The Systemic Inflammation Index: A New Candidate Minor Criterion in the Diagnosis of Polycythemia Vera
Abstract
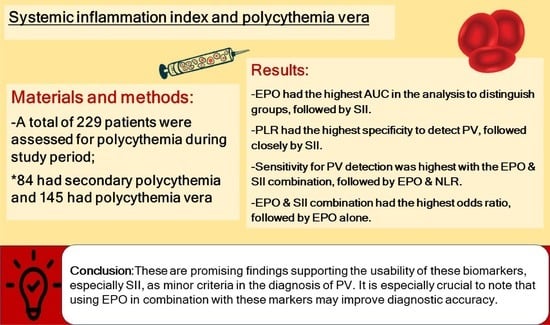
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting and Ethics
2.2. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2.1. Laboratory Analysis
2.2.2. Molecular Analyses
2.2.3. Bone Marrow Biopsy and Pathological Analysis
2.2.4. Smoking Status
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.J. A diagnostic roadmap for polycythemia. Korean J. Med. 2020, 95, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, R.; Zenciroglu, A. Evaluation of Neonatal Polycythemia in Terms of Gestational Age, Hematocrit, and Platelet Levels. Türkiye Çocuk Hast Derg. 2022, 16, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kwon, S.S.; Ji, Y.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, N.; Park, S.K.; Won, J.H.; Yoon, S.Y. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as new possible minor criteria for diagnosis of polycythemia vera. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2023, 45, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbui, T.; Thiele, J.; Gisslinger, H.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Guglielmelli, P.; Orazi, A.; Tefferi, A. The 2016 WHO classification and diagnostic criteria for myeloproliferative neoplasms: Document summary and in-depth discussion. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: Myeloid and histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krečak, I.; Holik, H.; Zekanović, I.; Morić Perić, M.; Marketin, T.; Coha, B.; Gverić-Krečak, V.; Vodanović, M.; Lucijanić, M. Thrombotic risk in secondary polycythemia resembles low-risk polycythemia vera and increases in specific subsets of patients. Thromb. Res. 2022, 209, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krečak, I.; Holik, H.; Morić Perić, M.; Zekanović, I.; Coha, B.; Gverić-Krečak, V.; Lucijanić, M. High platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio may differentiate polycythemia vera from secondary polycythemia. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2022, 134, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birgegård, G.; Wide, L. Serum erythropoietin in the diagnosis of polycythaemia and after phlebotomy treatment. Br. J. Haematol. 1992, 81, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossuz, P.; Girodon, F.; Donnard, M.; Latger-Cannard, V.; Dobo, I.; Boiret, N.; Lecron, J.C.; Binquet, C.; Barro, C.; Hermouet, S.; et al. Diagnostic value of serum erythropoietin level in patients with absolute erythrocytosis. Haematologica 2004, 89, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lupak, O.; Han, X.; Xie, P.; Mahmood, S.; Mohammed, H.; Donthireddy, V. The role of a low erythropoietin level for the polycythemia vera diagnosis. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2020, 80, 102355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez Luque, L.F.; Blackmon, A.L.; Ramanathan, G.; Fleischman, A.G. Key Role of Inflammation in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Instigator of Disease Initiation, Progression. and Symptoms. Curr. Hematol. Malign. Rep. 2019, 14, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcinkaya, A.; Samadi, A.; Lay, I.; Unal, S.; Sabuncuoglu, S.; Oztas, Y. Oxysterol concentrations are associated with cholesterol concentrations and anemia in pediatric patients with sickle cell disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2019, 79, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselbalch, H.C.; Holmström, M.O. Perspectives on interferon-alpha in the treatment of polycythemia vera and related myeloproliferative neoplasms: Minimal residual disease and cure? Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomrich, G.; Gruber, E.S.; Winkler, D.; Hollenstein, M.; Gnant, M.; Sahora, K.; Schindl, M. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) Predicts Poor Survival in Pancreatic Cancer Patients Undergoing Resection. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Kong, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J. Pre-treatment systemic immune-inflammation index is a useful prognostic indicator in patients with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 2993–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.-S.; Tan, J.; Zhou, X.-L.; Song, Y.-Q.; Song, Y.-J. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicting chemoradiation resistance and poor outcome in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatabe, S.; Eto, K.; Haruki, K.; Shiba, H.; Kosuge, M.; Ohkuma, M.; Ito, D.; Takeda, Y.; Sugano, H.; Sasaki, S.; et al. Signification of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index for prediction of prognosis after resecting in patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2020, 35, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersal, T.; Özkocaman, V.; Pınar, İ.E.; Yalçın, C.; Orhan, B.; Candar, Ö.; Çubukçu, S.; Koca, T.G.; Hunutlu, F.