Blood Digestion by Trypsin-Like Serine Proteases in the Replete Lyme Disease Vector Tick, Ixodes scapularis
Abstract
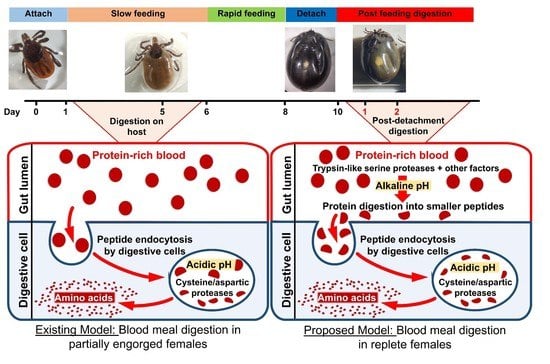
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tick Feeding and Sample Collection
2.2. Protease Expression
2.3. Sample Preparation for BApNA Assay
2.4. RNA Interference (RNAi)
2.5. Hemoglobin Degradation Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Transcript Expression
3.2. Active Trypsin in Tick life stages
3.3. Effect of Serine Proteases RNAi on Tick Blood-Feeding and Physiology
3.4. Hemoglobin Degradation by Tick Midgut Extract
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sonenshine, D.E. Biology of Ticks; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; Volume 1, pp. 122–157. [Google Scholar]
- Gulia-Nuss, M.; Nuss, A.B.; Meyer, J.M.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Sattelle, D.B.; Fuente, J.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Megy, K.; et al. Genomic insights into the Ixodes scapularis tick vector of Lyme disease. Nat. Commun. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulenga, A.; Erikson, K.A. Snapshot of the Ixodes scapularis degradome. Gene 2011, 482, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puente, X.S.; Sanchez, L.M.; Midgutierrez-Fernandez, A.; Velasco, G.; Lopez-Otin, C.A. Genomic view of the complexity of mammalian proteolytic systems. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; Di Cera, E. Serine peptidases: Classification, structure and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1220–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, P.B.; de Araujo, C.N.; Motta, F.N.; Praca, Y.R.; Charneau, S.; Dourado Bastos, I.M.; Santana, J.M. Proteases of haematophagous arthropod vectors are involved in blood-feeding, yolk formation and immunity—A review. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sojka, D.; Franta, Z.; Horn, M.; Hajdusek, O.; Caffrey, C.R.; Mares, M.; Kopacek, P. Profiling of proteolytic enzymes in the midgut of the tick Ixodes ricinus reveals an evolutionarily conserved network of aspartic and cysteine peptidases. Parasites Vectors 2008, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horn, M.; Nussbaumerova, M.; Sanda, M.; Kovarova, Z.; Srba, J.; Franta, Z.; Sojka, D.; Bogyo, M.; Caffrey, C.R.; Kopacek, P.; et al. Hemoglobin Digestion in Blood-Feeding Ticks: Mapping a Multipeptidase Pathway by Functional Proteomics. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvo, E.; Pham, V.M.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. An insight into the sialotranscriptome of the non-blood feeding Toxorhynchites amboinensis mosquito. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rascón, A.A., Jr.; Gearin, J.; Isoe, J.; Miesfeld, R.L. In vitro activation and enzyme kinetic analysis of recombinant midgut serine proteases from the Dengue vector mosquito Aedes aegypti. BMC Biochem. 2011, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gulia-Nuss, M.; Robertson, A.E.; Brown, M.R.; Strand, M.R. Insulin-like peptides and the target of rapamycin pathway coordinately regulate blood digestion and egg maturation in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, A.B.; Mathew, M.G.; Gulia-Nuss, M. Rearing Ixodes scapularis, the Black-legged Tick: Feeding Immature Stages on Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 123, e55286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazán, C.; Bonnet, S.; Cote, M.; Slovák, M.; Park, Y.; Šimo, L. A Versatile Model of Hard Tick Infestation on Laboratory Rabbits. