Leaching Kinetics of Zinc from Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) with Sulfuric Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Agitation Speed
3.2. Effect of Particle Size
3.3. Effect of H2SO4 Concentration
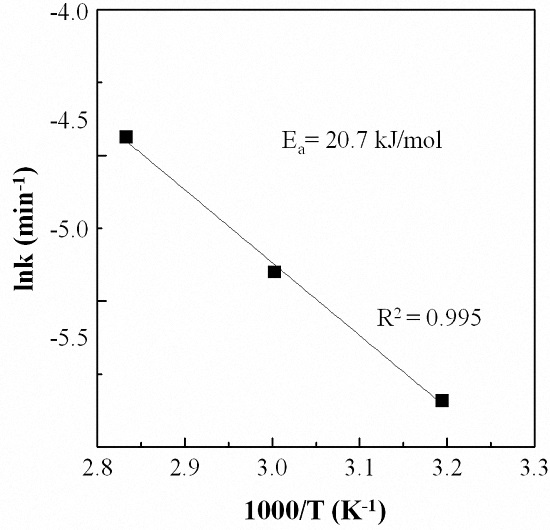
3.4. Effect of Reaction Temperature
3.5. Kinetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakamura, T. E-scrap recycling system and technologies in Japan. Geosyst. Eng. 2014, 17, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Yoo, C.S. Predicting a promising fusion technology in geoscience and mineral resources engineering using Korean patent data. Geosyst. Eng. 2014, 17, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.H.; Park, I.H.; Yoo, K.K.; Ryu, H.J. The effects of temperature and agitation speed on the leaching behaviors of tin and bismuth from spent lead free solder in nitric acid leach solution. Geosyst. Eng. 2015, 18, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, T.; Koyama, K.; Alam, S.; Tanaka, M.; Lee, J.C. Recovery of high purity copper cathode from printed circuit boards using ammoniacal sulfate or chloride solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.N.; Kellar, J.J.; Cross, W.M.; Safarzadeh, S. Opportunities and challenges for treating rare-earth elements. Geosyst. Eng. 2014, 17, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecucci, A.; Scott, K. Leaching and electrochemical recovery of copper, lead and tin from scrap printed circuit boards. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2002, 77, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veit, H.M.; Diehl, T.R.; Salami, A.P.; Rodrigues, J.D.S.; Bernardes, A.M.; Tenório, J.A.S. Utilization of magnetic and electrostatic separation in the recycling of printed circuit boards scrap. Waste. Manag. 2005, 25, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganji, S.M.S.A.; Shafaei, S.Z.; Goudarzi, N.; Azizi, A. Investigating the best mixture extraction systems in the separation of rare earth elements from nitric acid solution using Cyanex272, D2EHPA, and 8-Hydroxyquinoline. Geosyst. Eng. 2016, 19, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, C.; Kavitha, T.; Vidyasagar, S.; Narayanan, S.S. Classification of metals and plastics from printed circuit boards (PCB) using air classifier. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2008, 47, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Forssberg, E. Mechanical recycling of waste electric and electronic equipment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 99, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, H.; Guo, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Recycle technology for recovering resources and products from waste printed circuit boards. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.C. Disassembly and physical separation of electric/electronic components layered in printed circuit boards (PCB). J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinson, L.M.; Philipp, H.R. Zinc oxide varistors—A review. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 1986, 65, 639–646. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, G.; Yin, Q. Preparation of ZnO varistors by solution nano-coating technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2006, 130, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutknecht, T.; Gustafsson, A.; Forsgren, C.; Ekberg, C.; Steenari, B.M. Investigations into Recycling Zinc from Used Metal Oxide Varistors via pH Selective Leaching: Characterization, Leaching, and Residue Analysis. Sci. World. J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T. Leaching of zinc oxide in acidic solution. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 2489–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, M.; Yurten, M. Kinetics of Pb and Zn leaching from zinc plant residue by sodium hydroxide. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2015, 51, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.D.; Pina, P.S.; Lima, E.V.O.; da Silva, C.A.; Leão, V.A. Kinetics of sulphuric acid leaching of a zinc silicate calcine. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, F.; Wang, Y. Leaching kinetics of calcification roasting calcinate from multimetallic sulfide copper concentrate containing high content of lead and iron. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 149, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, M.S.; Jeong, J.K. Leaching behavior of nickel from waste multi-layer ceramic capacitors. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 86, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Yang, T.; Zhang, D.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Hao, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Wen, J. Leaching of low grade zinc oxide ores in NH4Cl-NH3 solutions with nitrilotriacetic acid as complexing agents. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 158, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Int.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 566–586. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, J.D.; Sharp, J.H. Method of Comparing Solid-State Kinetic Data and Its Application to the Decomposition of Kaolinite, Brucite, and BaCO3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1972, 55, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.H.; Brindley, G.W.; Achar, B.N.N. Numerical data for some commonly used solid stat reaction equations. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1966, 49, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.W.; Shibayama, A.; Murata, K.; Fujita, T. The effect of underwater explosion on the kinetics of alkaline leaching of roasted tungsten carbide scraps for recycling. Int. J. Soc. Mater. Eng. Resour. 2004, 12, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Metal | Zn | Sb | Bi | Co | Al | Ni | Sn | Ag | Ca | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt. % | 70.97 | 2.76 | 1.83 | 0.77 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| Particle Size | 105–210 μm | 53–105 μm | −53 μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| wt. % | 63.80 | 72.01 | 72.73 |
| Notation | Reaction Mechanism | Equation | m |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Diffusion | a2 = kt | 0.62 |
| D2 | Diffusion | (1 − a)ln(1 − a) + a = kt | 0.57 |
| D3 | Diffusion | [1 − (1 − a)1/3]2 = kt | 0.54 |
| D4 | Diffusion | 1 − 2a/3 − (1− a)2/3 = kt | 0.57 |
| F0 | Zero order | a = kt | 1.24 |
| F1 | First order reaction | −ln (1 − a) = kt | 1.00 |
| R2 | Interface reaction (contracting area) | 1 − (1 − a)1/2 = kt | 1.11 |
| R3 | Interface reaction (contracting volume) | 1 − (1 − a)1/3 = kt | 1.07 |
| A2 | Nucleation and growth | [−ln (1 − a)]1/2 = kt | 2.0 |
| A3 | Nucleation and growth | [−ln (1 − a)]1/3 = kt | 3.0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Lee, J. Leaching Kinetics of Zinc from Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) with Sulfuric Acid. Metals 2016, 6, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6080192
Kim Y, Lee J. Leaching Kinetics of Zinc from Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) with Sulfuric Acid. Metals. 2016; 6(8):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6080192
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Youngjin, and Jaeryeong Lee. 2016. "Leaching Kinetics of Zinc from Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) with Sulfuric Acid" Metals 6, no. 8: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6080192
APA StyleKim, Y., & Lee, J. (2016). Leaching Kinetics of Zinc from Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) with Sulfuric Acid. Metals, 6(8), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6080192