guerriero, C.; Cornali, K.; Albanese, M.; Costacurta, M.; Mercuri, N.B.; Di Daniele, N.; Noce, A. Linking Migraine to Gut Dysbiosis and Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazancioglu, R. Risk factors for chronic kidney disease: An update. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.H.; Park, S.K.; Kim, J.; Ahn, C. The KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD): A Korean Chronic Kidney Disease Cohort. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2022, 55, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, P.F.; Huang, J.; Fukagawa, M.; Hoy, W.; Jha, V.; Oh, K.H.; Sola, L.; Cockwell, P.; Levin, A.; Feldman, H.I.; et al. A collaborative, individual-level analysis compared longitudinal outcomes across the International Network of Chronic Kidney Disease (iNETCKD) cohorts. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1217–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; D’Alecy, L.G.; Anderson, M.A.; Basrur, V.; Feng, Y.; Brady, G.F.; Kim, D.I.; Wu, J.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Lahann, J.; et al. Constitutive release of CPS1 in bile and its role as a protective cytokine during acute liver injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9125–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasinghe, S.V.; Jang, Y.J.; Fontana, R.J.; Omary, M.B. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase-1 is a rapid turnover biomarker in mouse and human acute liver injury. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G355–G364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.E.; Li, F.; Pencina, M.J. Overlap Weighting: A Propensity Score Method That Mimics Attributes of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 2417–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurella, M.; Chertow, G.M.; Fried, L.F.; Cummings, S.R.; Harris, T.; Simonsick, E.; Satterfield, S.; Ayonayon, H.; Yaffe, K. Chronic kidney disease and cognitive impairment in elderly individuals: The health, aging, and body composition study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Yap, K.B.; Yeoh, L.Y.; Ng, T.P. Kidney function and cognitive and functional decline in elderly adults: Findings from the Singapore longitudinal aging study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Before Overlap-Weighting Adjustment | After Overlap-Weighting Adjustment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKD | Control | Standardized Difference | CKD | Control | Standardized Difference | |
| Age (y), n (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| 40–44 | 96 (0.62) | 384 (0.62) | 74 (0.65) | 74 (0.65) | ||
| 45–49 | 355 (2.30) | 1420 (2.30) | 257 (2.25) | 257 (2.25) | ||
| 50–54 | 896 (5.80) | 3584 (5.80) | 646 (5.65) | 646 (5.65) | ||
| 55–59 | 1754 (11.36) | 7016 (11.36) | 1283 (11.23) | 1283 (11.23) | ||
| 60–64 | 2146 (13.90) | 8584 (13.90) | 1566 (13.71) | 1566 (13.71) | ||
| 65–69 | 2420 (15.67) | 9680 (15.67) | 1773 (15.52) | 1773 (15.52) | ||
| 70–74 | 2687 (17.40) | 10,748 (17.40) | 1998 (17.49) | 1998 (17.49) | ||
| 75–79 | 2581 (16.71) | 10,324 (16.71) | 1930 (16.89) | 1930 (16.89) | ||
| 80–84 | 1681 (10.89) | 6724 (10.89) | 1261 (11.04) | 1261 (11.04) | ||
| ≥85 | 827 (5.36) | 3308 (5.36) | 635 (5.56) | 635 (5.56) | ||
| Sex, n (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| Male | 10,415 (67.44) | 41,660 (67.44) | 7721 (67.59) | 7721 (67.59) | ||
| Female | 5028 (32.56) | 20,112 (32.56) | 3702 (32.41) | 3702 (32.41) | ||
| Income, n (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| 1 (lowest) | 2649 (17.15) | 10,596 (17.15) | 1945 (17.03) | 1945 (17.03) | ||
