High-Yield One-Pot Recovery and Characterization of Nanostructured Cobalt Oxalate from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries and Successive Re-Synthesis of LiCoO2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Screening of Organic Acids
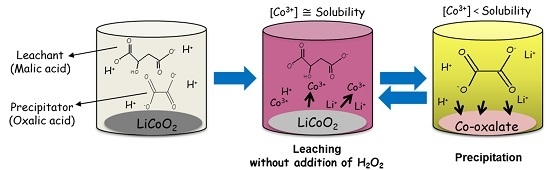
2.2. One-Pot Process
2.3. Synthesis of LiCoO2 Powder
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Screening Test of Organic Acids
3.2. Synthesis of LiCoO2 Powder from Co-Oxalate
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armand, M.; Tarascon, J.M. Building better batteries. Nature 2008, 451, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodenough, J.B.; Kim, Y. Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarascon, J.M.; Armand, M. Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 2001, 414, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vliet, O.; Brouwer, A.S.; Kuramochi, T.; van den Broek, M.; Faaij, A. Energy use, cost and CO2 emissions of electric cars. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 2298–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Meng, Y.S.; Bréger, J.; Grey, C.P.; Ceder, G. Electrodes with high power and high capacity for rechargeable lithium batteries. Science 2006, 311, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gaustad, G.; Babbitt, C.W.; Richa, K. Economies of scale for future lithium-ion battery recycling infrastructure. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, B.; Zhou, T.; Liu, D.; Hu, H.; Fan, S. Separation and recovery of metal values from leaching liquor of mixed-type of spent lithium-ion batteries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 144, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, D.; Han, K. Used lithium ion rechargeable battery recycling using Etoile-Rebatt technology. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Han, D.; Zuo, X. Recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion batteries with chemical deposition and solvent extraction. J. Power Sources 2005, 152, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Senanayake, G.; Sohn, J.; Shin, S.M. Recovery of cobalt sulfate from spent lithium ion batteries by reductive leaching and solvent extraction with Cyanex 272. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 100, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagnes, A.; Pospiech, B. A brief review on hydrometallurgical technologies for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, D.C.R.; Bernardes, A.M.; Tenório, J.A.S. An overview on the current processes for the recycling of batteries. J. Power Sources 2004, 135, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, J.F.; Busnardo, N.G.; Afonso, J.C. Recovery of valuable elements from spent Li-batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.; Kim, D.J.; Ralph, D.E.; Ahn, J.G.; Rhee, Y.H. Bioleaching of metals from spent lithium ion secondary batteries using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Xia, Y.; Wu, F.; Chen, S.; Li, L. Bioleaching mechanism of Co and Li from spent lithium-ion battery by the mixed culture of acidophilic sulfur-oxidizing and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6163–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupi, C.; Pasquali, M.; Dell’Era, A. Nickel and cobalt recycling from lithium-ion batteries by electrochemical processes. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, M.; Celante, V.G.; Pietre, M.K. Electrochemical recovery of cobalt and copper from spent Li-ion batteries as multilayer deposits. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 3309–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.M.; Santos, J.S.; Pereira, E.C.; Freitas, M. Electrodeposition of cobalt from spent Li-ion battery cathodes by the electrochemistry quartz crystal microbalance technique. J. Power Sources 2008, 185, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Amine, K. Recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries by ultrasonic-assisted leaching process. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Sohn, J.; Chang, H.; Senanayake, G.; Shin, S.M. Preparation of cobalt oxide from concentrated cathode material of spent lithium ion batteries by hydrometallurgical method. Adv. Powder Technol. 2010, 21, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dunn, J.B.; Zhang, X.X.; Gaines, L.; Chen, R.J.; Wu, F.; Amine, K. Recovery of metals from spent lithium-ion batteries with organic acids as leaching reagents and environmental assessment. J. Power Sources 2013, 233, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.A.; Prados, L.M.Z.; Majuste, D.; Mansur, M.B. Hydrometallurgical separation of aluminium, cobalt, copper and lithium from spent Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2009, 187, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ge, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, R.; Chen, S.; Wu, B. Recovery of cobalt and lithium from spent lithium ion batteries using organic citric acid as leachant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Qiu, K. Organic oxalate as leachant and precipitant for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Rhee, K.I. Preparation of LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2002, 109, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasova, I.I.; Dudeney, A.W.L.; Pilurzu, S. Glass sand processing by oxalic acid leaching and photocatalytic effluent treatment. