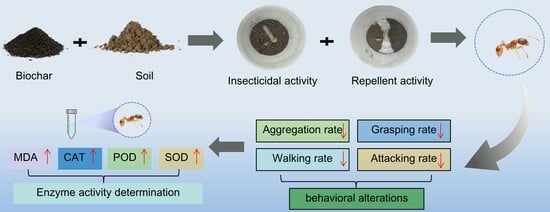
Toxicity and Behavioral Effects of Amending Soils with Biochar on Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. S. invicta for Testing
2.2. Biochar and Soil Preparation
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Observation of Biochar
2.4. Irritability Effect Bioassay
2.5. Insecticidal Activity Bioassay
2.6. Effects of Biochar-Amended Soil on the Behavior of S. invicta
2.6.1. Aggregation
2.6.2. Attack
2.6.3. Gripping
2.6.4. Walking
2.7. Enzyme Activity Test
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. SEM of Biochar
3.2. Effects of Soil Amendments with Biochar on the Irritability Effect of RIFA
3.3. Effects of Soil Amendments with Biochar on the Insecticidal Activity of RIFA
3.4. Effects of Soil Amendments with Biochar on the Behavior of RIFAs
3.5. Effects of Biochar on Activities SOD, POD, CAT, and MDA in RIFAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN: Gland, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lu, Y.Y. Impact of the red imported fire ant Solenopsis invicta Buren on biodiversity in South China: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Han, W.; Yin, Y.; Lei, J. Prediction of Spatiotemporal Invasive Risk of the Red Import Fire Ant, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), in China. Insects 2021, 12, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashied, A.; Ikhlaq, M.; Jaleel, W.; Akram, B.; Khan, M.F.A.; Mughal, A.N.; Mukhtar, A.; Bashir, M.A.; Shabir, K.; Saeed, R.; et al. Origin, Distribution, Biology and Integrated Management of Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): A Comprehensive Study. Plant Prot. 2023, 7, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Huang, S.A.; Lin, I.L.; Lin, C.C.; Lai, H.K.; Yang, C.H.; Huang, R.N. Establishment and social impacts of the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.; Khare, P. Impact of pyrolysis techniques on biochar characteristics: Application to soil. In Biochar Applications in Agriculture and Environment Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 33–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R.; Parikh, S.J.; Du, J.; Qi, F.; Willett, I.R. Influences of feedstock sources and pyrolysis temperature on the properties of biochar and functionality as adsorbents: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, B.; Reddy, P.V.L.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.S.; Pandey, S.K.; Kim, K.H. Benefits and limitations of biochar amendment in agricultural soils: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 227, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszczuk, P.; Josko, I.; Kusmierz, M. Biochar properties regarding to contaminants content and ecotoxicological assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliston, T.; Oliver, I.W. Ecotoxicological assessments of biochar additions to soil employing earthworm species Eisenia fetida and Lumbricus terrestris. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 33410–33418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Li, X.; Sanders, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ortega, Y.K.; Wang, D. Soil engineering by ants facilitates plant compensation for large herbivore removal of aboveground biomass. Ecology 2021, 102, e03312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Liu, F.; Peng, L. Impact of red imported fire ant nest-building on soil properties and bacterial communities in different habitats. Animals 2023, 13, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Advancement on techniques for the separation and maintenance of the red imported fire ant colonies. Insect Sci. 2007, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.T.; Ma, Z.W.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Luo, Y.P. Fumigant toxicity and behavioral alterations of six plant essential oils against the red fire ant (Solenopsis invicta Buren). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 68677–68690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tang, L.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.S.; Li, H.; Cheng, D.M.; Zhang, Z.Z. Repellent and fumigant activities of Eucalyptus globulus and Artemisia carvifolia essential oils against Solenopsis invicta. B Insectol. 2014, 67, 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Liao, Y.H.; Xie, L.J.; Zhang, Z.X.; Hu, W. Using essential oils from Citrus paradisi as a fumigant for Solenopsis invicta workers and evaluating the oils’ effect on worker behavior. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59665–59672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.L.; Hu, Y.Q.; Yang, L.P.; Lin, J.H.; Bai, H.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Tanvir, R.; Li, L.; Bai, M.; Zhang, Z.X.; et al. Fumigation activity of essential oils of Cinnamomum loureirii toward red imported fire ant workers. J. Pest Sci. 2023, 96, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.P.; Chen, H.Y.; Zheng, Q.; Luo, P.R.; Yan, W.J.; Huang, S.Q.; Cheng, D.M.; Xu, H.H.; Zhang, Z.Z. A β-cyclodextrin-functionalized metal–organic framework enhances the insecticidal activity of indoxacarb by affecting amino acid metabolism in red imported fire ants. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 458, 141417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Douds, D.D., Jr.; Boateng, A.A. Effect of biochar soil-amendments on Allium porrum growth and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus colonization. J. Plant Nutr. 2016, 39, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, I.; Gasc’o, G.; Plaza, C.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; M’endez, A. Choice of pyrolysis parameters for urban wastes affects soil enzymes and plant germination in a mediterranean soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniuk, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Bartminski, P. Chemical and ecotoxicological evaluation of biochar produced from residues of biogas production. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyers, S.L.; Spokas, K.A. Impact of biochar on earthworm populations: A review. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2011, 2011, 541592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intani, K.; Latif, S.; Islam, M.S.; Müller, J. Phytotoxicity of corncob biochar before and after heat treatment and washing. Sustainability 2019, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, W.; Li, Z. The effect of amending soils with biochar on the microhabitat preferences of Coptotermes formosanus (Blattodea: Rhinotermitidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Choi, G.H.; Park, B.J. Residual perfluorochemicals in the biochar from sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, V.; Shaheen, S.M.; Levizou, E.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Vithanage, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J. A critical prospective analysis of the potential toxicity of trace element regulation limits in soils worldwide: Are they protective concerning health risk assessment?—A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 819–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidemann, E.; Buss, W.; Edo, M.; Masek, O.; Jansson, S. Influence of pyrolysis temperature and production unit on formation of selected PAHs, oxy-PAHs, N-PACs, PCDDs, and PCDFs in biochar—A screening study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3933–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewska, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Oleszczuk, P. The dark side of black gold: Ecotoxicological aspects of biochar and biochar-amended soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Sarmah, A.K.; Kwon, E.E. Production and formation of biochar. In Biochar from Biomass and Waste; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 3–180. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Ng, W.; Wong, B.S.E.; Baeg, G.H.; Wang, C.H.; Ok, Y.S. Characterization and ecotoxicological investigation of biochar produced via slow pyrolysis: Effect of feedstock composition and pyrolysis conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Yu, I.K.M.; Cao, L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhang, S.; Ok, Y.S. A review of biochar-based catalysts for chemical synthesis, biofuel production, and pollution control. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, S.E.; Jensen, J.; Jakob, L.; Oleszczuk, P.; Hartnik, T.; Henriksen, T.; Okkenhaug, G.; Martinsen, V.; Cornelissen, G. Short-term effect of the soil amendments activated carbon, biochar, and ferric oxyhydroxide on bacteria and invertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8674–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasudai, R.; Matsubara, A.; Hsu, P.W.; Lee, C.C.; Lin, C.C.; Scotty Yang, C.C. Laboratory and field evaluations of two bait formulations against the invasive fire ant, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltz, B.A.; Suiter, D.R.; Gardner, W.A. Activity of bifenthrin, chlorfenapyr, fipronil, and thiamethoxam against red imported fire ants (hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C. Toxicity, horizontal transfer, and physiological and behavioral effects of cycloxaprid against Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 2228–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, M.K.; Su, N. Managing social insects of urban importance. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2012, 57, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Yuan, M.; Liu, X. The synthetic pyrethroid deltamethrin impairs zebrafish (Danio rerio) swim bladder development. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, R.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, J.; Gao, L.; Wang, H. Impacts of changing climate on the distribution of Solenopsis invicta Buren in Mainland China: Exposed urban population distribution and suitable habitat change. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Alginate Granule formulation promotes recovery of metarhizium anisopliae population. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2016, 32, 762. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kafle, L.; Wu, W.J.; Vander Meer, R.K.; Huang, Y.Y.; Shih, C.J. Micro-encapsulatedbait: Does it work with red imported fire ant, Solenosis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)? Sociobiology 2009, 53, 729–737. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Compositions Containing Insect Bait Coated with Zein. U.S. Patent 11 152 193, 12 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.Y.; Mu, C.L.; Gu, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.J. Impact of woodchip biochar amendment on the sorption and dissipation of pesticide acetamiprid in agricultural soils. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, F.J.G.; Pradas, E.G.; Pérez, M.F. Controlled release of isoproturon, imidacloprid, and cyromazine from alginate−bentonite-activated carbon formulations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 10053–10060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Céspedes, F.F.; Sánchez, M.V.; García, S.P.; Pérez, M.F. Modifying sorbents in controlled release formulations to prevent herbicides pollution. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, J.; Qin, M.; Liang, Y.; Lu, Y.; An, Y.; Luo, Y. Toxicity and Behavioral Effects of Amending Soils with Biochar on Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta. Insects 2024, 15, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010042
Fu J, Qin M, Liang Y, Lu Y, An Y, Luo Y. Toxicity and Behavioral Effects of Amending Soils with Biochar on Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta. Insects. 2024; 15(1):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010042
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Jiantao, Mingda Qin, Yue Liang, Yinglin Lu, Yuxing An, and Yanping Luo. 2024. "Toxicity and Behavioral Effects of Amending Soils with Biochar on Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta" Insects 15, no. 1: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010042
APA StyleFu, J., Qin, M., Liang, Y., Lu, Y., An, Y., & Luo, Y. (2024). Toxicity and Behavioral Effects of Amending Soils with Biochar on Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta. Insects, 15(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010042