Ionic Liquids as Additives of Coffee Bean Oil in Steel-Steel Contacts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coffee Bean Oil
2.2. Ionic Liquids
| Code | Structure | IUPAC Name | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cation | Anion | ||
| [THTDP][Deca] |  |  | Trihexyltetradecylphosphonium decanoate |
| [THTDP][NTf2] |  | Trihexyltetradecylphosphonium Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amide | |
2.3. Tribological Experiments
2.4. Viscosity, Density, and Thermal Stability of Lubricants
2.5. Wettability of Lubricants

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Viscosity, Density, and Thermal Stability of the Lubricants
| Lubricant | Density at 23 °C (g/cm3) | Kinematic Viscosity (cSt) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 °C | 100 °C | ||
| MG | 0.86 | 335 | 38.3 |
| CB | 0.85 | 53.5 | 9.4 |
| CB + 1% [THTDP][Deca] | 0.87 | 88.5 | 12.6 |
| CB + 2.5% [THTDP][Deca] | 0.86 | 148.3 | 19.2 |
| CB + 1% [THTDP][NTf2] | 0.87 | 61.6 | 10.5 |
| CB + 2.5% [THTDP][NTf2] | 0.89 | 174.1 | 21.3 |

3.2. Wettability of Lubricants

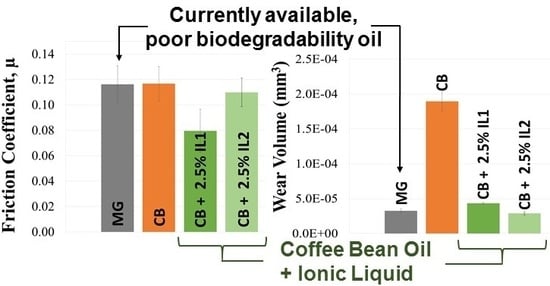
3.3. Tribological Properties







4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maleque, M.A.; Salit, M.S. Materials Selection and Design; SpringerBriefs: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Collings, J.A. Failure of Materials in Mechanical Design: Analysis, Prediction, Prevention; Wiley: Hoboken, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Sripada, P.K.; Sharma, R.V.; Dalai, A.K. Comparative study of tribological properties of trimethylolpropane-based biolubricants derived from methyl oleate and canola biodiesel. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 50, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.Q.A. A Comprehensive Review of Lubricant Chemistry, Technology, Selection and Design; ASTM: West Conshohocken, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nagendramma, P.; Kaul, S. Development of ecofriendly/biodegradable lubricants: An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 764–774. [Google Scholar]
- Erhan, S.Z.; Sharma, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Adhvaryu, A. Lubricant base stock potential of chemically modified vegetable oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8919–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Chen, L.; Jiang, D.; Zeng, H.; Yan, Z. Vegetable oil-based ionic liquid microemulsion biolubricants: Effect of integrated surfactants. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 62, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, N.W.M.; Kalam, M.A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Yunus, R. Experimental analysis of tribological properties of biolubricant with nanoparticle additive. Procedia Eng. 2013, 68, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarak, H.M.; Niza Mohamad, E.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; al Mahmud, K.A.H.; Habibullah, M.; Ashraful, A.M. The prospects of biolubricants as alternatives in automotive applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, L.; Jiang, D.; Yan, Z. Vegetable oil-based ionic liquid microemulsions and their potential as alternative renewable biolubricant basestocks. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 51, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, N.J.; Stachowiak, G.W. Vegetable oil-based lubricants—A review of oxidation. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, A.; Rustoy, E.; Baldessari, A.; Baltanás, M.A. Lubricants from chemically modified vegetable oils. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.-S.; Adhvaryu, A.; Erhan, S.Z. Preparation and properties of lubricant basestocks from epoxidized soybean oil and 2-ethylhexanol. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2003, 80, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-S.; Erhan, S.Z. Modification of epoxidized soybean oil for lubricant formulations with improved oxidative stability and low pour point. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, M.D.; Carrion, F.J.; Iglesias, P.; Jiménez, A.E.; Martínez-Nicolás, G.; Sanes, J. Ionic liquids interactions with materials surfaces applications in tribology and nanotechnology. MRS Proc. 2008, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.J.; Garvey, S.; Menezes, P.; Dietz, M.; Jen, T.C.; Lowell, M.L. Tribological performance of environmentally friendly ionic liquid lubricants. In Proceedings of the ASME/STLE 2012 International Joint Tribology Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 7–10 October, 2012; ASME: Denver, CO, USA, 2012; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Minami, I. Ionic liquids in tribology. Molecules 2009, 14, 2286–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, H.; Kubo, T.; Minami, I.; Mori, S. Effect and mechanism of additives for ionic liquids as new lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L. Room-temperature ionic liquids: A novel versatile lubricant. Chem. Commun. 