Identification and Field Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Components and Its Antagonist Produced by a Major Tea Pest, Archips strojny (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Pheromone Extraction
2.3. Gas Chromatography–Electroantennographic Detection (GC–EAD)
2.4. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS)
2.5. DMDS Derivatization of Pheromone Components
2.6. Field Trapping
2.7. Chemicals
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
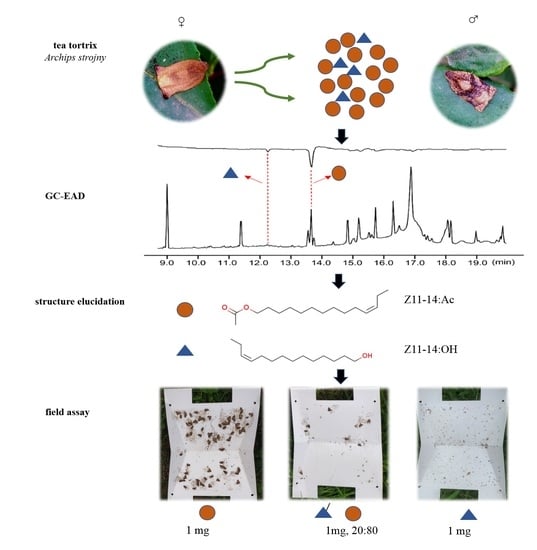
3.1. Male A. strojny Antennae Responded to Two Bioactive Components in Female Gland Extract
3.2. Chemical Structures of Bioactive Compounds 1 and 2
3.3. Attraction of Males to Synthetic Lures in the Field
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.M.; Zhou, L.; Yang, M.; Luo, F.J.; Lou, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Sun, H.Z.; Wang, X.R. Index design and safety evaluation of pesticides application based on a fuzzy AHP model for beverage crops: Tea as a case study. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.S.; Wheeler, W.J. The medicinal chemistry of tea. Drug Dev. Res. 2004, 61, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, F.; Kimura, K.; Saba, T.; Ogino, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Tanaka, J. Worldwide core collections of tea (Camellia sinensis) based on SSR markers. Tree Genet. Genom. 2014, 10, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranham, J.E. Tea pests and their control. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1966, 11, 491–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, X. An analysis on the world tea pests fauna. J. Tea Sci. 1989, 9, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, W.E. Tortricid Pests: Their biology, natural enemies and control. Am. Entomol. 1993, 39, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosugi, Y. Control of oriental tea tortrix, Homona magnanima and smaller tea tortrix, Adoxophyes honmai using a new type of mating disruptor in tea fields. Annu. Rep. Kanto-Tosan Plant Prot. Soc. 2001, 48, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, L.K.; Bhuyan, M.; Hazarika, B.N. Insect pests of tea and their management. Annu. Rev. Entomol 2009, 54, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, M.; Nakai, M.; Saito, Y.; Sato, Y.; Ishijima, C.; Kunimi, Y. Field efficacy and transmission of fast- and slow-killing nucleopolyhedroviruses that are infectious to Adoxophyes honmai (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Viruses 2015, 7, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, M.; Guo, H.; Yin, k.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Q. Preliminary study on morphological and biological characteristics of Archips strojny Razowski. Plant Prot. 2017, 43, 188–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, P.; Kong, Y.-S.; Liu, P.-P.; Jiang, C.-L.; Sun, M.-F.; Guo, G.-Y.; Liu, Z.-H. Temporal variation of the non-volatile compounds and key odorants in Xinyang Maojian green teas during the Spring and Autumn seasons. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, X. Impact of harvest season on bioactive compounds, amino acids and in vitro antioxidant capacity of white tea through multivariate statistical analysis. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 164, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.R.; McGhee, P.S.; Siegert, P.Y.; Adams, C.G.; Huang, J.; Grieshop, M.J.; Gut, L.J. General principles of attraction and competitive attraction as revealed by large-cage studies of moths responding to sex pheromone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, A.K. Neuroendocrine control of sex pheromone biosynthesis in Lepidoptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1993, 38, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.A.H.; George, J.; Reddy, G.V.P.; Zeng, X.; Guerrero, A. Latest developments in insect sex pheromone research and its application in agricultural pest management. Insects 2021, 12, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotak, J.N.; Patel, H.R. Pheromone based mating disruption technology—A new era in management of insects. Insect Environ. 