Characterization and Function of Two Short Peptidoglycan Recognition Proteins Involved in the Immunity of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Total RNA Extraction and First Strand cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Cloning of BdPGRP-SA and BdPGRP-SD
2.4. Characterization, Sequence Alignment, and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Immune Triggers Induction
2.7. RNA Interference (RNAi)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analysis, Alignments, and Phylogenetic Trees
3.2. Spatiotemporal Expression Analysis
3.3. Expression Induced by Microbial Challenges
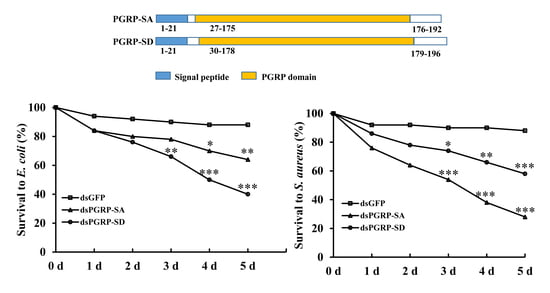
3.4. RNAi Bioassay
3.5. Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, J.A.; Reichhart, J.M. Drosophila innate immunity: An evolutionary perspective. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultmark, D. Drosophila immunity: Paths and patterns. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbrell, D.A.; Beutler, B. The evolution and genetics of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, B. The road to Toll. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J. The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 697–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A.J. Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. J. Immunol. 1989, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leulier, F.; Parquet, C.; Pili-Floury, S.; Ryu, J.-H.; Caroff, M.; Lee, W.-J.; Mengin-Lecreulx, D.; Lemaitre, B. The Drosophila immune system detects bacteria through specific peptidoglycan recognition. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, T.; Goldman, W.E.; Mellroth, P.; Steiner, H.; Fukase, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Harley, W.; Fox, A.; Golenbock, D.; Silverman, N. Monomeric and polymeric Gram-negative peptidoglycan but not purified LPS stimulate the Drosophila IMD pathway. Immunity 2004, 20, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenbak, C.R.; Ryu, J.H.; Leulier, F.; Pilifloury, S.; Parquet, C.; Hervé, M.; Chaput, C.; Boneca, I.G.; Lee, W.J.; Lemaitre, B. Peptidoglycan molecular requirements allowing detection by the Drosophila immune deficiency pathway. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 7339–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MyllymKi, H.; Valanne, S.; Rämet, M. The Drosophila Imd signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, V.; Gottar, M.; Matskevich, A.A.; Rutschmann, S.; Royet, J.; Belvin, M.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Ferrandon, D. Dual activation of the Drosophila toll pathway by two pattern recognition receptors. Science 2003, 302, 2126–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valanne, S.; Wang, J.H.; Rämet, M. The Drosophila Toll signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziarski, R. Recognition of bacterial peptidoglycan by the innate immune system. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2003, 60, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, T.; Liu, G.; Kang, D.; Ekengren, S.; Steiner, H.; Hultmark, D. A family of peptidoglycan recognition proteins in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13772–13777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, M.; Yao, F.; Yin, Y.; Zou, X.; Hou, L. Involvement of PGRP-SC2 from Artemia sinica in the innate immune response against bacteria and expression pattern at different developmental stages. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 67, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellroth, P.; Karlsson, J.; Steiner, H. A scavenger function for a Drosophila peptidoglycan recognition protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 7059–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidmanrémy, A.; Poidevin, M.; Hervé, M.; Welchman, D.P.; Paredes, J.C.; Fahlander, C.; Steiner, H.; Menginlecreulx, D.; Lemaitre, B. Drosophila immunity: Analysis of PGRP-SB1 expression, enzymatic activity and function. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17231. [Google Scholar]
- Royet, J.; Gupta, D.; Dziarski, R. Peptidoglycan recognition proteins: Modulators of the microbiome and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, T.; Reichhart, J.M.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Royet, J. Drosophila Toll is activated by Gram-positive bacteria through a circulating peptidoglycan recognition protein. Nature 2001, 414, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, V.; Vignal, C.; Boneca, I.G.; Michel, T.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Royet, J. Function of the drosophila pattern-recognition receptor PGRP-SD in the detection of Gram-positive bacteria. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Sagisaka, A. Involvement of peptidoglycan recognition protein l6 in activation of immune deficiency pathway in the immune responsive silkworm cells. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 92, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Feng, C.; Peng, Y.; Lu, Z. Peptidoglycan recognition protein-S5 functions as a negative regulator of the antimicrobial peptide pathway in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Gilbert, R.J.C.; Atilano, M.L.; Filipe, S.R.; Gay, N.J.; Ligoxygakis, P. Peptidoglycan recognition protein-SD provides versatility of receptor formation in Drosophila immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11881–11886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, P.; Bischoff, V.; Kellenberger, C.; Hetru, C.; Royet, J.; Roussel, A. Crystal structure of Drosophila PGRP-SD suggests binding to DAP-type but not lysine-type peptidoglycan. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatsenko, I.; Kondo, S.; Mengin-Lecreulx, D.; Lemaitre, B. PGRP-SD, an extracellular pattern-recognition receptor, enhances peptidoglycan-mediated activation of the Drosophila Imd pathway. Immunity 2016, 45, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.R.; Armstrong, K.F.; Carmichael, A.E.; Milne, J.R.; Raghu, S.; Roderick, G.K.; Yeates, D.K. Invasive phytophagous pests arising through a recent tropical evolutionary radiation: The Bactrocera dorsalis complex of fruit flies. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2005, 50, 293–319. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J.; Wei, D.; Dou, W.; Hu, F.; Liu, W.F.; Wang, J.J. Toxicities and synergistic effects of several insecticides against the oriental fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Feng, Y.C.; Wei, D.D.; Yuan, G.R.; Dou, W.; Wang, J.J. Female remating inhibition and fitness of Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae) associated with male accessory glands. Fla. Entomol. 2015, 98, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Jia, H.T.; Zhang, M.Y.; Li, R.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.J. Comparative analysis of differential gene expression profiling of sex-bias fat body of Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae) identifying a new vitellogenin gene. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2018, 111, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.M.; Dou, W.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.Z.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.J. In silico cloning and annotation of genes involved in the digestion, detoxification and RNA interference mechanism in the midgut of Bactrocera dorsalis [Hendel (Diptera: Tephritidae)]. Insect Mol. Biol. 2013, 22, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Wei, D.; Li, R.; Jia, H.T.; Liu, Y.W.; Taning, C.N.T.; Wang, J.J.; Smagghe, G. Cytoplasmic glutamine synthetase gene expression regulates larval development in Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 97, e21447. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.H.; Wei, D.; Yuan, G.R.; Jiang, H.B.; Dou, W.; Wang, J.J. Antimicrobial peptide gene cecropin-2 and defensin respond to peptidoglycan infection in the female adult of oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2017, 206, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Z.; Cong, L.; Niu, J.Z.; Dou, W.; Wang, J.J. Alternative splicing contributes to the coordinated regulation of ferritin subunit levels in Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Dou, W.; Jiang, H.B.; Wei, D.D.; Wei, D.; Niu, J.Z.; Wang, J.J. Determination of instars of Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). Fla. Entomol. 2017, 100, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Royet, J.; Reichhart, J.M.; Hoffmann, J.A. Sensing and signaling during infection in Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2005, 17, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Mariuzza, R.A. Peptidoglycan recognition proteins of the innate immune system. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Cai, S.; Zhang, S.; Luo, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J. A novel peptidoglycan recognition protein involved in the prophenoloxidase activation system and antimicrobial peptide production in Antheraea pernyi. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 86, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Beerntsen, B.T. Functional implications of the peptidoglycan recognition proteins in the immunity of the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Mol. Biol. 2015, 24, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, M. Peptidoglycan recognition proteins in hematophagous arthropods. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 83, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, G.; Christophides, G.K.; Meister, S.; Schultz, J.; White, K.P.; Barillas-Mury, C.; Kafatos, F.C. Genome expression analysis of Anopheles gambiae: Responses to injury, bacterial challenge, and malaria infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8814–8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, S.; Ariki, S.; Kawabata, S. Recognition of pathogens and activation of immune responses in Drosophila and horseshoe crab innate immunity. Immunobiology 2006, 211, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Beerntsen, B.T. Insights into the different functions of multiple peptidoglycan recognition proteins in the immune response against bacteria in the mosquito, Armigeres subalbatus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.J.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.C.; Saha, T.T.; Lu, Z.Y.; Lu, Z.Q.; Zou, Z. Comparative analysis of peptidoglycan recognition proteins in endoparasitoid wasp Microplitis mediator. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Tian, C.B.; Liu, S.H.; Wang, T.; Smagghe, G.; Jia, F.X.; Dou, W.; Wang, J.J. Transcriptome analysis to identify genes for peptides and proteins involved in immunity and reproduction from male accessory glands and ejaculatory duct of Bactrocera dorsalis. Peptides 2016, 80, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pili-Floury, S.; Leulier, F.; Takahashi, K.; Saigo, K.; Samain, E.; Ueda, R.; Lemaitre, B. In vivo RNA interference analysis reveals an unexpected role for GNBP1 in the defense against Gram-positive bacterial infection in Drosophila adults. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12848–12853. [Google Scholar]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, D.; Liu, Y.-W.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Wang, J.-J. Characterization and Function of Two Short Peptidoglycan Recognition Proteins Involved in the Immunity of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Insects 2019, 10, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10030079
Wei D, Liu Y-W, Zhang Y-X, Wang J-J. Characterization and Function of Two Short Peptidoglycan Recognition Proteins Involved in the Immunity of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Insects. 2019; 10(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Dong, Yu-Wei Liu, Ying-Xin Zhang, and Jin-Jun Wang. 2019. "Characterization and Function of Two Short Peptidoglycan Recognition Proteins Involved in the Immunity of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel)" Insects 10, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10030079
APA StyleWei, D., Liu, Y. -W., Zhang, Y. -X., & Wang, J. -J. (2019). Characterization and Function of Two Short Peptidoglycan Recognition Proteins Involved in the Immunity of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Insects, 10(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10030079