Ç.; Yavuz, Ş. Systemic inflammatory indices for predicting prognosis of myelofibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcinkaya, R.; Öz, F.N.; Durmuş, S.Y.; Fettah, A.; Kaman, A.; Teke, T.A.; Örün, U.A.; Tanır, G. Is There a Role for Laboratory Parameters in Predicting Coronary Artery Involvement in Kawasaki Disease? Klin. Padiatr. 2022, 234, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, E.J.; Scott, L.M.; Campbell, P.J.; East, C.; Fourouclas, N.; Swanton, S.; Vassiliou, G.S.; Bench, A.J.; Boyd, E.M.; Curtin, N.; et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 2005, 365, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivak, J.L. Polycythemia vera. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2018, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krečak, I.; Lucijanić, M. Can we use platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) to differentiate JAK2-unmutated erythrocytosis from polycythemia vera? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 108, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.S.; Yoon, S.Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, M.-Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, N.; Won, J.-H. Neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and carotid plaque burden in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Chang, Q.; Meng, X.; Gao, N.; Wang, W. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.-R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.-F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.-M.; Qiu, S.-J.; Zhou, J. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefaniuk, P.; Szymczyk, A.; Podhorecka, M. The Neutrophil to Lymphocyte and Lymphocyte to Monocyte Ratios as New Prognostic Factors in Hematological Malignancies—A Narrative Review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 2961–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, P.; Song, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ma, B.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z. Can the Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio Be Used to Determine Gastric Cancer Treatment Outcomes? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 7862469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ethier, J.-L.; Desautels, D.; Templeton, A.; Shah, P.S.; Amir, E. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krečak, I.; Holik, H.; Morić Perić, M.; Zekanović, I.; Coha, B.; Valovičić Krečak, M.; Gverić-Krečak, V.; Lucijanić, M. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios as prognostic biomarkers in polycythemia vera. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2022, 44, e145–e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krečak, I.; Lucijanić, M. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and accelerated atherosclerosis in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 2010–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucijanic, M.; Cicic, D.; Stoos-Veic, T.; Pejsa, V.; Lucijanic, J.; Fazlic Dzankic, A.; Vlasac Glasnovic, J.; Soric, E.; Skelin, M.; Kusec, R. Elevated Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte-ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Myelofibrosis: Inflammatory Biomarkers or Representatives of Myeloproliferation Itself? Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3157–3163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Chen, W.; Cheng, H.; Qiao, J.L.; Zhu, L.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Xu, K.L. Clinico-hematological profile and thrombotic/hemorrhagic events in 150 chinese patients with essential thrombocythemia. Leuk Res. 2018, 69, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carobbio, A.; Vannucchi, A.M.; De Stefano, V.; Masciulli, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Loscocco, G.G.; Ramundo, F.; Rossi, E.; Kanthi, Y.; Tefferi, A.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a novel predictor of venous thrombosis in polycythemia vera. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liao, C.; Tu, H.; Li, J. Association of inflammation and abnormal lipid metabolism with risk of thrombosis and thrombosis progression in patients with polycythemia vera: A retrospective study. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 3413–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, M.Z.; Dağlı, M.; Ünlü, A. The ratio of platelet/lymphocyte, the ratio of neutrophil/lymphocyte and some haemogram parameters related to thrombosis in essential thrombocytosis and polycythaemia vera. Biomed. Res. 2017, 28, 3036–3039. [Google Scholar]