| 2 | 1793 (11.61) | 7172 (11.61) | 1327 (11.62) | 1327 (11.62) | ||
| 3 | 2207 (14.29) | 8828 (14.29) | 1629 (14.26) | 1629 (14.26) | ||
| 4 | 3075 (19.91) | 12,300 (19.91) | 2269 (19.87) | 2269 (19.87) | ||
| 5 (highest) | 5719 (37.03) | 22,876 (37.03) | 4253 (37.23) | 4253 (37.23) | ||
| Region of residence, n (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| Urban | 6704 (43.41) | 26,816 (43.41) | 4958 (43.41) | 4958 (43.41) | ||
| Rural | 8739 (56.59) | 34,956 (56.59) | 6465 (56.59) | 6465 (56.59) | ||
| Obesity †, n (%) | 0.16 | 0.00 | ||||
| Underweight | 399 (2.58) | 2006 (3.25) | 312 (2.73) | 312 (2.73) | ||
| Normal | 4735 (30.66) | 22,085 (35.75) | 3614 (31.64) | 3614 (31.64) | ||
| Overweight | 4032 (26.11) | 16,509 (26.73) | 3009 (26.34) | 3009 (26.34) | ||
| Obese I | 5576 (36.11) | 19,449 (31.49) | 4027 (35.26) | 4027 (35.26) | ||
| Obese II | 701 (4.54) | 1723 (2.79) | 461 (4.03) | 461 (4.03) | ||
| Smoking status, n (%) | 0.02 | 0.00 | ||||
| Nonsmoker | 9726 (62.98) | 39,481 (63.91) | 7219 (63.19) | 7219 (63.19) | ||
| Past smoker | 1674 (10.84) | 6606 (10.69) | 1248 (10.92) | 1248 (10.92) | ||
| Current smoker | 4043 (26.18) | 15,685 (25.39) | 2957 (25.88) | 2957 (25.88) | ||
| Alcohol consumption, n (%) | 0.07 | 0.00 | ||||
| <1 time a week | 11,104 (71.90) | 42,476 (68.76) | 8119 (71.08) | 8119 (71.08) | ||
| ≥1 time a week | 4339 (28.10) | 19,296 (31.24) | 3303 (28.92) | 3303 (28.92) | ||
| SBP, mean (SD) | 131.87 (18.47) | 128.75 (16.37) | 0.18 | 130.90 (15.46) | 130.90 (7.31) | 0.00 |
| DBP, mean (SD) | 78.78 (11.60) | 78.16 (10.39) | 0.06 | 78.57 (9.86) | 78.57 (4.55) | 0.00 |
| Fasting blood glucose, mean (SD) | 116.16 (50.06) | 103.86 (29.10) | 0.30 | 110.38 (33.22) | 110.38 (17.83) | 0.00 |
| Total cholesterol, mean (SD) | 190.31 (45.76) | 193.28 (38.86) | 0.07 | 190.68 (39.06) | 190.68 (16.94) | 0.00 |
| CCI score, mean (SD) | 2.19 (2.20) | 1.11 (1.72) | 0.54 | 1.83 (1.67) | 1.83 (0.98) | 0.00 |
| Any migraine, n (%) | 349 (2.26) | 1901 (3.08) | 0.05 | 261 (2.28) | 347 (3.04) | 0.05 |
| Migraine with Aura | 16 (0.10) | 134 (0.22) | 0.03 | 13 (0.11) | 23 (0.20) | 0.02 |
| Migraine without Aura | 333 (2.16) | 1767 (2.86) | 0.05 | 248 (2.17) | 324 (2.84) | 0.04 |
| N of Event/ N of Total (%) | Follow-Up Duration (PY) | IR per 1000 (PY) | IRD (95% CI) | HRs for Migraine | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | p | Overlap-Weighted Model † | p | |||||
| Total participants | ||||||||
| CKD | 349/15,443 (2.26) | 65,152 | 5.36 | −0.62 (−1.27–0.02) | 0.86 (0.77–0.97) | 0.012 * | 0.89 (0.81–0.97) | 0.006 * |
| Control | 1901/61,772 (3.08) | 317,925 | 5.98 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Aged <70 years | ||||||||
| CKD | 237/7667 (3.09) | 42,360 | 5.59 | 0.07 (−0.70–0.86) | 0.99 (0.86–1.14) | 0.917 | 1.02 (0.91–1.13) | 0.769 |
| Control | 1105/30,668 (3.60) | 200,286 | 5.52 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Aged ≥70 years | ||||||||
| CKD | 112/7776 (1.44) | 22,792 | 4.91 | −1.86 (−2.99 to −0.71) | 0.68 (0.56–0.82) | <0.001 * | 0.69 (0.60–0.80) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 796/31,104 (2.56) | 117,639 | 6.77 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Male | ||||||||
| CKD | 193/10,415 (1.85) | 42,922 | 4.50 | −0.25 (−0.96–0.46) | 0.91 (0.78–1.06) | 0.234 | 0.93 (0.82–1.05) | 0.222 |
| Control | 994/41,660 (2.39) | 209,402 | 4.75 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Female | ||||||||
| CKD | 156/5028 (3.10) | 22,230 | 7.02 | −1.34 (−2.64 to −0.04) | 0.81 (0.69–0.96) | 0.017 * | 0.84 (0.73–0.95) | 0.006 * |