2021, 24, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Sarfraz, R.M.; Evenden, M.L.; Keddie, B.A.; Dosdall, L.M. Pheromone-mediated mating disruption: A powerful tool in insect pest management. Outlooks Pest. Manag. 2006, 17, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, T.; Yamamoto, M. Semiochemicals containing lepidopteran sex pheromones: Wonderland for a natural product chemist. J. Pestic. Sci. 2020, 45, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Yamakawa, R. Analyses of lepidopteran sex pheromones by mass spectrometry. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, R.; Tang, D.S.; Chow, Y.S.; Tseng, H.K. Sex pheromone components of female smaller tea tortrix moth, Adoxophyes sp. (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in Taiwan. J. Chem. Ecol. 1990, 16, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Tamaki, Y.; Yushima, T. Sex-pheromone of the tea tortrix moth-isolation and identification. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1979, 14, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabata, J.; Noguchi, H.; Kainoh, Y.; Mochizuki, F.; Sugie, H. Behavioral response to sex pheromone-component blends in the mating disruption-resistant strain of the smaller tea tortrix, Adoxophyes honmai Yasuda (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), and its mode of inheritance. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2007, 42, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witzgall, P.; Kirsch, P.; Cork, A. Sex pheromones and their impact on pest management. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, K.; Fukumoto, T.; Mochizuki, F.; Yamamoto, M.; Ando, T. Mating disruption of the Japanese giant looper in tea gardens permeated with synthetic pheromone and related compounds. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 100, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Ge, F.; Liu, X.H.; Wang, L.J.; Feng, F. Field experiments for controling the tea tussock moth, Euproctis pseudoconspersa, by mating disruption with sex pheromone. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2006, 43, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vang, L.; Thuy, H.N.; Khanh, C.N.Q.; Son, P.K.; Yan, Q.; Yamamoto, M.; Jinbo, U.; Ando, T. Sex pheromones of three citrus leafrollers, Archips atrolucens, Adoxophyes privatana, and Homona sp., inhabiting the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, H.R.; Arn, H.; Guerin, P.; Rauscher, S. Determination of double-bond position in monounsaturated acetates by mass-spectrometry of dimethyl disulfide adducts. Anal. Chem. 1983, 55, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vang, L.V.; Thy, T.T.; Hanh, D.K.; Linh, T.P.; Yamamoto, M.; Ando, T. Sex pheromone analysis and effective attraction of males of the cabbage webworm, Hellula undalis, inhabiting the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2020, 23, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Fujino, A.; Naka, H.; Dong, S.-L.; Ando, T. Chemical analysis of the female sex pheromone in Palpita nigropunctalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Li, H.D.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.F.; You, X.Y.; Zhou, J.; Mu, L.F.; Liu, S.J.; Kong, X.B.; Khuhro, S.A.; et al. Identification and field evaluation of the sex pheromone of Orthaga achatina (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List of Sex Pheromones and Attractants. Available online: https://lepipheromone.sakura.ne.jp/lepi_phero_list_eng.html (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Ando, T.; Kuroko, H.; Nakagaki, S.; Saito, O.; Oku, T.; Takahashi, N. 2-Component sex attractants for male moths of subfamily Tortricinae (Lepidoptera). Agric. Biol. Chem. 1978, 42, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Roelofs, W.; Hill, A.; Cardé, A.; Cardé, R.; Madsen, H.; Vakenti, J. Sex-pheromone of European leafroller, Archips Rosanus, Lepidoptera-Tortricidae. Environ. Entomol. 1976, 5, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonkin, A.F.; Triseleva, T.A. Identification of the sex pheromone components of the apple surface eating tortrix Archips podana Scop. (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Agrokhimiya 2003, 3, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherston, J.; Maclean, W. The occurrence of (E)-11-tetradecen-1-ol, a known sex attractant inhibitor, in the abdominal tips of virgin female eastern spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Can. Entomol. 