Effects of Constant versus Fluctuating Temperatures on Fitness Indicators of the Aphid Dysaphis plantaginea and the Parasitoid Aphidius matricariae
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Biological Material
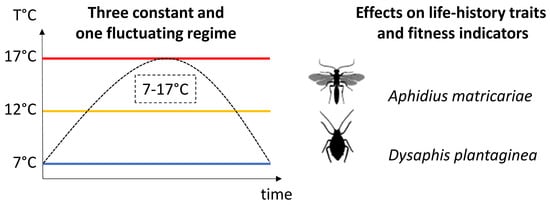
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Thermal Regimes
2.2.2. Aphids
2.2.3. Parasitoids
2.2.4. Fitness-Related Traits
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, M.W.; Mathews, C.R. Conservation Biological Control of Rosy Apple Aphid, Dysaphis plantaginea (Passerini), in Eastern North America. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blommers, L.H.M.; Helsen, H.H.M.; Vaal, F.W.N.M. Life History Data of the Rosy Apple Aphid Dysaphis plantaginea (Pass.) (Homopt., Aphididae) on Plantain and as Migrant to Apple. J. Pest Sci. 2004, 77, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reganold, J.P.; Glover, J.D.; Andrews, P.K.; Hinman, H.R. Sustainability of Three Apple Production Systems. Nature 2001, 410, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, S.; Brun, L.; Guinaudeau, J.; Sauphanor, B. Pesticide Use in Current and Innovative Apple Orchard Systems. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, J.; Fountain, M.; Markó, V.; Nagy, C. Arthropod Ecosystem Services in Apple Orchards and Their Economic Benefits: Arthropod Ecosystem Services in Apple Orchards. Ecol. Entomol. 2015, 40, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñarro, M.; Hemptinne, J.-L.; Dapena, E. Colonization of Apple Orchards by Predators of Dysaphis plantaginea: Sequential Arrival, Response to Prey Abundance and Consequences for Biological Control. BioControl 2005, 50, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bribosia, E.; Bylemans, D.; Migon, M.; Impe, G.V. In-Field Production of Parasitoids of Dysaphis plantaginea by Using the Rowan Aphid Dysaphis sorbi as Substitute Host. BioControl 2005, 50, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peusens, G.; Buntinx, L.; Gobin, B. Parasitation of the Parasitic Wasp Ephedrus persicae (Frogatt) on the Rosy Apple Aphid Dysaphis plantaginea (Passerini). Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2006, 71, 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Dib, H.; Libourel, G.; Warlop, F. Entomological and Functional Role of Floral Strips in an Organic Apple Orchard: Hymenopteran Parasitoids as a Case Study. J. Insect Conserv. 2012, 16, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dib, H.; Simon, S.; Sauphanor, B.; Capowiez, Y. The Role of Natural Enemies on the Population Dynamics of the Rosy Apple Aphid, Dysaphis plantaginea Passerini (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in Organic Apple Orchards in South-Eastern France. Biol. Control 2010, 55, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss, E.; Villiger, M.; Müller-Schärer, H. The Potential of Three Native Insect Predators to Control the Rosy Apple Aphid, Dysaphis plantaginea. Biol. Control 1999, 44, 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Kehrli, P.; Wyss, E. Effects of Augmentative Releases of the Coccinellid, Adalia bipunctata, and of Insecticide Treatments in Autumn on the Spring Population of Aphids of the Genus Dysaphis in Apple Orchards. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 99, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dib, H.; Jamont, M.; Sauphanor, B.; Capowiez, Y. The Feasibility and Efficacy of Early-Season Releases of a Generalist Predator (Forficula auricularia L.) to Control Populations of the RAA (Dysaphis Plantaginea Passerini) in Southeastern France. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2016, 106, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, V.-A.; Trigaux, A.; Moreau, A.; Hance, T. Study of Two Conditioning Methods of Parasitoids Used in Biological Control Prior to Inundative Releases in Apple Orchards. Eur. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 1, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boivin, G.; Hance, T.; Brodeur, J. Aphid Parasitoids in Biological Control. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, A.; Dagbert, T.; Le Goff, G.; Hance, T. La Lutte Biologique Contre Le Puceron Cendré Du Pommier Par Des Lâchers D’auxiliaires En Verger. 2013. Available online: http://www.proverbio-interreg.eu/images/medias/puceron_reduit.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Hance, T.; Kohandani-Tafresh, F.; Munaut, F. Biological Control. Aphids Crop. Pests 2017, 448–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriamont, A. Etude de l’impact Des Basses Températures Sur Les Activités Du Parasitoïde Aphidius matricariae Dans Le Cadre d’une Lutte Biologique Contre Le Puceron Cendré Du Pommier (Dysaphis plantaginea). Master’s Thesis, UCLouvain, Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huey, R.B.; Stevenson, R.D. Integrating Thermal Physiology and Ecology of Ectotherms: A Discussion of Approaches. Am. Zool. 1979, 19, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giri, M.K.; Pass, B.C.; Yeargan, K.V.; Parr, J.C. Behavior, Net Reproduction, Longevity, and Mummy-Stage Survival of Aphidius matricariae [Hym. Aphidiidae]. Entomophaga 1982, 27, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.C.; Gerth, W.J. Temperature-Dependent Development of Aphidius matricariae (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae), as a Parasitoid of the Russian Wheat Aphid. Environ. Entomol. 