Unexpected Diversity of Wolbachia Associated with Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
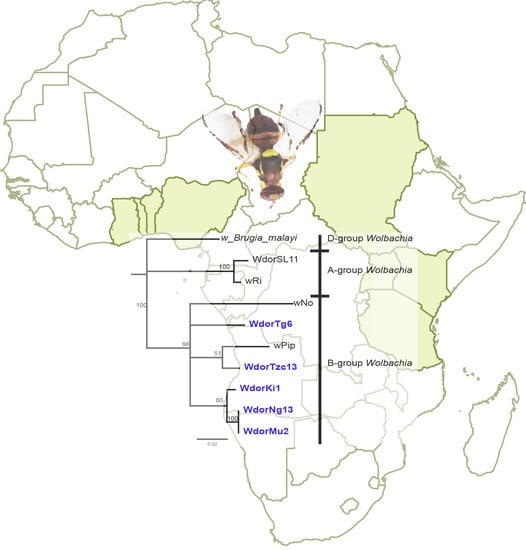
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dohino, T.; Hallman, G.J.; Grout, T.G.; Clarke, A.R.; Follett, P.A.; Cugala, D.R.; Minh Tu, D.; Murdita, W.; Hernandez, E.; Pereira, R.; et al. Phytosanitary treatments against Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae): Current situation and future prospects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- De Villiers, M.; Hattingh, V.; Kriticos, D.J.; Brunel, S.; Vayssières, J.; Sinzogan, A.; Billah, M.K.; Mohamed, S.A.; Mwatawala, M.; Abdelgader, H.; et al. The potential distribution of Bactrocera dorsalis: Considering phenology and irrigation patterns. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2016, 106, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, A.E.A.; Kriticos, D.J.; Leriche, A. The current and future potential geographical distribution of the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2007, 97, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA-APHIS. Oriental Fruit Fly Cooperative Eradication Program Los Angeles and Orange Counties, Califonia; U.S. Department of Agriculture Health Animal and Plant Inspection Service: Riverdale, MD, USA, 2014.
- Nugnes, F.; Russo, E.; Viggiani, G.; Bernardo, U. First record of an invasive fruit fly belonging to Bactrocera dorsalis complex (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Europe. Insects 2018, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, S.A.; Copeland, R.S.; White, I.M.; Manrakhan, A.; Billah, M.K. A new invasive fruit fly species from the Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) group detected in east Africa. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2003, 23, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekesi, S.; Billah, M.K.; Nderitu, P.W.; Lux, S.A.; Rwomushana, I. Evidence for competitive displacement of Ceratitis cosyra by the invasive fruit fly Bactrocera invadens (Diptera: Tephritidae) on mango and mechanisms contributing to the displacement. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankinga, C.M.; Isabirye, B.E.; Muyinza, H.; Rwomushana, I.; Stevenson, P.C.; Mayamba, A.; Aool, W.; Akol, A.M. Fruit fly infestation in mango: A threat to the horticultural sector in Uganda. Uganda J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ekesi, S.; De Meyer, M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Virgilio, M.; Borgemeister, C. Taxonomy, ecology and management of native and exotic fruit fly species in Africa. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zug, R.; Hammerstein, P. Still a host of hosts for Wolbachia: Analysis of recent data suggests that 40% of terrestrial arthropod species are infected. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 38544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenboecker, K.; Hammerstein, P.; Schlattmann, P.; Telschow, A.; Werren, J.H. How many species are infected with Wolbachia?—A statistical analysis of current data. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 281, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, L.A.; Araujo-Jnr, E.V.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Welch, J.J. The incidence of bacterial endosymbionts in terrestrial arthropods. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20150249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabalou, S.; Riegler, M.; Theodorakopoulou, M.; Stauffer, C.; Savakis, C.; Bourtzis, K. Wolbachia-induced cytoplasmic incompatibility as a means for insect pest population control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15042–15045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabalou, S.; Apostolaki, A.; Livadaras, I.; Franz, G.; Robinson, A.S.; Savakis, C.; Bourtzis, K. Incompatible insect technique: Incompatible males from a Ceratitis capitata genetic sexing strain. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2009, 132, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolaki, A.; Livadaras, I.; Saridaki, A.; Chrysargyris, A.; Savakis, C.; Bourtzis, K. Transinfection of the olive fruit fly Bactrocera oleae with Wolbachia: Towards a symbiont-based population control strategy. J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 135, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Walker, T.; O’Neill, S.L. Wolbachia and the biological control of mosquito-borne disease. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMeniman, C.J.; Roxanna, L.V.; Bodil, C.N.; Amy, F.W.C.; Manpreet, S.; Wang, Y.F.; O’Neill, S.L. Stable introduction of a life-shortening Wolbachia infection into the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Science 2009, 323, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambris, Z.; Cook, P.E.; Phuc, H.K.; Sinkins, S.P. Immune activation by life-shortening Wolbachia and reduced filarial competence in mosquitoes. Science 2009, 326, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkins, S.P. Wolbachia and cytoplasmic incompatibility in mosquitoes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nouhuys, S.; Kohonen, M.; Duplouy, A. Wolbachia increases the susceptibility of a parasitoid wasp to hyperparasitism. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 2984–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, N.; Casiraghi, M.; Salati, E.; Bazzocchi, C.; Bandi, C. How many Wolbachia supergroups exist? Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordenstein, S.; Rosengaus, R.B. Discovery of a novel Wolbachia supergroup in isoptera. Curr. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, N.; Paraskevopoulos, C.; Bourtzis, K.; O’Neill, S.L.; Werren, J.H.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Bandi, C. Taxonomic status of the intracellular bacterium Wolbachia pipientis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordenstein, S.R.; Paraskevopoulos, C.; Dunning Hotopp, J.C.; Sapountzis, P.; Lo, N.; Bandi, C.; Tettelin, H.; Werren, J.H.; Bourtzis, K. Parasitism and mutualism in Wolbachia: What the phylogenomic trees can and cannot say. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, V.I.D.; Fleming, V.M.; Feil, E.J.; Breeuwer, J.A.J. How diverse is the genus Wolbachia? Multiple-gene sequencing reveals a putatively new Wolbachia supergroup recovered from spider mites (Acari: Tetranychidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegeman, A.; Vanholme, B.; Jacob, J.; Vandekerckhove, T.T.M.; Claeys, M.; Borgonie, G.; Gheysen, G. An endosymbiotic bacterium in a plant-parasitic nematode: Member of a new Wolbachia supergroup. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustinos, A.A.; Diego, S.G.; Dionyssopoulou, E.; Moreira, M.; Papapanagiotou, A.; Scarvelakis, M.; Doudoumis, V.; Ramos, S.; Aguiar, A.F.; Borges, P.A.V.; et al. Detection and characterization of Wolbachia infections in natural populations of aphids: Is the hidden diversity fully unraveled? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, X.L.; Xia, W.Q.; Gui, J.D.; Yan, G.H.; Wang, X.W.; Liu, S.S. Diversity and evolution of the Wolbachia endosymbionts of Bemisia (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) whiteflies. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 2714–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowska, E.; Dragun-Damian, A.; Dabert, M.; Gerth, M. New Wolbachia supergroups detected in quill mites (Acari: Syringophilidae). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 30, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Jia, L.Y.; Xiao, J.H.; Huang, D.W. Discovery of a new Wolbachia supergroup in cave spider species and the lateral transfer of phage WO among distant hosts. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascar, J.; Chandler, C.H. A bioinformatics approach to identifying Wolbachia infections in arthropods. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, H.; Arthofer, W.; Riegler, M.; Bertheau, C.; Krumböck, S.; Köppler, K.; Vogt, H.; Teixeira, L.A.F.; Stauffer, C. Multiple Wolbachia infections in Rhagoletis pomonella. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2011, 139, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G.L.; Allsopp, P.G.; Brumbley, S.M.; Woolfit, M.; McGraw, E.A.; O’Neill, S.L. Variable infection frequency and high diversity of multiple strains of Wolbachia pipientis in Perkinsiella planthoppers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2165–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrdanz, R.L.; Wichmann, S.S. Wolbachia multilocus sequence typing of singly infected and multiply infected populations of northern corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, R.O.; Prezotto, L.F.; Perondini, A.L.P.; Marino, C.L.; Selivon, D. Wolbachia in guilds of Anastrepha fruit flies (Tephritidae) and parasitoid wasps (Braconidae). Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 39, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.H.; Zhu, D.H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Su, C.Y. High levels of multiple infections, recombination and horizontal transmission of Wolbachia in the Andricus mukaigawae (Hymenoptera; Cynipidae) communities. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valette, V.; Bitome Essono, P.Y.; Le Clec’h, W.; Johnson, M.; Bech, N.; Grandjean, F. Multi-infections of feminizing Wolbachia strains in natural populations of the terrestrial isopod Armadillidium vulgare. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.M.; Pietri, J.E.; Debec, A.; Russell, S.; Patel, B.; Sullivan, W. Mechanisms of horizontal cell-to-cell transfer of Wolbachia spp. in Drosophila melanogaster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeap, H.L.; Rašić, G.; Endersby-Harshman, N.M.; Lee, S.F.; Arguni, E.; Le Nguyen, H.; Hoffmann, A.A. Mitochondrial DNA variants help monitor the dynamics of Wolbachia invasion into host populations. Heredity 2016, 116, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, H.; Bertheau, C.; Egan, S.P.; Feder, J.L.; Riegler, M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Steiner, F.M.; Johannesen, J.; Kern, P.; Tuba, K.; et al. Evidence for a recent horizontal transmission and spatial spread of Wolbachia from endemic Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae) to invasive Rhagoletis cingulata in Europe. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 4101–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riegler, M.; Stauffer, C. Wolbachia infections and superinfections in cytoplasmically incompatible populations of the European cherry fruit fly Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera, Tephritidae). Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscrato, V.E.; Braz, A.S.K.; André, A.L.; Selivon, D.; Marino, C.L. Wolbachia in Anastrepha fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae). Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.; Martinez, H.; Lanzavecchia, S.B.; Conte, C.; Morán-aceves, B.M.; Toledo, J.; Liedo, P.; Asimakis, E.D.; Doudoumis, V.; Kyritsis, G.A.; et al. Wolbachia pipientis associated to tephritid fruit fly pests: From basic research to applications. BioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Martınez, H.; Toledo, J.; Liedo, P.; Mateos, M. Survey of heritable endosymbionts in Southern Mexico populations of the fruit fly species Anastrepha striata. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaprakash, A.; Hoy, M.A. Long PCR improves Wolbachia DNA amplification: Wsp sequences found in 76% of sixty-three arthropod species. Insect Mol. Biol. 2000, 9, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selivon, D.; Perondini, A.P.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Marino, C.L.; Lima, M.M.A.; Coscrato, V.E. Wolbachia endosymbiont in a species of the Anastrepha fraterculus complex (diptera: Tephritidae). Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2002, 42, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.S.; Mascarenhas, R.O.; Perondini, A.L.P.; Selivon, D. Occurrence of Wolbachia in Brazilian samples of Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Neotrop. Entomol. 2005, 34, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarakatsanou, A.; Diamantidis, A.D.; Papanastasiou, S.A.; Bourtzis, K.; Papadopoulos, N.T. Effects of Wolbachia on fitness of the Mediterranean fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 135, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.L.; Frommer, M.; Royer, J.E.; Shearman, D.C.A.; Riegler, M. Wolbachia pseudogenes and low prevalence infections in tropical but not temperate Australian tephritid fruit flies: Manifestations of lateral gene transfer and endosymbiont spillover? BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, J.L.; Frommer, M.; Shearman, D.C.A.A.; Riegler, M. Tropical tephritid fruit fly community with high incidence of shared Wolbachia strains as platform for horizontal transmission of endosymbionts. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 3622–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.L. Molecular Studies of Wolbachia and Sex-Determination Genes in Australian Bactrocera Species—Complementary Approaches to Improved Fruit Fly Control. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Western Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jamnongluk, W.; Kittayapong, P.; Baimai, V.; O’Neill, S.L. Wolbachia infections of tephritid fruit flies: Molecular evidence for five distinct strains in a single host species. Curr. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cui, L.; Li, Z. Diversity and phylogeny of Wolbachia infecting Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae) populations from China. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittayapong, P.; Milne, J.R.; Tigvattananont, S.; Baimai, V. Distribution of the reproduction-modifying bacteria, Wolbachia, in natural populations of tephritid fruit flies in Thailand. Sci. Asia 2000, 26, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, F.M.; Masiga, D.K.; Mohamed, S.A.; Salifu, D.; de Meyer, M.; Ekesi, S. Taxonomic identity of the invasive fruit fly pest, Bactrocera invadens: Concordance in morphometry and DNA barcoding. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 44862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, F.M.; Karam, N.; Ekesi, S.; De Meyer, M.; Bonomi, A.; Gomulski, L.M.; Scolari, F.; Gabrieli, P.; Siciliano, P.; Masiga, D.; et al. Uncovering the tracks of a recent and rapid invasion: The case of the fruit fly pest Bactrocera invadens (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Africa. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4798–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braig, H.R.; Zhou, W.; Dobson, S.L.; O’Neill, S.L. Cloning and characterization of a gene encoding the major surface protein of the bacterial endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, S.L.; Giordano, R.; Colbert, A.M.; Karr, T.L.; Robertson, H.M. 16S rRNA phylogenetic analysis of the bacterial endosymbionts associated with cytoplasmic incompatibility in insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 89, 2699–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, L.; Hotopp, J.C.D.; Jolley, K.A.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Biber, S.A.; Choudhury, R.R.; Hayashi, C.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Tettelin, H.; Werren, J.H. Multilocus sequence typing system for the endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7098–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Rohl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. 1994, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malloch, G.; Fenton, B. Super-infections of Wolbachia in byturid beetles and evidence for genetic transfer between A and B super-groups of Wolbachia. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, L.; Werren, J.H. Revisiting Wolbachia supergroup typing based on WSP: Spurious lineages and discordance with MLST. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 55, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Locality | Specimen Codes | Collection Year/ | Collection Sex/(n) | wsp+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nguruman, Kenya | H-Ng | 2008 | m (15) | 1 |
| Nguruman, Kenya | Ng | 2017 | f (15) | 0 |
| Kitui, Kenya | H-Ki | 2005 | m (15) | 0 |
| Kitui, Kenya | Ki | 2017 | f (15) | 1 |
| Muranga, Kenya | H-Mu | 2005 | m (15) | 1 |
| Muranga, Kenya | Mu | 2017 | f (15) | 0 |
| Embu, Kenya | Em | 2017 | f (15) | 0 |
| Dar es Salaam, Tanzania | H-Tz | 2009 | m (15) | 0 |
| Mwanza, Tanzania | Tz-ab | 2017 | m (30) | 0 |
| Morogoro, Tanzania | Tz-c | 2017 | m (15) | 1 |
| Kawanda, Uganda | H-Ug | 2007 | m (15) | 0 |
| Bunamwaya, Uganda | Ug-b | 2017 | m (30) | 0 |
| Khartoum, Sudan | H-Su | 2007 | m (15) | 1 |
| Kassala, Sudan | Su-a | 2017 | m (15) | 0 |
| Gezira, Sudan | Su-b | 2017 | m (15) | 0 |
| Singa, Sudan | Su-c | 2017 | m (15) | 0 |
| Zaria, Nigeria | H-Zr | 2005 | m (15) | 0 |
| Monts Kouffe, Benin | H-Be | 2009 | m (15) | 1 |
| Lome, Togo | H-Tg | 2009 | m (15) | 1 |
| UBG, Ghana | H-Gh | 2009 | m (15) | 1 |
| Ibadan, Nigeria | H-Ib | 2009 | m (15) | 0 |
| Ranbukpitiya, Sri Lanka | H-Sl | 2007 | m (15) | 2 |
| Samples | wsp + | 16S + | coxA + | fbpA + | gatB + | hcpA + | ftsZ + | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-Ng13 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | ||
| Ki1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | ||
| H-Mu2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | ||
| Tzc13 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| H-Su6 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| H-Be3 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| H-Gh4 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| H-Tg6 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | ||
| H-Sl6 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| H-Sl11 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gichuhi, J.; Khamis, F.M.; Van den Berg, J.; Ekesi, S.; Herren, J.K. Unexpected Diversity of Wolbachia Associated with Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Africa. Insects 2019, 10, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10060155
Gichuhi J, Khamis FM, Van den Berg J, Ekesi S, Herren JK. Unexpected Diversity of Wolbachia Associated with Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Africa. Insects. 2019; 10(6):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10060155
Chicago/Turabian StyleGichuhi, Joseph, Fathiya M. Khamis, Johnnie Van den Berg, Sunday Ekesi, and Jeremy K. Herren. 2019. "Unexpected Diversity of Wolbachia Associated with Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Africa" Insects 10, no. 6: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10060155
APA StyleGichuhi, J., Khamis, F. M., Van den Berg, J., Ekesi, S., & Herren, J. K. (2019). Unexpected Diversity of Wolbachia Associated with Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Africa. Insects, 10(6), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10060155