1974, 106, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardé, R.T.; Roelofs, W.L.; Doane, C.C. Natural inhibitor of the gypsy moth sex attractant. Nature 1973, 241, 474–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Guo, H.; Hou, C.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.-Q.; Wang, C.-Z. Olfactory perception and behavioral effects of sex pheromone gland components in Helicoverpa armigera and Helicoverpa assulta. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopez, C.; Ardanuy, A.; Eizaguirre, M.; Albajes, R. Pheromone antagonism in lepidopteran maize pests. IOBC/WPRS Bull. 2011, 72, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kehat, M.; Dunkelblum, E. Behavioral responses of male Heliothis armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) moths in a flight tunnel to combinations of components identified from female sex pheromone glands. J. Insect Behav. 1990, 3, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehat, M.; Gothilf, S.; Dunkelblum, E.; Greenberg, S. Field evaluation of female sex pheromone components of the cotton bollworm, Heliothis armigera. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1980, 27, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ai, D.; Jiang, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, G. A pheromone antagonist regulates optimal mating time in the moth Helicoverpa armigera. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1610–1615.e1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groot, A.T.; Nojima, S.; Heath, J.J.; Ammagarahalli, B.; van Wijk, M.; Claben, A.; Santangelo, R.G.; Lopez, J.; Schal, C. Alcohol contributes to attraction of Heliothis (= Chloridea) virescens males to females. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Treatment | Lure Composition (µg) | |
|---|---|---|
| Z11-14:OH | Z11-14:Ac | |
| A | 0 | 1000 |
| B | 50 | 950 |
| C | 100 | 900 |
| D | 200 | 800 |
| E | 400 | 600 |
| F | 1000 | 0 |
| CK | 0 | 0 |
| Compound | DB-23 GC Column | HP-5 GC Column | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT (min) | KI | RT (min) | KI | |
| Compound 1 | 18.29 | 2214 | 12.98 | 1678 |
| Compound 2 | 18.01 | 2194 | 14.40 | 1810 |
| Z11-14:OH | 18.28 | 2213 | 12.97 | 1678 |
| E11-14:OH | 17.93 | 2187 | 12.92 | 1673 |
| Z11-14:Ac | 18.01 | 2193 | 14.40 | 1810 |
| E11-14:Ac | 17.68 | 2168 | 14.35 | 1805 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, N.; Magsi, F.H.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, X.; Li, Z.; Bian, L.; Xiu, C.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Z. Identification and Field Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Components and Its Antagonist Produced by a Major Tea Pest, Archips strojny (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Insects 2022, 13, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13111056
Fu N, Magsi FH, Zhao Y, Cai X, Li Z, Bian L, Xiu C, Chen Z, Luo Z. Identification and Field Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Components and Its Antagonist Produced by a Major Tea Pest, Archips strojny (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Insects. 2022; 13(11):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13111056
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Nanxia, Fida Hussain Magsi, Yingjie Zhao, Xiaoming Cai, Zhaoqun Li, Lei Bian, Chunli Xiu, Zongmao Chen, and Zongxiu Luo. 2022. "Identification and Field Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Components and Its Antagonist Produced by a Major Tea Pest, Archips strojny (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae)" Insects 13, no. 11: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13111056
APA StyleFu, N., Magsi, F. H., Zhao, Y., Cai, X., Li, Z., Bian, L., Xiu, C., Chen, Z., & Luo, Z. (2022). Identification and Field Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Components and Its Antagonist Produced by a Major Tea Pest, Archips strojny (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Insects, 13(11), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13111056