Models for Prediction of Surface Roughness in a Face Milling Process Using Triangular Inserts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment Procedure
2.1. Aluminum Alloy
2.2. Face Milling Machine and Insert
2.3. Three Milling Cases Defined by Feed Rate
2.4. Surface Profile Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mathematical Roughness Prediction Model
3.1.1. Milling Case 1 (Small Feed Rate, f < R)
3.1.2. Milling Case 2 (Medium Feed Rate, R < f < 3R)
3.1.3. Milling Case 3 (Large Feed Rate, f > 3R)
3.2. Experimental Surface Roughness in Milling Process
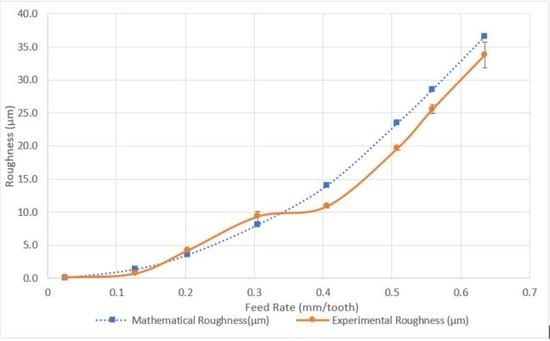
3.3. Comparison of Mathematical Model and Experimental Surface Roughness
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, W.; Guan, J.; Li, B.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J. Influence of Tool Assembly Error on Machined Surface in Peripheral Milling Process. Procedia CIRP 2015, 27, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medicus, K.; Davies, M.; Dutterer, B.; Evans, C.; Fielder, R. Tool Wear and Surface Finish in High Speed Milling of Aluminum Bronze. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2001, 5, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luejanda, S.; Jirapattarasilp, K. The Study of Surface Finish in Face Milling of Stainless Steel: AISI 304. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 650, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, H.; Abou-El-Hossein, K.; Mohamad, B.; Ghani, J.; Kadirgama, K. Investigating of Tool Wear, Tool Life and Surface Roughness When Machining of Nickel Alloy 242 with Using of Different Cutting Tools. Asian J. Sci. Res. 2008, 1, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeirani Filho, J.; Diniz, A. Influence of Cutting Conditions on Tool Life, Tool Wear and Surface Finish in the Face Milling Process. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 2002, 24, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S. Integrated Surface Modification Technology Development; Presentation in Seminar; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Knoxville, TN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Michail, S.K.; Barber, G. The Effects of Roughness on Piston Ring Lubrication Part I: Model Development. Tribol. Trans. 1995, 38, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.; Tung, S. Overview of Automotive Engine Friction and Reduction Trends—Effects of Surface, Material, and Lubricant-Additive Technologies. Friction 2016, 4, 1–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, S. The Critical Role of Surface Engineering in Automotive Tribology-Overview of Modern Advances and Challenges for the Future. In Proceedings of the Third Asia International Conference on Tribology, Kanazawa, Japan, 16–19 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Siripuram, R.; Stephens, J. Effects of Deterministic Asperity Geometry on Hydrodynamic Lubrication. ASME J. Tribol. 2004, 126, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocsak, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, T.; Wong, V. Analyzing the Effects of Three-Dimensional Cylinder Liner Surface Texture on Ring-Pack Performance with a Focus on Honing Groove Cross-Hatch Angle. In Proceedings of the ASME 2005 Internal Combustion Engine Division Fall Technical Conference, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 11–14 September 2005; pp. 621–632. [Google Scholar]
- Jocsak, J.; Wong, V.; Tian, T. The Effects of Cylinder Liner Finish on Piston Ring-Pack Friction. In Proceedings of the ASME 2004 Internal Combustion Engine Division Fall Technical Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 24–27 October 2004; pp. 841–849. [Google Scholar]
- Kalidass, S.; Palanisamy, P. Effect of Machining Parameters on Surface Roughness in End Milling of AISI 304 Steel Using Uncoated Solid Carbide Tools. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 12, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.; Konada, U.; Kwon, Y. A Novel Approach to Predict Surface Roughness in Machining Operations Using Fuzzy Set Theory. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2016, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.; Estrems, M.; Faura, F. Influence of Radial and Axial Runouts on Surface Roughness in Face Milling with Round Insert Cutting Tools. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Barber, G.; Jiang, Q.; Tung, S. Surface Roughness Model for Worn Inserts of Face Milling: Part I—Factors that Affect Arithmetic Surface Roughness. Tribol. Trans. 