2001, 21, 2244–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Truhan, J.J.; Dai, S.; Luo, H.; Blau, P.J. Ionic liquids with ammonium cations as lubricants or additives. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 22, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totolin, V.; Minami, I.; Gabler, C.; Dörr, N. Halogen-free borate ionic liquids as novel lubricants for tribological applications. Tribol. Int. 2013, 67, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; González, R.; Hernández Battez, A.; Viesca, J.L.; Monge, R.; Fernández-González, A.; Hadfield, M. Ionic liquids as a neat lubricant applied to steel-steel contacts. Tribol. Int. 2014, 72, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D. Short alkyl chain imidazolium ionic liquid additives in lubrication of three aluminium alloys with synthetic ester oil. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2012, 6, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Iglesias, P.; Carrión, F.J.; Martínez-Nicolás, G. 1-N-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids as neat lubricants and lubricant additives in steel-aluminium contacts. Wear 2006, 260, 766–782. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, A.E.; Bermúdez, M.D.; Iglesias, P. Lubrication of Inconel 600 with ionic liquids at high temperature. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, M.; Hadfield, M.; Viesca, J.L.; Thomas, B.; Hernández Battez, A.; Austen, S. Ionic liquids as tribological performance improving additive for in-service and used fully-formulated diesel engine lubricants. Wear 2015, 334–335, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viesca, J.L.; García, A.; Hernández Battez, A.; González, R.; Monge, R.; Fernández-González, A.; Hadfield, M. FAP- anion ionic liquids used in the lubrication of a steel-steel contact. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 52, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, T.; Sanes, J.; Bermúdez, M.D. Halogen-free phosphonate ionic liquids as precursors of abrasion resistant surface layers on AZ31B magnesium alloy. Coatings 2015, 5, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, R.; González, R.; Hernández Battez, A.; Fernández-González, A.; Viesca, J.L.; García, A.; Hadfield, M. Ionic liquids as an additive in fully formulated wind turbine gearbox oils. Wear 2015, 328–329, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrova, M.; Pagano, F.; Pejakovic, V.; Valea, A.; Kalin, M.; Igartua, A; Tojo, E. Pyridinium based dicationic ionic liquids as base lubricants or lubricant additives. Tribol. Int. 2015, 82, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Coffee Organitation. Annual Review 2011/2012. Avilable online: http://www.ico.org/show_news.asp?id=319 (accessed on July 2015).
- Silva, M.A.; Nebra, S.A.; Machado Silva, M.J.; Sanchez, C.G. The use of biomass residues in the Brazilian soluble coffee industry. Biomass Bioenerg. 1998, 14, 457–467. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.; Truhan, J.J. An efficient method for accurately determining wear volumes of sliders with non-flat wear scars and compound curvatures. Wear 2006, 261, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawes, S.D.; Hainsworth, S.V.; Blake, P.; Ryder, K.S.; Abbott, A.P. Lubrication of steel/steel contacts by choline chloride ionic liquids. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 37, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, P.; Mcnabb, K.B. Improving wear performance of wind turbine gearboxes using ionic liquids as additives of lubricants. In Proceedings of the VIII Iberian Conference on Tribology Ibertrib 2015, Cartagena, Colombia, 18–19 June 2015; pp. 23–28.
- Minami, I.; Inada, T.; Sasaki, R.; Nanao, H. Tribo-chemistry of phosphonium-derived ionic liquids. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dyck, J.; Graham, T.W.; Luo, H.; Leonard, D.N.; Qu, J. Ionic liquids composed of phosphonium cations and organophosphate, carboxylate, and sulfonate anions as lubricant antiwear additives. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13301–13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grace, J.; Vysochanska, S.; Lodge, J.; Iglesias, P. Ionic Liquids as Additives of Coffee Bean Oil in Steel-Steel Contacts. Lubricants 2015, 3, 637-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3040637
Grace J, Vysochanska S, Lodge J, Iglesias P. Ionic Liquids as Additives of Coffee Bean Oil in Steel-Steel Contacts. Lubricants. 2015; 3(4):637-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3040637
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrace, James, Solomiya Vysochanska, Jeffrey Lodge, and Patricia Iglesias. 2015. "Ionic Liquids as Additives of Coffee Bean Oil in Steel-Steel Contacts" Lubricants 3, no. 4: 637-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3040637
APA StyleGrace, J., Vysochanska, S., Lodge, J., & Iglesias, P. (2015). Ionic Liquids as Additives of Coffee Bean Oil in Steel-Steel Contacts. Lubricants, 3(4), 637-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants3040637