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T. Morphology-controllable synthesis of cobalt oxalates and their conversion to mesoporous Co3O4 nanostructures for application in supercapacitors. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 6482–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, W.A.; Cheah, Y.L.; Wong, C.L.; Prasanth, R.; Hng, H.H.; Madhavi, S. Mesoporous cobalt oxalate nanostructures as high-performance anode materials for lithium-ion batteries: Ex-situ electrochemical mechanistic study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 16316–16325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, K.; Jones, P.C.; Wiseman, P.J.; Goodenough, J.B. LixCoO2 (0 < x < −1): A new cathode material for batteries of high energy density. Mater. Res. Bull. 1980, 15, 783–789. [Google Scholar]
- Iriyama, Y.; Inaba, M.; Abe, T.; Ogumi, Z. Preparation of c-axis oriented thin films of LiCoO2 by pulsed laser deposition and their electrochemical properties. J. Power Sources 2001, 94, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshio, M.; Tanaka, H.; Tominaga, K.; Noguchi, H. Synthesis of LiCoO2 from cobalt—Organic acid complexes and its electrode behaviour in a lithium secondary battery. J. Power Sources 1992, 40, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Kanoh, H.; Ooi, K. Preparation of Lithium Cobalt Oxide by LiCl-Flux Method for Lithium Rechargeable Batteries. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 1998, 1, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Baker, P.J.; Grant, P.S. Fabrication and electrical properties of bulk textured LiCoO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 1856–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, J.B.; Dudney, N.J.; Neudecker, B.J.; Hart, F.X.; Jun, H.P.; Hackney, S.A. Preferred orientation of polycrystalline LiCoO2 films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Park, C.; Kim, J.; Shin, D. Lattice orientation control of lithium cobalt oxide cathode film for all-solid-state thin film batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 226, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bates, J.B.; Hart, F.X.; Sales, B.C.; Zuhr, R.A.; Robertson, J.D. Characterization of thin-film rechargeable lithium batteries with lithium cobalt oxide cathodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 3203–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wei, W.; Ma, M.; Qi, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L. Sol-gel synthesis and electrochemical properties of c-axis oriented LiCoO2 for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51483–51488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, P.G.; Scrosati, B.; Tarascon, J.M. Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2930–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Wong, C.C.; Wang, Y. Crystal engineering of nanomaterials to widen the lithium ion rocking “Express Way”: A case in LiCoO2. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 5629–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Y.; Hosono, E.; Saito, T.; Okubo, M.; Nishio-Hamane, D.; Oh-ishi, K.; Kudo, T.; Zhou, H. Electrospinning synthesis of wire-structured LiCoO2 for electrode materials of high-power Li-ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 10774–10780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Ren, Y.; Mu, D.; Liu, X.; Yang, G.; Wu, F. Effect of lithium carbonate precipitates on the electrochemical cycling stability of LiCoO2 cathodes at a high voltage. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 10196–10203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.P.; Twesten, R.D.; Balasubramanian, M.; Petrov, I.; McBreen, J.; Amine, K. Surface changes on LiNi0.8Co0.2O2 particles during testing of high-power lithium-ion cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2002, 4, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, Y.M.; Lim, H.; Moon, J.-H.; Lee, H.-N.; Son, S.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.-J. High-Yield One-Pot Recovery and Characterization of Nanostructured Cobalt Oxalate from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries and Successive Re-Synthesis of LiCoO2. Metals 2017, 7, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7080303
Park YM, Lim H, Moon J-H, Lee H-N, Son SH, Kim H, Kim H-J. High-Yield One-Pot Recovery and Characterization of Nanostructured Cobalt Oxalate from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries and Successive Re-Synthesis of LiCoO2. Metals. 2017; 7(8):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7080303
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Young Min, Hana Lim, Ji-Hoon Moon, Ho-Nyun Lee, Seong Ho Son, Hansung Kim, and Hyun-Jong Kim. 2017. "High-Yield One-Pot Recovery and Characterization of Nanostructured Cobalt Oxalate from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries and Successive Re-Synthesis of LiCoO2" Metals 7, no. 8: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7080303
APA StylePark, Y. M., Lim, H., Moon, J.-H., Lee, H.-N., Son, S. H., Kim, H., & Kim, H.-J. (2017). High-Yield One-Pot Recovery and Characterization of Nanostructured Cobalt Oxalate from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries and Successive Re-Synthesis of LiCoO2. Metals, 7(8), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7080303