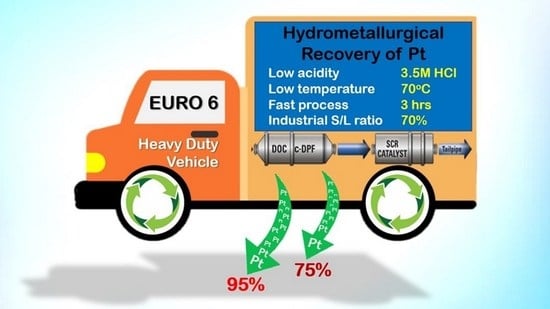
Figure 1.
A typical configuration of the diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC), catalyzed diesel particulate filter (c-DPF) and selective reduction catalyst (SCR) systems in diesel heavy-duty vehicles (HDVs) (Euro VI emission standards).
Figure 2.
Flowsheet preprocessing of DOC and c-DPF.
Figure 3.
Flowsheet of proposed hydrometallurgical process for Pt recovery from DOC and c-DPF.
Figure 4.
Calibration curve for Pt in the loading range 600–2800 ppm.
Figure 5.
Calibration curve for Pt in the loading range <600 ppm.
Figure 6.
Structure of a diesel oxidation catalyst.
Figure 7.
(a) Small piece of the catalyst (DOC) (b) Image from the optical microscope in 5× magnification.
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the structure of a diesel particulate filter (DPF).
Figure 9.
(a) The analyzed small piece of the inner part of the filter (c-DPF) (b) Image from the optical microscope in 5× magnification.
Figure 10.
(a) The analyzed small piece of the inlet or outlet surface of the filter (c-DPF). (b) Image from the optical microscope in 5× magnification.
Figure 11.
Possible Pt distribution configurations on c-DPF: (a) the catalyst is homogeneously distributed on the channels surface; or (b) the catalyst is distributed on the main body of the cordierite, where it has been mixed with the washcoat and the cordierite before the cordierite preparation.
Figure 12.
Surface and horizontal cross-section from the inlet/outlet (Sample A) and the inner part of the particulate filter c-DPF.
Figure 13.
SEM images of the cross-section for samples A (inlet/outlet of the filter) and B (inner part of the filter).
Figure 14.
EDS analysis for Ce, Zr, and Pt on the cross-section for samples A (inlet/outlet of the filter) and B (inner part of the filter).
Figure 15.
SEM images of the surface of the channels from Sample A and Sample B from the inlet/outlet and the inner part of the particulate filter, respectively.
Figure 16.
EDS analysis for Ce, Zr, and Pt on the surface of the channels for Sample A, point B (inlet/outlet of the filter) and Sample B, point C and D (inner part of the filter).
Figure 17.
Pt extraction yield from unpretreated DOC and c-DPF, respectively, with 3 M HCl, 1% vol H2O2, 4.5 M NaCl, and S/L ratio 70% at 70 °C for 3 h.
Figure 18.
(a) Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of DOC, under a heating rate of 10 °C/min. (b) The weight variation at 1000 °C for 200 min.
Figure 19.
(a) Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the c-DPF, under a heating rate of 10 °C/min. (b) The weight variation at 1000 °C for 200 min.
Figure 20.
Change in color of the DOC catalysts during the calcination at 600 °C, 800 °C and 900 °C, respectively.
Figure 21.
Change in color of the c-DPF during calcination at 600 °C, 800 °C and 900 °C, respectively.
Figure 22.
Pt extraction yield from unpretreated and thermal pretreated (600 °C, 800 °C and 900 °C) DOC and c-DPF, respectively, with 3 M HCl, 1% vol H2O2, 4.5M NaCl, and S/L ratio 70% at 70 °C for 3 h.
Figure 23.
XRD patterns of DOC before and after calcination at 800 °C for 2 h.
Figure 24.
XRD patterns of c-DPF before and after calcination at 800 °C for 2 h.
Figure 25.
Pt kinetic behavior of DOC and c-DPF for 0.5–6 leaching time with 3 M HCl, 1% vol H2O2, 4.5 M NaCl, and S/L ratio 70% at 70 °C.
Figure 26.
Summary of recovery rates for Pt from the DOC catalysts and c-DPF filters for 3 M HCl, 4.5 M NaCl, H2O2 1% vol, and S/L 70% at 70 °C.