1994, 23, 1304–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.A.; Talebi, A.; Fathipour, Y.; Baniameri, V. Effect of Temperature on Life History of Aphidius colemani and Aphidius matricariae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), Two Parasitoids of Aphis gossypii and Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, B.; Baumgärtner, J.; Delucchi, V. Life Table Statistics of Three Apple Aphids, Dysaphis plantaginea, Rhopalosiphum insertum, and Aphis pomi (Homoptera, Aphididae), at Constant Temperatures. Z. Für Angew. Entomol. 1985, 99, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, D. Temperature and Organism Size—A Biological Law for Ectotherms? In Advances in Ecological Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 25, pp. 1–58. ISBN 978-0-12-013925-5. [Google Scholar]
- Le Lann, C.; Wardziak, T.; van Baaren, J.; van Alphen, J.J.M. Thermal Plasticity of Metabolic Rates Linked to Life-History Traits and Foraging Behaviour in a Parasitic Wasp: Temperature Affects Physiology and Behaviour of a Parasitoid. Funct. Ecol. 2011, 25, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hance, T.; van Baaren, J.; Vernon, P.; Boivin, G. Impact of Extreme Temperatures on Parasitoids in a Climate Change Perspective. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tougeron, K.; Damien, M.; Le Lann, C.; Brodeur, J.; Van Baaren, J. Rapid Responses of Winter Aphid-Parasitoid Communities to Climate Warming. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruel, J.J.; Ayres, M.P. Jensen’s Inequality Predicts Effects of Environmental Variation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colinet, H.; Sinclair, B.J.; Vernon, P.; Renault, D. Insects in Fluctuating Thermal Environments. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambrechts, L.; Paaijmans, K.P.; Fansiri, T.; Carrington, L.B.; Kramer, L.D.; Thomas, M.B.; Scott, T.W. Impact of Daily Temperature Fluctuations on Dengue Virus Transmission by Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7460–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bannerman, J.A.; Gillespie, D.R.; Roitberg, B.D. The Impacts of Extreme and Fluctuating Temperatures on Trait-Mediated Indirect Aphid-Parasitoid Interactions. Ecol. Entomol. 2011, 36, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffs, C.T.; Leather, S.R. Effects of Extreme, Fluctuating Temperature Events on Life History Traits of the Grain Aphid, Sitobion avenae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2014, 150, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.-Y.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Xu, Y.-Y. Effects of Constant and Fluctuating Temperatures on Development and Reproduction of Megoura crassicauda and Aphis craccivora (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Entomol. Fennica 2018, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayu, M.S.Y.I.; Ullah, M.S.; Takano, Y.; Gotoh, T. Impact of Constant versus Fluctuating Temperatures on the Development and Life History Parameters of Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 72, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colinet, H.; Renault, D.; Hance, T.; Vernon, P. The Impact of Fluctuating Thermal Regimes on the Survival of a Cold-Exposed Parasitic Wasp, Aphidius colemani. Physiol. Entomol. 2006, 31, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lenth, R.; Singmann, H.; Love, J.; Buerkner, P.; Herve, M. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means. R Package Version 2018, 1, 3. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/emmeans/emmeans.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, H.S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 2nd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Therneau, T.M. A Package for Survival Analysis in R. R Package Version 3.2-10. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-Project.Org/Package=survival (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Lüdecke, D.; Makowski, D.; Waggoner, P.; Patil, I. Performance: Assessment of Regression Models Performance. R Package Version. 0.4. 2020, 7. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/performance/performance.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Shi, P.-J.; Reddy, G.V.P.; Chen, L.; Ge, F. Comparison of Thermal Performance Equations in Describing Temperature-Dependent Developmental Rates of Insects: (I) Empirical Models. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2016, 109, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Baaren, J.; Outreman, Y.; Boivin, G. Effect of Low Temperature Exposure on Oviposition Behaviour and Patch Exploitation Strategy in Parasitic Wasps. Anim. Behav. 