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 140, 57994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Pooraiiouby, R.; Guzman, B.; Vu, P.; Gulia-Nuss, M.; Nuss, A.B. Dynamics of Insulin Signaling in the Black-Legged Tick, Ixodes scapularis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorgine, M.H.; Logullo, C.; Zingali, R.B.; Paiva-Silva, G.O.; Juliano, L.; Oliveira, P.L. A Heme-binding Aspartic Proteinase from the Eggs of the Hard Tick Boophilus microplus. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28659–28665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayakawa, T.; Kondo, T.; Yamazaki, Y.; Linuma, Y.; Mizuno, R. A simple and specific determination of trypsin in human duodenal juice. Gastroenterol. Jpn. 1980, 15, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, C.R.; Betschart, B.; Billingsley, P.F.; Freyvogel, T.A. Post-feeding induction of trypsin in the midmidgut of Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Culicidae) is separable into two cellular phases. Insect Biochem. 1991, 21, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, F.A.; Lins, U.; Bechara, G.H.; Oliveira, P.L. Tracing heme in a living cell: Hemoglobin degradation and heme traffic in digest cells of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, J.M. The midgut hemolysin of Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Parasitol. 1988, 74, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulenga, A.; Sugimoto, C.; Ingram, G.; Ohashi, K.; Misao, O. Characterization of two cDNAs encoding serine proteinases from the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 31, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Tsuji, N.; Islam, M.K.; Huang, X.; Motobu, M.; Alim, M.A.; Fujisaki, K. Molecular and reverse genetic characterization of serine proteinase-induced hemolysis in the midmidgut of the ixodid tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Tsuji, N.; Islam, M.K.; Alim, M.A.; Hatta, T.; Huang, X.; Fujisaki, K. A set of serine proteinase paralogs are required for blood-digestion in the ixodid tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.E. Some histological changes which occur in the midgut epithelium of Ixodes ricinus females during gorging and up to oviposition. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1954, 48, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perner, J.; Provazník, J.; Schrenková, J.; Urbanová, V.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Kopáček, P. RNA-seq analyses of the midgut from blood- and serum-fed Ixodes ricinus ticks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepomuceno, D.B.; Santos, V.C.; Araujo, R.N.; Pereira, M.H.; Sant’Anna, M.R.; Moreira, L.A.; Gontijo, N.F. pH control in the midgut of Aedes aegypti under different nutritional conditions. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 3355–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erban, T.; Hubert, J. Determination of pH in regions of the midguts of acaridid mites. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brune, A.; Emerson, D.; Breznak, J.A. The termite midgut microflora as an oxygen sink-microelectrode determination of oxygen and ph gradients in midguts of lower and higher termites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, J.F. Insect acid-base physiology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2001, 46, 221–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, M.; Brune, A. Physiological properties of the midgut lumen of terrestrial isopods (Isopoda: Oniscidea): Adaptive to digesting lignocellulose? J. Comp. Physiol. B 2005, 175, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.M.; Brune, A.; Walenciak, O. Midgut pH, redox conditions and oxygen levels in an aquatic caterpillar: Potential effects on the fate of ingested tannins. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sojka, D.; Franta, Z.; Frantová, H.; Bartosová, P.; Horn, M.; Váchová, J.; O’Donoghue, A.J.; Eroy-Reveles, A.A.; Craik, C.S.; Knudsen, G.M.; et al. Characterization of gut-associated cathepsin D hemoglobinase from tick Ixodes ricinus (IrCD1). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21152–21163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franta, Z.; Sojka, D.; Frantova, H.; Dvorak, J.; Horn, M.; JindrichSrba, P.T.; Mares, M.; Schneider, E.; Craik, C.S.; McKerrow, J.H.; et al. IrCL1—The haemoglobinolytic cathepsin L of the hard tick, Ixodes ricinus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, N.; Miyoshi, T.; Battsetseg, B.; Matsuo, T.; Xuan, X.; Fujisaki, K. A cysteine protease is critical for Babesia spp. transmission in Haemaphysalis ticks. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Gene Name and Accession Number | Primer Pair Sequence | Annealing Temp °C |
|---|---|---|
| Cathepsin D (Aspartic) ISCW023880/ XM_002416473.1 | ||
| IscapCathDFwd | CCCTTCCGTGTGGTGTTTG | 55 |
| IscapCathDRev | AGTAGCCCTTGGTTGAGACAG | 55 |
| Cathepsin L (Cysteine) ISCW024899/ XM_002416305.1 | ||
| IscapCathLFwd | GACTTCCAGATGTACCAGGGC | 55 |
| IscapCathLRev | GAAGGATGCGGAAGTAGCCG | 55 |
| Cathepsin L (Cysteine) ISCW000076/ XM_002404428.1 | ||
| IscapCathL2Fwd | AAGTGGCCCCACTGCAACTC | 55 |
| IscapCathL2Rev | TTACCCGTAACCGCAGGAATG | 55 |
| Cathepsin C (Cysteine) ISCW03494/ XM_002400742.1 | ||
| IscapCathCFwd | CGTTAACTACGTGTCCCCTG | 57 |
| IscapCathCRev | TAGTTGCCGACGTAATGCC | 57 |
| Legumain (Apartic) ISCW015983/ XM_002402043.1 | ||
| IscapLegumainFwd | CCCCTGGAGTGGTCATCAAC | 55 |
| IscapLegumainRev | TAAGTGTTTCGGAGGGCGTC | 55 |
| Serine Protease 1 ISCW021184/ XM_002405400.1 | ||
| IscapSP1Fwd | AGCCTAATCAATCAAGGGCG | 58 |
| IscapSP1Rev | GACCAGTTTAGGGATGCGAG | 58 |
| Serine Protease 2 ISCW006427/ XM_002435219.1 | ||
| IscapSP2Fwd | ATCCACGTTGGGAACCTTTC | 58 |
| IscapSP2Rev | CAATGGTCAAACGCCTTTCC | 58 |
| Serine Protease 3 ISCW010371/ XM_002402819.1 | ||
| IscapSP3Fwd | TCTACGAGTTCCTGGGACAG | 58 |
| IscapSP3Rev | GGACCAGGGAATAATCGTCG | 58 |
| Serine Protease 4 ISCW007492/ XM_002404245.1 | ||
| IscapSP4Fwd | GCTTCGTCGAAAAAGCTCAC | 58 |
| IscapSP4FRev | CAACTCTCGGCGATCTCTTC | 58 |
| Leucine Aminopeptidase ISCW023735/ XM_002416067.1 | ||
| IscapLAPFwd | ACGCCCATTCTCTCACCAAG | 55 |
| IscapLAPRev | TTCGGACCCACTGCATTCTC | 55 |
| Tubulin ISCW005137/ XM_002402966.1 | ||
| IscapB-TubFwd | TGAATGACCTGGTGTCCGAG | 55–58 |
| IscapB-TubRev | GCAAAGCTGTTCAAGCCTCT | 55–58 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reyes, J.; Ayala-Chavez, C.; Sharma, A.; Pham, M.; Nuss, A.B.; Gulia-Nuss, M. Blood Digestion by Trypsin-Like Serine Proteases in the Replete Lyme Disease Vector Tick, Ixodes scapularis. Insects 2020, 11, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030201
Reyes J, Ayala-Chavez C, Sharma A, Pham M, Nuss AB, Gulia-Nuss M. Blood Digestion by Trypsin-Like Serine Proteases in the Replete Lyme Disease Vector Tick, Ixodes scapularis. Insects. 2020; 11(3):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030201
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyes, Jeremiah, Cuauhtemoc Ayala-Chavez, Arvind Sharma, Michael Pham, Andrew B. Nuss, and Monika Gulia-Nuss. 2020. "Blood Digestion by Trypsin-Like Serine Proteases in the Replete Lyme Disease Vector Tick, Ixodes scapularis" Insects 11, no. 3: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030201
APA StyleReyes, J., Ayala-Chavez, C., Sharma, A., Pham, M., Nuss, A. B., & Gulia-Nuss, M. (2020). Blood Digestion by Trypsin-Like Serine Proteases in the Replete Lyme Disease Vector Tick, Ixodes scapularis. Insects, 11(3), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030201