- Hacibekiroglu, T.; Akinci, S.; Basturk, A.; Inal, B.; Guney, T.; Bakanay, S.M.; Dilek, I. Evaluation of Inflammation Parameters in Philadelphia Negative Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasia Patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 5159–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Diagnosis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Secondary Polycythemia (n = 84) | Polycythemia Vera (n = 145) | p | |
| Age (n = 229) | 44.67 ± 15.59 | 56.78 ± 13.30 | <0.001 a |
| Sex (n = 229) | |||
| Male | 68 (80.95%) | 96 (66.21%) | 0.026 c |
| Female | 16 (19.05%) | 49 (33.79%) | |
| Splenomegaly (n = 227) | 0 (0.00%) | 39 (27.08%) | <0.001 c |
| Smoking status (n = 201) | |||
| Non-smoker | 34 (41.98%) | 70 (58.33%) | 0.060 c |
| Ex-smoker | 12 (14.81%) | 10 (8.33%) | |
| Smoker | 35 (43.21%) | 40 (33.33%) | |
| WBC (×103) (n = 229) | 8.11 (6.72–9.93) | 10.80 (8.47–12.56) | <0.001 b |
| RBC (×106) (n = 229) | 5.90 ± 0.52 | 6.60 ± 1.05 | <0.001 a |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) (n = 229) | 18.02 ± 1.03 | 17.95 ± 1.73 | 0.696 a |
| Hematocrit (%) (n = 229) | 52.72 ± 3.77 | 55.31 ± 5.92 | <0.001 a |
| MCV (fL) (n = 229) | 89.19 ± 5.32 | 85.12 ± 9.20 | <0.001 a |
| Lymphocyte (×103) (n = 229) | 2.43 (2.12–2.90) | 2.06 (1.65–2.66) | <0.001 b |
| Neutrophil (×103) (n = 229) | 4.58 (3.70–6.49) | 7.27 (5.38–8.95) | <0.001 b |
| Eosinophil (×103) (n = 229) | 0.16 (0.09–0.26) | 0.27 (0.18–0.42) | <0.001 b |
| Platelet (×103) (n = 229) | 228.5 (195.5–273.5) | 407 (301–615) | <0.001 b |
| LDH (mg/dL) (n = 224) | 197 (166–221) | 260 (209–345) | <0.001 b |
| Erythropoietin (mU/mL) (n = 218) | 8.00 (6.20–11.50) | 2.10 (1.20–4.25) | <0.001 b |
| NLR (n = 229) | 1.92 (1.51–2.35) | 3.29 (2.40–4.88) | <0.001 b |
| PLR (n = 229) | 94.37 (78.72–114.06) | 216.85 (136.65–290.42) | <0.001 b |
| SII (×103) (n = 229) | 432.33 (335.97–582.93) | 1479.11 (872.41–2526.75) | <0.001 b |
| * JAK2 V617F positivity (n = 227) | 0 (0.00%) | 126 (86.90%) | <0.001 c |
| * JAK2 exon 12 positivity (n = 67) | 0 (0.00%) | 4 (16.67%) | 0.014 d |
| Thrombosis history (n = 229) | 13 (15.48%) | 37 (25.52%) | 0.108 c |
| Bone marrow biopsy (n = 229) | |||
| No CMPD findings | 84 (100.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | <0.001 e |
| PV findings | 0 (0.00%) | 142 (97.93%) | |
| Post-polycythemia MF | 0 (0.00%) | 3 (2.07%) | |
| Cut-off | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | PPV | NPV | AUC (95% CI) | pa | pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPO | <4.85 | 79.41% | 87.80% | 82.57% | 91.53% | 72.00% | 0.886 (0.841–0.931) | <0.001 | - |
| NLR | ≥2.35 | 77.93% | 76.19% | 77.29% | 84.96% | 66.67% | 0.803 (0.745–0.861) | <0.001 | 0.018 |
| PLR | ≥135 | 76.55% | 90.48% | 81.66% | 93.28% | 69.09% | 0.871 (0.825–0.917) | <0.001 | 0.709 |
| SII | ≥803 | 80.69% | 89.29% | 83.84% | 92.86% | 72.82% | 0.885 (0.841–0.929) | <0.001 | 0.934 |
| EPO & NLR † | - | 88.97% | 71.95% | 82.57% | 84.03% | 79.73% | 0.805 (0.739–0.870) | <0.001 | 0.010 |
| EPO & PLR † | - | 86.76% | 78.05% | 83.49% | 86.76% | 78.05% | 0.824 (0.762–0.886) | <0.001 | 0.055 |
| EPO & SII † | - | 89.71% | 86.59% | 88.53% | 91.73% | 83.53% | 0.881 (0.829–0.933) | <0.001 | 0.883 |
| Unadjusted | Adjusted † | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| EPO, <4.85 | 27.771 (12.715–60.655) | <0.001 | 29.636 (12.477–70.394) | <0.001 |
| NLR, ≥2.35 | 11.300 (5.975–21.372) | <0.001 | 8.768 (4.512–17.038) | <0.001 |
| PLR, ≥135 | 31.015 (13.611–70.673) | <0.001 | 27.572 (11.587–65.607) | <0.001 |
| SII, ≥803 | 34.821 (15.568–77.887) | <0.001 | 28.109 (12.345–64.006) | <0.001 |
| EPO and NLR | 20.693 (10.061–42.558) | <0.001 | 19.130 (8.860–41.306) | <0.001 |
| EPO and PLR | 23.309 (11.338–47.919) | <0.001 | 28.709 (12.493–65.973) | <0.001 |
| EPO and SII | 56.247 (24.230–130.568) | <0.001 | 48.519 (20.287–116.039) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gulturk, E.; Kapucu, K. The Systemic Inflammation Index: A New Candidate Minor Criterion in the Diagnosis of Polycythemia Vera. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14050471
Gulturk E, Kapucu K. The Systemic Inflammation Index: A New Candidate Minor Criterion in the Diagnosis of Polycythemia Vera. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(5):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14050471
Chicago/Turabian StyleGulturk, Emine, and Korhan Kapucu. 2024. "The Systemic Inflammation Index: A New Candidate Minor Criterion in the Diagnosis of Polycythemia Vera" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 5: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14050471
APA StyleGulturk, E., & Kapucu, K. (2024). The Systemic Inflammation Index: A New Candidate Minor Criterion in the Diagnosis of Polycythemia Vera. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(5), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14050471