| Control | 907/20,112 (4.51) | 108,523 | 8.36 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Low-income group | ||||||||
| CKD | 153/6649 (2.30) | 27,737 | 5.52 | −0.83 (−1.85–0.19) | 0.84 (0.70–0.99) | 0.042 * | 0.86 (0.76–0.98) | 0.029 * |
| Control | 874/26,596 (3.29) | 137,732 | 6.35 | 1 | 1 | |||
| High-income group | ||||||||
| CKD | 196/8794 (2.23) | 37,415 | 5.24 | −0.46 (−1.30–0.37) | 0.89 (0.76–1.04) | 0.130 | 0.90 (0.80–1.02) | 0.087 |
| Control | 1027/35,176 (2.92) | 180,193 | 5.70 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Urban resident | ||||||||
| CKD | 152/6704 (2.27) | 30,005 | 5.07 | −0.32 (−1.23–0.58) | 0.91 (0.76–1.08) | 0.283 | 0.93 (0.81–1.06) | 0.277 |
| Control | 777/26,816 (2.90) | 144,150 | 5.39 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Rural resident | ||||||||
| CKD | 197/8739 (2.25) | 35,147 | 5.61 | −0.86 (−1.77–0.05) | 0.83 (0.72–0.97) | 0.019 * | 0.86 (0.76–0.96) | 0.009 * |
| Control | 1124/34,956 (3.22) | 173,775 | 6.47 | 1 | 1 | |||
| N of Event/ N of Total (%) | Follow-Up Duration (PY) | IR per 1000 (PY) | IRD (95% CI) | HRs for Migraine with Aura | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | p | Overlap-Weighted Model † | p | |||||
| Total participants | ||||||||
| CKD | 16/15,443 (0.10) | 66,982 | 0.24 | −0.17 (−0.33 to −0.01) | 0.55 (0.33–0.92) | 0.024 * | 0.63 (0.44–0.92) | 0.016 * |
| Control | 134/61,772 (0.22) | 328,027 | 0.41 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Aged <70 years | ||||||||
| CKD | 13/7667 (0.17) | 43,686 | 0.30 | −0.10 (−0.30–0.10) | 0.71 (0.40–1.28) | 0.261 | 0.82 (0.53–1.26) | 0.363 |
| Control | 82/30,668 (0.27) | 206,799 | 0.40 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Aged ≥70 years | ||||||||
| CKD | 3/7776 (0.04) | 23,296 | 0.13 | −0.30 (−0.57 to −0.03) | 0.27 (0.09–0.88) | 0.029 * | 0.30 (0.14–0.67) | 0.003 * |
| Control | 52/31,104 (0.17) | 121,228 | 0.43 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Male | ||||||||
| CKD | 10/10,415 (0.10) | 43,836 | 0.23 | −0.09 (−0.27–0.09) | 0.66 (0.34–1.28) | 0.219 | 0.73 (0.45–1.19) | 0.208 |
| Control | 69/41,660 (0.17) | 214,318 | 0.32 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Female | ||||||||
| CKD | 6/5028 (0.12) | 23,146 | 0.26 | −0.31 (−0.63–0.01) | 0.43 (0.19–1.00) | 0.049 * | 0.52 (0.29–0.93) | 0.029 * |
| Control | 65/20,112 (0.32) | 113,709 | 0.57 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Low-income group | ||||||||
| CKD | 10/6649 (0.15) | 28,543 | 0.35 | −0.14 (−0.42–0.13) | 0.67 (0.34–1.29) | 0.228 | 0.75 (0.46–1.22) | 0.249 |
| Control | 70/26,596 (0.26) | 142,342 | 0.49 | 1 | 1 | |||
| High-income group | ||||||||
| CKD | 6/8794 (0.07) | 38,439 | 0.16 | −0.18 (−0.38–0.01) | 0.43 (0.19–0.99) | 0.047 * | 0.50 (0.28–0.89) | 0.018 * |
| Control | 64/35,176 (0.18) | 185,685 | 0.34 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Urban resident | ||||||||
| CKD | 9/6704 (0.13) | 30,786 | 0.29 | −0.05 (−0.28–0.17) | 0.80 (0.40–1.63) | 0.544 | 0.92 (0.54–1.59) | 0.777 |
| Control | 51/26,816 (0.19) | 148,297 | 0.34 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Rural resident | ||||||||
| CKD | 7/8739 (0.08) | 36,196 | 0.19 | −0.27 (−0.50 to −0.04) | 0.39 (0.18–0.85) | 0.018 * | 0.45 (0.26–0.76) | 0.003 * |
| Control | 83/34,956 (0.24) | 179,730 | 0.46 | 1 | 1 | |||
| N of Event/ N of Total (%) | Follow-Up Duration (PY) | IR per 1000 (PY) | IRD (95% CI) | HRs for Migraine without Aura | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | p | Overlap-Weighted Model † | p | |||||
| Total participants | ||||||||