2001, 44, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felho, C.; Karpuschewski, B.; Kundrak, J. Surface Roughness modelling in Face Milling. In Proceedings of the 15th CIRP Conference on Modelling of Machining Operations, Karlsruhe, Germany, 11–12 June 2015; pp. 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Escalona, P.; Maropoulos, P.G. A Geometrical Model for Surface Roughness Prediction When Face Milling Al 7075-T7351 with Square Insert Tools. J. Manuf. Syst. 2015, 36, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothroyd, G.; Knight, W.A. Fundamentals of Machining and Machine Tools, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 168. [Google Scholar]












| Elements | Percentage Composition |
|---|---|
| Si | 0.4–0.8 |
| Cu | 0.15–0.4 |
| Zn | 0.25 |
| Fe | 0.7 |
| Mn | 0.15 |
| Cr | 0.04–0.35 |
| Ni | 0.05 |
| Pb | 0.05 |
| Sn | 0.05 |
| Ti | 0.15 |
| Mg | 0.8–1.2 |
| Al | 95.85–98.56 |
| Nose Radius (mm) | Feed Rate (mm/tooth) | Spindle Speed (rpm) | Depth of Cut (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.397 | 0.0254 | 300 | 0.15 |
| 0.127 | |||
| 0.203 | |||
| 0.305 | |||
| 0.406 | |||
| 0.508 | |||
| 0.559 | |||
| 0.635 |
| Nose Radius (mm) | Case I or II | Feed Rate (mm/tooth) | Filter (µm) | Roughness (µm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | Average | ||||
| 0.397 | Small | 0.0254 | 25.4 | 0.160 | 0.171 | 0.162 | 0.160 | 0.176 | 0.170 |
| 0.127 | 127 | 0.730 | 0.751 | 0.739 | 0.756 | 0.740 | 0.740 | ||
| 0.203 | 203 | 4.056 | 4.159 | 4.197 | 4.307 | 4.331 | 4.210 | ||
| 0.305 | 305 | 8.722 | 8.961 | 9.074 | 10.827 | 9.149 | 9.347 | ||
| Medium | 0.406 | 406 | 11.197 | 10.912 | 10.442 | 10.940 | 11.068 | 10.912 | |
| 0.508 | 508 | 23.171 | 20.184 | 17.871 | 19.105 | 18.089 | 19.684 | ||
| 0.559 | 559 | 26.109 | 24.352 | 25.676 | 26.108 | 25.677 | 25.584 | ||
| 0.635 | 635 | 30.886 | 31.055 | 35.021 | 36.829 | 35.192 | 33.797 | ||
| Feed Rate (mm/Tooth) | γ | θ | Mathematical Roughness (µm) | Experimental Roughness (µm) | Error | Feed Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0254 | 0.033 | 0.019 | 0.054 | 0.170 | 214.81% | Small feed rate |
| 0.127 | 0.167 | 0.096 | 1.365 | 0.740 | 45.79% | |
| 0.203 | 0.270 | 0.155 | 3.527 | 4.210 | 19.36% | |
| 0.305 | 0.412 | 0.234 | 8.089 | 9.350 | 15.59% | |
| 0.406 | 0.562 | 0.316 | 14.036 | 10.912 | 22.26% | Medium feed rate |
| 0.508 | 0.707 | 0.4 | 23.444 | 19.684 | 16.04% | |
| 0.559 | 0.777 | 0.441 | 28.521 | 25.584 | 10.30% | |
| 0.635 | 0.88 | 0.501 | 36.545 | 33.797 | 7.52% |
| Nose Radius (mm) | Feed Rate (mm/Tooth) | Previous Research Ra (µm) [9] | Current Research Ra (µm) | Percentage Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.397 | 0.0254 | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0 |
| 0.127 | 1.365 | 1.365 | 0 | |
| 0.203 | 3.527 | 3.527 | 0 | |
| 0.305 | 8.089 | 8.089 | 0 | |
| 0.406 | 14.8 | 14.036 | 5.16% | |
| 0.508 | 24.101 | 23.444 | 2.73% | |
| 0.559 | 29.962 | 28.521 | 4.81% | |
| 0.635 | 40.765 | 36.545 | 10.35% |
| Nose Radius (mm) | Feed Rate (mm/Tooth) | Previous Research Ra (µm) [12] | Current Research Ra (µm) | Percentage Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.397 | 0.0254 | 0.052 | 0.054 | 3.85% |
| 0.127 | 1.304 | 1.365 | 4.67% | |
| 0.203 | 3.332 | 3.527 | 5.85% | |
| 0.305 | 7.527 | 8.089 | 7.54% | |
| 0.406 | 13.328 | 14.036 | 5.31% | |
| 0.508 | 20.866 | 23.444 | 12.36% | |
| 0.559 | 25.266 | 28.521 | 12.88% | |
| 0.635 | 32.603 | 36.545 | 12.09% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Wang, B.; Barber, G.C.; Gu, J.; Schall, J.D. Models for Prediction of Surface Roughness in a Face Milling Process Using Triangular Inserts. Lubricants 2019, 7, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7010009
Wang R, Wang B, Barber GC, Gu J, Schall JD. Models for Prediction of Surface Roughness in a Face Milling Process Using Triangular Inserts. Lubricants. 2019; 7(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rui, Bingxu Wang, Gary C. Barber, Jie Gu, and J.David Schall. 2019. "Models for Prediction of Surface Roughness in a Face Milling Process Using Triangular Inserts" Lubricants 7, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7010009
APA StyleWang, R., Wang, B., Barber, G. C., Gu, J., & Schall, J. D. (2019). Models for Prediction of Surface Roughness in a Face Milling Process Using Triangular Inserts. Lubricants, 7(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7010009