2005, 70, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delava, E.; Fleury, F.; Gibert, P. Effects of Daily Fluctuating Temperatures on the Drosophila–Leptopilina boulardi Parasitoid Association. J. Therm. Biol. 2016, 60, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsolver, J.G.; Ragland, G.J.; Diamond, S.E. Evolution in a Constant Environment: Thermal Fluctuations and Thermal Sensitivity of Laboratory and Field Populations of Manduca sexta. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 2009, 63, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragland, G.J.; Kingsolver, J.G. The Effect of Fluctuating Temperatures on Ectotherm Life-History Traits: Comparisons among Geographic Populations of Wyeomyia smithii. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2008, 10, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Have, T.M.; De Jong, G. Adult Size in Ectotherms: Temperature Effects on Growth and Differentiation. J. Theor. Biol. 1996, 183, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærsgaard, A.; Pertoldi, C.; Loeschcke, V.; Blanckenhorn, W.U. The Effect of Fluctuating Temperatures During Development on Fitness-Related Traits of Scatophaga stercoraria (Diptera: Scathophagidae). Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foray, V.; Desouhant, E.; Gibert, P. The Impact of Thermal Fluctuations on Reaction Norms in Specialist and Generalist Parasitic Wasps. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 28, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.L.; Huey, R.B. Why “Suboptimal” Is Optimal: Jensen’s Inequality and Ectotherm Thermal Preferences. Am. Nat. 2008, 171, E102–E118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marshall, K.E.; Sinclair, B.J. Repeated Stress Exposure Results in a Survival–Reproduction Trade-off in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.L.; Quiring, D.T. Interactions between Size and Temperature Influence Fecundity and Longevity of a Tortricid Moth, Zeiraphera canadensis. Oecologia 1993, 93, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enjin, A. Humidity Sensing in Insects—From Ecology to Neural Processing. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, D. Insect Photoperiodism: Seasonal Development on a Revolving Planet. Eur. J. Entomol. 2020, 117, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, J.; Pollard, E. Fluctuations in Resource Availability and Insect Populations. Oecologia 1981, 50, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerman, J.A.; Roitberg, B.D. Impact of Extreme and Fluctuating Temperatures on Aphid-Parasitoid Dynamics. Oikos 2014, 123, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paaijmans, K.P.; Heinig, R.L.; Seliga, R.A.; Blanford, J.I.; Blanford, S.; Murdock, C.C.; Thomas, M.B. Temperature Variation Makes Ectotherms More Sensitive to Climate Change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Temperature Regime | Pre-reproductive Period (Days) | Longevity (Days) | Total Offspring | Immature Mortality Level (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant 7 °C | 37.5 ± 1.3 [8] d | 51.0 ± 8.3 b | 22.0 ± 4.1 a | 33.3 |
| Constant 12 °C | 27.9 ± 0.8 [9] c | 36.1 ± 4.2 ab | 31.4 ± 4.7 b | 25.0 |
| Constant 17 °C | 15.4 ± 0.7 [9] a | 29.3 ± 3.3 a | 44.7 ± 6.3 c | 25.0 |
| Fluctuating 7–17 °C | 21.0 ± 0.6 [10] b | 40.7 ± 1.9 ab | 34.1 ± 4.2 bc | 16.7 |
| Parasitoids | Aphids | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Regime | Mass (µg) | Size (mm) | Mass (µg) | Size (mm) |
| Constant 7 °C | 116.0 ± 8.4 b | 0.59 ± 0.03 b | 111.8 ± 7.7 b | 1.20 ± 0.04 b |
| (♂113.6 ± 12.6; ♀118.3 ± 11.6) | (♂0.56 ± 0.04; ♀0.63 ± 0.03) | |||
| Constant 12 °C | 103.5 ± 7.2 ab | 0.52 ± 0.03 ab | 82.7 ± 4.7 a | 1.12 ± 0.02 b |
| (♂95.1 ± 10.8; ♀113.8 ± 8.2) | (♂0.48 ± 0.04; ♀0.57 ± 0.02) * | |||
| Constant 17 °C | 91.2 ± 5.5 a | 0.46 ± 0.02 a | 80.6 ± 3.9 a | 0.94 ± 0.05 a |
| (♂80.8 ± 9.8; ♀98.1 ± 5.9) | (♂0.41 ± 0.03; ♀0.50 ± 0.03) * | |||
| Fluctuating 7–17 °C | 103.1 ± 6.4 ab | 0.50 ± 0.02 ab | 101.5 ± 3.1 b | 1.08 ± 0.01 b |
| (♂97.9 ± 11.2; ♀107.8 ± 7.4) | (♂0.47 ± 0.04; ♀0.52 ± 0.03) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tougeron, K.; Ferrais, L.; Renard, M.-E.; Hance, T. Effects of Constant versus Fluctuating Temperatures on Fitness Indicators of the Aphid Dysaphis plantaginea and the Parasitoid Aphidius matricariae. Insects 2021, 12, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100855
Tougeron K, Ferrais L, Renard M-E, Hance T. Effects of Constant versus Fluctuating Temperatures on Fitness Indicators of the Aphid Dysaphis plantaginea and the Parasitoid Aphidius matricariae. Insects. 2021; 12(10):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100855
Chicago/Turabian StyleTougeron, Kévin, Louise Ferrais, Marie-Eve Renard, and Thierry Hance. 2021. "Effects of Constant versus Fluctuating Temperatures on Fitness Indicators of the Aphid Dysaphis plantaginea and the Parasitoid Aphidius matricariae" Insects 12, no. 10: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100855
APA StyleTougeron, K., Ferrais, L., Renard, M. -E., & Hance, T. (2021). Effects of Constant versus Fluctuating Temperatures on Fitness Indicators of the Aphid Dysaphis plantaginea and the Parasitoid Aphidius matricariae. Insects, 12(10), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100855