Table 1.
Pt leaching efficiencies from unpretreated DOC obtained when using different S/L ratio.
| Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) |
|---|
| Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| Not Calcined | 10% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 33.9 |
| Not Calcined | 30% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 36.9 |
| Not Calcined | 50% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 30.2 |
| Not Calcined | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 48.5 |
Table 2.
Pt leaching efficiencies from calcined DOC obtained when using different S/L ratios.
| Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) |
|---|
| Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| Calcined 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 95.2 |
| Calcined 800 °C | 80% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 95.7 |
Table 3.
Pt leaching efficiencies from calcined c-DPF when using different S/L ratios.
| Catalyzed Diesel Particulate Filter (c-DPF) |
|---|
| Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| Calcined 800 °C | 10% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 76.0 |
| Calcined 800 °C | 30% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 76.5 |
| Calcined 800 °C | 50% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 76.2 |
| Calcined 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 74.4 |
Table 4.
Extraction yields of DOC for different HCl concentrations with 70% S/L ratio.
| Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) |
|---|
| Thermal Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 95.5 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 4 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 95.4 |
Table 5.
Pt extraction yields from DOC for different HCl concentrations with 80% S/L ratio.
| Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) |
|---|
| Thermal Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| 800 °C | 80% | 3.0 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 95.7 |
| 800 °C | 80% | 3.5 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 95.3 |
| 800 °C | 80% | 6.0M | 1% | 4.5 M | 95.8 |
Table 6.
Pt extraction yields of c-DPF for different HCl concentrations.
| Catalyzed-Diesel Particulate Filter (c-DPF) |
|---|
| Thermal Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| 800 °C | 70% | 2 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 74.3 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 74.4 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 6 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 77.0 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 9 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 77.9 |
Table 7.
Pt leaching rate from DOC for different H2O2 concentrations.
| Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) |
|---|
| Thermal Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| 800 °C | 70% | 4 M | 0.5% | 4.5 M | 96.2 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 4 M | 1.0% | 4.5 M | 95.4 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 4 M | 1.5% | 4.5 M | 95.5 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 4 M | 3.0% | 4.5 M | 95.4 |
Table 8.
Pt leaching rate from c-DPF for different H2O2 concentrations.
| Catalyzed-Diesel Particulate Filter (c-DPF) |
|---|
| Thermal Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 0.5% | 4.5 M | 73.0 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1.0% | 4.5 M | 74.4 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1.5% | 4.5 M | 73.5 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 3.0% | 4.5 M | 73.5 |
Table 9.
Pt leaching rate of DOC for different times.
| Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) |
|---|
| Thermal Pretreatment | Time, h | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| 800 °C | 0.5 | 80% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 56.0 |
| 800 °C | 1.0 | 80% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 94.8 |
| 800 °C | 2.0 | 80% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 95.3 |
| 800 °C | 3.0 | 80% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 95.1 |
Table 10.
Pt leaching rate of c-DPF for different times.
| Catalyzed-Diesel Particulate Filter (c-DPF) |
|---|
| Thermal Pretreatment | Time, h | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| 800 °C | 0.5 | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 66.4 |
| 800 °C | 1.0 | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 69.7 |
| 800 °C | 2.0 | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 67.8 |
| 800 °C | 3.0 | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 74.4 |
| 800 °C | 4.0 | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 73.9 |
| 800 °C | 6.0 | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 73.7 |
Table 11.
Pt leaching yields of DOC for different NaCl concentrations.
| Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) |
|---|
| Thermal Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| 800 °C | 80% | 3 M | 1% | 3.0 M | 94.6 |
| 800 °C | 80% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 94.8 |
| 800 °C | 80% | 3 M | 1% | 5.0 M | 93.8 |
| 800 °C | 80% | 3 M | 1% | 6.0 M | 95.0 |
Table 12.
Pt leaching yields of DPF for different NaCl concentrations.
| Catalyzed Diesel Particulate Filter (c-DPF) |
|---|
| Thermal Pretreatment | S/L Ratio | HCl | H2O2, vol | NaCl | Pt Recovery, % |
|---|
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 3.0 M | 73.4 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 4.5 M | 74.4 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 5.0 M | 73.3 |
| 800 °C | 70% | 3 M | 1% | 6.0 M | 74.3 |