| CKD | 333/15,443 (2.16) | 65,241 | 5.10 | −0.44 (−1.06–0.18) | 0.89 (0.79–1.00) | 0.05 | 0.90 (0.83–0.99) | 0.029 * |
| Control | 1767/61,772 (2.86) | 318,765 | 5.54 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Aged <70 years | ||||||||
| CKD | 224/7667 (2.92) | 42,441 | 5.28 | 0.19 (−0.56–0.93) | 1.02 (0.88–1.17) | 0.829 | 1.03 (0.92–1.16) | 0.581 |
| Control | 1023/30,668 (3.34) | 200,857 | 5.09 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Aged ≥70 years | ||||||||
| CKD | 109/7776 (1.40) | 22,800 | 4.78 | −1.53 (−2.63 to −0.43) | 0.71 (0.58–0.86) | <0.001 * | 0.72 (0.62–0.83) | <0.001 * |
| Control | 744/31,104 (2.39) | 117,908 | 6.31 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Male | ||||||||
| CKD | 183/10,415 (1.76) | 42,966 | 4.26 | −0.15 (−0.84–0.54) | 0.93 (0.79–1.09) | 0.374 | 0.94 (0.83–1.07) | 0.355 |
| Control | 925/41,660 (2.22) | 209,834 | 4.41 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Female | ||||||||
| CKD | 150/5028 (2.98) | 22,275 | 6.73 | −1.00 (−2.25–0.26) | 0.84 (0.71–1.00) | 0.055 | 0.86 (0.75–0.98) | 0.024 * |
| Control | 842/20,112 (4.19) | 108,931 | 7.73 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Low-income group | ||||||||
| CKD | 143/6649 (2.15) | 27,803 | 5.14 | −0.68 (−1.65–0.30) | 0.85 (0.71–1.02) | 0.079 | 0.87 (0.76–1.00) | 0.051 |
| Control | 804/26,596 (3.02) | 138,156 | 5.82 | 1 | 1 | |||
| High-income group | ||||||||
| CKD | 190/8794 (2.16) | 37,438 | 5.08 | −0.25 (−1.07–0.55) | 0.92 (0.79–1.08) | 0.299 | 0.93 (0.82–1.05) | 0.238 |
| Control | 963/35,176 (2.74) | 180,609 | 5.33 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Urban resident | ||||||||
| CKD | 143/6704 (2.13) | 30,046 | 4.76 | −0.27 (−1.14–0.61) | 0.92 (0.77–1.10) | 0.347 | 0.93 (0.81–1.07) | 0.287 |
| Control | 726/26,816 (2.71) | 144,470 | 5.03 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Rural resident | ||||||||
| CKD | 190/8739 (2.17) | 35,195 | 5.40 | −0.57 (−1.45–0.30) | 0.87 (0.75–1.02) | 0.081 | 0.89 (0.79–1.00) | 0.054 |
| Control | 1041/34,956 (2.98) | 174,295 | 5.97 | 1 | 1 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, M.J.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, M.-J.; Yoo, D.M.; Lee, N.-E.; Han, K.M.; Kim, N.Y.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, E.S. Associations between Chronic Kidney Disease and Migraine Incidence: Findings from a Korean Longitudinal Big Data Study. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040356
Kwon MJ, Kim J-K, Kim M-J, Yoo DM, Lee N-E, Han KM, Kim NY, Kang HS, Choi HG, Kim ES. Associations between Chronic Kidney Disease and Migraine Incidence: Findings from a Korean Longitudinal Big Data Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(4):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040356
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Mi Jung, Jwa-Kyung Kim, Min-Jeong Kim, Dae Myoung Yoo, Na-Eun Lee, Kyeong Min Han, Nan Young Kim, Ho Suk Kang, Hyo Geun Choi, and Eun Soo Kim. 2024. "Associations between Chronic Kidney Disease and Migraine Incidence: Findings from a Korean Longitudinal Big Data Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 4: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040356
APA StyleKwon, M. J., Kim, J. -K., Kim, M. -J., Yoo, D. M., Lee, N. -E., Han, K. M., Kim, N. Y., Kang, H. S., Choi, H. G., & Kim, E. S. (2024). Associations between Chronic Kidney Disease and Migraine Incidence: Findings from a Korean Longitudinal Big Data Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(4), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040356